Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RI CW B
RI CW B
Uploaded by
mangalraj900Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Accp 2021 P 1Document584 pagesAccp 2021 P 1Sarra HassanNo ratings yet
- Great Vegetarian Dishes - KurmaDocument288 pagesGreat Vegetarian Dishes - Kurmas100% (1)
- Level 2 Ques (1) RTDocument34 pagesLevel 2 Ques (1) RTVishal Sharma100% (1)
- RI CW 7Document8 pagesRI CW 7Saut Maruli Tua SamosirNo ratings yet
- Radiography AsntDocument82 pagesRadiography AsntIdeal Naradmuni100% (1)
- RT Safety Questions 12Document6 pagesRT Safety Questions 12mangalraj900100% (1)
- ITT Mackay Instruction Manual For Model 3030A-3030AR Synthesized Receiver Issue 3 June 1982Document110 pagesITT Mackay Instruction Manual For Model 3030A-3030AR Synthesized Receiver Issue 3 June 1982antoniNo ratings yet
- RI CW 2Document6 pagesRI CW 2Saut Maruli Tua Samosir100% (1)
- Radiographic Interpretation Assessment: Multi - Choice Question Paper (MSR-ARI-1) NameDocument5 pagesRadiographic Interpretation Assessment: Multi - Choice Question Paper (MSR-ARI-1) NameSaut Maruli Tua Samosir50% (2)
- RI CW 4Document6 pagesRI CW 4Saut Maruli Tua SamosirNo ratings yet
- Level I Radiography TestDocument33 pagesLevel I Radiography Testndi101100% (1)
- RT L2 General Examination PaperDocument4 pagesRT L2 General Examination PaperdaddadNo ratings yet
- RI CW 3Document6 pagesRI CW 3Saut Maruli Tua Samosir100% (2)
- Radiographic Interpretation: For The Radiographic Examination of Metallic Materials Using X-And Gamma-Rays"Document8 pagesRadiographic Interpretation: For The Radiographic Examination of Metallic Materials Using X-And Gamma-Rays"Saut Maruli Tua SamosirNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Interpretation: Coursework 3Document5 pagesRadiographic Interpretation: Coursework 3Mangalraj MadasamyNo ratings yet
- RT Practice QuestionDocument65 pagesRT Practice Questionlinh vu75% (4)
- RI CW 8Document8 pagesRI CW 8Saut Maruli Tua SamosirNo ratings yet
- RI CW 9Document8 pagesRI CW 9Saut Maruli Tua SamosirNo ratings yet
- AWS Radio Graphic InterpreterDocument5 pagesAWS Radio Graphic InterpreterShrey Gupta0% (1)
- RT Level IIDocument17 pagesRT Level IIHussain AL-AqilNo ratings yet
- RI CW 6Document7 pagesRI CW 6Saut Maruli Tua SamosirNo ratings yet
- Level 2 QuestionDocument22 pagesLevel 2 QuestionFuaz SukaryaNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Testing (RT) Level - 2 Specific Exam-2Document7 pagesRadiographic Testing (RT) Level - 2 Specific Exam-2Mohammed Aljawhar100% (1)
- Radiography Testing Level I and IIDocument16 pagesRadiography Testing Level I and IIJoshnewfoundNo ratings yet
- RT - Specific ExamDocument3 pagesRT - Specific ExamAslaoui100% (1)
- PTIIGENERALDocument5 pagesPTIIGENERALsaenal rapiNo ratings yet
- RI CW 1Document6 pagesRI CW 1Saut Maruli Tua SamosirNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particles Testing Eng РаздаткаDocument10 pagesMagnetic Particles Testing Eng Раздаткаoluwatobi ajayiNo ratings yet
- PRR CalculationDocument4 pagesPRR CalculationnavitaNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Emission Testing Review QuestionsDocument66 pagesAcoustic Emission Testing Review QuestionsRosber ZarateNo ratings yet
- Q&A RT I, II and III 10 07 06Document72 pagesQ&A RT I, II and III 10 07 06wefew0% (1)
- LPT Spe QB 2Document6 pagesLPT Spe QB 2Aruchamy SelvakumarNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle TestingDocument3 pagesMagnetic Particle TestingAnu AnoopNo ratings yet
- NDT RT RepairDocument1 pageNDT RT RepairpraveentienNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Testing (Paper - 03)Document4 pagesRadiographic Testing (Paper - 03)Hussain ShariffNo ratings yet
- RT FGFDocument30 pagesRT FGFIke Duaka100% (1)
- RT FGFDocument30 pagesRT FGFRaoFarhanNo ratings yet
- VT Level IIIDocument4 pagesVT Level IIIHuy IpNo ratings yet
- 1100 Gorman RT-UT Presentation For CTMS Oct 07Document29 pages1100 Gorman RT-UT Presentation For CTMS Oct 07Sagar NaduvinamaniNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-2Document7 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-2kingstonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial IIIDocument21 pagesTutorial IIIravindra_jivaniNo ratings yet
- Selenium 75Document0 pagesSelenium 75vrapciudorianNo ratings yet
- MT Level - I QB 5Document8 pagesMT Level - I QB 5kingstonNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-1Document7 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-1kingstonNo ratings yet
- Inspeccion VisualDocument11 pagesInspeccion VisualRueda JoanNo ratings yet
- 8 - 2 - 1-043 - Penetrant Testing Examination Guide For Initial CertificationDocument28 pages8 - 2 - 1-043 - Penetrant Testing Examination Guide For Initial Certificationajayachuth97100% (1)
- Asnt Recer RT QB Level IDocument9 pagesAsnt Recer RT QB Level Ikingston100% (1)
- Regulatory Guide: June, 2019 PNRA-RG-904.06 (Rev.0)Document40 pagesRegulatory Guide: June, 2019 PNRA-RG-904.06 (Rev.0)Shahbaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lavender International NDT LTD: Page 1 of 4 Lavender International: Magnetic Particle Assessments: Module 6-1Document20 pagesLavender International NDT LTD: Page 1 of 4 Lavender International: Magnetic Particle Assessments: Module 6-1Arun Senthil Nathan ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- 1.radiographic Testing LeveL II PRESENTATIONDocument139 pages1.radiographic Testing LeveL II PRESENTATIONpandab bkNo ratings yet
- An Rso Manual Revision July16 2015Document363 pagesAn Rso Manual Revision July16 2015Nevada Technical Associates100% (1)
- Rusayl Institute Ultrasonic Testing - Level Ii Ut Q Bank - 4Document9 pagesRusayl Institute Ultrasonic Testing - Level Ii Ut Q Bank - 4kingstonNo ratings yet
- Level Ii QuestionsDocument19 pagesLevel Ii QuestionsAmit Sindhya0% (1)
- As RI GEN 001 With AnswersDocument6 pagesAs RI GEN 001 With AnswersKarthikeyan GanesanNo ratings yet
- PT PracticalDocument40 pagesPT PracticalShyam Sundar GayenNo ratings yet
- MT Level - I QB 4Document8 pagesMT Level - I QB 4kingstonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document10 pagesChapter 1kingstonNo ratings yet
- Ut Q Bank 12 Bhide 100 QBDocument25 pagesUt Q Bank 12 Bhide 100 QBkingstonNo ratings yet
- Radiation Safety of X Ray Generators and Other Radiation Sources Used for Inspection Purposes and for Non-medical Human Imaging: Specific Safety GuideFrom EverandRadiation Safety of X Ray Generators and Other Radiation Sources Used for Inspection Purposes and for Non-medical Human Imaging: Specific Safety GuideNo ratings yet
- Non-Destructive Evaluation of Corrosion and Corrosion-assisted CrackingFrom EverandNon-Destructive Evaluation of Corrosion and Corrosion-assisted CrackingRaman SinghNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Interpretation: Coursework 2Document5 pagesRadiographic Interpretation: Coursework 2Mangalraj MadasamyNo ratings yet
- RT IDocument22 pagesRT Ijohn shepard100% (1)
- TRading StrategyDocument4 pagesTRading Strategymangalraj900No ratings yet
- Angel SuggestedDocument4 pagesAngel Suggestedmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Product Presentation PDFDocument56 pagesProduct Presentation PDFmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Overload.: Nice Weld Shame About The FusionDocument5 pagesOverload.: Nice Weld Shame About The Fusionmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Diamond Engineering (Chennai) PVT LTD.,: Welder Qualification Test RecordDocument1 pageDiamond Engineering (Chennai) PVT LTD.,: Welder Qualification Test Recordmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Set 3Document4 pagesSet 3mangalraj900No ratings yet
- Welding Quality Control Plan (WQCP) Requirements: OrganizationDocument2 pagesWelding Quality Control Plan (WQCP) Requirements: Organizationmangalraj900No ratings yet
- A New Detection Sensor For Wire Rope Based On Open Magnetization MethodDocument9 pagesA New Detection Sensor For Wire Rope Based On Open Magnetization Methodmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Open Vision OVDX Intro JakeDocument18 pagesOpen Vision OVDX Intro Jakemangalraj900No ratings yet
- Set 1Document5 pagesSet 1mangalraj900No ratings yet
- Finite Element Method Characterization of 3D Magnetic Flux Leakage Signal of Crack Discontinuities at Multiple Liftoff ValuesDocument8 pagesFinite Element Method Characterization of 3D Magnetic Flux Leakage Signal of Crack Discontinuities at Multiple Liftoff Valuesmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Scanner ImageDocument1 pageScanner Imagemangalraj900No ratings yet
- Questions Usage 2Document6 pagesQuestions Usage 2mangalraj900No ratings yet
- RPP Aramco Safety PDFDocument10 pagesRPP Aramco Safety PDFmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Questions Usage 1Document6 pagesQuestions Usage 1mangalraj900No ratings yet
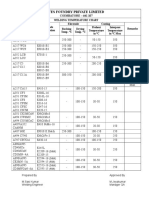
- Veeyes Foundry Private Limited: COIMBATORE - 641 107Document1 pageVeeyes Foundry Private Limited: COIMBATORE - 641 107mangalraj900No ratings yet
- Fdgrgsttyrtertwrtmt Training Evaluation Exam Name Date: ExaminerDocument6 pagesFdgrgsttyrtertwrtmt Training Evaluation Exam Name Date: Examinermangalraj900No ratings yet
- Property, Plant and Equipment (IAS 16.Pptx NEW LATESTDocument47 pagesProperty, Plant and Equipment (IAS 16.Pptx NEW LATESTNick254No ratings yet
- FMG 4-24-13 Christopher McDaniel-CSI Technologies-Cement Spacer Design and TestingDocument20 pagesFMG 4-24-13 Christopher McDaniel-CSI Technologies-Cement Spacer Design and TestingDoni KurniawanNo ratings yet
- JKR Geotechnical SpecificationDocument9 pagesJKR Geotechnical SpecificationSousei No Keroberos100% (1)
- Learnings of PLC & ScadaDocument31 pagesLearnings of PLC & Scadakarthik prapannaNo ratings yet
- Flow of Heat Question and AnswersDocument4 pagesFlow of Heat Question and AnswersKunal SumukNo ratings yet
- Basing News Item FixDocument20 pagesBasing News Item FixYesika Nur WandaNo ratings yet
- Affordability and Subsidies in Public Urban Transport - World BankDocument53 pagesAffordability and Subsidies in Public Urban Transport - World Bankchequeado100% (2)
- Hartalega Annual Report 2019 - Part 1Document57 pagesHartalega Annual Report 2019 - Part 1tanushara0No ratings yet
- Hemhem Crown - WikipediaDocument2 pagesHemhem Crown - WikipediamanandpatelNo ratings yet
- Dexter 1x01 - PilotDocument67 pagesDexter 1x01 - PilotmarkayartNo ratings yet
- 3-4. SST3005. Rocks and Minerals. KHMYDocument40 pages3-4. SST3005. Rocks and Minerals. KHMYFARAH HIDAYAHNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Transients: When The Steady-State Design Fails!Document58 pagesHydraulic Transients: When The Steady-State Design Fails!gustavods8990No ratings yet
- 29 Degree Sakoian & AckerDocument4 pages29 Degree Sakoian & AckerALCHEMISTTNo ratings yet
- Lease Contract EnglishDocument7 pagesLease Contract EnglishRajendra T PankhadeNo ratings yet
- @canotes - Final Customs Question Bank May, Nov 20 by ICAI PDFDocument111 pages@canotes - Final Customs Question Bank May, Nov 20 by ICAI PDFPraneelNo ratings yet
- Chain LengthDocument2 pagesChain Lengthjhurem18No ratings yet
- P1-F Revision For Midyear - Listening - The Sydney Opera HouseDocument4 pagesP1-F Revision For Midyear - Listening - The Sydney Opera HouseYusuf Can SözerNo ratings yet
- Led LCD Monitor: Owner'S ManualDocument35 pagesLed LCD Monitor: Owner'S ManualJulia ONo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument50 pagesUntitledKatrina F JonesNo ratings yet
- Tds Cassida Grease Rls Series EngDocument2 pagesTds Cassida Grease Rls Series Engmussawer hasnainNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 Article - 2Document8 pagesCovid 19 Article - 2Kiruba KaranNo ratings yet
- Leather Goods - Sialkot 2020Document12 pagesLeather Goods - Sialkot 2020Sanchita GuptaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Waveform Generation in FPGADocument7 pagesPeriodic Waveform Generation in FPGAnm2007kNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Entrepreneurship Successfully Launching New Ventures Ma 4th Edition Bruce Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Entrepreneurship Successfully Launching New Ventures Ma 4th Edition Bruce Test Bank PDFferiacassant100% (14)
- Inspection and Maintenance of Steel Girders-4Document10 pagesInspection and Maintenance of Steel Girders-4vpmohammedNo ratings yet
- MNU-1651-51 (x51121 - E)Document264 pagesMNU-1651-51 (x51121 - E)HoppeHNo ratings yet
- Conversion and CalculationDocument40 pagesConversion and CalculationJhonel MelgarNo ratings yet
RI CW B
RI CW B
Uploaded by
mangalraj900Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RI CW B
RI CW B
Uploaded by
mangalraj900Copyright:
Available Formats
WORLD CENTRE FOR MATERIALS JOINING TECHNOLOGY
Radiographic Interpretation
Coursework 2
Answer all questions
1. Besides serving as a filter, screens of high atomic number, such as lead and lead
antimony, also:
a) Decrease the source-to-film distance needed for a proper radiograph
b) Provide some image intensifying action
c) Permit the use of higher speed film
d) Decrease the graininess in a radiograph
2. X-ray films with large grain size:
a) will produce radiographs with better definition than film with small grain size
b) have slower speeds than those with a relatively small grain size
c) have higher speeds than those with a relatively small grain size
d) will take longer to expose properly than film with relatively small grain size
3. The uneven distribution of developed grains within the emulsion of a processed X-ray
film causes the subjective impression of:
a) graininess
b) streakiness
c) spots
d) white scum
4. A good radiograph is obtained at an amperage of 15 ma and a time of 1 min. If the
amperage is changed to 5 ma and all other conditions remain the same what exposure
time will be necessary to obtain the a radiograph of the same quality?
a) 4 minutes
b) 1 minutes
c) 3 minutes
d) 10 seconds
5. In order to achieve uniformity of development over the area of an X-ray film during
manual processing:
a) the film should be placed in a dryer after being developed
b) the developer should be agitated by means of mechanical stirrers or pumps
c) the film should be agitated while in the developer
d) the film should be transferred directly from the developer to the fixer.
Page 1 RI-cw2 doc.
WORLD CENTRE FOR MATERIALS JOINING TECHNOLOGY
6. The density difference between two selected areas of a radiograph is known as:
a) unsharpness
b) radiographic contrast
c) specific activity
d) subject density
7. When producing radiographs, if the kilovoltage is increased:
a) the subject contrast decreases
b) the film contrast decreases
c) the subject contrast increases
d) the film contrast increases
8. Accidental movement of the specimen or film during exposure or the use of too small an
FFD will:
a) produce a radiograph with poor contrast
b) make it impossible to detect large discontinuities
c) result in unsharpness of the radiograph
d) result in a fogged radiograph
9. The normal development time for manually processing X-ray film is:
a) Is dependant on temperature of developer
b) Is not dependant on temperature of developer
c) Dependant on temperature of fixer
d) Dependant on exposure time
10. Lead screens in contact with the film during exposure increase film density because:
a) they emit electrons when exposed to X and gamma rays.
b) they absorb the shorter wavelength radiation more than the long wavelength primary
radiation
c) they intensify the photographic effect of the scattered radiation.
d) none of the above.
11. The sharpness of the outline in the image of the radiograph is a measure of:
a) subject contrast
b) radiographic definition
c) radiographic contrast
d) film contrast
Page 2 RI-cw2 doc.
WORLD CENTRE FOR MATERIALS JOINING TECHNOLOGY
12. The amount of unsharpness or blurring of a radiograph is:
a) directly proportional to the OFD and inversely to the size of the focal spot
b) directly proportional to the size of the focal spot and inversely proportional to the
source-to-object distance
c) inversely proportional to the OFD and directly proportional to the source-to-object
distance
d) inversely proportional to the size of the focal spot and the object-to-film distance
13. The range of thickness over which densities are satisfactory for interpretation is a
measure of the:
a) subject contrast of a radiograph
b) sensitivity of a radiograph
c) latitude of a radiograph
d) definition of a radiograph
14. The slope of a straight line joining two points of specified densities on a characteristic
curve of a film is known as the:
a) speed of the curve
b) latitude
c) average gradient
d) density
15. In film radiography, penetrameters are usually placed:
a) between the intensifying screen and the film
b) on the source side of the test object
c) on the film side of the test object
d) between the operator and the radiation source
16. Three liquids which are essential to process an exposed film properly are:
a) stop bath, acetic acid and water
b) developer, stop bath, and H0
c) developer, fixer and water
d) acetic acid, fixer and stop bath
17. The two most common causes for excessively high density radiographs are:
a) insufficient washing and overdevelopment
b) contaminated fixer and insufficient washing
c) overexposure and contaminated fixer
d) overexposure and overdevelopment
Page 3 RI-cw2 doc.
WORLD CENTRE FOR MATERIALS JOINING TECHNOLOGY
18. The ability to detect a small discontinuity or flaw is called:
a) radiographic contrast
b) radiographic sensitivity
c) radiographic density
d) radiographic resolution
19. Movement, geometry and screen contact are 3 factors that affect radiographic:
a) contrast
b) unsharpness
c) reticulation
d) density
20. The difference between the densities of two areas of a radiograph is called:
a) Radiographic contrast
b) subject contrast
c) film contrast
d) definition
21. To prevent back scatter from reaching an X-ray film, it is customary to:
a) back the exposure holder with a thick sheet of lead
b) place a mask between the specimen and the front surface of the film
c) back the exposure holder with a thick layer of cardboard
d) place a filter near the X-ray tube
22. Static marks, which are black tree-like or circular marks on a radiograph, are often caused
by:
a) film being bent when inserted in a cassette or holder
b) foreign material or dirt embedded in screens
c) scratches on lead foil screens
d) improper film handling techniques
23. The purpose of agitating an X-ray film during development is to:
a) protect the film from excessive pressure
b) renew the developer at the surface of the film
c) disperse unexposed silver grains on the film surface
d) prevent reticulation
Page 4 RI-cw2 doc.
WORLD CENTRE FOR MATERIALS JOINING TECHNOLOGY
24. A penetrameter is used to measure:
a) the size of discontinuities in a part
b) the density of the film
c) the amount of film contrast
d) the quality of the radiographic technique
25. A fluorescent intensifying screen will:
a) transform X-ray energy into visible or ultraviolet light to which a photographic
emulsion is sensitive
b) result in reticulation
c) decrease the graininess of the image when using gamma rays
d) increase the definition in a radiograph
Page 5 RI-cw2 doc.
You might also like
- Accp 2021 P 1Document584 pagesAccp 2021 P 1Sarra HassanNo ratings yet
- Great Vegetarian Dishes - KurmaDocument288 pagesGreat Vegetarian Dishes - Kurmas100% (1)
- Level 2 Ques (1) RTDocument34 pagesLevel 2 Ques (1) RTVishal Sharma100% (1)
- RI CW 7Document8 pagesRI CW 7Saut Maruli Tua SamosirNo ratings yet
- Radiography AsntDocument82 pagesRadiography AsntIdeal Naradmuni100% (1)
- RT Safety Questions 12Document6 pagesRT Safety Questions 12mangalraj900100% (1)
- ITT Mackay Instruction Manual For Model 3030A-3030AR Synthesized Receiver Issue 3 June 1982Document110 pagesITT Mackay Instruction Manual For Model 3030A-3030AR Synthesized Receiver Issue 3 June 1982antoniNo ratings yet
- RI CW 2Document6 pagesRI CW 2Saut Maruli Tua Samosir100% (1)
- Radiographic Interpretation Assessment: Multi - Choice Question Paper (MSR-ARI-1) NameDocument5 pagesRadiographic Interpretation Assessment: Multi - Choice Question Paper (MSR-ARI-1) NameSaut Maruli Tua Samosir50% (2)
- RI CW 4Document6 pagesRI CW 4Saut Maruli Tua SamosirNo ratings yet
- Level I Radiography TestDocument33 pagesLevel I Radiography Testndi101100% (1)
- RT L2 General Examination PaperDocument4 pagesRT L2 General Examination PaperdaddadNo ratings yet
- RI CW 3Document6 pagesRI CW 3Saut Maruli Tua Samosir100% (2)
- Radiographic Interpretation: For The Radiographic Examination of Metallic Materials Using X-And Gamma-Rays"Document8 pagesRadiographic Interpretation: For The Radiographic Examination of Metallic Materials Using X-And Gamma-Rays"Saut Maruli Tua SamosirNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Interpretation: Coursework 3Document5 pagesRadiographic Interpretation: Coursework 3Mangalraj MadasamyNo ratings yet
- RT Practice QuestionDocument65 pagesRT Practice Questionlinh vu75% (4)
- RI CW 8Document8 pagesRI CW 8Saut Maruli Tua SamosirNo ratings yet
- RI CW 9Document8 pagesRI CW 9Saut Maruli Tua SamosirNo ratings yet
- AWS Radio Graphic InterpreterDocument5 pagesAWS Radio Graphic InterpreterShrey Gupta0% (1)
- RT Level IIDocument17 pagesRT Level IIHussain AL-AqilNo ratings yet
- RI CW 6Document7 pagesRI CW 6Saut Maruli Tua SamosirNo ratings yet
- Level 2 QuestionDocument22 pagesLevel 2 QuestionFuaz SukaryaNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Testing (RT) Level - 2 Specific Exam-2Document7 pagesRadiographic Testing (RT) Level - 2 Specific Exam-2Mohammed Aljawhar100% (1)
- Radiography Testing Level I and IIDocument16 pagesRadiography Testing Level I and IIJoshnewfoundNo ratings yet
- RT - Specific ExamDocument3 pagesRT - Specific ExamAslaoui100% (1)
- PTIIGENERALDocument5 pagesPTIIGENERALsaenal rapiNo ratings yet
- RI CW 1Document6 pagesRI CW 1Saut Maruli Tua SamosirNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particles Testing Eng РаздаткаDocument10 pagesMagnetic Particles Testing Eng Раздаткаoluwatobi ajayiNo ratings yet
- PRR CalculationDocument4 pagesPRR CalculationnavitaNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Emission Testing Review QuestionsDocument66 pagesAcoustic Emission Testing Review QuestionsRosber ZarateNo ratings yet
- Q&A RT I, II and III 10 07 06Document72 pagesQ&A RT I, II and III 10 07 06wefew0% (1)
- LPT Spe QB 2Document6 pagesLPT Spe QB 2Aruchamy SelvakumarNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle TestingDocument3 pagesMagnetic Particle TestingAnu AnoopNo ratings yet
- NDT RT RepairDocument1 pageNDT RT RepairpraveentienNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Testing (Paper - 03)Document4 pagesRadiographic Testing (Paper - 03)Hussain ShariffNo ratings yet
- RT FGFDocument30 pagesRT FGFIke Duaka100% (1)
- RT FGFDocument30 pagesRT FGFRaoFarhanNo ratings yet
- VT Level IIIDocument4 pagesVT Level IIIHuy IpNo ratings yet
- 1100 Gorman RT-UT Presentation For CTMS Oct 07Document29 pages1100 Gorman RT-UT Presentation For CTMS Oct 07Sagar NaduvinamaniNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-2Document7 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-2kingstonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial IIIDocument21 pagesTutorial IIIravindra_jivaniNo ratings yet
- Selenium 75Document0 pagesSelenium 75vrapciudorianNo ratings yet
- MT Level - I QB 5Document8 pagesMT Level - I QB 5kingstonNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-1Document7 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-1kingstonNo ratings yet
- Inspeccion VisualDocument11 pagesInspeccion VisualRueda JoanNo ratings yet
- 8 - 2 - 1-043 - Penetrant Testing Examination Guide For Initial CertificationDocument28 pages8 - 2 - 1-043 - Penetrant Testing Examination Guide For Initial Certificationajayachuth97100% (1)
- Asnt Recer RT QB Level IDocument9 pagesAsnt Recer RT QB Level Ikingston100% (1)
- Regulatory Guide: June, 2019 PNRA-RG-904.06 (Rev.0)Document40 pagesRegulatory Guide: June, 2019 PNRA-RG-904.06 (Rev.0)Shahbaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lavender International NDT LTD: Page 1 of 4 Lavender International: Magnetic Particle Assessments: Module 6-1Document20 pagesLavender International NDT LTD: Page 1 of 4 Lavender International: Magnetic Particle Assessments: Module 6-1Arun Senthil Nathan ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- 1.radiographic Testing LeveL II PRESENTATIONDocument139 pages1.radiographic Testing LeveL II PRESENTATIONpandab bkNo ratings yet
- An Rso Manual Revision July16 2015Document363 pagesAn Rso Manual Revision July16 2015Nevada Technical Associates100% (1)
- Rusayl Institute Ultrasonic Testing - Level Ii Ut Q Bank - 4Document9 pagesRusayl Institute Ultrasonic Testing - Level Ii Ut Q Bank - 4kingstonNo ratings yet
- Level Ii QuestionsDocument19 pagesLevel Ii QuestionsAmit Sindhya0% (1)
- As RI GEN 001 With AnswersDocument6 pagesAs RI GEN 001 With AnswersKarthikeyan GanesanNo ratings yet
- PT PracticalDocument40 pagesPT PracticalShyam Sundar GayenNo ratings yet
- MT Level - I QB 4Document8 pagesMT Level - I QB 4kingstonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document10 pagesChapter 1kingstonNo ratings yet
- Ut Q Bank 12 Bhide 100 QBDocument25 pagesUt Q Bank 12 Bhide 100 QBkingstonNo ratings yet
- Radiation Safety of X Ray Generators and Other Radiation Sources Used for Inspection Purposes and for Non-medical Human Imaging: Specific Safety GuideFrom EverandRadiation Safety of X Ray Generators and Other Radiation Sources Used for Inspection Purposes and for Non-medical Human Imaging: Specific Safety GuideNo ratings yet
- Non-Destructive Evaluation of Corrosion and Corrosion-assisted CrackingFrom EverandNon-Destructive Evaluation of Corrosion and Corrosion-assisted CrackingRaman SinghNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Interpretation: Coursework 2Document5 pagesRadiographic Interpretation: Coursework 2Mangalraj MadasamyNo ratings yet
- RT IDocument22 pagesRT Ijohn shepard100% (1)
- TRading StrategyDocument4 pagesTRading Strategymangalraj900No ratings yet
- Angel SuggestedDocument4 pagesAngel Suggestedmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Product Presentation PDFDocument56 pagesProduct Presentation PDFmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Overload.: Nice Weld Shame About The FusionDocument5 pagesOverload.: Nice Weld Shame About The Fusionmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Diamond Engineering (Chennai) PVT LTD.,: Welder Qualification Test RecordDocument1 pageDiamond Engineering (Chennai) PVT LTD.,: Welder Qualification Test Recordmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Set 3Document4 pagesSet 3mangalraj900No ratings yet
- Welding Quality Control Plan (WQCP) Requirements: OrganizationDocument2 pagesWelding Quality Control Plan (WQCP) Requirements: Organizationmangalraj900No ratings yet
- A New Detection Sensor For Wire Rope Based On Open Magnetization MethodDocument9 pagesA New Detection Sensor For Wire Rope Based On Open Magnetization Methodmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Open Vision OVDX Intro JakeDocument18 pagesOpen Vision OVDX Intro Jakemangalraj900No ratings yet
- Set 1Document5 pagesSet 1mangalraj900No ratings yet
- Finite Element Method Characterization of 3D Magnetic Flux Leakage Signal of Crack Discontinuities at Multiple Liftoff ValuesDocument8 pagesFinite Element Method Characterization of 3D Magnetic Flux Leakage Signal of Crack Discontinuities at Multiple Liftoff Valuesmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Scanner ImageDocument1 pageScanner Imagemangalraj900No ratings yet
- Questions Usage 2Document6 pagesQuestions Usage 2mangalraj900No ratings yet
- RPP Aramco Safety PDFDocument10 pagesRPP Aramco Safety PDFmangalraj900No ratings yet
- Questions Usage 1Document6 pagesQuestions Usage 1mangalraj900No ratings yet
- Veeyes Foundry Private Limited: COIMBATORE - 641 107Document1 pageVeeyes Foundry Private Limited: COIMBATORE - 641 107mangalraj900No ratings yet
- Fdgrgsttyrtertwrtmt Training Evaluation Exam Name Date: ExaminerDocument6 pagesFdgrgsttyrtertwrtmt Training Evaluation Exam Name Date: Examinermangalraj900No ratings yet
- Property, Plant and Equipment (IAS 16.Pptx NEW LATESTDocument47 pagesProperty, Plant and Equipment (IAS 16.Pptx NEW LATESTNick254No ratings yet
- FMG 4-24-13 Christopher McDaniel-CSI Technologies-Cement Spacer Design and TestingDocument20 pagesFMG 4-24-13 Christopher McDaniel-CSI Technologies-Cement Spacer Design and TestingDoni KurniawanNo ratings yet
- JKR Geotechnical SpecificationDocument9 pagesJKR Geotechnical SpecificationSousei No Keroberos100% (1)
- Learnings of PLC & ScadaDocument31 pagesLearnings of PLC & Scadakarthik prapannaNo ratings yet
- Flow of Heat Question and AnswersDocument4 pagesFlow of Heat Question and AnswersKunal SumukNo ratings yet
- Basing News Item FixDocument20 pagesBasing News Item FixYesika Nur WandaNo ratings yet
- Affordability and Subsidies in Public Urban Transport - World BankDocument53 pagesAffordability and Subsidies in Public Urban Transport - World Bankchequeado100% (2)
- Hartalega Annual Report 2019 - Part 1Document57 pagesHartalega Annual Report 2019 - Part 1tanushara0No ratings yet
- Hemhem Crown - WikipediaDocument2 pagesHemhem Crown - WikipediamanandpatelNo ratings yet
- Dexter 1x01 - PilotDocument67 pagesDexter 1x01 - PilotmarkayartNo ratings yet
- 3-4. SST3005. Rocks and Minerals. KHMYDocument40 pages3-4. SST3005. Rocks and Minerals. KHMYFARAH HIDAYAHNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Transients: When The Steady-State Design Fails!Document58 pagesHydraulic Transients: When The Steady-State Design Fails!gustavods8990No ratings yet
- 29 Degree Sakoian & AckerDocument4 pages29 Degree Sakoian & AckerALCHEMISTTNo ratings yet
- Lease Contract EnglishDocument7 pagesLease Contract EnglishRajendra T PankhadeNo ratings yet
- @canotes - Final Customs Question Bank May, Nov 20 by ICAI PDFDocument111 pages@canotes - Final Customs Question Bank May, Nov 20 by ICAI PDFPraneelNo ratings yet
- Chain LengthDocument2 pagesChain Lengthjhurem18No ratings yet
- P1-F Revision For Midyear - Listening - The Sydney Opera HouseDocument4 pagesP1-F Revision For Midyear - Listening - The Sydney Opera HouseYusuf Can SözerNo ratings yet
- Led LCD Monitor: Owner'S ManualDocument35 pagesLed LCD Monitor: Owner'S ManualJulia ONo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument50 pagesUntitledKatrina F JonesNo ratings yet
- Tds Cassida Grease Rls Series EngDocument2 pagesTds Cassida Grease Rls Series Engmussawer hasnainNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 Article - 2Document8 pagesCovid 19 Article - 2Kiruba KaranNo ratings yet
- Leather Goods - Sialkot 2020Document12 pagesLeather Goods - Sialkot 2020Sanchita GuptaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Waveform Generation in FPGADocument7 pagesPeriodic Waveform Generation in FPGAnm2007kNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Entrepreneurship Successfully Launching New Ventures Ma 4th Edition Bruce Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Entrepreneurship Successfully Launching New Ventures Ma 4th Edition Bruce Test Bank PDFferiacassant100% (14)
- Inspection and Maintenance of Steel Girders-4Document10 pagesInspection and Maintenance of Steel Girders-4vpmohammedNo ratings yet
- MNU-1651-51 (x51121 - E)Document264 pagesMNU-1651-51 (x51121 - E)HoppeHNo ratings yet
- Conversion and CalculationDocument40 pagesConversion and CalculationJhonel MelgarNo ratings yet