Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Passive Voice - Verb Table
Passive Voice - Verb Table
Uploaded by
Juan Pablo Gomez Martinez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views1 pageThe document discusses the conjugation of the verb "to be" in passive voice constructions in English. It notes that the verb "to be" is conjugated based on the tense of the original active verb, while the past participle of the main verb remains the same. Examples are provided of active and passive voice sentences using different tenses, demonstrating how the verb "to be" changes form but the past participle stays the same. Key tenses and their corresponding forms of "to be" are listed for reference.
Original Description:
Original Title
passive voice - verb table
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the conjugation of the verb "to be" in passive voice constructions in English. It notes that the verb "to be" is conjugated based on the tense of the original active verb, while the past participle of the main verb remains the same. Examples are provided of active and passive voice sentences using different tenses, demonstrating how the verb "to be" changes form but the past participle stays the same. Key tenses and their corresponding forms of "to be" are listed for reference.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views1 pagePassive Voice - Verb Table
Passive Voice - Verb Table
Uploaded by
Juan Pablo Gomez MartinezThe document discusses the conjugation of the verb "to be" in passive voice constructions in English. It notes that the verb "to be" is conjugated based on the tense of the original active verb, while the past participle of the main verb remains the same. Examples are provided of active and passive voice sentences using different tenses, demonstrating how the verb "to be" changes form but the past participle stays the same. Key tenses and their corresponding forms of "to be" are listed for reference.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
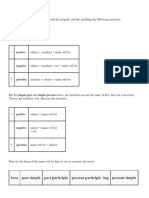
Lo difícil de “passive voice” es la conjugación del verbo [be].
Si el verbo en la oración activa está en presente
simple, el verbo [be] en la oración pasiva también será en presente simple más el “past participle” del verbo
original. Si el verbo en la oración activa está en futuro con “will”, el verbo [be] en la oración pasiva también será en
futuro con “will” más el “past participle” del verbo original.
Mira:
ACTIVE VOICE PASSIVE VOICE
SUBJECT [VERB] object + … SUBJECT [BE] past …
(orginal participle
object) (of original
verb)
Present A lot of watch the news The news is watched by a lot of
simple people every day. people
every day.
Past simple A lot of watched the news The news was watched by a lot of
people on people on
11/09/01 11/09/01
Future with A lot of will watch the news The news will be watched by a lot of
“will” people tomorrow. people
tomorrow.
Modal A lot of must the news to The news must be watched by a lot of
verbs people watch be well- people to
informed. be
successful.
Present A lot of are the news The news is being watched by a lot of
continuous people watching right now. people right
now.
Present A lot of have the news The news has been watched by a lot of
perfect people watched during their people
life. throughout
history.
Fíjense que en la columna “past participle”, el forma del verbo no cambia! Queda igual: watched.
Pero miren en la columna [be] … Aquí cambia el verbo [be] en que depende en el tiempo.
Entonces si el tiempo es: El verbos [be] está conjugado así:
PRESENT SIMPLE am
is
are
PRESENT CONTINUOUS am being
is being
are being
PAST SIMPLE was
were + PAST PARTICIPLE!
PAST CONTINUOUS was being
were being
FUTURE WITH WILL will be
MODAL VERBS (can, must, etc.) must be
can be
should be
PRESENT PERFECT has been
have been
PAST PERFECT had been
You might also like
- Ser EstarDocument12 pagesSer EstarHome Languages East UWCSEA100% (1)
- Palmenia KielioppiDocument22 pagesPalmenia KielioppierkkiankaraNo ratings yet
- GMAT Verbal Test StrategyDocument60 pagesGMAT Verbal Test StrategyLalitMohanPandeyNo ratings yet
- PASSIVE VOICE - WorsheetDocument4 pagesPASSIVE VOICE - Worsheetdaniel delgado perezNo ratings yet
- Integrated Course Unit 8Document20 pagesIntegrated Course Unit 8WildanNo ratings yet
- Active - Passive VoiceDocument8 pagesActive - Passive VoiceFATIMANo ratings yet
- The Passive VoiceDocument3 pagesThe Passive VoiceisabelgilguerreroNo ratings yet
- English Is Spoken in Many CountriesDocument2 pagesEnglish Is Spoken in Many CountriescndnzNo ratings yet
- Basic Tenses With Be: + PositiveDocument6 pagesBasic Tenses With Be: + Positiveomkar digamabar sononeNo ratings yet
- Bab - La Conjugacin Ingls To - PaleDocument2 pagesBab - La Conjugacin Ingls To - PaleTomNo ratings yet
- Review of Passive ConstructionsDocument2 pagesReview of Passive ConstructionsMOUGANGNo ratings yet
- Conjugación Del Verbo en Inglés Con: Present Preterite Present ContinuousDocument1 pageConjugación Del Verbo en Inglés Con: Present Preterite Present Continuousdavid sricamNo ratings yet
- Basic Tenses With BEDocument5 pagesBasic Tenses With BEFarahNo ratings yet
- Basic TensesDocument3 pagesBasic TensesSyafqhNo ratings yet
- Voz Pasiva TeoriaDocument3 pagesVoz Pasiva TeoriaDaniel D'assaroNo ratings yet
- Conjugação Do Verbo To Be em Inglês - Conjugador de Verbos Bab - LaDocument1 pageConjugação Do Verbo To Be em Inglês - Conjugador de Verbos Bab - LaLéo Primoroso Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Tabla Conjugacion Verbo To BeDocument2 pagesTabla Conjugacion Verbo To BeNataly BarreraNo ratings yet
- Conjugare To HAVEDocument2 pagesConjugare To HAVEcris100% (1)
- EstrellasDocument1 pageEstrellasMaribel Sanchez HenestrosaNo ratings yet
- Nota GrammarDocument7 pagesNota GrammarAlmizan Hanim Ab KadirNo ratings yet
- Bab - La Conjugare Englez To - BeDocument2 pagesBab - La Conjugare Englez To - BeAx AxNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument7 pagesReported SpeechAnnapurna GNo ratings yet
- The Passive - LM IvDocument8 pagesThe Passive - LM IvLidia Asbel FernándezNo ratings yet
- Unlocking Italian Irregular Verbs Elisas Italian SchoolDocument25 pagesUnlocking Italian Irregular Verbs Elisas Italian Schoolcheli villalbaNo ratings yet
- Conjugacion Verbos Ingles PDFDocument19 pagesConjugacion Verbos Ingles PDFMarcela MuñozNo ratings yet
- La Voz Pasiva 2Document6 pagesLa Voz Pasiva 2Ines Rodri MorenoNo ratings yet
- Passive and Active Voice (1) Passive and Active VoiceDocument5 pagesPassive and Active Voice (1) Passive and Active VoiceSergioNo ratings yet
- Conjugaison Du Verbe Être en Anglais To Be PDFDocument1 pageConjugaison Du Verbe Être en Anglais To Be PDFfranckNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument37 pagesIlovepdf MergedmarracheNo ratings yet
- Direct Speech and Indirect SpeechDocument4 pagesDirect Speech and Indirect SpeechAndreea PatrauteanuNo ratings yet
- Verbo To Be CompletoDocument5 pagesVerbo To Be CompletoDenise VilelaNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument20 pagesPassive VoiceFabricio Moncada SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Diktan Sonra - Madan Önce Boyunca & Süresince Özel KullanimlarDocument1 pageDiktan Sonra - Madan Önce Boyunca & Süresince Özel KullanimlarAnonymous rJi74AWkNo ratings yet
- Tarea Conjugacion de VerbosDocument8 pagesTarea Conjugacion de VerbosRudy ValladaresNo ratings yet
- Estudo de InglesDocument6 pagesEstudo de InglesLuke TryoutNo ratings yet
- PassiveDocument2 pagesPassiveEmre BaliNo ratings yet
- PassiveDocument2 pagesPassiveFurkan KasaNo ratings yet
- Be A General Overview of Time Constructions and Us Classroom Posters Grammar Guides 108867Document1 pageBe A General Overview of Time Constructions and Us Classroom Posters Grammar Guides 108867AndreeaMateiNo ratings yet
- Verb Conjugation #7 Present With A Future Value: Lesson NotesDocument4 pagesVerb Conjugation #7 Present With A Future Value: Lesson NotesTamim RahmanNo ratings yet
- Bab - La Conjugao Ingls HaveDocument2 pagesBab - La Conjugao Ingls HavelillyNo ratings yet
- Number Pronoun Be Form (Present) Be Form (Past) Future From Have FromDocument2 pagesNumber Pronoun Be Form (Present) Be Form (Past) Future From Have FromPadhy ParthosarathiNo ratings yet
- Futur Simple Et Futur ProcheDocument3 pagesFutur Simple Et Futur ProcheJigar ShahNo ratings yet
- PASSive VoiceDocument2 pagesPASSive VoiceCarlos Henrique DE PaulaNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice 1Document19 pagesPassive Voice 1Rehan ArdiNo ratings yet
- Active and Possive Voice 1Document12 pagesActive and Possive Voice 1rayke azzamiNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument4 pagesActive and Passive VoiceOJ RIONo ratings yet
- The Passive Voice: Active PasiveDocument2 pagesThe Passive Voice: Active PasiveAlejandro Hernandez MirasNo ratings yet
- Translate Into Romanian: Thinking of To Roar in That Way Over A Saint in Heaven.'' (Emily Bronte-Wuthering Heights)Document4 pagesTranslate Into Romanian: Thinking of To Roar in That Way Over A Saint in Heaven.'' (Emily Bronte-Wuthering Heights)Aurelian WNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice - Ielts and InversionDocument4 pagesPassive Voice - Ielts and InversionJoseMa Aral100% (1)
- Passive VoiceDocument3 pagesPassive VoiceAlba Domingo CrusatNo ratings yet
- Statements:: Reported SpeechDocument2 pagesStatements:: Reported Speechlpa_20No ratings yet
- Italian 3 1 AudiobookDocument168 pagesItalian 3 1 AudiobookBurcu BurcuNo ratings yet
- English 7-Q2-Lecture 4-Voices of VerbDocument1 pageEnglish 7-Q2-Lecture 4-Voices of VerbArcee Joy RadovanNo ratings yet
- Aula 13 - Passive VoiceDocument30 pagesAula 13 - Passive VoiceJucilene SantosNo ratings yet
- Miraa Active and PassiveDocument9 pagesMiraa Active and PassiveMira FebrianelNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument10 pagesTensesShyamala KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- Verbos AuxiliaresDocument20 pagesVerbos Auxiliaresapi-3724827100% (13)
- The Seven Generations and The Seven Grandfather TeachingsFrom EverandThe Seven Generations and The Seven Grandfather TeachingsNo ratings yet
- Expression and Literature: Common Tumbuka Ideophones and their UsageFrom EverandExpression and Literature: Common Tumbuka Ideophones and their UsageNo ratings yet
- T14 PDFDocument24 pagesT14 PDFÁlvaro Sánchez AbadNo ratings yet
- 9 Ә КТПDocument21 pages9 Ә КТПNazkonti NazkontiNo ratings yet
- Judgement and PripositionsDocument7 pagesJudgement and Pripositionschememartinez29No ratings yet
- CONDITIONALDocument25 pagesCONDITIONALShiella Mae Vispo100% (1)
- Disonariu Kabuverdeanu 1994Document81 pagesDisonariu Kabuverdeanu 1994JanetNo ratings yet
- Prefixes - Vocabulary - EnglishClubDocument3 pagesPrefixes - Vocabulary - EnglishClubElke Wonders100% (1)
- Linking Verbs: Linking Verb Linking Verb Linking Verb Linking VerbDocument1 pageLinking Verbs: Linking Verb Linking Verb Linking Verb Linking VerbFelipe FCNo ratings yet
- The Nuts and Bolts of Arabic English PDFDocument341 pagesThe Nuts and Bolts of Arabic English PDFAli Muhammad YousifNo ratings yet
- This Quiz Will Test Your Recognition of SubjectDocument10 pagesThis Quiz Will Test Your Recognition of SubjectSmy LeiiNo ratings yet
- Tips For Ielts - Unit 1 - ReadingDocument17 pagesTips For Ielts - Unit 1 - ReadingNajmul HasanNo ratings yet
- LEXICOLOGY I - Lectures: Lecture 1 - IntroductionDocument80 pagesLEXICOLOGY I - Lectures: Lecture 1 - IntroductionPavla JanouškováNo ratings yet
- Sing Adjectives: Universidad Autónoma de Baja California Facultad de Idiomas Tronco Común Morfologia Del Segundo IdiomaDocument17 pagesSing Adjectives: Universidad Autónoma de Baja California Facultad de Idiomas Tronco Común Morfologia Del Segundo IdiomaYaritza Gisell AguilarNo ratings yet
- Teaching Upsr Note ExpansionDocument19 pagesTeaching Upsr Note ExpansionHasnah Ibrahim HasnahNo ratings yet
- Article Simple Sentence PDFDocument7 pagesArticle Simple Sentence PDFmaimunah0% (1)
- Chapter - 4 TenseDocument31 pagesChapter - 4 TenseAbhishek VermaNo ratings yet
- Notes English 1423 24 25Document37 pagesNotes English 1423 24 25AhmadNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 Word Formation Online 2nd Term 20-21Document84 pagesCh. 5 Word Formation Online 2nd Term 20-21AmalNo ratings yet
- Subject and Verb Agreement Quiz 1Document11 pagesSubject and Verb Agreement Quiz 1Kimberly Roxas50% (2)
- b2 U4 6min Gram PhrasalsDocument4 pagesb2 U4 6min Gram PhrasalsAhmed AbdelhaseebNo ratings yet
- Giant Panda Mei Xiang Gives Birth at National Zoo: Academic English Workshop 2 NameDocument3 pagesGiant Panda Mei Xiang Gives Birth at National Zoo: Academic English Workshop 2 NameManuel HNNo ratings yet
- A Lot, Many, Much, Few, Little StudentDocument10 pagesA Lot, Many, Much, Few, Little StudentValentina García CoronadoNo ratings yet
- English Tenses Manual: Turi4BDocument10 pagesEnglish Tenses Manual: Turi4BRichy HernándezNo ratings yet
- WGK01 01 Pef 20190815Document50 pagesWGK01 01 Pef 20190815RafaNo ratings yet
- Active Voice, Passive Voice: Subject Verb ObjectDocument4 pagesActive Voice, Passive Voice: Subject Verb ObjectMarishka BivolNo ratings yet
- Spanish Grammar in Context Third Edition 3nbsped 3966871463Document457 pagesSpanish Grammar in Context Third Edition 3nbsped 3966871463Dina Zapata100% (1)
- Unit 7: Right or Wrong?Document40 pagesUnit 7: Right or Wrong?Minh TrangNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs List: Infinitive Past Simple Past Participle TranslationDocument2 pagesIrregular Verbs List: Infinitive Past Simple Past Participle TranslationmontseNo ratings yet
- Teaching Adverbs - (Literacy Strategy Guide)Document8 pagesTeaching Adverbs - (Literacy Strategy Guide)Princejoy ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Predicate Nouns and AdjectivesDocument7 pagesPredicate Nouns and Adjectivesapi-257262131No ratings yet