Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Poster Presentation - B. Haemato PDF
Poster Presentation - B. Haemato PDF
Uploaded by
rrCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Calculated Fields in WorkdayDocument203 pagesCalculated Fields in Workdaysudeep chowdary100% (4)
- MCQ OrthoDocument45 pagesMCQ OrthodentistsurorNo ratings yet
- Haematology Test Name Results Biological Reference Interval Units Specimen Test Method CBC - Complete Blood CountDocument2 pagesHaematology Test Name Results Biological Reference Interval Units Specimen Test Method CBC - Complete Blood CountlijoNo ratings yet
- Robert Donington - Interpretation of Early Music PDFDocument616 pagesRobert Donington - Interpretation of Early Music PDFandres bonilla torres100% (10)
- Straight Line Past Papers Unit 1 Outcome 1 AnswersDocument13 pagesStraight Line Past Papers Unit 1 Outcome 1 AnswersNarendra MupparajuNo ratings yet
- Abnormal RBC Morphology PMB and MwaDocument2 pagesAbnormal RBC Morphology PMB and MwaPaul BandaNo ratings yet
- RBCWBC Abnormalities FinalDocument13 pagesRBCWBC Abnormalities FinalAlanah JaneNo ratings yet
- Hereditary SpherocytosisDocument26 pagesHereditary SpherocytosisVivek PatelNo ratings yet
- Pappenheimer Bodies: Lom-Oc, VillanuevaDocument16 pagesPappenheimer Bodies: Lom-Oc, VillanuevaSHUPATUSSAINo ratings yet
- Patholo Le2Document31 pagesPatholo Le2bitangyarahNo ratings yet
- RBC&WBC AbnormalitiesDocument10 pagesRBC&WBC AbnormalitiesDeomicah SolanoNo ratings yet
- Normocytic Normochromic AnemiaDocument18 pagesNormocytic Normochromic AnemiaElaizha PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 SummaryDocument4 pagesChapter 23 SummaryMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- RBC AnomaliesDocument10 pagesRBC AnomaliesSHUPATUSSAINo ratings yet
- BMLT Sem III Class Note Fate of RBCDocument1 pageBMLT Sem III Class Note Fate of RBCSubhasish BarikNo ratings yet
- Notes Lecture No 3 Cell Injury and MechanismDocument5 pagesNotes Lecture No 3 Cell Injury and MechanismDr-Rukhshanda RamzanNo ratings yet
- Hematology: FANER, Ned Denebe LACANILAO, Sunshine NUCUM, Billie Kim PAGADUAN, Maribec PUA, MonalisaDocument31 pagesHematology: FANER, Ned Denebe LACANILAO, Sunshine NUCUM, Billie Kim PAGADUAN, Maribec PUA, MonalisatzuquinoNo ratings yet
- ANEMIAS (Sickle Cell Anemia With Pathophysiology)Document31 pagesANEMIAS (Sickle Cell Anemia With Pathophysiology)mabec pagaduan70% (10)
- Color Atlas of Haematology 2000Document20 pagesColor Atlas of Haematology 2000Zahraa Al-Sayed100% (1)
- Pathology Question AnswerDocument4 pagesPathology Question AnswerDr-Rukhshanda RamzanNo ratings yet
- Blood Cell AnomaliesDocument4 pagesBlood Cell AnomaliesCiullaeNo ratings yet
- Pathology A - RBC and Bleeding Disorders (Bitun, 2015)Document19 pagesPathology A - RBC and Bleeding Disorders (Bitun, 2015)jlcocm-2022-00028No ratings yet
- Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument37 pagesSickle Cell Anemiahazelposis75% (4)
- Red Blood Cell Disorders Part 1 and 2Document7 pagesRed Blood Cell Disorders Part 1 and 2babael.zuher123No ratings yet
- Subject: Anemia - Defects of Red Blood Cell Membrane Production Discipline: PhysiopathologyDocument30 pagesSubject: Anemia - Defects of Red Blood Cell Membrane Production Discipline: PhysiopathologyCristina Teodora BerbecaruNo ratings yet
- Concept Map ExampleDocument2 pagesConcept Map ExampleLorrieNo ratings yet
- Hemapathology Case: Adrian Joe G. CaballesDocument15 pagesHemapathology Case: Adrian Joe G. CaballesAdrian CaballesNo ratings yet
- Spherocytes: RBC AnomaliesDocument9 pagesSpherocytes: RBC AnomaliesSHUPATUSSAINo ratings yet
- LEC 5 RBC METABOLISM AND Membrane StructureDocument30 pagesLEC 5 RBC METABOLISM AND Membrane StructureFrancis ValdezNo ratings yet
- HS 202 - 1Document5 pagesHS 202 - 1trina santiagoNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Anemia IntrinsicDocument14 pagesHemolytic Anemia IntrinsicSophia Gail ChingNo ratings yet
- 3 RBCDocument5 pages3 RBCAnusuya SNo ratings yet
- Pyshio Reviewer 1st ShiftingDocument9 pagesPyshio Reviewer 1st ShiftingMary Heart SanchezNo ratings yet
- RBC Disorder 2Document9 pagesRBC Disorder 2Dongho ShinNo ratings yet
- TentiranDocument8 pagesTentirandebby nirmasariNo ratings yet
- 10 - Rapidly Progressing GlomerulonephristisDocument26 pages10 - Rapidly Progressing Glomerulonephristisf3er3No ratings yet
- III. FINAL Nursing Care of Clients With Disturbances in Male Female Reproduction Sexuality EditedVersionDocument26 pagesIII. FINAL Nursing Care of Clients With Disturbances in Male Female Reproduction Sexuality EditedVersionKurt PepitoNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Anemia Part II - Microcytic and Macrocytic Anemia - Revised - Copy-3Document6 pagesWeek 9 Anemia Part II - Microcytic and Macrocytic Anemia - Revised - Copy-3Yoodge YoodgeNo ratings yet
- Congenital and Acquired Hemolytic Anemias: Ellis J. Neufeld MD, PHDDocument63 pagesCongenital and Acquired Hemolytic Anemias: Ellis J. Neufeld MD, PHDRabi DhakalNo ratings yet
- DR Samson Ehe Teron SPPK Clinical PthologistDocument31 pagesDR Samson Ehe Teron SPPK Clinical PthologistMaria JozilynNo ratings yet
- M6 BloodDocument7 pagesM6 BloodNel joy PaurilloNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Part I - BloodDocument123 pagesCirculatory System Part I - BloodAngelyn DomingoNo ratings yet
- Membrane DeformabilityDocument2 pagesMembrane DeformabilityKenneth Jake BatiduanNo ratings yet
- 2 CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH Reviewer 2Document4 pages2 CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH Reviewer 2manuelNo ratings yet
- Blood Is The "River of Life" That Surges Within UsDocument16 pagesBlood Is The "River of Life" That Surges Within UsKyle LumingkitNo ratings yet
- WBC Morphologic DefectDocument8 pagesWBC Morphologic DefectMARY KAYE YVONNE OTILLANo ratings yet
- MBB 324 Lecture15 IUP Misfolding RecyclingQADocument49 pagesMBB 324 Lecture15 IUP Misfolding RecyclingQASarahNo ratings yet
- RBC Production and DestructionDocument44 pagesRBC Production and DestructionNehemiah FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Ischemic Acute Renal Failure: Michael S. Goligorsky Wilfred LieberthalDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Ischemic Acute Renal Failure: Michael S. Goligorsky Wilfred LieberthaleekimsamonteNo ratings yet
- EyrthrokineticsDocument4 pagesEyrthrokineticsKenneth Jake BatiduanNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Urology SystemDocument130 pagesPathology of Urology SystemAmirahNo ratings yet
- HEMA LEC - ErythrocytesDocument5 pagesHEMA LEC - Erythrocytescherrycayari13No ratings yet
- ch10 Biomembrane structure-LODISHDocument79 pagesch10 Biomembrane structure-LODISHHurmat AmnaNo ratings yet
- Hi Stop Hath Ology 2Document22 pagesHi Stop Hath Ology 2vivek govardhanamNo ratings yet
- Blood and Blood ComponentsDocument51 pagesBlood and Blood ComponentsJeevitha VanithaNo ratings yet
- Cell Injury and Death: By: Taleya HidayatullahDocument49 pagesCell Injury and Death: By: Taleya HidayatullahtaleyaNo ratings yet
- Blood FunctionsDocument3 pagesBlood FunctionshelloaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3Document12 pagesTopic 3Ria AccadNo ratings yet
- Cellular InjuryDocument4 pagesCellular InjuryKLIPPNo ratings yet
- Exercise No.4: Cell MembraneDocument28 pagesExercise No.4: Cell MembraneconnievelardeNo ratings yet
- Organelle/ Inclusion Functions LM Features EM Features Associated DiseasesDocument6 pagesOrganelle/ Inclusion Functions LM Features EM Features Associated DiseasesAine CebedoNo ratings yet
- Red Blood Cells, Functions, Diseases A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment, And Related ConditionsFrom EverandRed Blood Cells, Functions, Diseases A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment, And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Liver: Biology and PathobiologyFrom EverandThe Liver: Biology and PathobiologyIrwin M. AriasNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Deficit di piruvato chinasi per pazienti e sostenitori: Una rara malattia genetica che colpisce I globuli rossi Informazioni + assunzione del controllo = migliore risultatoFrom EverandFast Facts: Deficit di piruvato chinasi per pazienti e sostenitori: Una rara malattia genetica che colpisce I globuli rossi Informazioni + assunzione del controllo = migliore risultatoNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Basis of Haematological CancersFrom EverandThe Genetic Basis of Haematological CancersSabrina TosiNo ratings yet
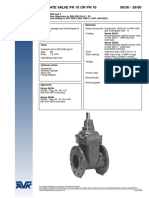
- Avk Gate Valve PN 10 or PN 16 06/30 - 26/00Document2 pagesAvk Gate Valve PN 10 or PN 16 06/30 - 26/00Popescu OctavianNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine in PeruDocument12 pagesWind Turbine in PeruChristian Ramos NievesNo ratings yet
- Vani's Blog 1Document21 pagesVani's Blog 1priyaNo ratings yet
- The History and Evolution of QuaternionsDocument3 pagesThe History and Evolution of QuaternionsAnton Van WykNo ratings yet
- Tower Bersama Group: Pt. Telekomunikasi SelularDocument2 pagesTower Bersama Group: Pt. Telekomunikasi SelularResti OktavianiNo ratings yet
- SST Lin Dan HsiehDocument14 pagesSST Lin Dan HsiehMUHAMMAD SIDIKNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 6ES7214-1AG40-0XB0: General InformationDocument10 pagesData Sheet 6ES7214-1AG40-0XB0: General InformationPCNo ratings yet
- Driveline: SectionDocument345 pagesDriveline: SectionLuis BarriosNo ratings yet
- Image Segmentation by Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Algorithm With A Novel Penalty Term Yong YangDocument15 pagesImage Segmentation by Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Algorithm With A Novel Penalty Term Yong Yangdragon_287No ratings yet
- Quality Assurance of Pressure-Sensitive Tapes: Standard Practice ForDocument6 pagesQuality Assurance of Pressure-Sensitive Tapes: Standard Practice ForYoga PradanaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Investment Information and Security TransactionDocument22 pagesCHAPTER 3 Investment Information and Security TransactionTika TimilsinaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Objetc Tracking Method Using Kalman FilterDocument5 pagesMultiple Objetc Tracking Method Using Kalman FiltermaxzoelNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth TrainingDocument1 pageBluetooth TrainingsyedtNo ratings yet
- Masonry TutorialDocument45 pagesMasonry TutorialGajendra Joshi100% (2)
- Business Model CanvasDocument4 pagesBusiness Model CanvasRetno Wulan AgustinNo ratings yet
- Chem 23 Precipitation Titration Determin PDFDocument6 pagesChem 23 Precipitation Titration Determin PDFKobe AcobNo ratings yet
- Service ManualDocument429 pagesService ManualChris CoulsonNo ratings yet
- Bpo C Chapter 14Document64 pagesBpo C Chapter 14Mutia SafitriNo ratings yet
- Udaan Class XI Physics Part 1 PDFDocument714 pagesUdaan Class XI Physics Part 1 PDFManivannanNo ratings yet
- C 143 - C 143M - 03 Slump TestDocument4 pagesC 143 - C 143M - 03 Slump TestHaris Alam100% (1)
- Condition Monitoring Through Non Destructive TechniqueDocument27 pagesCondition Monitoring Through Non Destructive Techniquepraveenkumar_bs2005No ratings yet
- PowerPath Family For Windows 6.2 and Minor Releases Release NotesDocument23 pagesPowerPath Family For Windows 6.2 and Minor Releases Release Noteskasimmsn0% (1)
- Flexible Sprinkler ConnectionDocument5 pagesFlexible Sprinkler ConnectionOwais AhmedNo ratings yet
- How FACTS Controllers Function in An AC Transmission System: Series Controllers TopicsDocument16 pagesHow FACTS Controllers Function in An AC Transmission System: Series Controllers TopicsAwesomegalNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation Sheet - HoodDocument4 pagesDesign Calculation Sheet - HoodSumanth GundetiNo ratings yet
Poster Presentation - B. Haemato PDF
Poster Presentation - B. Haemato PDF
Uploaded by
rrOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Poster Presentation - B. Haemato PDF
Poster Presentation - B. Haemato PDF
Uploaded by
rrCopyright:
Available Formats
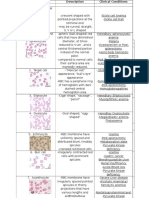
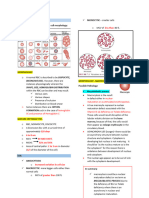
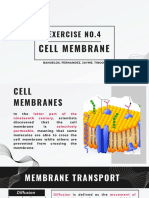
ACANTHOCYTES/SPUR CELLS CODOCYTES/ TARGET CELLS
Appearance:
Spiked membranes
Varying size and
surface
distribution.
Appearance/ characteristics:
Uneven
projections
Has a dark center (a central
Smallwr than
hemoglobinzed area) surrounded
normal RBC
by a white ring followed by a
darker outer ringcontaining a
band of hemoglobin.
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE In electron microscope, they
appear thin and in a bell shape.
It lies in their vulnerability to splenic Has a disproportional increase in
trapping and destruction due to their the surface area membrane to
morphology, which ultimately leads to volume ratio - gives the cells
hemolytic anemia. decreased osmotic fragility
COMMON CAUSE CONDITIONS
Severe liver dysfunction LCAT may be decreased in liver
Abetalipoproteinnemia disease. Decreased enzymatic
disease
Aneroxia nervosa activity increases the cholesterol
Liver
to phospholipid ratio, producing
an absolute increase in surface
HOW DOES IT HAPPEN? area of the red blood cell
membranes.
deficiency
Alterations Alterations Decrease in hemoglobin
in in content relative to surface
iron
membrane membrane area is probably the reason
for the appearance of target
proteins lipids cells.
splenectomy
If splenic macrophage
function is abnormal or absent
because of splenectomy,
Post-
altered erythrocytes will not be
removed from the circulation
Diseases such as efficiently. Therefore, increased
abetalipoproteinemia, severe liver numbers of target cells may be
dysfunction and aneroxia nervosa observed.
affects the cholesterol and protein
content of RBC, altering the fluidity of
the cells and causing the cell to
undergo morphological changes leading
to the formation of spur cells.
You might also like
- Calculated Fields in WorkdayDocument203 pagesCalculated Fields in Workdaysudeep chowdary100% (4)
- MCQ OrthoDocument45 pagesMCQ OrthodentistsurorNo ratings yet
- Haematology Test Name Results Biological Reference Interval Units Specimen Test Method CBC - Complete Blood CountDocument2 pagesHaematology Test Name Results Biological Reference Interval Units Specimen Test Method CBC - Complete Blood CountlijoNo ratings yet
- Robert Donington - Interpretation of Early Music PDFDocument616 pagesRobert Donington - Interpretation of Early Music PDFandres bonilla torres100% (10)
- Straight Line Past Papers Unit 1 Outcome 1 AnswersDocument13 pagesStraight Line Past Papers Unit 1 Outcome 1 AnswersNarendra MupparajuNo ratings yet
- Abnormal RBC Morphology PMB and MwaDocument2 pagesAbnormal RBC Morphology PMB and MwaPaul BandaNo ratings yet
- RBCWBC Abnormalities FinalDocument13 pagesRBCWBC Abnormalities FinalAlanah JaneNo ratings yet
- Hereditary SpherocytosisDocument26 pagesHereditary SpherocytosisVivek PatelNo ratings yet
- Pappenheimer Bodies: Lom-Oc, VillanuevaDocument16 pagesPappenheimer Bodies: Lom-Oc, VillanuevaSHUPATUSSAINo ratings yet
- Patholo Le2Document31 pagesPatholo Le2bitangyarahNo ratings yet
- RBC&WBC AbnormalitiesDocument10 pagesRBC&WBC AbnormalitiesDeomicah SolanoNo ratings yet
- Normocytic Normochromic AnemiaDocument18 pagesNormocytic Normochromic AnemiaElaizha PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 SummaryDocument4 pagesChapter 23 SummaryMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- RBC AnomaliesDocument10 pagesRBC AnomaliesSHUPATUSSAINo ratings yet
- BMLT Sem III Class Note Fate of RBCDocument1 pageBMLT Sem III Class Note Fate of RBCSubhasish BarikNo ratings yet
- Notes Lecture No 3 Cell Injury and MechanismDocument5 pagesNotes Lecture No 3 Cell Injury and MechanismDr-Rukhshanda RamzanNo ratings yet
- Hematology: FANER, Ned Denebe LACANILAO, Sunshine NUCUM, Billie Kim PAGADUAN, Maribec PUA, MonalisaDocument31 pagesHematology: FANER, Ned Denebe LACANILAO, Sunshine NUCUM, Billie Kim PAGADUAN, Maribec PUA, MonalisatzuquinoNo ratings yet
- ANEMIAS (Sickle Cell Anemia With Pathophysiology)Document31 pagesANEMIAS (Sickle Cell Anemia With Pathophysiology)mabec pagaduan70% (10)
- Color Atlas of Haematology 2000Document20 pagesColor Atlas of Haematology 2000Zahraa Al-Sayed100% (1)
- Pathology Question AnswerDocument4 pagesPathology Question AnswerDr-Rukhshanda RamzanNo ratings yet
- Blood Cell AnomaliesDocument4 pagesBlood Cell AnomaliesCiullaeNo ratings yet
- Pathology A - RBC and Bleeding Disorders (Bitun, 2015)Document19 pagesPathology A - RBC and Bleeding Disorders (Bitun, 2015)jlcocm-2022-00028No ratings yet
- Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument37 pagesSickle Cell Anemiahazelposis75% (4)
- Red Blood Cell Disorders Part 1 and 2Document7 pagesRed Blood Cell Disorders Part 1 and 2babael.zuher123No ratings yet
- Subject: Anemia - Defects of Red Blood Cell Membrane Production Discipline: PhysiopathologyDocument30 pagesSubject: Anemia - Defects of Red Blood Cell Membrane Production Discipline: PhysiopathologyCristina Teodora BerbecaruNo ratings yet
- Concept Map ExampleDocument2 pagesConcept Map ExampleLorrieNo ratings yet
- Hemapathology Case: Adrian Joe G. CaballesDocument15 pagesHemapathology Case: Adrian Joe G. CaballesAdrian CaballesNo ratings yet
- Spherocytes: RBC AnomaliesDocument9 pagesSpherocytes: RBC AnomaliesSHUPATUSSAINo ratings yet
- LEC 5 RBC METABOLISM AND Membrane StructureDocument30 pagesLEC 5 RBC METABOLISM AND Membrane StructureFrancis ValdezNo ratings yet
- HS 202 - 1Document5 pagesHS 202 - 1trina santiagoNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Anemia IntrinsicDocument14 pagesHemolytic Anemia IntrinsicSophia Gail ChingNo ratings yet
- 3 RBCDocument5 pages3 RBCAnusuya SNo ratings yet
- Pyshio Reviewer 1st ShiftingDocument9 pagesPyshio Reviewer 1st ShiftingMary Heart SanchezNo ratings yet
- RBC Disorder 2Document9 pagesRBC Disorder 2Dongho ShinNo ratings yet
- TentiranDocument8 pagesTentirandebby nirmasariNo ratings yet
- 10 - Rapidly Progressing GlomerulonephristisDocument26 pages10 - Rapidly Progressing Glomerulonephristisf3er3No ratings yet
- III. FINAL Nursing Care of Clients With Disturbances in Male Female Reproduction Sexuality EditedVersionDocument26 pagesIII. FINAL Nursing Care of Clients With Disturbances in Male Female Reproduction Sexuality EditedVersionKurt PepitoNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Anemia Part II - Microcytic and Macrocytic Anemia - Revised - Copy-3Document6 pagesWeek 9 Anemia Part II - Microcytic and Macrocytic Anemia - Revised - Copy-3Yoodge YoodgeNo ratings yet
- Congenital and Acquired Hemolytic Anemias: Ellis J. Neufeld MD, PHDDocument63 pagesCongenital and Acquired Hemolytic Anemias: Ellis J. Neufeld MD, PHDRabi DhakalNo ratings yet
- DR Samson Ehe Teron SPPK Clinical PthologistDocument31 pagesDR Samson Ehe Teron SPPK Clinical PthologistMaria JozilynNo ratings yet
- M6 BloodDocument7 pagesM6 BloodNel joy PaurilloNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Part I - BloodDocument123 pagesCirculatory System Part I - BloodAngelyn DomingoNo ratings yet
- Membrane DeformabilityDocument2 pagesMembrane DeformabilityKenneth Jake BatiduanNo ratings yet
- 2 CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH Reviewer 2Document4 pages2 CELL INJURY AND CELL DEATH Reviewer 2manuelNo ratings yet
- Blood Is The "River of Life" That Surges Within UsDocument16 pagesBlood Is The "River of Life" That Surges Within UsKyle LumingkitNo ratings yet
- WBC Morphologic DefectDocument8 pagesWBC Morphologic DefectMARY KAYE YVONNE OTILLANo ratings yet
- MBB 324 Lecture15 IUP Misfolding RecyclingQADocument49 pagesMBB 324 Lecture15 IUP Misfolding RecyclingQASarahNo ratings yet
- RBC Production and DestructionDocument44 pagesRBC Production and DestructionNehemiah FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Ischemic Acute Renal Failure: Michael S. Goligorsky Wilfred LieberthalDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Ischemic Acute Renal Failure: Michael S. Goligorsky Wilfred LieberthaleekimsamonteNo ratings yet
- EyrthrokineticsDocument4 pagesEyrthrokineticsKenneth Jake BatiduanNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Urology SystemDocument130 pagesPathology of Urology SystemAmirahNo ratings yet
- HEMA LEC - ErythrocytesDocument5 pagesHEMA LEC - Erythrocytescherrycayari13No ratings yet
- ch10 Biomembrane structure-LODISHDocument79 pagesch10 Biomembrane structure-LODISHHurmat AmnaNo ratings yet
- Hi Stop Hath Ology 2Document22 pagesHi Stop Hath Ology 2vivek govardhanamNo ratings yet
- Blood and Blood ComponentsDocument51 pagesBlood and Blood ComponentsJeevitha VanithaNo ratings yet
- Cell Injury and Death: By: Taleya HidayatullahDocument49 pagesCell Injury and Death: By: Taleya HidayatullahtaleyaNo ratings yet
- Blood FunctionsDocument3 pagesBlood FunctionshelloaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3Document12 pagesTopic 3Ria AccadNo ratings yet
- Cellular InjuryDocument4 pagesCellular InjuryKLIPPNo ratings yet
- Exercise No.4: Cell MembraneDocument28 pagesExercise No.4: Cell MembraneconnievelardeNo ratings yet
- Organelle/ Inclusion Functions LM Features EM Features Associated DiseasesDocument6 pagesOrganelle/ Inclusion Functions LM Features EM Features Associated DiseasesAine CebedoNo ratings yet
- Red Blood Cells, Functions, Diseases A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment, And Related ConditionsFrom EverandRed Blood Cells, Functions, Diseases A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment, And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Liver: Biology and PathobiologyFrom EverandThe Liver: Biology and PathobiologyIrwin M. AriasNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Deficit di piruvato chinasi per pazienti e sostenitori: Una rara malattia genetica che colpisce I globuli rossi Informazioni + assunzione del controllo = migliore risultatoFrom EverandFast Facts: Deficit di piruvato chinasi per pazienti e sostenitori: Una rara malattia genetica che colpisce I globuli rossi Informazioni + assunzione del controllo = migliore risultatoNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Basis of Haematological CancersFrom EverandThe Genetic Basis of Haematological CancersSabrina TosiNo ratings yet
- Avk Gate Valve PN 10 or PN 16 06/30 - 26/00Document2 pagesAvk Gate Valve PN 10 or PN 16 06/30 - 26/00Popescu OctavianNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine in PeruDocument12 pagesWind Turbine in PeruChristian Ramos NievesNo ratings yet
- Vani's Blog 1Document21 pagesVani's Blog 1priyaNo ratings yet
- The History and Evolution of QuaternionsDocument3 pagesThe History and Evolution of QuaternionsAnton Van WykNo ratings yet
- Tower Bersama Group: Pt. Telekomunikasi SelularDocument2 pagesTower Bersama Group: Pt. Telekomunikasi SelularResti OktavianiNo ratings yet
- SST Lin Dan HsiehDocument14 pagesSST Lin Dan HsiehMUHAMMAD SIDIKNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 6ES7214-1AG40-0XB0: General InformationDocument10 pagesData Sheet 6ES7214-1AG40-0XB0: General InformationPCNo ratings yet
- Driveline: SectionDocument345 pagesDriveline: SectionLuis BarriosNo ratings yet
- Image Segmentation by Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Algorithm With A Novel Penalty Term Yong YangDocument15 pagesImage Segmentation by Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Algorithm With A Novel Penalty Term Yong Yangdragon_287No ratings yet
- Quality Assurance of Pressure-Sensitive Tapes: Standard Practice ForDocument6 pagesQuality Assurance of Pressure-Sensitive Tapes: Standard Practice ForYoga PradanaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Investment Information and Security TransactionDocument22 pagesCHAPTER 3 Investment Information and Security TransactionTika TimilsinaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Objetc Tracking Method Using Kalman FilterDocument5 pagesMultiple Objetc Tracking Method Using Kalman FiltermaxzoelNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth TrainingDocument1 pageBluetooth TrainingsyedtNo ratings yet
- Masonry TutorialDocument45 pagesMasonry TutorialGajendra Joshi100% (2)
- Business Model CanvasDocument4 pagesBusiness Model CanvasRetno Wulan AgustinNo ratings yet
- Chem 23 Precipitation Titration Determin PDFDocument6 pagesChem 23 Precipitation Titration Determin PDFKobe AcobNo ratings yet
- Service ManualDocument429 pagesService ManualChris CoulsonNo ratings yet
- Bpo C Chapter 14Document64 pagesBpo C Chapter 14Mutia SafitriNo ratings yet
- Udaan Class XI Physics Part 1 PDFDocument714 pagesUdaan Class XI Physics Part 1 PDFManivannanNo ratings yet
- C 143 - C 143M - 03 Slump TestDocument4 pagesC 143 - C 143M - 03 Slump TestHaris Alam100% (1)
- Condition Monitoring Through Non Destructive TechniqueDocument27 pagesCondition Monitoring Through Non Destructive Techniquepraveenkumar_bs2005No ratings yet
- PowerPath Family For Windows 6.2 and Minor Releases Release NotesDocument23 pagesPowerPath Family For Windows 6.2 and Minor Releases Release Noteskasimmsn0% (1)
- Flexible Sprinkler ConnectionDocument5 pagesFlexible Sprinkler ConnectionOwais AhmedNo ratings yet
- How FACTS Controllers Function in An AC Transmission System: Series Controllers TopicsDocument16 pagesHow FACTS Controllers Function in An AC Transmission System: Series Controllers TopicsAwesomegalNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation Sheet - HoodDocument4 pagesDesign Calculation Sheet - HoodSumanth GundetiNo ratings yet