Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 viewsNeostigmine (TUSOM - Pharmwiki) PDF
Neostigmine (TUSOM - Pharmwiki) PDF
Uploaded by
pooja lokhandeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Health Teaching Plan CompleteDocument23 pagesHealth Teaching Plan CompleteDr. Oscar Arquiza100% (1)
- Obat AnestehesiDocument81 pagesObat Anestehesiedwinwedya_878246109No ratings yet
- NeostigmineDocument4 pagesNeostigmineDonna Lyn B. DizonNo ratings yet
- Pyridostigmine BromideDocument4 pagesPyridostigmine BromideRavinderenPichan100% (1)
- Speaker: DR Srikanth AlladiDocument71 pagesSpeaker: DR Srikanth AlladisrikanthalladiNo ratings yet
- Anticholinesterases and Sugammadex: Dr. Sachana KC 1 Year Resident Department of AnesthesiologyDocument64 pagesAnticholinesterases and Sugammadex: Dr. Sachana KC 1 Year Resident Department of AnesthesiologyKshitizma GiriNo ratings yet
- Principles of An-Tiplatelet Therapy: DR Htet Htet Htethtet@Imu - Edu.MyDocument36 pagesPrinciples of An-Tiplatelet Therapy: DR Htet Htet Htethtet@Imu - Edu.MyAbby LiewNo ratings yet
- Drugs and Myasthenia GravisDocument2 pagesDrugs and Myasthenia Gravisskyclad_21100% (1)
- Treatmentofmyasthenia Gravis: Constantine Farmakidis,, Mamatha Pasnoor,, Mazen M. Dimachkie,, Richard J. BarohnDocument27 pagesTreatmentofmyasthenia Gravis: Constantine Farmakidis,, Mamatha Pasnoor,, Mazen M. Dimachkie,, Richard J. BarohnMomeneo NeoNo ratings yet
- Desirable Properties of PSA Pharmacologic AgentsDocument42 pagesDesirable Properties of PSA Pharmacologic AgentsMarjan HusniNo ratings yet
- Medical Management 3 Objectives of ManagementDocument4 pagesMedical Management 3 Objectives of ManagementSaima Sawal SalicNo ratings yet
- Cytotec® Misoprostol TabletsDocument12 pagesCytotec® Misoprostol Tabletssuhandi71No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyBij Hilario100% (1)
- Nihms 1045187Document33 pagesNihms 1045187Lissaberti AmaliahNo ratings yet
- Mestinon: Ame of The MedicineDocument6 pagesMestinon: Ame of The MedicinekhanztheconzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OR AreaDocument7 pagesDrug Study OR AreaVal FielNo ratings yet
- ZetamycinDocument6 pagesZetamycinelcapitano vegetaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System-2Document8 pagesAutonomic Nervous System-2محمد علي حميدNo ratings yet
- Antinauseants and AntiemeticsDocument8 pagesAntinauseants and AntiemeticsHamad AlshabiNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Medical Treatments For Endometriosis-Associated Pelvic PainDocument12 pagesReview Article: Medical Treatments For Endometriosis-Associated Pelvic PainponekNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Trigeminal NeuralgiaDocument16 pagesTreatment of Trigeminal NeuralgianaimNo ratings yet
- AntiemeticsDocument2 pagesAntiemeticsdr.anuthomas14No ratings yet
- Pleiotropic Effects of StatinsDocument5 pagesPleiotropic Effects of StatinsFathur RahmanNo ratings yet
- AMINOGLYCOSIDESDocument15 pagesAMINOGLYCOSIDESGareth BaleNo ratings yet
- Jurnal SheilaDocument17 pagesJurnal SheilaselaNo ratings yet
- Department of Pharmacology: Prof. Dr. Asya RehmanDocument15 pagesDepartment of Pharmacology: Prof. Dr. Asya RehmanGareth BaleNo ratings yet
- Principles of Antiplatelet Therapy: DR Htet Htet Htethtet@Imu - Edu.MyDocument36 pagesPrinciples of Antiplatelet Therapy: DR Htet Htet Htethtet@Imu - Edu.MyAbby Liew100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyHazel Kaye CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Symphatomimetics As Tocolytic DrugsDocument13 pagesSymphatomimetics As Tocolytic DrugsndutembemNo ratings yet
- Approach To MCAS Diagnosis and RX PDFDocument3 pagesApproach To MCAS Diagnosis and RX PDFmalamatiyya100% (6)
- Class Indications: MetronidazoleDocument3 pagesClass Indications: MetronidazoleDwi WulandariNo ratings yet
- GENTAMICIN - Gentamicin Sulfate Injection, Solution Fresenius Kabi USA, LLCDocument23 pagesGENTAMICIN - Gentamicin Sulfate Injection, Solution Fresenius Kabi USA, LLCStefi MaryNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide HCL Metoclopramide Inj 10mg-2ml IreDocument7 pagesMetoclopramide HCL Metoclopramide Inj 10mg-2ml IresiripNo ratings yet
- 1 Osteo and Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument62 pages1 Osteo and Rheumatoid ArthritisIbrahim BarhamNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Neuromuscular Junction: Myasthenia GravisDocument7 pagesDisorders of The Neuromuscular Junction: Myasthenia GravisZain AlAbideen AlTaeeNo ratings yet
- Antiemetics and ProkineticsDocument29 pagesAntiemetics and ProkineticsGilbert Girising100% (1)
- Cytotec Misoprostol Tablets: Reference ID: 3217917Document14 pagesCytotec Misoprostol Tablets: Reference ID: 3217917Maryam ZahraNo ratings yet
- Saba Hanif Presentation...Document19 pagesSaba Hanif Presentation...Saba KhanNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis: Association of British Neurologists' Management GuidelinesDocument14 pagesMyasthenia Gravis: Association of British Neurologists' Management Guidelinesafm26No ratings yet
- Inject Able ContraceptivesDocument67 pagesInject Able Contraceptivessalah subbahNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument7 pagesGentamicin: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchAdrian ArnasaputraNo ratings yet
- Otezla 10 MG Film-Coated Tablets: 1. Name of The Medicinal ProductDocument22 pagesOtezla 10 MG Film-Coated Tablets: 1. Name of The Medicinal ProductSunil SewakNo ratings yet
- Otezla 10 MG Film-Coated Tablets: 1. Name of The Medicinal ProductDocument22 pagesOtezla 10 MG Film-Coated Tablets: 1. Name of The Medicinal ProductSunil SewakNo ratings yet
- Emetics and Antiemetics DrugsDocument15 pagesEmetics and Antiemetics DrugsrajenderNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Tersering Di PuskesmasDocument5 pagesPenyakit Tersering Di PuskesmasRama Al MaduriNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spondylosis MedicationDocument3 pagesCervical Spondylosis MedicationhendrayatiranyNo ratings yet
- Anti Emetics and Anti SpasmodicsDocument13 pagesAnti Emetics and Anti SpasmodicsGabriel KidagayoNo ratings yet
- Physiology SomatostatinDocument5 pagesPhysiology Somatostatinivan diandyNo ratings yet
- JCM 11 01597Document23 pagesJCM 11 01597rafael rocha novaesNo ratings yet
- Eti Nurwening Sholikhah: Department of Pharmacology & Therapy Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah MadaDocument43 pagesEti Nurwening Sholikhah: Department of Pharmacology & Therapy Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah MadaadystiNo ratings yet
- Systemic Anti-Infl Ammatory AgentsDocument5 pagesSystemic Anti-Infl Ammatory Agentsbebek sakitNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyArdrina SappariNo ratings yet
- Mizollen Tablets: 1. Name of The Medicinal ProductDocument6 pagesMizollen Tablets: 1. Name of The Medicinal Productddandan_2No ratings yet
- ��تجميعات الفارما�Document4 pages��تجميعات الفارما�Turky TurkyNo ratings yet
- LapsusDocument23 pagesLapsushamba allahNo ratings yet
- Esmeron 10 MG/ML Solution For Injection Rocuronium Bromide Prescribing InformationDocument3 pagesEsmeron 10 MG/ML Solution For Injection Rocuronium Bromide Prescribing InformationVeeta Ruchi LieNo ratings yet
- Name of The Medicinal ProductDocument6 pagesName of The Medicinal ProductasdwasdNo ratings yet
- Antipatelet Drug TherapyDocument6 pagesAntipatelet Drug TherapySayali KhandaleNo ratings yet
- Vis AnneDocument22 pagesVis AnneImelda AtikaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Orientation SlidesDocument88 pagesCase Study Orientation SlidesJoseph Emmanuel CandaNo ratings yet
- Manjula PDocument6 pagesManjula PRanjani PNo ratings yet
- Oral White and Red LesionsDocument71 pagesOral White and Red LesionsHanin AbukhiaraNo ratings yet
- New Thesis With Corrections Grad School CorrectionsDocument62 pagesNew Thesis With Corrections Grad School Correctionsapi-535934790No ratings yet
- Thrombosis Research: Letter To The Editors-in-ChiefDocument3 pagesThrombosis Research: Letter To The Editors-in-ChiefRia GandaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ronald Frans, SP - THT-KL, MKes.Document12 pagesDr. Ronald Frans, SP - THT-KL, MKes.alpriani patrasNo ratings yet
- K180428Document8 pagesK180428Tony ChenNo ratings yet
- PSORIASISDocument9 pagesPSORIASISDianne BernardoNo ratings yet
- Citralife English TestimoniesDocument10 pagesCitralife English TestimoniesNajwa Mohd NorNo ratings yet
- HFOV High-Frequency-Oscillatory-VentilationDocument22 pagesHFOV High-Frequency-Oscillatory-VentilationJZNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: RationaleDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Rationaleimnas100% (1)
- Dr. Stefan Sacu ResearchDocument7 pagesDr. Stefan Sacu Researchpeiras2011No ratings yet
- Rehabilitation After Amputation of The Lower Limb in The Course of Diabetic Foot SyndromeDocument7 pagesRehabilitation After Amputation of The Lower Limb in The Course of Diabetic Foot SyndromeNoreen PunjwaniNo ratings yet
- Hysteroscopy Newsletter Vol 2 Issue 3 EnglishDocument22 pagesHysteroscopy Newsletter Vol 2 Issue 3 EnglishLuisNo ratings yet
- 05a Aravind Eye Hospital, Madurai, IndiaDocument4 pages05a Aravind Eye Hospital, Madurai, IndiaSubhadra HaribabuNo ratings yet
- History Taking and PEDocument30 pagesHistory Taking and PEMelissa Salayog100% (1)
- Laboratory Critical Values List: Analytes Age Group Critical Low Critical High/ Toxic UnitsDocument2 pagesLaboratory Critical Values List: Analytes Age Group Critical Low Critical High/ Toxic Unitsmelita ratnaNo ratings yet
- Red and White Blood Cell DisordersDocument11 pagesRed and White Blood Cell DisordersVittorio Di PaoloNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Drug MonitoringDocument10 pagesTherapeutic Drug MonitoringAnnie SethiNo ratings yet
- First Aid General PathologyDocument8 pagesFirst Aid General PathologyHamza AshrafNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapeutics For Advanced Practice A Practical Approach Ebook PDFDocument62 pagesPharmacotherapeutics For Advanced Practice A Practical Approach Ebook PDFrosanne.hahn846100% (46)
- M G Jedar2012.PDF (PDFDrive)Document190 pagesM G Jedar2012.PDF (PDFDrive)Vrushabh DharmikNo ratings yet
- Op GhaiDocument9 pagesOp GhaiParth MittalNo ratings yet
- DevicesDocument36 pagesDevicesKUMUTHA MALAR A/P PARMESWARANNo ratings yet
- Vascular RehabilitationDocument10 pagesVascular RehabilitationSuman DeyNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument7 pagesAssignmentAkilesh MNo ratings yet
- INOTROPESDocument48 pagesINOTROPESUnihealth Southwoods NursingNo ratings yet
- Caring For Your Central LineDocument20 pagesCaring For Your Central Lineapi-311857882No ratings yet
- PICO & Search Strategy Worksheet: Name: Macayla GreinerDocument6 pagesPICO & Search Strategy Worksheet: Name: Macayla Greinerapi-407402630No ratings yet
Neostigmine (TUSOM - Pharmwiki) PDF
Neostigmine (TUSOM - Pharmwiki) PDF
Uploaded by
pooja lokhande0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views1 pageOriginal Title
neostigmine [TUSOM _ Pharmwiki].pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views1 pageNeostigmine (TUSOM - Pharmwiki) PDF
Neostigmine (TUSOM - Pharmwiki) PDF
Uploaded by
pooja lokhandeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
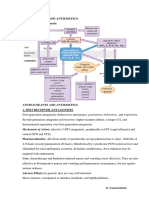
Neostigmine
Trade Names: generic, Prostigmin ®
Drug Class: Carbamate Anticholinesterase, Cholinomimetic
Mechanism of Action:
Inhibits the hydrolysis of acetylcholine by competing with acetylcholine for attachment to acetylcholinesterase at sites
of cholinergic transmission
It enhances cholinergic action by facilitating the transmission of impulses across neuromuscular junctions
It also has a direct cholinomimetic effect on skeletal muscle and possibly on autonomic ganglion cells
Because it contains a quaternary ammonium group it does not cross the blood-brain barrier
Indications:
For symptomatic treatment of myasthenia gravis
Its greatest usefulness is in prolonged therapy where no difficulty in swallowing is present
In acute myasthenic crisis where difficulty in breathing and swallowing is present, the parenteral form (neostigmine
methylsulfate) should be used. The patient can be transferred to the oral form as soon as it can be tolerated.
Off label: non-obstructive ileus (paralysis of the bowel) (Thompson & Magnuson, 2012; Kasi, 2013)
Contraindications:
Patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug
Contraindicated in patients with peritonitis or mechanical obstruction of the intestinal or urinary tract
Side Effects:
Generally due to an exaggeration of pharmacological effects of which salivation and fasiculation are the most common
Bowel cramps and diarrhea may also occur
For a more complete list, see the rxlist.com [http://www.rxlist.com/prostigmin-drug.htm] reference
Pharmacokinetics:
Neostigmine bromide is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration
As a rule, 15 mg of neostigmine bromide given orally is equivalent to 0.5 mg of neostigmine methylsulfate given
parenterally
Major drug Interactions:
Certain aminoglycoside antibiotics, especially neomycin, streptomycin and kanamycin, have a mild but definite
nondepolarizing blocking action which may accentuate neuromuscular block. These antibiotics should be used in the
myasthenic patient only where definitely indicated.
References:
Kasi PM (2013): The use of intravenous neostigmine in palliation of severe ileus. Case Reports in Gastrointestinal
Medicine Volume 2013 Article ID 796739, 4 pages. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/796739
[http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/796739]
Pappano AJ (2012) [http://libproxy.tulane.edu:2048/login?url=http://www.accessmedicine.com/content.aspx?aID=55820947]
Cholinoceptor-Activating & Cholinesterase-Inhibiting Drugs (Chapter 7). In: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology. 12e. Katzung
BG, Masters SB, Trevor AJ (Editors). McGraw-Hill / Lange. (Access-Medicine)
Thompson M, Magnuson B (2012): Management of postoperative ileus. Orthopedics 35(3):213-217. DOI:
10.3928/01477447-20120222-08
rxlist.com [http://www.rxlist.com/prostigmin-drug.htm] (Prostigmin ®)
Keywords
neostigmine
neostigmine.txt · Last modified: 2015/09/16 14:46 by cclarks
You might also like
- Health Teaching Plan CompleteDocument23 pagesHealth Teaching Plan CompleteDr. Oscar Arquiza100% (1)
- Obat AnestehesiDocument81 pagesObat Anestehesiedwinwedya_878246109No ratings yet
- NeostigmineDocument4 pagesNeostigmineDonna Lyn B. DizonNo ratings yet
- Pyridostigmine BromideDocument4 pagesPyridostigmine BromideRavinderenPichan100% (1)
- Speaker: DR Srikanth AlladiDocument71 pagesSpeaker: DR Srikanth AlladisrikanthalladiNo ratings yet
- Anticholinesterases and Sugammadex: Dr. Sachana KC 1 Year Resident Department of AnesthesiologyDocument64 pagesAnticholinesterases and Sugammadex: Dr. Sachana KC 1 Year Resident Department of AnesthesiologyKshitizma GiriNo ratings yet
- Principles of An-Tiplatelet Therapy: DR Htet Htet Htethtet@Imu - Edu.MyDocument36 pagesPrinciples of An-Tiplatelet Therapy: DR Htet Htet Htethtet@Imu - Edu.MyAbby LiewNo ratings yet
- Drugs and Myasthenia GravisDocument2 pagesDrugs and Myasthenia Gravisskyclad_21100% (1)
- Treatmentofmyasthenia Gravis: Constantine Farmakidis,, Mamatha Pasnoor,, Mazen M. Dimachkie,, Richard J. BarohnDocument27 pagesTreatmentofmyasthenia Gravis: Constantine Farmakidis,, Mamatha Pasnoor,, Mazen M. Dimachkie,, Richard J. BarohnMomeneo NeoNo ratings yet
- Desirable Properties of PSA Pharmacologic AgentsDocument42 pagesDesirable Properties of PSA Pharmacologic AgentsMarjan HusniNo ratings yet
- Medical Management 3 Objectives of ManagementDocument4 pagesMedical Management 3 Objectives of ManagementSaima Sawal SalicNo ratings yet
- Cytotec® Misoprostol TabletsDocument12 pagesCytotec® Misoprostol Tabletssuhandi71No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyBij Hilario100% (1)
- Nihms 1045187Document33 pagesNihms 1045187Lissaberti AmaliahNo ratings yet
- Mestinon: Ame of The MedicineDocument6 pagesMestinon: Ame of The MedicinekhanztheconzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OR AreaDocument7 pagesDrug Study OR AreaVal FielNo ratings yet
- ZetamycinDocument6 pagesZetamycinelcapitano vegetaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System-2Document8 pagesAutonomic Nervous System-2محمد علي حميدNo ratings yet
- Antinauseants and AntiemeticsDocument8 pagesAntinauseants and AntiemeticsHamad AlshabiNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Medical Treatments For Endometriosis-Associated Pelvic PainDocument12 pagesReview Article: Medical Treatments For Endometriosis-Associated Pelvic PainponekNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Trigeminal NeuralgiaDocument16 pagesTreatment of Trigeminal NeuralgianaimNo ratings yet
- AntiemeticsDocument2 pagesAntiemeticsdr.anuthomas14No ratings yet
- Pleiotropic Effects of StatinsDocument5 pagesPleiotropic Effects of StatinsFathur RahmanNo ratings yet
- AMINOGLYCOSIDESDocument15 pagesAMINOGLYCOSIDESGareth BaleNo ratings yet
- Jurnal SheilaDocument17 pagesJurnal SheilaselaNo ratings yet
- Department of Pharmacology: Prof. Dr. Asya RehmanDocument15 pagesDepartment of Pharmacology: Prof. Dr. Asya RehmanGareth BaleNo ratings yet
- Principles of Antiplatelet Therapy: DR Htet Htet Htethtet@Imu - Edu.MyDocument36 pagesPrinciples of Antiplatelet Therapy: DR Htet Htet Htethtet@Imu - Edu.MyAbby Liew100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyHazel Kaye CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Symphatomimetics As Tocolytic DrugsDocument13 pagesSymphatomimetics As Tocolytic DrugsndutembemNo ratings yet
- Approach To MCAS Diagnosis and RX PDFDocument3 pagesApproach To MCAS Diagnosis and RX PDFmalamatiyya100% (6)
- Class Indications: MetronidazoleDocument3 pagesClass Indications: MetronidazoleDwi WulandariNo ratings yet
- GENTAMICIN - Gentamicin Sulfate Injection, Solution Fresenius Kabi USA, LLCDocument23 pagesGENTAMICIN - Gentamicin Sulfate Injection, Solution Fresenius Kabi USA, LLCStefi MaryNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide HCL Metoclopramide Inj 10mg-2ml IreDocument7 pagesMetoclopramide HCL Metoclopramide Inj 10mg-2ml IresiripNo ratings yet
- 1 Osteo and Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument62 pages1 Osteo and Rheumatoid ArthritisIbrahim BarhamNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Neuromuscular Junction: Myasthenia GravisDocument7 pagesDisorders of The Neuromuscular Junction: Myasthenia GravisZain AlAbideen AlTaeeNo ratings yet
- Antiemetics and ProkineticsDocument29 pagesAntiemetics and ProkineticsGilbert Girising100% (1)
- Cytotec Misoprostol Tablets: Reference ID: 3217917Document14 pagesCytotec Misoprostol Tablets: Reference ID: 3217917Maryam ZahraNo ratings yet
- Saba Hanif Presentation...Document19 pagesSaba Hanif Presentation...Saba KhanNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis: Association of British Neurologists' Management GuidelinesDocument14 pagesMyasthenia Gravis: Association of British Neurologists' Management Guidelinesafm26No ratings yet
- Inject Able ContraceptivesDocument67 pagesInject Able Contraceptivessalah subbahNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument7 pagesGentamicin: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchAdrian ArnasaputraNo ratings yet
- Otezla 10 MG Film-Coated Tablets: 1. Name of The Medicinal ProductDocument22 pagesOtezla 10 MG Film-Coated Tablets: 1. Name of The Medicinal ProductSunil SewakNo ratings yet
- Otezla 10 MG Film-Coated Tablets: 1. Name of The Medicinal ProductDocument22 pagesOtezla 10 MG Film-Coated Tablets: 1. Name of The Medicinal ProductSunil SewakNo ratings yet
- Emetics and Antiemetics DrugsDocument15 pagesEmetics and Antiemetics DrugsrajenderNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Tersering Di PuskesmasDocument5 pagesPenyakit Tersering Di PuskesmasRama Al MaduriNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spondylosis MedicationDocument3 pagesCervical Spondylosis MedicationhendrayatiranyNo ratings yet
- Anti Emetics and Anti SpasmodicsDocument13 pagesAnti Emetics and Anti SpasmodicsGabriel KidagayoNo ratings yet
- Physiology SomatostatinDocument5 pagesPhysiology Somatostatinivan diandyNo ratings yet
- JCM 11 01597Document23 pagesJCM 11 01597rafael rocha novaesNo ratings yet
- Eti Nurwening Sholikhah: Department of Pharmacology & Therapy Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah MadaDocument43 pagesEti Nurwening Sholikhah: Department of Pharmacology & Therapy Faculty of Medicine Universitas Gadjah MadaadystiNo ratings yet
- Systemic Anti-Infl Ammatory AgentsDocument5 pagesSystemic Anti-Infl Ammatory Agentsbebek sakitNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyArdrina SappariNo ratings yet
- Mizollen Tablets: 1. Name of The Medicinal ProductDocument6 pagesMizollen Tablets: 1. Name of The Medicinal Productddandan_2No ratings yet
- ��تجميعات الفارما�Document4 pages��تجميعات الفارما�Turky TurkyNo ratings yet
- LapsusDocument23 pagesLapsushamba allahNo ratings yet
- Esmeron 10 MG/ML Solution For Injection Rocuronium Bromide Prescribing InformationDocument3 pagesEsmeron 10 MG/ML Solution For Injection Rocuronium Bromide Prescribing InformationVeeta Ruchi LieNo ratings yet
- Name of The Medicinal ProductDocument6 pagesName of The Medicinal ProductasdwasdNo ratings yet
- Antipatelet Drug TherapyDocument6 pagesAntipatelet Drug TherapySayali KhandaleNo ratings yet
- Vis AnneDocument22 pagesVis AnneImelda AtikaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Orientation SlidesDocument88 pagesCase Study Orientation SlidesJoseph Emmanuel CandaNo ratings yet
- Manjula PDocument6 pagesManjula PRanjani PNo ratings yet
- Oral White and Red LesionsDocument71 pagesOral White and Red LesionsHanin AbukhiaraNo ratings yet
- New Thesis With Corrections Grad School CorrectionsDocument62 pagesNew Thesis With Corrections Grad School Correctionsapi-535934790No ratings yet
- Thrombosis Research: Letter To The Editors-in-ChiefDocument3 pagesThrombosis Research: Letter To The Editors-in-ChiefRia GandaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ronald Frans, SP - THT-KL, MKes.Document12 pagesDr. Ronald Frans, SP - THT-KL, MKes.alpriani patrasNo ratings yet
- K180428Document8 pagesK180428Tony ChenNo ratings yet
- PSORIASISDocument9 pagesPSORIASISDianne BernardoNo ratings yet
- Citralife English TestimoniesDocument10 pagesCitralife English TestimoniesNajwa Mohd NorNo ratings yet
- HFOV High-Frequency-Oscillatory-VentilationDocument22 pagesHFOV High-Frequency-Oscillatory-VentilationJZNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: RationaleDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Rationaleimnas100% (1)
- Dr. Stefan Sacu ResearchDocument7 pagesDr. Stefan Sacu Researchpeiras2011No ratings yet
- Rehabilitation After Amputation of The Lower Limb in The Course of Diabetic Foot SyndromeDocument7 pagesRehabilitation After Amputation of The Lower Limb in The Course of Diabetic Foot SyndromeNoreen PunjwaniNo ratings yet
- Hysteroscopy Newsletter Vol 2 Issue 3 EnglishDocument22 pagesHysteroscopy Newsletter Vol 2 Issue 3 EnglishLuisNo ratings yet
- 05a Aravind Eye Hospital, Madurai, IndiaDocument4 pages05a Aravind Eye Hospital, Madurai, IndiaSubhadra HaribabuNo ratings yet
- History Taking and PEDocument30 pagesHistory Taking and PEMelissa Salayog100% (1)
- Laboratory Critical Values List: Analytes Age Group Critical Low Critical High/ Toxic UnitsDocument2 pagesLaboratory Critical Values List: Analytes Age Group Critical Low Critical High/ Toxic Unitsmelita ratnaNo ratings yet
- Red and White Blood Cell DisordersDocument11 pagesRed and White Blood Cell DisordersVittorio Di PaoloNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Drug MonitoringDocument10 pagesTherapeutic Drug MonitoringAnnie SethiNo ratings yet
- First Aid General PathologyDocument8 pagesFirst Aid General PathologyHamza AshrafNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapeutics For Advanced Practice A Practical Approach Ebook PDFDocument62 pagesPharmacotherapeutics For Advanced Practice A Practical Approach Ebook PDFrosanne.hahn846100% (46)
- M G Jedar2012.PDF (PDFDrive)Document190 pagesM G Jedar2012.PDF (PDFDrive)Vrushabh DharmikNo ratings yet
- Op GhaiDocument9 pagesOp GhaiParth MittalNo ratings yet
- DevicesDocument36 pagesDevicesKUMUTHA MALAR A/P PARMESWARANNo ratings yet
- Vascular RehabilitationDocument10 pagesVascular RehabilitationSuman DeyNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument7 pagesAssignmentAkilesh MNo ratings yet
- INOTROPESDocument48 pagesINOTROPESUnihealth Southwoods NursingNo ratings yet
- Caring For Your Central LineDocument20 pagesCaring For Your Central Lineapi-311857882No ratings yet
- PICO & Search Strategy Worksheet: Name: Macayla GreinerDocument6 pagesPICO & Search Strategy Worksheet: Name: Macayla Greinerapi-407402630No ratings yet