Professional Documents
Culture Documents
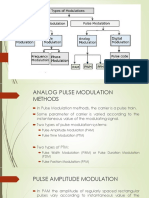
Analog Pulse Modulation
Analog Pulse Modulation
Uploaded by
Vaishnav PsOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Analog Pulse Modulation
Analog Pulse Modulation
Uploaded by
Vaishnav PsCopyright:
Available Formats
PULSE MODULATION
Pulse Modulation is the process of changing a binary pulse signal to represent the
information to be transmitted. It consists of sampling analog information signals and then
converting those samples into discrete pulses & transporting the pulses from source to
destination over a physical transmission medium.
In pulse modulation some parameter of a pulse train is varied in accordance with the
message signal. Broadly pulse modulation can be classified into:
i) Analog Pulse Modulation
ii) Digital Pulse Modulation: The message signal is represented in a form that is
discrete in both time and amplitude. Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) is an example.
ANALOG PULSE MODULATION
In analog pulse modulation information is transmitted in analog form, but the
transmission takes place at discrete times. A periodic pulse train is used as the carrier wave &
some characteristic feature of each pulse (Amplitude, duration or position) is varied in a
continuous manner in accordance with the corresponding sample value of the message signal.
There are 3 types of Analog Pulse Modulation:
i) Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM)
ii) Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) or Pulse Duration Modulation (PDM) or Pulse
Length Modulation (PLM)
iii) Pulse Position Modulation (PPM)
ANALOG PULSE MODULATION v/s DIGITAL PULSE MODULATION
Analog pulse modulation systems use sampling process to maintain continuous
amplitude representation of the message signal.
Digital pulse modulation systems use not only the sampling process but also the
quantization process, which is non-reversible. Quantization provides a representation of the
message signal that is discrete in both time and amplitude. Digital pulse modulation makes it
possible to exploit the full power of DSP techniques.
PULSE AMPLITUDE MODULATION (PAM)
Pulse amplitude modulation is defined as the process of varying the amplitude of the
pulse in proportion to the instantaneous variations of message signal.
GENERATION OF PAM
Let the message signal be given by
𝑣𝑚 = 𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑚 𝑡
ANALOG PULSE MODULATION Page 1
If x(t) is a periodic signal with period T0, then it should satisfy the definition stated as x(t) =
x(t+T0). The pulse train is a periodic signal with fundamental period T0. Then the information
present in each period of the pulse train is given by
𝑝 = 𝑉𝑝 0≤𝑡≤∆
=0 0 ≤ 𝑡 ≤ 𝑇0
where Δ is the width of the pulse.
The Pulse Amplitude Modulated wave in the time domain is obtained by multiplying the
message with the pulse train and is given by
𝑝𝑎 = 𝑝 × 𝑣𝑚
Substituting ‘p’ in the above equation,
𝑝𝑎 = 𝑉𝑝 𝑉𝑚 sin 𝜔𝑚 𝑡 0≤𝑡≤∆
=0 0 ≤ 𝑡 ≤ 𝑇0
Figure below shows the message, pulse train and PAM signal. In the figure we can
see that the amplitude of the pulses is varying with respect to the amplitude of analog
modulating signal, like in case of Amplitude Modulation (AM). But the major difference is
that unlike AM, here the carrier wave is a pulse train rather than continuous wave signal.
DEMODULATION OF PAM
PAM stores the message in the baseband itself. They essentially represent the
message information at discrete instants of time as a variation in pulse amplitude. We can
recover the message, that is, reconstruct the approximate version of the continuous time
signal from them when needed as shown in figure.
ANALOG PULSE MODULATION Page 2
The PAM signal can be passed through a Low Pass Filter which retains essentially the
low frequency message signal and smoothing out the pulse train information.
PULSE WIDTH MODULATION (PWM)
Pulse width modulation (PWM) is defined as the process of varying the width of the
pulse in proportion to the instantaneous variations of message.
GENERATION OF PWM
Let Δ be the width of the pulse in the unmodulated pulse train. In PWM
∆∝ 𝑣𝑚
Mathematically, the width of the pulse in PWM signal is given by
∆𝑚 = ∆(1 + 𝑣𝑚 )
When there is no message (𝑣𝑚 = 0) then the width of the pulse will be equal to the original
width Δ. For positive values of message, the width will be proportionately increasing by
(1 + 𝑣𝑚 ) factor. For negative values of message, the decreases by (1 − 𝑣𝑚 ) factor.
Figure below shows the generation of PWM signal. In this technique the amplitude of
the signal is constant and only the width is varying. PWM technique is similar to frequency
modulation because, by the variation in the width of the pulses, the frequency of the pulses in
the PWM signal shows variation.
ANALOG PULSE MODULATION Page 3
DEMODULATION OF PWM
PWM stores the message in the baseband itself. They essentially represent the
message information at discrete instants of time as a variation in pulse width. The
demodulation of message from PWM is not so simple as the demodulation of PAM, since
visually the message information is not available as amplitude variations. The demodulation
process first converts PWM to PAM and then performs low pass filtering.
PULSE POSITION MODULATION (PPM)
Pulse position modulation (PPM) is defined as the process of varying the position of
the pulse with respect to the instantaneous variations of the message signal.
GENERATION OF PPM
Let tp indicates the timing instant of the leading or trailing edge of the pulse in each period of
the pulse train. In PPM
𝑡𝑝 ∝ 𝑣𝑚
Mathematically, the position of the leading or trailing edge of the pulse (in each period) in
PPM signal is given by
𝑡𝑝 = 𝑓(𝑣𝑚 )
When there is no message, then the position of the leading or trailing edge of the pulse will
be equal to the original position and hence tp = 0. For positive values of message, the position
will be proportionately shifted right by 𝑡𝑝 = 𝑓(𝑣𝑚 ). For negative values of message, the
position will be proportionately shifted by -𝑡𝑝 = −𝑓(𝑣𝑚 ) factor. One way of generating PPM
is to generate PWM and post-process the same to get PPM
The figure below shows the generation of PPM signal. Here the pulse amplitude and
the pulse width are the two constant that does not show variation with the amplitude of the
modulating signal but only the position shows variation.
ANALOG PULSE MODULATION Page 4
DEMODULATION OF PPM
PPM stores the message in the baseband itself. They essentially represent the message
information at discrete instants of time as a variation in pulse position. The demodulation of
message from PPM is not so simple as the demodulation of PAM, since visually the message
information is not available as amplitude variations. The demodulation process first converts
PPM to PAM and then performs low pass filtering.
ANALOG PULSE MODULATION Page 5
COMPARISON OF PAM, PWM & PPM
ANALOG PULSE MODULATION Page 6
You might also like
- Basic Electronics and Communication Engineering (21ELN14/21ELN24) - Analog and Digital Communication (Module 4)Document154 pagesBasic Electronics and Communication Engineering (21ELN14/21ELN24) - Analog and Digital Communication (Module 4)Shrishail BhatNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Paper - 5Document14 pagesUnit 2 - Paper - 5Maheswari RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) - Working, Types & Its ApplicationsDocument15 pagesPulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) - Working, Types & Its ApplicationsSubhajit DasNo ratings yet
- Mod PamDocument7 pagesMod PamGanesh Kumar CNo ratings yet
- Communication Engineering Unit 4 Lecture 1Document28 pagesCommunication Engineering Unit 4 Lecture 1Deepak SinghNo ratings yet
- University of Tripoli Faculty of Engineering Department of Electrical and Electronic EngineeringDocument8 pagesUniversity of Tripoli Faculty of Engineering Department of Electrical and Electronic EngineeringManal SalimNo ratings yet
- Pulse Amplitude Modulation: TheoryDocument4 pagesPulse Amplitude Modulation: Theorymukulgrd1No ratings yet
- Digital Modulation TechniquesDocument34 pagesDigital Modulation TechniquesAkash ModiNo ratings yet
- Pulse ModulationDocument10 pagesPulse ModulationNitishNo ratings yet
- Pulse Modulation: UNIT-6Document49 pagesPulse Modulation: UNIT-6NaliniNo ratings yet
- مروان الناجي (analog)Document5 pagesمروان الناجي (analog)مروان الحاسيNo ratings yet
- Pulse ModulationDocument32 pagesPulse ModulationZelalem BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Pulse Amplitude ModulationDocument5 pagesPulse Amplitude ModulationAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pulse - Modulation Introduction and Advantages ApplicationsDocument11 pagesPulse - Modulation Introduction and Advantages ApplicationsSree MedhaNo ratings yet
- Pulse ModulationDocument74 pagesPulse ModulationAnvesh MagantiNo ratings yet
- Pulse Modulation Pulse Modulation: Multimedia PresentationDocument24 pagesPulse Modulation Pulse Modulation: Multimedia PresentationsavitrinaikNo ratings yet
- Experiment 04 Modulation (PAM) : Pulse Amplitude ObjectiveDocument8 pagesExperiment 04 Modulation (PAM) : Pulse Amplitude ObjectiveMUHAMMAD AMMARNo ratings yet
- AC ReportDocument19 pagesAC ReportshriyaNo ratings yet
- Pulse Amplitude ModulationDocument10 pagesPulse Amplitude ModulationSara AhmedNo ratings yet
- Adc Unit 4 MaterialDocument70 pagesAdc Unit 4 MaterialsrinithaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Pulse Mod PDFDocument32 pagesChapter 5 Pulse Mod PDFAtish RanjanNo ratings yet
- Pulse ModulationDocument9 pagesPulse Modulationجلال عواد كاظم جودةNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 1 Modulation and Demodulation of PAM, PWM, PPM AimDocument5 pagesExperiment No: 1 Modulation and Demodulation of PAM, PWM, PPM AimJose DahlsonNo ratings yet
- Communication 2Document31 pagesCommunication 2chinnureddyseelam07No ratings yet
- AC Btech 3rd SemDocument10 pagesAC Btech 3rd SemYash BudhwarNo ratings yet
- Pulse Amplitude ModulationDocument19 pagesPulse Amplitude ModulationShubhangBaghelNo ratings yet
- Difference Between PAMDocument17 pagesDifference Between PAMultra dubsNo ratings yet
- Difference Between PAMDocument17 pagesDifference Between PAMultra dubsNo ratings yet
- Pulse Modulation D3: Stremler 371-399Document12 pagesPulse Modulation D3: Stremler 371-399Ali KocherNo ratings yet
- Pulse ModulationDocument63 pagesPulse ModulationAbhishek DadhichNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document38 pagesUnit 4DONIKA MARKANDENo ratings yet
- Sampling Theorem: EEE323 Communication Systems II 16Document16 pagesSampling Theorem: EEE323 Communication Systems II 16Ayad A. ABDULKAFINo ratings yet
- ريهام خالد جوحي PAMDocument8 pagesريهام خالد جوحي PAMريهام خالد جوحيNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Pulse Width and Pulse Position ModulationDocument3 pagesExperiment 9 Pulse Width and Pulse Position ModulationVaibhav ZadeNo ratings yet
- PULSEDocument6 pagesPULSESuresh JKNo ratings yet
- Iare-Dc 444Document164 pagesIare-Dc 444Pandu KNo ratings yet
- Pulse Modulation: Term PaperDocument23 pagesPulse Modulation: Term PaperNikita GargNo ratings yet
- C Sai Bhavana CSlab Matlab3Document12 pagesC Sai Bhavana CSlab Matlab3Anirudh KamarajNo ratings yet
- Pulse ModulationDocument61 pagesPulse ModulationAmitDwivediNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication - Pulse ModulationDocument6 pagesAnalog Communication - Pulse ModulationcdrupwestNo ratings yet
- CH 4 1Document47 pagesCH 4 1elias asefaNo ratings yet
- ECE3001-Analog Communication Systems Digital Assignment 3Document13 pagesECE3001-Analog Communication Systems Digital Assignment 3Kiron JayeshNo ratings yet
- Objective:: To Study Pulse Width Modulation and Demodulation Using 555 Timer ICDocument15 pagesObjective:: To Study Pulse Width Modulation and Demodulation Using 555 Timer ICSambhav Chaturvedi100% (1)
- Generation and Detection of PAM, PWM and PPM: Experiment Number 3 AIM Software RequiredDocument6 pagesGeneration and Detection of PAM, PWM and PPM: Experiment Number 3 AIM Software RequiredAyush devNo ratings yet
- 2 Pulse Analog Modulation PDFDocument18 pages2 Pulse Analog Modulation PDFSkillstronNo ratings yet
- Comms 2Document6 pagesComms 2JONNA ACABONo ratings yet
- Pulse ModulationDocument12 pagesPulse Modulationhlrw100% (1)
- Analog Pulse Modulation: Prof. Umesh Yadava Department of Physics DDU Gorakhpur University GorakhpurDocument15 pagesAnalog Pulse Modulation: Prof. Umesh Yadava Department of Physics DDU Gorakhpur University GorakhpurSahil SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Pam PWM PPMDocument16 pagesPam PWM PPMعقيل سعدNo ratings yet
- Pulse ModulationDocument61 pagesPulse ModulationRavi GuptaNo ratings yet
- EEng 3210-ch3Document13 pagesEEng 3210-ch3Goitom HaileNo ratings yet
- ECE3202 ch4Document12 pagesECE3202 ch4Temesgen workiyeNo ratings yet
- 19EC2105 ADC: Pulse Modulation SystemsDocument33 pages19EC2105 ADC: Pulse Modulation SystemsAli BaigNo ratings yet
- Pulse Amplitude ModulationDocument4 pagesPulse Amplitude ModulationSuzette SabidoNo ratings yet
- Pulse Position ModulationDocument3 pagesPulse Position ModulationSneha BorahNo ratings yet
- ADC Exp-06Document5 pagesADC Exp-06anika tabassumNo ratings yet
- Digital TransmissionDocument12 pagesDigital TransmissionOrlando BangayanNo ratings yet
- Digital Transmission (Pulse Modulation)Document61 pagesDigital Transmission (Pulse Modulation)Fritz FatigaNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems: Pulse ModulationDocument39 pagesCommunication Systems: Pulse ModulationMubashir GhaffarNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation TechDocument63 pagesDigital Modulation Techgaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Analog CommunicationsDocument69 pagesAnalog CommunicationsShravani ChandakaNo ratings yet
- FinalsDocument7 pagesFinalsZel LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Data Transmission ExercisesDocument23 pagesData Transmission ExercisesSubash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications SyllabusDocument1 pageDigital Communications Syllabustendua_13No ratings yet
- Voice Otp Ic PDFDocument24 pagesVoice Otp Ic PDFAmarjith ValancheryNo ratings yet
- Sharp LC 55cuf8372es ManDocument76 pagesSharp LC 55cuf8372es ManAleksandar KostadinovNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code Modulation SamplingDocument99 pagesPulse Code Modulation SamplingMulk Raj100% (1)
- Creation of PRA - Procedure For OCB283Document9 pagesCreation of PRA - Procedure For OCB283Jayakrishna ReddyNo ratings yet
- Digital CommunicationMCQDocument3 pagesDigital CommunicationMCQZahid Yousuf0% (1)
- Experimental Study of Voice Over IP Services OverDocument6 pagesExperimental Study of Voice Over IP Services OverAkash SahaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Communication Engineering PracticalDocument30 pagesPrinciples of Communication Engineering PracticalTechniworkNo ratings yet
- Syllabus & Scheme For M.Tech. (ECE)Document27 pagesSyllabus & Scheme For M.Tech. (ECE)Siddharth SidNo ratings yet
- TM202B Software GuideDocument176 pagesTM202B Software GuidepvelasquezrNo ratings yet
- 02.1 Review QuestionsDocument2 pages02.1 Review Questionsreagan oloyaNo ratings yet
- SHA MAN 0174 - Ver6Document100 pagesSHA MAN 0174 - Ver6Daniel DrăganNo ratings yet
- A Matlab Implementation of A DPCM Encoder and DecoderDocument11 pagesA Matlab Implementation of A DPCM Encoder and DecodervishalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Ecm413 PDFDocument57 pagesChapter 3 Ecm413 PDFCaha yANo ratings yet
- Exercise Chap 2Document3 pagesExercise Chap 2chantinh_hd190No ratings yet
- Mwedc Lab ManualDocument74 pagesMwedc Lab ManualAllanki Sanyasi RaoNo ratings yet
- PCM TesterDocument10 pagesPCM TestertatasrbaNo ratings yet
- CS 601 Quiz Topic Wise Data CommunicationDocument49 pagesCS 601 Quiz Topic Wise Data CommunicationAminNo ratings yet
- Compact Disc: How Products Are MadeDocument11 pagesCompact Disc: How Products Are MadeNrupur PrashantNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS Fax and Modem Services Over IP Application Guide: Release 12.4 (4) T October 2005Document206 pagesCisco IOS Fax and Modem Services Over IP Application Guide: Release 12.4 (4) T October 2005Oleksiy OsiychukNo ratings yet
- Bec604 - Communication Eng Ii PDFDocument265 pagesBec604 - Communication Eng Ii PDFddNo ratings yet
- P0157-O2 Sensor 2/2 Circuit Low: 2007 Aspen (4.7L Magnum) - HGDocument8 pagesP0157-O2 Sensor 2/2 Circuit Low: 2007 Aspen (4.7L Magnum) - HGWillie AustineNo ratings yet
- Creation of PRA - Procedure For OCB283Document9 pagesCreation of PRA - Procedure For OCB283srikanth.2335528No ratings yet
- Data CommunicationsDocument231 pagesData CommunicationsKenNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Lecture-2Document73 pagesDigital Communication Lecture-2Fela Nicholas AdekunleNo ratings yet
- Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) .: Basic Elements of PCMDocument2 pagesPulse Code Modulation (PCM) .: Basic Elements of PCMPathan MehemudNo ratings yet