Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7 PDF
Chapter 7 PDF
Uploaded by
YARLAGADDA_NANICopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Afan Oromo-English English - Afan Oromo DictionaryDocument129 pagesAfan Oromo-English English - Afan Oromo DictionaryShimelis M. Bedane92% (12)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Cable Suspended Pedestrian Bridge Design For Rural Construction - FINALDocument94 pagesCable Suspended Pedestrian Bridge Design For Rural Construction - FINALMichael Hii100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Payment Certificate No 5 FINALDocument11 pagesPayment Certificate No 5 FINALale hopeju200975% (4)
- Ed 226615Document57 pagesEd 226615ale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- WR401 01 Design of SyphonDocument7 pagesWR401 01 Design of Syphonale hopeju2009100% (1)
- Weir ConstructionDocument157 pagesWeir Constructionale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Stilling BasinDocument5 pagesStilling Basinale hopeju2009100% (1)
- 2 3 Guidelines For Structural Design of SHP ProjectsDocument41 pages2 3 Guidelines For Structural Design of SHP Projectsnlnmurthy28100% (1)
- Hydraulic Design of Energy Dissipators For Culverts and Channels-HEC-14Document286 pagesHydraulic Design of Energy Dissipators For Culverts and Channels-HEC-14Carlos AndresNo ratings yet
- River MorphologyDocument20 pagesRiver Morphologyale hopeju2009100% (1)
- Lecture 3Document9 pagesLecture 3ale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Barrages PresentationDocument109 pagesBarrages PresentationFaisal RashidNo ratings yet
- CE404 03 Stilling BasinsDocument10 pagesCE404 03 Stilling BasinsAbhishek Shah100% (1)
- CVE471 Lecture Notes 4 - SpillwaysDocument85 pagesCVE471 Lecture Notes 4 - Spillwaysale hopeju2009100% (12)
- CD WorkDocument4 pagesCD Workale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Enla ReportDocument6 pagesEnla Reportale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Weir DesignDocument5 pagesWeir Designale hopeju2009100% (1)
- Design of AqueductDocument5 pagesDesign of Aqueducthari_shresthaNo ratings yet
- Exercise-Design of Weir-Option 1Document6 pagesExercise-Design of Weir-Option 1ale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2ale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- CoverpagesinteDocument2 pagesCoverpagesinteale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Interim Payment Certificate No. 07Document1 pageInterim Payment Certificate No. 07ale hopeju2009100% (1)
- Design of A Barrage MSDocument70 pagesDesign of A Barrage MSale hopeju2009100% (3)
- Characteristics of Technical WritingDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Technical Writingale hopeju2009100% (2)
- Bar Schedules For PC 5Document51 pagesBar Schedules For PC 5ale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Design Manual For Low Volume Roads Part FDocument229 pagesDesign Manual For Low Volume Roads Part FMichael KaziNo ratings yet
- Bridge LoadingDocument18 pagesBridge Loadingale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Chapter 36Document40 pagesChapter 36ale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- BridgesDocument35 pagesBridgesale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Calculation of Scoring Resistance in Gear DevicesDocument18 pagesCalculation of Scoring Resistance in Gear DevicesSwarnava PaulNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet PC: Filament SpecificationsDocument3 pagesTechnical Data Sheet PC: Filament SpecificationsVladimir SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Bulklite™ 1400: Product ManualDocument90 pagesBulklite™ 1400: Product ManualBac Ho VanNo ratings yet
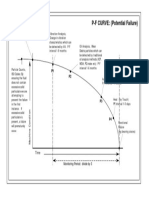
- P-F CURVE: (Potential Failure) : Vibration Analysis, Point Where Failure Starts To OccurDocument1 pageP-F CURVE: (Potential Failure) : Vibration Analysis, Point Where Failure Starts To OccurOscar Marino Campo BonellNo ratings yet
- Tut 2 2013Document2 pagesTut 2 2013iwineverythingNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric ChemistryDocument44 pagesAtmospheric ChemistryTayyab AkhlassNo ratings yet
- PHYS13071 Assessment 2012 - AssiDocument7 pagesPHYS13071 Assessment 2012 - AssiKevin CollinsNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review 2nd QuarterDocument4 pagesPointers To Review 2nd QuarterZaira Clarisse de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Trabajo 02 2021-1Document2 pagesTrabajo 02 2021-1Sebastiàn RugelesNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Analysis of Folded Plate Structures by Simplified Bending Theory and Ansys ProgramDocument8 pagesComparison of Analysis of Folded Plate Structures by Simplified Bending Theory and Ansys Programimad rashidNo ratings yet
- Solution: Conservation of EnergyDocument8 pagesSolution: Conservation of Energydist2235No ratings yet
- Jentoft Diffusereflectance 101204Document56 pagesJentoft Diffusereflectance 101204Joe Vito MorabitoNo ratings yet
- Nptel: Introduction To Composites - Web CourseDocument3 pagesNptel: Introduction To Composites - Web CourseAnu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of Composite Laminated Beams Using ANSYSDocument6 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Composite Laminated Beams Using ANSYSVikramNo ratings yet
- IB Çalışma SorularıDocument99 pagesIB Çalışma SorularıAziz Samet ZorluNo ratings yet
- VRV Testing Check SheetDocument2 pagesVRV Testing Check SheetJahangir Hassan100% (1)
- Drag ForceDocument9 pagesDrag ForceImran BahaNo ratings yet
- Gas Natural1Document12 pagesGas Natural1ISRAEL RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion Mcqs With Key by STUDY CORNERDocument8 pagesForce and Motion Mcqs With Key by STUDY CORNERamsal200416No ratings yet
- Test SokDocument14 pagesTest SokFirzan100% (5)
- Ipho - Problems of 2nd and 9th IPhODocument10 pagesIpho - Problems of 2nd and 9th IPhOAbhishek JaisinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Ellipsoid, Geoid, Gravity, Geodesy, and Geophysics - Li - G - TutDocument10 pagesTutorial Ellipsoid, Geoid, Gravity, Geodesy, and Geophysics - Li - G - TutSuta VijayaNo ratings yet
- MechanicalsealDocument7 pagesMechanicalsealSidne SilvaNo ratings yet
- Heat Capacity Ratios For GasesDocument8 pagesHeat Capacity Ratios For Gasesapi-317118983No ratings yet
- Astm D 648Document14 pagesAstm D 648廖修賢No ratings yet
- Proton Radiotherapy PDFDocument342 pagesProton Radiotherapy PDFAlexandre Mana100% (1)
- White Michael FRST 497 Graduating Essay 2010Document28 pagesWhite Michael FRST 497 Graduating Essay 2010Muhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- JET ST Tropical Easterly Jet and MonsoonsDocument3 pagesJET ST Tropical Easterly Jet and Monsoonspradeep krNo ratings yet
- Tability: HapterDocument48 pagesTability: HapterDan ManeaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements PPT 11Document32 pagesClassification of Elements PPT 11Aditya SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet
Chapter 7 PDF
Chapter 7 PDF
Uploaded by
YARLAGADDA_NANIOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7 PDF
Chapter 7 PDF
Uploaded by
YARLAGADDA_NANICopyright:
Available Formats
7.
BEARINGS AND RAILINGS
BEARINGS
Bearings are structural devices positioned between the bridge superstructure and the
substructure.
Their principal functions are as follows:
1. To transmit loads from the superstructure to the substructure, and
2. To accommodate relative movements between the superstructure and the substructure.
Movements should be accommodated properly and these result from
a) longitudinal movement due to temperature changes-reversible
b) rotation due to deflection of girders- live load deflection is reversible
c) vertical movement due to settlement of support- irreversible
d) movement due to shrinkage, creep or prestressing-irreversible
Bearings are categorized in to two as
a) Fixed bearings – are fixed against translation, but free to rotate
b) Expansion bearings-are free to translate and rotate
Selection of the type depends on the type of superstructure, type of substructure supports
and the length of the span.
- A simply supported span requires fixed bearings at one and expansion joints at the
other.
- A continuous girder require fixed bearing at one and expansion bearing on all
other supports
- A two span girder will have fixed bearing at the centre support and expansion
bearings at the two abutments
Bearings are important components of bridges and call for care in design, skill in
execution, regular attention in maintenance. Faulty design or malfunctioning bearings due
Fundamentals of Bridges Design 54
to clogging by debris have often resulted in collapse of bridges due to the high stresses
induced due to restrained motion.
On certain major bridges bearing cost is as high as 10-15% of the total cost. It is worth
designing carefully and inspecting regularly for maintenance.
Types of Bearings
For slab bridges no special bearings are provided because the translational movement is
very small. Edges of supports are beveled to allow for rotation.
The following are the different types of bearings for girder bridges
- Sliding plate bearing- is the simplest type of bearing. This utilizes one plate
sliding on another. This type is used for bridges up to 30m span. Flat plates were
common but due to freezing and high frictional forces the surface of the upper
plate is slightly curved as shown in Figure below.
Figure: Sliding plate bearing
Fundamentals of Bridges Design 55
- Roller bearing- in this type rotation is accommodated by the pin and translation
by the use of a roller or a group of rollers. See Figure below. This is used for
spans of moderate length.
Figure: Roller bearing
- Rocker bearing- this is used for longer spans and is used to accommodate large
live load deflections. See Figure below.
Figure: Rocker bearing
In seismic areas suitable guides should be provided to prevent the roller and
rocker components from being displaced off abutments and piers during
earthquakes.
- Elastomeric bearing- is made of a polymeric substance called elastomer (either
natural or synthetic rubber).
Fundamentals of Bridges Design 56
This can be reinforced with steel plates, which are usually the case, or may be
unreinforced. This is very strong in compression and relatively week in shear,
thus allowing horizontal displacement. This has shown good weathering
performance and so incurs low maintenance cost. This type is favored for
bearings. This is used for medium to large spans. See Figure below.
Figure: Elastomeric bearing
- Lead Rubber bearing-is an elastomeric bearing equipped with lead core and is
used in highly seismic areas. See Figure below. Under normal loading conditions,
the lead core resists lateral loads. Under seismically induced dynamic loads,
however, the lead core yields and assists the elastomeric material in resisting
loads while at the same time accommodating lateral flexibility.
Fundamentals of Bridges Design 57
RAILINGS
Railings are provided along edges of bridges for protection of traffic and pedestrian.
There are three types of railings.
1. Traffic railings
2. Pedestrian railings
3. Combination railings
The following guideline indicate the application of various types of rails
- Traffic railings is used when a bridge is for the execution use of highway traffic
- A combination railing in conjunction with raised curb and side walk is used on
low-speed highways.
- On high speed highways the pedestrian path should have both an out board
pedestrian railing and an inboard combination railing
Aesthetics and freedom of view from passing vehicles should also be taken in to
consideration.
Traffic Railing
The primary purpose of traffic railings is to contain and redirect errant vehicles.
Specifically they serve the purposes of
- primarily containing the average vehicle
- protecting the occupants of a vehicle in collision with the railing
- protecting other vehicles near the collision
- protecting people and property on roadway and nearby areas underneath
A traffic railing should provide a smooth and continuous face on the traffic side.
Steel and concrete posts should set back from the face to the rail.
Fundamentals of Bridges Design 58
Pedestrian Railing
Pedestrian railing can be made from concrete, metal and timber.
A pedestrian walkway should be separated from roadway by a barrier curb, traffic railing
or combination railing.
Combination Railing
Consists of traffic and pedestrian railings
Fundamentals of Bridges Design 59
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Afan Oromo-English English - Afan Oromo DictionaryDocument129 pagesAfan Oromo-English English - Afan Oromo DictionaryShimelis M. Bedane92% (12)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Cable Suspended Pedestrian Bridge Design For Rural Construction - FINALDocument94 pagesCable Suspended Pedestrian Bridge Design For Rural Construction - FINALMichael Hii100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Payment Certificate No 5 FINALDocument11 pagesPayment Certificate No 5 FINALale hopeju200975% (4)
- Ed 226615Document57 pagesEd 226615ale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- WR401 01 Design of SyphonDocument7 pagesWR401 01 Design of Syphonale hopeju2009100% (1)
- Weir ConstructionDocument157 pagesWeir Constructionale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Stilling BasinDocument5 pagesStilling Basinale hopeju2009100% (1)
- 2 3 Guidelines For Structural Design of SHP ProjectsDocument41 pages2 3 Guidelines For Structural Design of SHP Projectsnlnmurthy28100% (1)
- Hydraulic Design of Energy Dissipators For Culverts and Channels-HEC-14Document286 pagesHydraulic Design of Energy Dissipators For Culverts and Channels-HEC-14Carlos AndresNo ratings yet
- River MorphologyDocument20 pagesRiver Morphologyale hopeju2009100% (1)
- Lecture 3Document9 pagesLecture 3ale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Barrages PresentationDocument109 pagesBarrages PresentationFaisal RashidNo ratings yet
- CE404 03 Stilling BasinsDocument10 pagesCE404 03 Stilling BasinsAbhishek Shah100% (1)
- CVE471 Lecture Notes 4 - SpillwaysDocument85 pagesCVE471 Lecture Notes 4 - Spillwaysale hopeju2009100% (12)
- CD WorkDocument4 pagesCD Workale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Enla ReportDocument6 pagesEnla Reportale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Weir DesignDocument5 pagesWeir Designale hopeju2009100% (1)
- Design of AqueductDocument5 pagesDesign of Aqueducthari_shresthaNo ratings yet
- Exercise-Design of Weir-Option 1Document6 pagesExercise-Design of Weir-Option 1ale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2ale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- CoverpagesinteDocument2 pagesCoverpagesinteale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Interim Payment Certificate No. 07Document1 pageInterim Payment Certificate No. 07ale hopeju2009100% (1)
- Design of A Barrage MSDocument70 pagesDesign of A Barrage MSale hopeju2009100% (3)
- Characteristics of Technical WritingDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Technical Writingale hopeju2009100% (2)
- Bar Schedules For PC 5Document51 pagesBar Schedules For PC 5ale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Design Manual For Low Volume Roads Part FDocument229 pagesDesign Manual For Low Volume Roads Part FMichael KaziNo ratings yet
- Bridge LoadingDocument18 pagesBridge Loadingale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Chapter 36Document40 pagesChapter 36ale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- BridgesDocument35 pagesBridgesale hopeju2009No ratings yet
- Calculation of Scoring Resistance in Gear DevicesDocument18 pagesCalculation of Scoring Resistance in Gear DevicesSwarnava PaulNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet PC: Filament SpecificationsDocument3 pagesTechnical Data Sheet PC: Filament SpecificationsVladimir SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Bulklite™ 1400: Product ManualDocument90 pagesBulklite™ 1400: Product ManualBac Ho VanNo ratings yet
- P-F CURVE: (Potential Failure) : Vibration Analysis, Point Where Failure Starts To OccurDocument1 pageP-F CURVE: (Potential Failure) : Vibration Analysis, Point Where Failure Starts To OccurOscar Marino Campo BonellNo ratings yet
- Tut 2 2013Document2 pagesTut 2 2013iwineverythingNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric ChemistryDocument44 pagesAtmospheric ChemistryTayyab AkhlassNo ratings yet
- PHYS13071 Assessment 2012 - AssiDocument7 pagesPHYS13071 Assessment 2012 - AssiKevin CollinsNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review 2nd QuarterDocument4 pagesPointers To Review 2nd QuarterZaira Clarisse de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Trabajo 02 2021-1Document2 pagesTrabajo 02 2021-1Sebastiàn RugelesNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Analysis of Folded Plate Structures by Simplified Bending Theory and Ansys ProgramDocument8 pagesComparison of Analysis of Folded Plate Structures by Simplified Bending Theory and Ansys Programimad rashidNo ratings yet
- Solution: Conservation of EnergyDocument8 pagesSolution: Conservation of Energydist2235No ratings yet
- Jentoft Diffusereflectance 101204Document56 pagesJentoft Diffusereflectance 101204Joe Vito MorabitoNo ratings yet
- Nptel: Introduction To Composites - Web CourseDocument3 pagesNptel: Introduction To Composites - Web CourseAnu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of Composite Laminated Beams Using ANSYSDocument6 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Composite Laminated Beams Using ANSYSVikramNo ratings yet
- IB Çalışma SorularıDocument99 pagesIB Çalışma SorularıAziz Samet ZorluNo ratings yet
- VRV Testing Check SheetDocument2 pagesVRV Testing Check SheetJahangir Hassan100% (1)
- Drag ForceDocument9 pagesDrag ForceImran BahaNo ratings yet
- Gas Natural1Document12 pagesGas Natural1ISRAEL RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion Mcqs With Key by STUDY CORNERDocument8 pagesForce and Motion Mcqs With Key by STUDY CORNERamsal200416No ratings yet
- Test SokDocument14 pagesTest SokFirzan100% (5)
- Ipho - Problems of 2nd and 9th IPhODocument10 pagesIpho - Problems of 2nd and 9th IPhOAbhishek JaisinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Ellipsoid, Geoid, Gravity, Geodesy, and Geophysics - Li - G - TutDocument10 pagesTutorial Ellipsoid, Geoid, Gravity, Geodesy, and Geophysics - Li - G - TutSuta VijayaNo ratings yet
- MechanicalsealDocument7 pagesMechanicalsealSidne SilvaNo ratings yet
- Heat Capacity Ratios For GasesDocument8 pagesHeat Capacity Ratios For Gasesapi-317118983No ratings yet
- Astm D 648Document14 pagesAstm D 648廖修賢No ratings yet
- Proton Radiotherapy PDFDocument342 pagesProton Radiotherapy PDFAlexandre Mana100% (1)
- White Michael FRST 497 Graduating Essay 2010Document28 pagesWhite Michael FRST 497 Graduating Essay 2010Muhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- JET ST Tropical Easterly Jet and MonsoonsDocument3 pagesJET ST Tropical Easterly Jet and Monsoonspradeep krNo ratings yet
- Tability: HapterDocument48 pagesTability: HapterDan ManeaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements PPT 11Document32 pagesClassification of Elements PPT 11Aditya SRIVASTAVANo ratings yet