Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geology
Geology
Uploaded by
Chrix Avalomes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesEverything
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEverything
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesGeology
Geology
Uploaded by
Chrix AvalomesEverything
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
The Work of Ice
(Group 1) 3 Periods of Cenozoic Era 1. Movement by ice
EARTH: SURFACE, STRUCTURE, & EARTH 1. Paleogene 2. Transport by ice
4 Sphere of the Earth 2. Neogene 3. Glacial erosion
1. Atmosphere 3. Quaternary 4. Glacial deposit
2. Hydrosphere Division of Periods 5. Landforms
3. Biosphere 1. Cambrian 6. Landforms association
4. Geosphere 2. Ordovician and Silurian 7. Post-Depositional Changes
3 Broad Rock Groups 3. Devonian Other Mass Transport
1. Igneous rocks 4. Carboniferous 1. Rainfall
2. Sedimentary rocks 5. Permian 2. Ground water
3. Metamorphic rock 6. Triassic 3. Slope instability
3 Layers of the Earth 7. Jurassic Processes in:
1. Crust 8. Cretaceous Chemical Weathering
Continental crust 9. Paleogene 1. Solution
Oceanic crust 10. Neogene 2. Oxidation
2. Mantle 11. Quaternary 3. Reduction
3. Core Fold Mountain Belts 4. Hydration
Outer core 1. Orogenic Belt (orogeny) 5. Hydrolysis
Inner core 2. Epeirogenic Movement 6. Leaching
2 Types of Plates (epeirogeny) 7. Cation exchange
1. Ocean plates Mechanical Weathering
2. Continental plates 1. Mechanical Unloading
3 Types of Plate Boundary (Group 3) SURFACE PROCESSES 2. Mechanical Loading
1. Divergent Weathering 3. Thermal loading
2. Convergent 1. Chemical weathering 4. Wetting and drying
Continent collision 2. Mechanical weathering 5. Crystallization
Oceanic crust collision 3. Unloading 6. Pneumatic loading
Ocean collision 4. Frost action
3. Transform 5. Permafrost
6. Frost heaving (Group 4) MINERALS
7. Insolation Most Abundant Elements
8. Biological weathering 1. Oxygen
(Group 2) GEOLOGICAL HISTORY 9. Erosion and decomposition 2. Silicon
Theories The Work of Rivers 3. Aluminum
1. James Hutton 1. Valleys 4. Iron
2. William Smith 2. Grade and rejuvenation 5. Calcium
Division of Eons 3. Waterfalls and gorges 6. Magnesium
1. Hadean eon 4. River pattern 7. Sodium
2. Archean eon 5. River deposit 8. Potassium
3. Proterozoic eon 6. Deltas 9. Titanium
Lower The Work of Sea 10. Hydrogen
Middle 1. Tides and currents 11. Manganese
Upper 2. Tidal surges 12. Phosphorous
4. Phanerozoic eon 3. Waves Formation of Minerals
Division of Eras 4. Coastal erosion 1. Crystallization from melt
1. Precambrian era 5. Coastal marine deposit 2. Precipitation from water
2. Palaeozoic era 6. Spits and bar 3. Biological activity
Older Paleozoic Rocks 7. Cuspate forelands 4. Change to more stable state
Trilobites 8. Barriers 5. Precipitation from vapor
Brachiopods 9. Mud flats Properties of Minerals
Graptolites 10. Coral reefs 1. Habit
Newer Palaeozoic Rocks 11. Open sea deposits 2. Color
Fish The Work of Wind 3. Streak
Reef-knolls/ bioherms 1. Wind erosion 4. Luster
Cephalopods 2. Wind-formed deposit 5. Cleavage
Lepidodendron 3. Coastal and hills 6. Specific gravity
3. Mesozoic era 4. Desert dunes 7. Hardness
4. Cenozoic 5. Loess
Groups of Minerals (Group 6) SEDIMENTARY ROCKS (Group 7) METAMORPHIC ROCKS
1. Silicate 4 Phases of Generation of Sedimentary Types Of Metamorphic Rock
Silicate tetrahedron Rock 1. Ortho-metamorphic rock
Isolated tetrahedron 1. Weathering and Erosion 2. Para-metamorphic rock
Single chain silicates 2. Transportation
Double chain silicates 3. Deposition Types Of Metamorphism:
Sheet silicates 4. Lithification 1. Contact metamorphism
Framework silicate Components of Sed Rocks 2. Regional metamorphism
2. Carbonates 1. Clastic
3. Oxides Conglomerate Factors Controlling Characteristics Of
4. Sulfides Sandstone Metamorphic Rock:
5. Phosphates Shale 1. Composition of the parent rock
6. Native elements 2. Organic 2. Temperature
Coal 3. Pressure
Fossiliferous-mestone 4. Fluids
(group 5) IGNEOUS ROCKS 3. Chemical 5. Time
2 Different Types of Igneous Rocks Limestone
1. Extrusive Salt Kinds Of Metamorphism:
2. Intrusive Texture of Sedimentary Rocks 1. Geothermal
Different Igneous Intrusion 1. Environments of Deposition 2. Dynamic or kinetic
1. Dikes 2. Continental environments 3. Hydrothermal
2. Sills 3. Shelf sea environments 4. Contact
3. Laccoliths 4. Deep sea environments
4. Plutons 5. Detrital sedimentary rock Kinds Of Metamorphic Rocks:
5. Lopoliths 6. Rudaceous deposit 1. Gneiss
6. Batholiths 7. Conglomerate 2. Schist
7. Stocks 8. Grit 3. Slate
Composition Type of Igneous Rock 9. Sedimentary mineral deposit 4. Quartzite
1. Felsic Rock 10. Construction materials 5. Marble
2. Intermediate Rock 11. Minerals for chemicals 6. Phylite
3. Mafic and Ultramafic Rocks 12. Placer deposit
Texture of Igneous Rocks 13. Organic fuels Classification Of Metamorphic Rock:
1. Phaneritic / Coarse Grained Coal 1. Foliated metamorphic rock
2. Non-foliated metamorphic rock
2. Aphanitic / Fine grained Oil and Gas
3. Vesicular
4. Pyroclastic
5. Glassy
6. Porphyritic
Different Igneous Rock
1. Ultrabasic Rocks
Picrate
Serpentinite
2. Basic Rocks
Gabbro
Dolerite
Basalts
3. Intermediate Rocks
Diorites
Andesite
4. Acid Rocks
Granite
Granodiorite
5. Alkaline
Syenite
Trachyte
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- ELECTROLESS NICKEL PLATING - (Glenn - O. - Mallory, - Juan - B. - Hajdu) - PDFDocument532 pagesELECTROLESS NICKEL PLATING - (Glenn - O. - Mallory, - Juan - B. - Hajdu) - PDFJonathan Bi Nguyen100% (1)
- AcetaldehydeDocument10 pagesAcetaldehydeDinesh guhanNo ratings yet
- Facts at Your Fingertips-48-60Document13 pagesFacts at Your Fingertips-48-60Aatish ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- ATP: Adenosine TriphosphateDocument3 pagesATP: Adenosine TriphosphateClaire ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Acrylic Emulsion Adhesive, MethodDocument8 pagesAcrylic Emulsion Adhesive, MethodAien Nabieyla1607No ratings yet
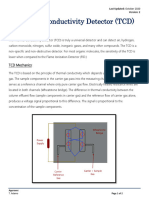
- GC TCDDocument2 pagesGC TCDDheesha GNo ratings yet
- 02 Ib Chemistry (SL+HL) - S1.4 Counting Particles by Mass - The MoleDocument70 pages02 Ib Chemistry (SL+HL) - S1.4 Counting Particles by Mass - The MolericardochavezrNo ratings yet
- Project Final Report 321Document48 pagesProject Final Report 321viplavpassionNo ratings yet
- Asm 19294Document3 pagesAsm 19294shaureya13tsNo ratings yet
- PetroluemDocument37 pagesPetroluemAhmed AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Remember TheseDocument34 pagesRemember Thesem_alodat6144No ratings yet
- White Rust On Galvanized and Galvanized Pre-Painted SteelDocument8 pagesWhite Rust On Galvanized and Galvanized Pre-Painted SteelNabendu BhaumikNo ratings yet
- Caprolactam Process DescriptionDocument8 pagesCaprolactam Process DescriptionJohannah Jane Abuel100% (2)
- Reviewer in Kinetics (FOGLER Based)Document4 pagesReviewer in Kinetics (FOGLER Based)Ralph Mattew PalomariaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6. Chemical Reactions and Ionic EquationsDocument24 pagesTopic 6. Chemical Reactions and Ionic EquationsJoseph MusabukaNo ratings yet
- EP0257845A2Document56 pagesEP0257845A2Jen RealNo ratings yet
- Oxidation ReactionDocument21 pagesOxidation ReactionNor AzilaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Basic Geriatric Nursing 5 Edition Gloria Hoffman WoldDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Basic Geriatric Nursing 5 Edition Gloria Hoffman Woldtossilyvolagef6z3100% (40)
- Pages From Glencoe - Chemistry - Matter and Change (Mcgraw 2008) ch8Document40 pagesPages From Glencoe - Chemistry - Matter and Change (Mcgraw 2008) ch8api-261034721No ratings yet
- Effects of Postharvest Application of Methyl Jasmonate On Physicochemical Characteristics and Antioxidant System of The Blueberry FruitDocument8 pagesEffects of Postharvest Application of Methyl Jasmonate On Physicochemical Characteristics and Antioxidant System of The Blueberry FruitFernando Herrero SinNo ratings yet
- s3 - Sweetening ProcessDocument38 pagess3 - Sweetening ProcessMd Abid AfridiNo ratings yet
- Lignin 3Document61 pagesLignin 3Arpit DubeyNo ratings yet
- Mercaptan Content of The Atmosphere: Standard Test Method ForDocument4 pagesMercaptan Content of The Atmosphere: Standard Test Method ForCynthia GutierrezNo ratings yet
- .4 Polypyrrole: Current Applications and Future ChallengesDocument3 pages.4 Polypyrrole: Current Applications and Future ChallengesFahad ShakeelNo ratings yet
- FAQ's - NDT - MFL Magnetic Flux Leakage Storage Tank Inspection PDFDocument2 pagesFAQ's - NDT - MFL Magnetic Flux Leakage Storage Tank Inspection PDFJai PatelNo ratings yet
- Copper Sulfate Lab Report FormDocument4 pagesCopper Sulfate Lab Report FormXiomara JorgaNo ratings yet
- HILICDocument11 pagesHILICMaria TănaseNo ratings yet
- AkzoNobel TB HlbEmulsionsDocument15 pagesAkzoNobel TB HlbEmulsionspajaron200No ratings yet
- Practice Text 1Document5 pagesPractice Text 1Juan Rodriguez OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- MelaninDocument14 pagesMelaninTimothy100% (2)