Professional Documents
Culture Documents
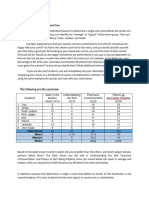
Student T-Distribution
Student T-Distribution
Uploaded by
Rao Abdul Wahab AkramCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- SOCI 301 Final Notes Chapter 5 - Hypothesis TestingDocument8 pagesSOCI 301 Final Notes Chapter 5 - Hypothesis TestingJustin LomatNo ratings yet
- 120Chap2A20Normal20Distribution 1Document9 pages120Chap2A20Normal20Distribution 1Benj Lascano FabiaNo ratings yet
- Session On Confidence IntervalDocument13 pagesSession On Confidence Intervalsingharyan0096No ratings yet
- T DistributionDocument13 pagesT DistributionDiya GoelNo ratings yet
- TdistDocument2 pagesTdistFaris AissaouiNo ratings yet
- Z DistributionDocument2 pagesZ DistributionAamir MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Estimation of Parameters Part 1Document47 pagesLecture 5 Estimation of Parameters Part 1Da YongNo ratings yet
- Standard Error: Sampling DistributionDocument5 pagesStandard Error: Sampling DistributionErica YamashitaNo ratings yet
- Estimation and Cofidence Intervals: Inferential StatisticsDocument4 pagesEstimation and Cofidence Intervals: Inferential StatisticsMiguel Angel CarrilloNo ratings yet
- How To Find The MeanDocument4 pagesHow To Find The Meanapi-150547803No ratings yet
- Definition MeanDocument4 pagesDefinition Meanapi-140032165No ratings yet
- HypothesisDocument11 pagesHypothesissonnetthomasNo ratings yet
- Find MeanDocument4 pagesFind Meanapi-140032165No ratings yet
- What Is MeanDocument4 pagesWhat Is Meanapi-143521979No ratings yet
- Normal Distribution Research PaperDocument8 pagesNormal Distribution Research Paperh0251mhq100% (1)
- Stats AssignDocument6 pagesStats AssignCarl Tristan GodaNo ratings yet
- Notes RMDocument2 pagesNotes RMAlisNo ratings yet
- Difference of Means Test (T-Test)Document2 pagesDifference of Means Test (T-Test)June DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Statistics IntroDocument12 pagesLab 3 Statistics Intro9yzdrvyhp9No ratings yet
- Normal Distribution1Document8 pagesNormal Distribution1ely san100% (1)
- Intern ReportDocument16 pagesIntern ReportAravind KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Statistics GlossaryDocument3 pagesStatistics Glossaryapi-3836734No ratings yet
- ZGE1104 Chapter 4Document7 pagesZGE1104 Chapter 4Mae RocelleNo ratings yet
- 6 STUDENTS T Distribution 2Document8 pages6 STUDENTS T Distribution 2gianmeowcruzNo ratings yet
- Basics of Statistics For PostgraduatesDocument5 pagesBasics of Statistics For PostgraduatesWahid QureshiNo ratings yet
- Identifying Types of VariablesDocument5 pagesIdentifying Types of VariablesAnonymous LusWvyNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Central Tendency For Ungrouped DataDocument27 pagesWeek 13 Central Tendency For Ungrouped Datablesstongga2002No ratings yet
- Bea 159 Ads 1Document6 pagesBea 159 Ads 1acbdNo ratings yet
- Distributions of Sample MeansDocument2 pagesDistributions of Sample MeansRichard HampsonNo ratings yet
- Standard DeviationDocument11 pagesStandard DeviationJAHLEL SHELAH TRILLESNo ratings yet
- Introduction To StatisticsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Statistics22100629No ratings yet
- Unit-Iv 1. Testing of HypothesisDocument28 pagesUnit-Iv 1. Testing of Hypothesismalleda haneeshNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 Area Under The Stanard Normal CurveDocument7 pagesAssignment 4 Area Under The Stanard Normal CurveAkamonwa KalengaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing: Definition: The Hypothesis Testing Refers To The Predefined Formal Procedures That Are Used byDocument4 pagesHypothesis Testing: Definition: The Hypothesis Testing Refers To The Predefined Formal Procedures That Are Used byAbrar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To StatisticsDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Statisticsmayur shettyNo ratings yet
- Student T TestDocument2 pagesStudent T TestSFLMasekoNo ratings yet
- ContinuousDocument11 pagesContinuousDinaol TikuNo ratings yet
- Population - Entire Group of Individuals About Which We Want Information. Sample - Part of The Population From Which We Actually Collect InformationDocument5 pagesPopulation - Entire Group of Individuals About Which We Want Information. Sample - Part of The Population From Which We Actually Collect Informationlauren smithNo ratings yet
- DMA 1 ReviewOfProbabilityDocument45 pagesDMA 1 ReviewOfProbability[CO - 174] Shubham MouryaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics MBADocument7 pagesDescriptive Statistics MBAKritika Jaiswal100% (2)
- Statistics For Management - 2Document14 pagesStatistics For Management - 2Nandhini P Asst.Prof/MBA100% (3)
- Statistics - The Big PictureDocument4 pagesStatistics - The Big PicturenaokiNo ratings yet
- Profed 10Document4 pagesProfed 10Junel SildoNo ratings yet
- Student's T-Test: History Uses Assumptions Unpaired and Paired Two-Sample T-TestsDocument13 pagesStudent's T-Test: History Uses Assumptions Unpaired and Paired Two-Sample T-TestsNTA UGC-NET100% (1)
- Abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz: Alternative HypothesisDocument8 pagesAbcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz: Alternative Hypothesisabhinandabarman1168No ratings yet
- Sampling Distribution,: College of Information and Computing SciencesDocument11 pagesSampling Distribution,: College of Information and Computing SciencesArt IjbNo ratings yet
- Z and T TestDocument7 pagesZ and T TestshraddhaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Sta-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesDescriptive Sta-WPS OfficeMarcialNo ratings yet
- Standard ScoreDocument2 pagesStandard Scoreamiba45No ratings yet
- Weighted Mean, Z-Test and T-TestDocument6 pagesWeighted Mean, Z-Test and T-TestRosenia BaliNo ratings yet
- When Do You Use The T DistributionDocument4 pagesWhen Do You Use The T DistributionDerek DamNo ratings yet
- Distribution, Normal Distribution, Standard Normal Distribution, Central Limit Theorem, Standard Error, Estimators and EstimatesDocument13 pagesDistribution, Normal Distribution, Standard Normal Distribution, Central Limit Theorem, Standard Error, Estimators and EstimatesMUKUND TIWARINo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument3 pagesNormal DistributionAthulya MkNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics NotesDocument6 pagesBiostatistics Notesdeepanjan sarkarNo ratings yet
- BAA Class NotesDocument16 pagesBAA Class Notesprarabdhasharma98No ratings yet
- Mathematical Exploration StatisticsDocument9 pagesMathematical Exploration StatisticsanhhuyalexNo ratings yet
- Confidence Intervals, Student - S T Distribution, Margin of ErrorDocument11 pagesConfidence Intervals, Student - S T Distribution, Margin of ErrorMukund TiwariNo ratings yet
Student T-Distribution
Student T-Distribution
Uploaded by
Rao Abdul Wahab AkramOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Student T-Distribution
Student T-Distribution
Uploaded by
Rao Abdul Wahab AkramCopyright:
Available Formats
In probability and statistics, Student's t-distribution (or simply the t-distribution) is
any member of a family of continuous probability distributions that arises when
estimating the mean of a normally distributed population in situations where the sample
size is small and the population standard deviation is unknown. It was developed
by William Sealy Gosset under the pseudonym Student.
Student'st
Probability density function
Cumulative distribution function
Parameters
The t-distribution plays a role in a number of widely used statistical analyses,
including Student's t-test for assessing the statistical significance of the difference
between two sample means, the construction of confidence intervals for the difference
between two population means, and in linear regression analysis. The Student's t-
distribution also arises in the Bayesian analysis of data from a normal family.
If we take a sample of n observations from a normal distribution, then the t-distribution
with degrees of freedom can be defined as the distribution of the location of the
sample mean relative to the true mean, divided by the sample standard deviation, after
multiplying by the standardizing term . I’m this way, the t-distribution can be used to
construct a confidence interval for the true mean.
The t-distribution is symmetric and bell-shaped, like the normal distribution, but has
heavier tails, meaning that it is more prone to producing values that fall far from its
mean. This makes it useful for understanding the statistical behavior of certain types of
ratios of random quantities, in which variation in the denominator is amplified and may
produce outlying values when the denominator of the ratio falls close to zero. The
Student's t-distribution is a special case of the generalised hyperbolic distribution.
You might also like
- SOCI 301 Final Notes Chapter 5 - Hypothesis TestingDocument8 pagesSOCI 301 Final Notes Chapter 5 - Hypothesis TestingJustin LomatNo ratings yet
- 120Chap2A20Normal20Distribution 1Document9 pages120Chap2A20Normal20Distribution 1Benj Lascano FabiaNo ratings yet
- Session On Confidence IntervalDocument13 pagesSession On Confidence Intervalsingharyan0096No ratings yet
- T DistributionDocument13 pagesT DistributionDiya GoelNo ratings yet
- TdistDocument2 pagesTdistFaris AissaouiNo ratings yet
- Z DistributionDocument2 pagesZ DistributionAamir MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Estimation of Parameters Part 1Document47 pagesLecture 5 Estimation of Parameters Part 1Da YongNo ratings yet
- Standard Error: Sampling DistributionDocument5 pagesStandard Error: Sampling DistributionErica YamashitaNo ratings yet
- Estimation and Cofidence Intervals: Inferential StatisticsDocument4 pagesEstimation and Cofidence Intervals: Inferential StatisticsMiguel Angel CarrilloNo ratings yet
- How To Find The MeanDocument4 pagesHow To Find The Meanapi-150547803No ratings yet
- Definition MeanDocument4 pagesDefinition Meanapi-140032165No ratings yet
- HypothesisDocument11 pagesHypothesissonnetthomasNo ratings yet
- Find MeanDocument4 pagesFind Meanapi-140032165No ratings yet
- What Is MeanDocument4 pagesWhat Is Meanapi-143521979No ratings yet
- Normal Distribution Research PaperDocument8 pagesNormal Distribution Research Paperh0251mhq100% (1)
- Stats AssignDocument6 pagesStats AssignCarl Tristan GodaNo ratings yet
- Notes RMDocument2 pagesNotes RMAlisNo ratings yet
- Difference of Means Test (T-Test)Document2 pagesDifference of Means Test (T-Test)June DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Statistics IntroDocument12 pagesLab 3 Statistics Intro9yzdrvyhp9No ratings yet
- Normal Distribution1Document8 pagesNormal Distribution1ely san100% (1)
- Intern ReportDocument16 pagesIntern ReportAravind KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Statistics GlossaryDocument3 pagesStatistics Glossaryapi-3836734No ratings yet
- ZGE1104 Chapter 4Document7 pagesZGE1104 Chapter 4Mae RocelleNo ratings yet
- 6 STUDENTS T Distribution 2Document8 pages6 STUDENTS T Distribution 2gianmeowcruzNo ratings yet
- Basics of Statistics For PostgraduatesDocument5 pagesBasics of Statistics For PostgraduatesWahid QureshiNo ratings yet
- Identifying Types of VariablesDocument5 pagesIdentifying Types of VariablesAnonymous LusWvyNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Central Tendency For Ungrouped DataDocument27 pagesWeek 13 Central Tendency For Ungrouped Datablesstongga2002No ratings yet
- Bea 159 Ads 1Document6 pagesBea 159 Ads 1acbdNo ratings yet
- Distributions of Sample MeansDocument2 pagesDistributions of Sample MeansRichard HampsonNo ratings yet
- Standard DeviationDocument11 pagesStandard DeviationJAHLEL SHELAH TRILLESNo ratings yet
- Introduction To StatisticsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Statistics22100629No ratings yet
- Unit-Iv 1. Testing of HypothesisDocument28 pagesUnit-Iv 1. Testing of Hypothesismalleda haneeshNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 Area Under The Stanard Normal CurveDocument7 pagesAssignment 4 Area Under The Stanard Normal CurveAkamonwa KalengaNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing: Definition: The Hypothesis Testing Refers To The Predefined Formal Procedures That Are Used byDocument4 pagesHypothesis Testing: Definition: The Hypothesis Testing Refers To The Predefined Formal Procedures That Are Used byAbrar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To StatisticsDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Statisticsmayur shettyNo ratings yet
- Student T TestDocument2 pagesStudent T TestSFLMasekoNo ratings yet
- ContinuousDocument11 pagesContinuousDinaol TikuNo ratings yet
- Population - Entire Group of Individuals About Which We Want Information. Sample - Part of The Population From Which We Actually Collect InformationDocument5 pagesPopulation - Entire Group of Individuals About Which We Want Information. Sample - Part of The Population From Which We Actually Collect Informationlauren smithNo ratings yet
- DMA 1 ReviewOfProbabilityDocument45 pagesDMA 1 ReviewOfProbability[CO - 174] Shubham MouryaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics MBADocument7 pagesDescriptive Statistics MBAKritika Jaiswal100% (2)
- Statistics For Management - 2Document14 pagesStatistics For Management - 2Nandhini P Asst.Prof/MBA100% (3)
- Statistics - The Big PictureDocument4 pagesStatistics - The Big PicturenaokiNo ratings yet
- Profed 10Document4 pagesProfed 10Junel SildoNo ratings yet
- Student's T-Test: History Uses Assumptions Unpaired and Paired Two-Sample T-TestsDocument13 pagesStudent's T-Test: History Uses Assumptions Unpaired and Paired Two-Sample T-TestsNTA UGC-NET100% (1)
- Abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz: Alternative HypothesisDocument8 pagesAbcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz: Alternative Hypothesisabhinandabarman1168No ratings yet
- Sampling Distribution,: College of Information and Computing SciencesDocument11 pagesSampling Distribution,: College of Information and Computing SciencesArt IjbNo ratings yet
- Z and T TestDocument7 pagesZ and T TestshraddhaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Sta-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesDescriptive Sta-WPS OfficeMarcialNo ratings yet
- Standard ScoreDocument2 pagesStandard Scoreamiba45No ratings yet
- Weighted Mean, Z-Test and T-TestDocument6 pagesWeighted Mean, Z-Test and T-TestRosenia BaliNo ratings yet
- When Do You Use The T DistributionDocument4 pagesWhen Do You Use The T DistributionDerek DamNo ratings yet
- Distribution, Normal Distribution, Standard Normal Distribution, Central Limit Theorem, Standard Error, Estimators and EstimatesDocument13 pagesDistribution, Normal Distribution, Standard Normal Distribution, Central Limit Theorem, Standard Error, Estimators and EstimatesMUKUND TIWARINo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument3 pagesNormal DistributionAthulya MkNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics NotesDocument6 pagesBiostatistics Notesdeepanjan sarkarNo ratings yet
- BAA Class NotesDocument16 pagesBAA Class Notesprarabdhasharma98No ratings yet
- Mathematical Exploration StatisticsDocument9 pagesMathematical Exploration StatisticsanhhuyalexNo ratings yet
- Confidence Intervals, Student - S T Distribution, Margin of ErrorDocument11 pagesConfidence Intervals, Student - S T Distribution, Margin of ErrorMukund TiwariNo ratings yet