Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Optical Commuications Lesson Plan
Optical Commuications Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
Shaik Sohel PashaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Optical Commuications Lesson Plan
Optical Commuications Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
Shaik Sohel PashaCopyright:
Available Formats
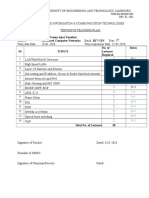
DEPARTMENT OF …ECE
COURSE PLAN: 2019 - 2020
Academic Year 2019-20 Class IV
Subject Name OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS Subject Code EC851PE
Faculty Name SHAIK SOHEL PASHA Total No. of Periods 70
Commencement of Completion of
16th Dec 2019 7th April 2020
Instruction Instruction
Date of I MID Exam 10th to 12th Feb 2019 Date of II MID Exam 8th to 11th April 2020
Prerequisites: Fundamentals of Electromagnetic theory, Principles of Communication Systems.
Course Objectives: The objectives of the course are:
To realize the significance of optical fiber communications.
To understand the construction and characteristics of optical fiber cable.
To develop the knowledge of optical signal sources and power launching.
To identify and understand the operation of various optical detectors.
To understand the design of optical systems and WDM.
Date of completion
Reason
Principal/
Week Unit Lecture for
No. No. No. Topic Proposed Actual deviation HOD
Historical development,
L1 The general system 16-12-19
Advantages of Optical Fiber 17-12-19
L2
Communications
Optical Fiber Wave Guides- 18-12-19
L3 Introduction
L4 Ray Theory Transmission 19-12-19
Total Internal Reflection 20-12-19
1 UNIT- L5
1 L6 Acceptance Angle 23-12-19
L7 Numerical Aperture 24-12-19
L8 Skew Rays 27-12-19
L9 Cylindrical Fibers- Modes 28-12-19
V number 30-12-19
2 L10
L11 Mode Coupling 31-12-19
L12 Step Index Fibers 2/1/2020
3 L13 Graded Index Fibers 3/1/2020
Cut Off Wavelength, Mode 4/1/2020
L14 Field Diameter
L15 Effective Refractive Index 6/1/2020
L16 Fiber Materials Glass, 7/1/2020
L17 Halide, Active Glass 8/1/2020
Chalgenide Glass, Plastic
4 L18
Optical Fibers 9/1/2020
5 L19 Attenuation, Absorption 10/1/2020
Scattering and Bending
Losses, Core and Cladding
L20
Losses 17-01-20
Information Capacity
L21
Determination 18-01-20
Group Delay, Types
L22 of Dispersion 20-01-20
UNIT- L23 Material Dispersion 21-01-20
2
L24 Wave-Guide Dispersion 22-01-20
Polarization Mode
L25 Dispersion 23-01-20
L26 Intermodal Dispersion 24-01-20
L27 Pulse Broadening 25-01-20
Optical Fiber Connectors,
L28 Connector Types 27-01-20
Single Mode Fiber
Connectors, Connector
6 L29 Return Loss 28-01-20
L30 Splicing Techniques 29-01-20
Splicing Single Mode
L31 Fibers 30-01-20
Fiber Alignment and Joint
L32
Loss 31-01-20
L33 Multimode Fiber Joints 1/2/2020
L34 Single Mode Fiber Joints 3/2/2020
7 L35 LEDs, Structures, Materials 4/2/2020
L36 Quantum Efficiency 5/2/2020
UNIT-
3 L37 Power, Modulation, 6/2/2020
L38 Power Bandwidth Product 7/2/2020
Injection Laser Diodes-
L39 Modes 8/2/2020
L40 Threshold Conditions 13-02-20
External, Quantum
L41
8 Efficiency 14-02-20
Laser Diode Rate
L42 Equations, 15-02-20
9 L43 Resonant Frequencies 17-02-20
L44
Reliability of LED, & ILD.
18-02-20
Output Patterns, Power
L45 Coupling 19-02-20
L46 Power Launching 20-02-20
Equilibrium Numerical
L47 Aperture 22-02-20
Laser Diode to Fiber
10 L48 Coupling 24-02-20
Physical Principles of PIN and
L49 APD 25-02-20
L50 Detector Response Time 26-02-20
Temperature Effect on
L51 Avalanche Gain 27-02-20
Comparison of Photo
11 L52 Detectors 28-02-20
L53 Optical Receiver Operation 2/3/2020
UNIT-
4 Fundamental Receiver
L54 Operation 5/3/2020
12 L55 Digital Signal Transmission 6/3/2020
L56 Error Sources, 9/3/2020
L57 Digital Receiver Performance, 10/3/2020
L58 Probability of Errors 11/3/2020
13 L59 Quantum Limit 12/3/2020
L60 Analog Receivers. 16-03-20
L61 Optical System
14
Design,Considerations 17-03-20
Component Choice,
L62 Multiplexing 18-03-20
Point-to- Point
L63 Links, System Considerations 19-03-20
Link Power Budget with
L64 Examples, 20-03-20
Overall Fiber Dispersion
UNIT- in Multi-Mode and Single
5 Mode Fibers,
L65 23-03-20
Rise Time Budget with
15 L66 Examples 24-03-20
L67 Transmission Distance 26-03-20
L68 Line Coding in Optical Links 27-03-20
WDM, Necessity, Principles,
L69 Types of WDM 30-03-20
Measurement of
Attenuation and
16 L70 Dispersion, Eye Pattern 2/4/2020
TEXT BOOKS:
Optical Fiber Communications – Gerd Keiser, MC GRAW HILL EDUCATION, 4th Edition, 2008.
Optical Fiber Communications – John M. Senior, Pearson Education, 3rd Edition, 2009.
REFERENCES:
Fiber Optic Communications – D.K. Mynbaev , S.C. Gupta and Lowell L. Scheiner,
Pearson Education, 2005.
Text Book on Optical Fibre Communication and its Applications – S.C.Gupta, PHI,
2005.
Fiber Optic Communication Systems – Govind P. Agarwal , John Wiley, 3rd Ediition,
2004.
Introduction to Fiber Optics by Donald J.Sterling Jr. – Cengage learning, 2004.
COURSE OUTCOMES: At the end of the course, the student will be able to:
Understand and analyze the constructional parameters of optical fibres.
Be able to design an optical system.
Estimate the losses due to attenuation, absorption, scattering and bending.
Compare various optical detectors and choose suitable one for different applications.
Signature of the Faculty Signature of the HOD
With date with date
You might also like
- Ece-Vii-optical Fiber Communication NotesDocument254 pagesEce-Vii-optical Fiber Communication NotesLokesh100% (1)
- Physics Digital NotesDocument83 pagesPhysics Digital NotesArun MozhiNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document4 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Premal PatelNo ratings yet
- 18 1st Sem ACN TPDocument1 page18 1st Sem ACN TPNaeem Aijaz YousfaniNo ratings yet
- EM AND OPTICS PROJECT 3 (1st)Document51 pagesEM AND OPTICS PROJECT 3 (1st)Durgesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Oc r16 1-6 Units NotesDocument255 pagesOc r16 1-6 Units NotesSayali PaunikarNo ratings yet
- MtechlessonDocument10 pagesMtechlessonmaheshwarivikas1982No ratings yet
- Digital Communications Printable PDFDocument42 pagesDigital Communications Printable PDFStarz EdgeNo ratings yet
- Anand Institute of Higher Technology KAZHIPATTUR - 603 103Document5 pagesAnand Institute of Higher Technology KAZHIPATTUR - 603 103addssdfaNo ratings yet
- Motorola1981-82OptoelectronicDataBook Text PDFDocument287 pagesMotorola1981-82OptoelectronicDataBook Text PDFFLAVIONo ratings yet
- 20ec702 OCN Digital Notes Unit 2 - 24.7.23Document94 pages20ec702 OCN Digital Notes Unit 2 - 24.7.234113 PAVITHRA KNo ratings yet
- 20ec702 OCN Unit 1 Digital Notes Updated 17.07.23 (Autosaved)Document100 pages20ec702 OCN Unit 1 Digital Notes Updated 17.07.23 (Autosaved)4113 PAVITHRA KNo ratings yet
- ECEPurdue MOSFET Lundstrom L2.4Document15 pagesECEPurdue MOSFET Lundstrom L2.4alNo ratings yet
- Gpon PresentationDocument44 pagesGpon Presentationekskalibur450No ratings yet
- LPCMOSVD Assignment Questions-31-10-2023Document2 pagesLPCMOSVD Assignment Questions-31-10-2023anisankarhari25No ratings yet
- Computer Network IIDocument1 pageComputer Network IIdavigeNo ratings yet
- LESSENGERS Introduction 2023Document8 pagesLESSENGERS Introduction 2023lioraran oferNo ratings yet
- Gpon PresentationDocument44 pagesGpon Presentationekskalibur450No ratings yet
- ELECTRONICS KOE-048 Lecture PlanDocument2 pagesELECTRONICS KOE-048 Lecture PlanSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic CollimatorDocument3 pagesFiber Optic CollimatorWagner PeresNo ratings yet
- STD 12 PCMB CT4 - 5 Nov 2023Document1 pageSTD 12 PCMB CT4 - 5 Nov 2023sagarikaarun06No ratings yet
- SV6030P Single-Chip 802.11 B/G/N MAC/BB/Radio With SDIO/SPI - SLAVE InterfaceDocument28 pagesSV6030P Single-Chip 802.11 B/G/N MAC/BB/Radio With SDIO/SPI - SLAVE Interfaceapi-432313169No ratings yet
- 1 4902696320751370571Document289 pages1 4902696320751370571hello worldNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Electronics (10) & Electronics and Communication Engineering (11) SUBJECT CODE: 2161005Document4 pagesGujarat Technological University: Electronics (10) & Electronics and Communication Engineering (11) SUBJECT CODE: 2161005charanjeet singhNo ratings yet
- Common Lesson Plan FormatDocument3 pagesCommon Lesson Plan FormatArun Madapura SomannaNo ratings yet
- Ece-Vii-Optical Fiber Communication U1Document63 pagesEce-Vii-Optical Fiber Communication U1Rohini HMNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Communications With References New9docxDocument3 pagesFiber Optic Communications With References New9docxDurga Prasad TumulaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: and NetworkingDocument6 pagesLesson Plan: and Networkinghema_swizNo ratings yet
- Hillstone Transceiver Module Reference GuideDocument36 pagesHillstone Transceiver Module Reference GuideAndrew KupiecNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Connector Handbook - Ver2Document62 pagesOptical Fiber Connector Handbook - Ver2GcNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Connector Handbook - Ver 1.6Document61 pagesOptical Fiber Connector Handbook - Ver 1.6markpriceNo ratings yet
- 4P-4M-A2 Product SpecificationDocument5 pages4P-4M-A2 Product SpecificationTan Teck jinnNo ratings yet
- Lora DocumentationDocument47 pagesLora DocumentationwayadeljdideNo ratings yet
- 10EC72Document177 pages10EC72Odoch HerbertNo ratings yet
- P&SC HandoutDocument5 pagesP&SC HandoutSunny BNo ratings yet
- EC604 - Optical Fiber CommunicationDocument3 pagesEC604 - Optical Fiber CommunicationRonak05No ratings yet
- Composite Materials NewDocument74 pagesComposite Materials NewSns ImunNo ratings yet
- RRVV 65b r4vb v2 Product SpecificationsDocument5 pagesRRVV 65b r4vb v2 Product SpecificationsFrensel PetronaNo ratings yet
- Eee F426 1259 PDFDocument3 pagesEee F426 1259 PDFAnant ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 6Document34 pagesKuliah 6sarifebruaniNo ratings yet
- FIBERDocument7 pagesFIBERsamyNo ratings yet
- Requirements FY2021Document3 pagesRequirements FY2021Sweekrit ThakurNo ratings yet
- Ec6202 Scad MSM PDFDocument92 pagesEc6202 Scad MSM PDFManjuladevi KannanNo ratings yet
- OFC2010Document4 pagesOFC2010Rajashekhargouda PatilNo ratings yet
- 20ES1402Document2 pages20ES140220501a05b9No ratings yet
- SV6051P Single-Chip 802.11 B/G/N MAC/BB/Radio With SDIO InterfaceDocument26 pagesSV6051P Single-Chip 802.11 B/G/N MAC/BB/Radio With SDIO InterfaceinfosolutionNo ratings yet
- Basic of Optical Fiber 1Document5 pagesBasic of Optical Fiber 1maryamNo ratings yet
- SK6812 LED DatasheetDocument16 pagesSK6812 LED Datasheetjakalae5263No ratings yet
- Seneca College: Fiber Optics CommunicationsDocument13 pagesSeneca College: Fiber Optics CommunicationsSana AminNo ratings yet
- Ece-Vii-Optical Fiber Communication NotesDocument254 pagesEce-Vii-Optical Fiber Communication NotesRakesh ChakmaNo ratings yet
- RRVV 65a r4vb Product SpecificationsDocument5 pagesRRVV 65a r4vb Product SpecificationsFrensel PetronaNo ratings yet
- Eee 4 Ei8075 FoliDocument8 pagesEee 4 Ei8075 FoliS.Dhandayuthapani SundaramoorthyNo ratings yet
- Eee 4 Ei8075 FoliDocument8 pagesEee 4 Ei8075 FoliS.Dhandayuthapani SundaramoorthyNo ratings yet
- Session Planner and Syllabus CoverageDocument5 pagesSession Planner and Syllabus CoverageSurekha PittaNo ratings yet
- IV Year ECDocument20 pagesIV Year ECrgegNo ratings yet
- CMS ECAL Data Links Sub-Project Specification (Feasibility Study Report)Document26 pagesCMS ECAL Data Links Sub-Project Specification (Feasibility Study Report)broovaNo ratings yet
- Raport Dialux 8m115W25mDocument13 pagesRaport Dialux 8m115W25mFlorincrihanNo ratings yet
- Microwave System - Chapter 1Document64 pagesMicrowave System - Chapter 1Chhen SophaninNo ratings yet
- Illot Nanophotonics2020Document17 pagesIllot Nanophotonics2020Ramón José Pérez MenéndezNo ratings yet
- Specialty Optical Fibers HandbookFrom EverandSpecialty Optical Fibers HandbookAlexis MendezNo ratings yet
- Chu Chin Chow - Libretto (Typescript)Document68 pagesChu Chin Chow - Libretto (Typescript)nathan_hale_jrNo ratings yet
- GK Today Current Affairs June 2016Document273 pagesGK Today Current Affairs June 2016Enforcement OfficerNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Company List December 2018Document478 pagesConsolidated Company List December 2018Rishabh GhaiNo ratings yet
- Laurie Baker: (The Brick Master of Kerala)Document8 pagesLaurie Baker: (The Brick Master of Kerala)Malik MussaNo ratings yet
- 2170908Document19 pages2170908bhavikNo ratings yet
- The New National Building Code Implementing Rules and RegulationsDocument2 pagesThe New National Building Code Implementing Rules and RegulationsJoey Sarmiento Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Nâng Cao 1 - 1 BảnDocument4 pagesNâng Cao 1 - 1 BảnThu TàiNo ratings yet
- ECL-ACC980 ManualDocument4 pagesECL-ACC980 ManualAneal LiverpoolNo ratings yet
- Brown Vintage Timeline History Infographics (21.59 × 33.02 CM)Document1 pageBrown Vintage Timeline History Infographics (21.59 × 33.02 CM)John Erick AlmojuelaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 SequencesDocument4 pagesTopic 3 SequencesWan Aziah100% (1)
- Francisco Pagdanganan, Complainant, vs. Atty. Romeo C. Plata, Respondent.Document9 pagesFrancisco Pagdanganan, Complainant, vs. Atty. Romeo C. Plata, Respondent.ChristineNo ratings yet
- DeputationDocument8 pagesDeputationAnand MauryaNo ratings yet
- 12-32 List of Events Shelter Bus - TTC Nov 1-12 - All Depts (2) - CensoredDocument26 pages12-32 List of Events Shelter Bus - TTC Nov 1-12 - All Depts (2) - CensoredThe Globe and MailNo ratings yet
- F R N W: Rench Evolutionary Apoleonic ArsDocument7 pagesF R N W: Rench Evolutionary Apoleonic ArsevansauroNo ratings yet
- HVAC ValidationDocument15 pagesHVAC Validationpiyusharora1964100% (3)
- Research On Process of Raising Funds Through QipDocument5 pagesResearch On Process of Raising Funds Through QipRachit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Floyd Edwrads Memorial Scholarship Terms of Reference 2017Document3 pagesFloyd Edwrads Memorial Scholarship Terms of Reference 2017Aswin HarishNo ratings yet
- Fotip ResumeDocument3 pagesFotip Resumeapi-529088054No ratings yet
- Dishonour of Cheques and Negotiable Instruments - Legalsutra - Law Students' Knowledge-Base - Law School Projects, Moot Court Memorials, Class and Case Notes and More!Document8 pagesDishonour of Cheques and Negotiable Instruments - Legalsutra - Law Students' Knowledge-Base - Law School Projects, Moot Court Memorials, Class and Case Notes and More!Himanshu Mene100% (1)
- Aluminium Phosphide, A Highly Hazardous Pesticide, and A Suicide Poison in Southern Province of ZambiaDocument2 pagesAluminium Phosphide, A Highly Hazardous Pesticide, and A Suicide Poison in Southern Province of ZambiaSimon TemboNo ratings yet
- Crane Fabrication Standard Kit: Main Locations GH PhilosophyDocument2 pagesCrane Fabrication Standard Kit: Main Locations GH PhilosophyFiroz PawaskarNo ratings yet
- Sew Infrastructure 1 Ebs Case Study 214465Document6 pagesSew Infrastructure 1 Ebs Case Study 214465Arun BatraNo ratings yet
- Rubric of Acrilik Color PaintingDocument1 pageRubric of Acrilik Color PaintingUliManullangNo ratings yet
- A Project Study On "BANKING AT HDFC BANK LTD.": MBA in Banking (Finance)Document99 pagesA Project Study On "BANKING AT HDFC BANK LTD.": MBA in Banking (Finance)Hitesh kumar jenaNo ratings yet
- Members Members Shohanur Rahman Rahnuma Nur Elma Adnan Sami Khan Fatema Tuz Zohora Hasan UZ Zaman Safika Mashiat Sunjana Alam SamaDocument11 pagesMembers Members Shohanur Rahman Rahnuma Nur Elma Adnan Sami Khan Fatema Tuz Zohora Hasan UZ Zaman Safika Mashiat Sunjana Alam SamaShohanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Calculate Size of SolarDocument2 pagesCalculate Size of SolarMuhammad SalmanNo ratings yet
- CodaDocument15 pagesCodaShashi KartikyaNo ratings yet
- A Concept Paper About LoveDocument5 pagesA Concept Paper About LoveStephen Rivera100% (1)
- SUMAWAY - Nevada V CasugaDocument2 pagesSUMAWAY - Nevada V CasugaTintin SumawayNo ratings yet
- MOD2 Statement of Cash FlowsDocument2 pagesMOD2 Statement of Cash FlowsGemma DenolanNo ratings yet