Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Properties of Nucleic Acids
Properties of Nucleic Acids
Uploaded by
RYANA ELLIS MANUCOMOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Properties of Nucleic Acids
Properties of Nucleic Acids
Uploaded by
RYANA ELLIS MANUCOMCopyright:
Available Formats
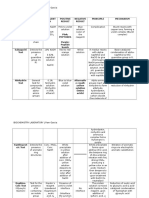
PROPERTIES OF NUCLEIC ACIDS
DNA RNA
Consist of a double helix single-stranded
due to the H-bonds between consisting of nitrogenous bases A, U,
complementary bases, A-T and G-C. G, C
DENATURATION
Structure – the unwinding of the DNA double helix
resulting from a break in the H-bonds
between bases GC and AT.
RENATURATION OR ANNEALING
– the rewinding of the separated DNA
strands, restoration of H-bond between
bases GC and AT
Solutions Because it is single-stranded,
- viscous at pH 7.0 & 25°C it is less viscous than DNA solutions.
- due to rigidity of the double helix
& high length/diameter ratio
- less viscous at high temperatures
(80-90°C)
- MELTING POINT or
TRANSITORY TEMPERATURE (Tm)
Consistency
— temperature at which 50% of the double
helix is unwound
- Higher Tm — more GC pairs;
Lower Tm — more AT pairs.
*When T and pH is returned to the optimum
range, the DNA anneals and viscous
consistency is restored.
Soluble in salt solutions with high concentration.
in weak alkali such as NH3.
Solubility Sparingly soluble in cold water
Insoluble in alcohol
in salt solutions with low concentration
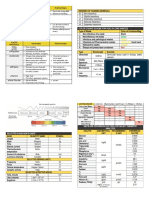
Nitrogenous bases are absorbed by UV light strongly at 260 nm
Unwinding (denaturation) of DNA
Unwinding (denaturation) of DNA
- causes disruption of H-bonding Generally have higher absorption than
DNA because it is single stranded
between strands — exposes the N bases
resulting into a “hyperchromic effect”
Hyperchromic effect
— increased absorbance at 260 nm
Rewinding (renaturation or annealing)
- causes “hypochromic effect”
Hypochromic effect”
— decreased absorbance at 260 nm
UV Absorption
This is the basis for evaluating the purity of nucleic acid extracts.
Purity of nucleic acids is expressed as
! A260/A280 – used as relative measure of NA/protein content of a DNA sample.
Proteins (i.e. with WYF) absorb strongly at 280 nm.
Good quality DNA sample ranges from 1.8-2.0
Pure isolated DNA is 1.8.
Therefore, if absorbance is < 1.8, there is increased contamination by protein;
if absorbance is >1.8, there is an increased contamination of RNA or denaturation of DNA.
! A260/A230 - used as relative measure of NA/X or
other contaminants such as: polysaccharides, phenols or salts.
These contaminants absorb strongly at 230 nm. Ideal value is 2.0.
Amount of protein contaminants and isolated NA
— estimated using the Optical Density Monogram
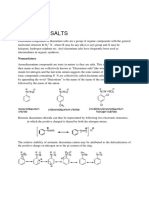
QUALITATIVE TESTS
The mixture is heated — remove excess sulfuric acid
→ colorless sulfur trioxide gas.
Concentrated nitric acid — added to provide a
strongly acidic medium in which the product is insoluble
→ optimizing precipitation of the product
Phosphate ion
— reacts with ammonium molybdate in nitric acid
→ yellow crystalline precipitate of
TEST FOR PHOSPHATES (PO4-3) ammonium phosphomolybdate
*The precipitate is formed slowly from the solution.
Ionic representation of the reaction
:
PO4-3 + H2SO4 → H3PO4
x’ss H2SO4 + Δ → SO3 ↑
PO4-3 + 3NH4+ + 12MoO4-2 +24H+ →
(NH4)3PO4·12 MoO3↓ + 12 H2O
yellow crystalline ppt
QUALITATIVE TESTS
(for Deoxyribose) DIPHENYLAMINE OR DISCHE (1930) TEST
Reagent: diphenylamine in conc. H2SO4
Positive Result: blue complex/compound (λmax = 595 nm)
This reaction is given by 2’-deoxypentoses in general and is not specific
for DNA. In DNA, only the deoxyribose of the purine nucleotide reacts so
that the value obtained represents half of the total deoxyribose present.
(for Ribose) BIAL’S ORCINOL TEST
TEST FOR SUGARS
Reagent:
Positive Result: blue-green coloration
This reaction is not absolutely specific for pentoses since prolonged
heating of some hexoses yields hydroxymethyl furfural which also reacts
with orcinol to give a colored complex (False-positive result). This test is
also not specific for ribose, it is a general test for pentoses (5-C
monosaccharides).
It is frequently employed for the estimation of RNA.
(for Purines) MUREXIDE TEST
Result: Red coloration — due to the formation of murexide.
TEST FOR
NITROGENOUS BASES
(for Pyrimidines) WHEELER-JOHNSON TEST
Result: Purple coloration
Sx → bromine water →boil to remove excess → Ba(OH)2 → purple color
due to Ba+2 salt of dialuric acid
You might also like
- Isolation and Characterization of Nucleic AcidDocument4 pagesIsolation and Characterization of Nucleic AcidIsabella Guce67% (3)
- Biochem Lab 1ADocument7 pagesBiochem Lab 1ARandy MascoNo ratings yet
- Bryson, Elzbieta - Willis, Jacqueline - Foundation Mathematics For Biosciences (2017, Pearson)Document383 pagesBryson, Elzbieta - Willis, Jacqueline - Foundation Mathematics For Biosciences (2017, Pearson)Faycel HIZINo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Virtual Chemistry Lab DNA ExtractionDocument4 pagesVirtual Chemistry Lab DNA ExtractionPedrosa NardNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid ExperimentDocument2 pagesNucleic Acid Experimentjvlegaspi7463valNo ratings yet
- Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Chemical CharacterizationDocument5 pagesRibonucleic Acid (RNA) Chemical CharacterizationnimrovNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab Con NucleicDocument27 pagesBiochem Lab Con NucleicChristine Ho70% (10)
- KDocument39 pagesKdansuper50% (2)
- Biochem Post Lab Discussion Experiment 1A and 1BDocument3 pagesBiochem Post Lab Discussion Experiment 1A and 1BAngel DiangNo ratings yet
- UV-Visible Spectroscopy Part 2Document37 pagesUV-Visible Spectroscopy Part 2hemanth7nitcNo ratings yet
- Biochem LabDocument6 pagesBiochem LabShyenNo ratings yet
- Isolation & Characterization of Dna: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesIsolation & Characterization of Dna: ObjectivesKrizzi Dizon GarciaNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 5 - Nucleic AcidDocument6 pagesExperiment - 5 - Nucleic Acidduldulao.jaysanNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of Nucleic AcidDocument4 pagesIsolation and Characterization of Nucleic AcidLinggonilus MasturandaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Characterization of Ribonucleic AcidDocument3 pagesChemical Characterization of Ribonucleic AcidAngeloMuñozNo ratings yet
- 3 - Acid Base Titration in Nonaqueous - DSWDocument27 pages3 - Acid Base Titration in Nonaqueous - DSWbrianNo ratings yet
- Qualitative TestsDocument36 pagesQualitative Testsanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Arzadon Lab5Document11 pagesArzadon Lab5Kim TangoNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Physical Properties of Nucleic AcidsDocument6 pagesChemical and Physical Properties of Nucleic AcidsSherlock Wesley ConanNo ratings yet
- (When The Difference in Boiling Point Is Not Much)Document4 pages(When The Difference in Boiling Point Is Not Much)Sanju PatelNo ratings yet
- Hydrolysis of Nucleic Acids: Group 8Document25 pagesHydrolysis of Nucleic Acids: Group 8kiki parkNo ratings yet
- Isolation of RNADocument2 pagesIsolation of RNAALLEN SERGIO DIZONNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 30 16.4 Interpreting PH CurvesDocument45 pagesChemistry 30 16.4 Interpreting PH CurvesSarah KhaderNo ratings yet
- 4500 NitrogenoDocument6 pages4500 NitrogenoErick Michael GarciaNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of DNADocument5 pagesIsolation and Characterization of DNAgeorgiana0% (1)
- MINANO, Czefiah Jade: Group No. 3 - MT205 - M, TH 7:30 - 12:00Document6 pagesMINANO, Czefiah Jade: Group No. 3 - MT205 - M, TH 7:30 - 12:00Princess Kaye MangayaNo ratings yet
- BCH 706 Abs Spectrophotometry - 63424Document19 pagesBCH 706 Abs Spectrophotometry - 63424zshanali6236No ratings yet
- Rna Formal ReportDocument3 pagesRna Formal ReportErwin ManipolNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Summary SheetDocument15 pagesOrganic Chemistry Summary SheetLeah BertaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-21 at 2.33.44 PMDocument8 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-21 at 2.33.44 PMsalmafmohamed444No ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Color ReactionsDocument3 pagesExperiment 2 - Color ReactionsPam GarciaNo ratings yet
- Comparing AciditiesDocument2 pagesComparing AciditiesKim ThaiNo ratings yet
- Mira 89Document11 pagesMira 89Kenneth Jake BatiduanNo ratings yet
- Testing For ProteinsDocument7 pagesTesting For ProteinskulangkatunNo ratings yet
- Lecture3-Tools in Molecular BiologyDocument68 pagesLecture3-Tools in Molecular BiologyHoàng NamNo ratings yet
- CC Wall NotesDocument10 pagesCC Wall NotesCamella Beatrice Lujan ValleNo ratings yet
- 202003291608409191arun Sethi Diazonium CompoundsDocument12 pages202003291608409191arun Sethi Diazonium CompoundsMarwan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document5 pagesExperiment 2Lloaana 12No ratings yet
- 153L NE GROUP 3 Experiment 6 Isolation Hydrolysis and Qualitative Analysis of RNA From YeastsDocument9 pages153L NE GROUP 3 Experiment 6 Isolation Hydrolysis and Qualitative Analysis of RNA From YeastsShaina BitaizarNo ratings yet
- Liebermann Nitroso Test and Ninhydrin TestDocument4 pagesLiebermann Nitroso Test and Ninhydrin Testartemis MontecastroNo ratings yet
- Department of Mining, Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, University of The Philippines, Diliman, Quezon CityDocument4 pagesDepartment of Mining, Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, University of The Philippines, Diliman, Quezon CityRochelle ManchamNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of AminesDocument35 pagesThe Chemistry of AminessamNo ratings yet
- All Drugs - Chemical Tests1-3 PDFDocument3 pagesAll Drugs - Chemical Tests1-3 PDFALINo ratings yet
- All Drugs - Chemical TestsDocument3 pagesAll Drugs - Chemical TestsVishnu KiranNo ratings yet
- Hyperchromic EffectDocument7 pagesHyperchromic EffectvictorNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna 1Document27 pagesDna Rna 1ابوبكر خلف اللهNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of Ribonucleic Acid From YeastDocument4 pagesIsolation and Characterization of Ribonucleic Acid From YeastPatrick Daniel Libiran100% (1)
- Biochem Post Lab 4bDocument7 pagesBiochem Post Lab 4bJessica Lorenz PablicoNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of Nucleic Acids From An Onion (Allium Cepa)Document3 pagesIsolation and Characterization of Nucleic Acids From An Onion (Allium Cepa)AyaAlforqueNo ratings yet
- Habb - HBB 231 Notes - June 2024Document196 pagesHabb - HBB 231 Notes - June 2024AmandaNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of RNADocument3 pagesIsolation and Characterization of RNAEvans DionNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab Final Exam Notes 2Document7 pagesChem Lab Final Exam Notes 2Jaira Emmarina100% (1)
- PHA6112LAB - Experiment 4 Nucleic Acids ReviewerDocument8 pagesPHA6112LAB - Experiment 4 Nucleic Acids ReviewerMarie Eloise BugayongNo ratings yet
- Sop AirDocument24 pagesSop AirRohini GadhaweNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet-Visible Spectrophotometry: Submitted by Paritala Jagadeesh B.PharmDocument14 pagesUltraviolet-Visible Spectrophotometry: Submitted by Paritala Jagadeesh B.Pharmkavya nainitaNo ratings yet
- Lone Pair DelocalizationDocument6 pagesLone Pair DelocalizationGIORGIA MERIEN ILAONo ratings yet
- 3 Chemlab Expt 12 Characterization of Nucleic AcidsDocument8 pages3 Chemlab Expt 12 Characterization of Nucleic AcidsFaith DomingoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document4 pagesExperiment 4Sheri Williams0% (1)
- Lab 1st-ExamDocument9 pagesLab 1st-ExamRia Mikaella LadreraNo ratings yet
- Benzocaine Syntheisi Via Fischer EsterificationDocument7 pagesBenzocaine Syntheisi Via Fischer EsterificationXiang Yu100% (7)
- Act02 NucleicAcidExtractionDocument9 pagesAct02 NucleicAcidExtractionTinetine Dizon MalqueridoNo ratings yet
- (Medika) Nucleic Acid Extractor-LibexDocument37 pages(Medika) Nucleic Acid Extractor-LibexRidayat SisNo ratings yet
- Thermo Scientific Genejet Plant Rna Purification Mini Kit #K0801, #K0802Document13 pagesThermo Scientific Genejet Plant Rna Purification Mini Kit #K0801, #K0802Annisa AmaliaNo ratings yet
- MBB 130.1 Lab NotesDocument5 pagesMBB 130.1 Lab NotesJonathan ChanNo ratings yet
- CHE4350 Lab Manual S12Document99 pagesCHE4350 Lab Manual S12DesmondNo ratings yet
- Maestronano Pro Spectrophotometer: Instruction ManualDocument40 pagesMaestronano Pro Spectrophotometer: Instruction ManualYuriAlexanderEspinozaPugaNo ratings yet
- Rna Formal ReportDocument3 pagesRna Formal ReportErwin ManipolNo ratings yet
- Dneasy Plant Mini Kit and Dneasy Plant Maxi Kit Handbook: For Dna Isolation From Plant TissueDocument28 pagesDneasy Plant Mini Kit and Dneasy Plant Maxi Kit Handbook: For Dna Isolation From Plant TissueEl-Agamy ProbeNo ratings yet
- DNA Quantification ProtocolDocument4 pagesDNA Quantification Protocolme_dayakar100% (1)
- MTPC 140: Molecular Biology and DiagnosticsDocument40 pagesMTPC 140: Molecular Biology and DiagnosticsValdez Francis ZaccheauNo ratings yet
- TRIzol Max Bacterial RNA Isolation KitDocument4 pagesTRIzol Max Bacterial RNA Isolation KitYanchen WenNo ratings yet
- EN QuantiTect Reverse Transcription Handbook PDFDocument32 pagesEN QuantiTect Reverse Transcription Handbook PDFFelp ScholzNo ratings yet
- Bio201 Lab Report 5.1Document28 pagesBio201 Lab Report 5.1tobokav208No ratings yet
- Castro Et Al. 2017. RNA Isolation Microalgae IquitosDocument7 pagesCastro Et Al. 2017. RNA Isolation Microalgae IquitosLeonardo Mendoza CarbajalNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lab Report 4Document5 pagesBiochemistry Lab Report 4Lih XuanNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Analysis Template For ChemicalDocument4 pagesCertificate of Analysis Template For ChemicalMon J. KamadNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Direct-Zol - 96 Magbead RnaDocument8 pagesInstruction Manual: Direct-Zol - 96 Magbead RnaVIRAL WORLD IDNo ratings yet
- Techniques in Mol Biology Lab ManualDocument35 pagesTechniques in Mol Biology Lab ManualBalew GetaNo ratings yet
- Mega Script T7 KitDocument33 pagesMega Script T7 KitkitamandaNo ratings yet
- 15 - Chapter 5 ResultsDocument63 pages15 - Chapter 5 ResultsJobin John PR15BI1001No ratings yet
- RNA Isolation ProtocolDocument4 pagesRNA Isolation ProtocolSannan TareenNo ratings yet
- MEGAscript™ RNAi Kit User GuideDocument36 pagesMEGAscript™ RNAi Kit User GuidesdfsfNo ratings yet
- 09 UV Absorption PDFDocument4 pages09 UV Absorption PDFyongqeeNo ratings yet
- Basic Sirna Resuspension ProtocolDocument2 pagesBasic Sirna Resuspension ProtocolPratik KulkarniNo ratings yet
- MB Exp2Document6 pagesMB Exp2XiuQingNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of DNADocument75 pagesIsolation and Characterization of DNANathaniel CastasusNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Isolasi DNADocument3 pagesJurnal Isolasi DNARhyanPrajaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document3 pagesExperiment 6Shalfiq Mat ZariNo ratings yet