Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Reviewer Q3 G10
Science Reviewer Q3 G10
Uploaded by
Jenny Ann SantosOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Reviewer Q3 G10
Science Reviewer Q3 G10
Uploaded by
Jenny Ann SantosCopyright:
Available Formats
SCIENCE REVIEWER
Nervous System - nervous system connects all your body parts and transmits signals from one part to another
Major Divisions and Parts of the Nervous System
1. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) - serves as the main processing center for the entire nervous system.
a. Brain - is an organ located within the skull that functions as organizer and distributor of information for the body.
Cerebrum – controls activity and thought
Cerebellum – controls posture, balance, and coordination
Brain Stem - controls automatic functions such as breathing, digestion, heart rate, and blood pressure
b. Spinal Cord - serves as a channel for signals between the brain and the rest of the body
2. PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (PNS)- connects the central nervous system to the organs and limbs.
a. Somatic Nervous System - is associated with the voluntary control of body movements
Spinal Nerves – the nerves that carry motor and sensory signals between the spinal cord and the body
Cranial Nerves – the nerve fibers that carry information into and out of the brain stem
b. Autonomic Nervous System - is associated with the involuntary control of body movements and
Sympathetic - it is activated when the body is in a dynamic role or stress
Parasympathetic - it maintains body functions and restores the body to normal or relaxed mode
THE NERVE CELL
- it is the basic unit of the nervous system
- it is also called neurons
- has a cell body containing the nucleus
Neuron - has a cell body containing the nucleus. Projecting out from the cell body are root-like structures. These are the
dendrites and axons.
Dendrites - carry impulses towards the cell body
- a single dendrites can be over one meter long
Axons - carry impulses away from the cell body
- can be grouped together into cable-like bundles called nerve
Nerve Impulse - is a combination of an electrical charge and a chemical reaction
- is not a flow of electricity, but an electrochemical signal moving along a neuron
Neurotransmitter - When a nerve impulse comes to the end of an axon, it produces the chemical
Synapse - It is chemical crosses the space between neurons
Nervous System is assisted by 5 sense organs - the eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin
Endocrine System - is composed of glands that secrete different types of hormones that affect almost every cell
FUNCTION OF ENDOCRINE
- Endocrine glands secrete chemicals known as hormones into the bloodstream, which carries them throughout the body
- The endocrine system sends signals all over the body
Pituitary - stimulates growth, and controls the functions of other glands
Thyroid - regulates body metabolism, and causes storage of calcium in bones
Parathyroid - controls the calcium levels in your body, and normalizes bone growth
Thymus - enables the body to produce certain antibodies
Adrenal - prepares the body for action, controls the heart rate and breathing in times of emergency
Pancreas - regulates blood sugar levels
Reproductive
Testes (Males) - control maturation and male characteristics
Ovaries (Females) - influence female traits, and support reproductive function
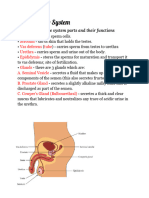
THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Part Function
Testis Produces sperm cells
Scrotum Sac of skin that holds the testis
Penis Deposits sperms into the vagina during mating
Vas deferens (tube) Carries sperm from testes to urethra
Urethra Carries sperm and urine out of the body
Glands Provide liquid in which sperm can swim
a. seminal vesicle - Secretes a fluid that makes up most of the components of the semen
b. prostate gland - Secretes a slightly alkaline milky fluid that is discharged as part of the semen
c. bulbourethral gland - Secretes a thick and clear mucus that lubricates and neutralizes the any trace of acidic urine in
the urethra
THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
The female reproductive system has the following functions:
1. Produces female sex cells
2. Receives sperm cells from the male
3. Nurtures the development of and provides nourishment for the new individual
Part Function
Ovary produces egg cells
Oviduct Serve as passageway of eggs from the ovary to the uterus; site of egg fertilization
Uterus Serve as site of egg implantation; is where the fertilized egg develops
Vagina receives the penis of male during mating
The Role of Hormones in Female and Male Reproductive Systems
FEMALE
- Prepare the uterus so a baby can grow in it
- Control the growth and release of eggs
- Control stretching of uterus
MALE
- Nourish the sperm cells
- Keep the reproductive system properly functioning
DNA & RNA STRUCTURE
Basis of Comparison DNA RNA
Number of strand 2 1
Location in the cell nucleus cytoplasm
Type of sugar deoxyribose ribose
Nitrogenous bases A–T A–U
C- G C-G
DNA Replication - the process in which the DNA is copied
Enzymes - chemicals that speed up chemical reaction
DNA REPLICATION KEY PLAYERS
1. Helicase – the unzipping enzyme
2. DNA Polymerase – the builder
3. Primase – the initializer/primer
4. Ligase – gluer
OKAZAKI FRAGMENTS - are short sequences of DNA nucleotides (which are synthesized discountinously and later linked
together by the enzyme)
SEMICONSERVATIVE REPLICATION - would produce two copies that each continued one of the original strands and one new
strand
Protein Synthesis - the process of making protein
STEPS IN PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
1. Transcription - process of copying DNA sequence into RNA.
2. Translation - process of converting information in mRNA into a sequence of amino acids in a protein.
Genetic Code - set of rules that specify the codons in DNA or RNA that corresponds to the amino acids in proteins
Amino Acid - the building blocks of a protein molecule
Codon - each set of three nitrogenous bases in mRNA representing an amino acid or a start/stop signal
Anticodon - the complement of the mRNA; triplet code in the tRNA
mRNA - messenger RNA; brings information from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm
rRNA- ribosomal RNA; hold tightly to the mRNA and use its information to assemble amino acids
tRNA - transfer RNA; a type of RNA that attach the correct amino acid to the protein chain that is being synthesized in the
ribosome
Mutation - any change in the DNA sequence
Mutagen - is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA
Gene Mutation - is a permanent change in the DNA sequence that makes up a gene.
Chromosomal Mutation - occurs at the chromosome level resulting in gene deletion, duplication or rearrangement that may
occur during the cell cycle and meiosis. It maybe caused by parts of chromosomes breaking off or rejoining incorrectly.
KINDS OF CHROMOSOMAL MUTATION
Deletion - a mutation in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is last during DNA replication
Duplication - involves the production of one or more copies of a gene or region of a chromosome
Inversion - is a chromosome rearrangement in which a segment of a chromosome is reversed end to end
Translocation - is a chromosome abnormality caused by rearrangement of parts between non homologous
Human Karyotyping - a karyotype is an image of the full set of chromosomes of an individual that displays the normal number,
size, and shape
HUMAN KARYOTYPE
- Male Chromosomes (XY)
- Female Chromosomes (XX)
Genetic Engineering
- is the modification of an organisms genetic composition by artificial means, often involving the transfer of species traits, or
genes, from one organism into a plant or animal of an entirely different species.
Cri Du Chat - is caused by the deletion of part of the short arm of chromosome 5. “Cri du chat” is French, and the condition is
so named because affected babies make high-pitched cries that sound like a cat. Affected individuals have wide-set eyes, a
small head and jaw, are moderately to severely mentally retarded, and very short
Down’s Syndrome - is usually caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21(trisomy 21). Characteristics include decreased
muscle tone, stockier build, asymmetrical skull, slanting eyes and mild to moderate mental retardation.
Edward’s Syndrome - which is the second most common trisomy after Down’s syndrome, is a trisomy of chromosome 18.
Symptoms include mental and motor retardation and numerous congenital anomalies causing serious health problems. About
99% die in infancy. However, those who live past their first birthday, usually are quite healthy thereafter. They have a
characteristic hand appearance with clenched hands and overlapping fingers.
Klinefelter’s Syndrome - Klinefelter’s syndrome (XXY). Men with this condition are usually sterile and tend to have longer
arms and legs and to be taller than their peers. They are often shy and quiet and have a higher incidence of speech delay.
Turner’S Syndrome - (X instead of XX or XY). Female sexual characteristics are present but underdeveloped. They often have a
short stature, low hairline, abnormal eye features and bone development and a “caved-in” appearance to the chest
Fossils - are examples of evidence that paleontologists use in studying evolution
- They are traces of organisms that lived in the past and were preserved by natural process or catastrophic events
- they can be remains of organisms when include bones, shells, teeth and also feces embedded in rocks, peat, resin and ice
2 TYPES OF FOSSILS
Impression or Imprint - are shallow external molds left by animal or plan tissues with little or no organic materials present
Compression - is the other side with more organic material
EVIDENCE FROM EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT
Embryo - is an early stage of development in organisms
HINT OF EVOLUTION FROM COMPARATIVE ANATOMY
Homologous Structures - may perform different functions in the species living in the different environment, or it may have the
same origin but different functions
Analogous Structures - have similar functions but different origin
THEORIES OF EVOLUTION
JEAN BAPTISTE DE LAMARCK
- was the first evolutionist to believe that organisms change overtime
- “THE THEORY OF ACQUIRED CHARACTERISTICS”
CHARLES DARWIN
- Darwin suggested that selection also takes place in nature in selective breeding, farmer identifies and selects the best and
desirable trait to propagate
- in “THE THEORY OF NATURAL SELECTION”, environmental factors promote the survival of the fittest and eliminate the less fit
Divergent Evolution - is the splitting of an ancestral population into two or more sub-populations that are geographically
isolated from one to another
Convergence Evolution- is an increase in similarities among species derived from different ancestors as a result of similar
adaptations to similar environment
Radiometric Dating - a method used to determined the age of rocks using the decay of radio active isotopes (Carbon - 14)
prevent in rocks
VALUES OF SPECIES ACCORDING TO CATEGORIES
Direct Economic Value - if their products are sources of food, medicine, clothing, shelter, and energy
Indirect Economic Value - a species has an economic values if there are benefits produced by the organism without using them
Aesthethic Value - a lot of species provides visual are artistic enjoyment like a forested landscape and the calming beauty of
natural park
ECOSYSTEM: BIODIVERSITY
Ecosystem- a large community of living organisms in a particular area.
Biodiversity - is a term that describe how varied living things are in a specific area
Organisms - are part of biodiversity and maybe economically and ecologically valuable
THE UPS AND DOWN OF POPULATION GROWTH
Population - is a group of organisms of the same species that live in a certain area
Ecologists - regularly monitor the number of organisms in many population
Birth or Natality Rate - the number of birth in a population
Death or Mortality Rate - the number of organisms that are dying in a population
* if the birth rate is greater than death rate, a population will grow
* if the death rate is greater than birth rate, then the population will decrease
You might also like
- Technical PDFDocument41 pagesTechnical PDFSergio Sandoval100% (3)
- Dna and Rna Grade 10 TopicsDocument16 pagesDna and Rna Grade 10 TopicsJewel Tan100% (1)
- Unit 3 Module 1Document6 pagesUnit 3 Module 1heide100% (1)
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module2:Week 2Document11 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module2:Week 2Hazel Kim Balacy100% (1)
- Grade 10 3rd Quarter Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesGrade 10 3rd Quarter Science ReviewerZayin DelMundoNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 10 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience Grade 10 3rd Quarter ReviewerDiego ConopioNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Reviewer in Science 10Document9 pages3rd Quarter Reviewer in Science 10cali anna100% (1)
- Central Nervous System (CNS B. Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesCentral Nervous System (CNS B. Autonomic Nervous SystemCid TristeNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Science ReviewerDocument6 pages4th Quarter Science ReviewerMaxine JulianaNo ratings yet
- Science q1 ReviewerDocument9 pagesScience q1 ReviewerG13 Intal, AnikaNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTSDocument3 pagesHANDOUTSElaiza Eline LaguaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 ReviewerDocument2 pagesGrade 10 ReviewerLanie De la TorreNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Quarter 1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 10 Quarter 1 ReviewerLeslie IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 3Document16 pagesScience 10 Quarter 3Ela Mae Gumban GuanNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - 3rd Quarter BIOLOGY (Key Concepts: Nervous System)Document3 pagesGrade 10 - 3rd Quarter BIOLOGY (Key Concepts: Nervous System)Ionacer Viper100% (3)
- Science Exam ReviewerDocument12 pagesScience Exam ReviewerRhyssa BacaniNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science ReviewerDocument2 pagesGrade 10 Science ReviewerVannie MonderoNo ratings yet
- Mapeh G10 Reviewer Q1Document17 pagesMapeh G10 Reviewer Q1Hanna Samantha LisingNo ratings yet
- Reviewer MapehDocument5 pagesReviewer MapehMark Joseph De Gracia100% (1)
- Science Grade 10 (Exam Prep)Document6 pagesScience Grade 10 (Exam Prep)Venice Solver100% (3)
- MAPEH REVIEWER GRADE 10 3rd QDocument4 pagesMAPEH REVIEWER GRADE 10 3rd QAstre JrNo ratings yet
- Fil 10 Q1 ReviewerDocument6 pagesFil 10 Q1 ReviewerJamela PalomoNo ratings yet
- Handouts in Science 10Document2 pagesHandouts in Science 10CRISTIAN PORTUGALNo ratings yet
- Science Notes - 2nd QuarterDocument5 pagesScience Notes - 2nd QuarterRanz EnriquezNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS 10 REVIEWER - 4th QuarterDocument10 pagesMATHEMATICS 10 REVIEWER - 4th QuarterGeromme TudNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Reviewer in English 10Document3 pages3rd Quarter Reviewer in English 10cali annaNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Science Exam ReviewerDocument6 pages1st Term Science Exam ReviewerAndie MorenoNo ratings yet
- Math Reviewer GR 10 3RD Quarter PDFDocument9 pagesMath Reviewer GR 10 3RD Quarter PDFAlyzza Grande Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Buenasher Learning Academy IncDocument4 pagesBuenasher Learning Academy IncEl CruzNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q4 SLM7Document13 pagesScience 10 Q4 SLM7RAYMUND RODILLO0% (1)
- MAPEH 10 Handout - 3Document4 pagesMAPEH 10 Handout - 3Toni Rose Sayson50% (2)
- This Study Resource Was: Science 10: 1 Quarter ReviewerDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Science 10: 1 Quarter ReviewerKathrina ValienteNo ratings yet
- 2ND Grading Reviewer in ScienceDocument4 pages2ND Grading Reviewer in ScienceVannie Mondero50% (2)
- Mapeh Reviewer 3rd QuarterDocument3 pagesMapeh Reviewer 3rd QuarterIceyYamaha60% (5)
- Grade 10 First Quarter SummaryDocument3 pagesGrade 10 First Quarter SummaryAdrian Tastar100% (1)
- Reviewer in English 10Document2 pagesReviewer in English 10EdLoi TangguiyacNo ratings yet
- Q3 MAPEH Grade 10 - LASDocument19 pagesQ3 MAPEH Grade 10 - LASjhamilla AdajarNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Q 4 Module 2Document3 pagesActivity 1 Q 4 Module 2orcullo100% (1)
- Science 10 ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 10 ReviewerAmber RamosNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System G10Document27 pagesEndocrine System G10Cyril CauilanNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Summary of q1Document2 pagesScience 10 Summary of q1Aldrin Lumantas100% (1)
- GRADE 10 SCIENCE 3rd QuarterDocument3 pagesGRADE 10 SCIENCE 3rd Quartergerald quijanoNo ratings yet
- English Quarter 1 Reviewer Grade 10Document2 pagesEnglish Quarter 1 Reviewer Grade 10arieannie katlyNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Reviewer in MAPEHDocument4 pagesGrade 10 Reviewer in MAPEHLoraine Antonette CupoNo ratings yet
- TG - Science 10 - Q3 PDFDocument121 pagesTG - Science 10 - Q3 PDFEmely Secretario50% (2)
- Science10 Q4L2Document5 pagesScience10 Q4L2Clyde KirbyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 1ST GradingDocument23 pagesReviewer 1ST Gradingpretty raul100% (2)
- Organization, Neurons, Basic Functions of Synapses, and NeurotransmittersDocument3 pagesOrganization, Neurons, Basic Functions of Synapses, and Neurotransmitters22 - Fernandez, Lyza Mae D.No ratings yet
- Music Reviewer 4th QuarterDocument3 pagesMusic Reviewer 4th QuarterDezscyrie Pearl LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesGERRY CHEL LAURENTENo ratings yet
- 3rd PEriodical Math 1Document4 pages3rd PEriodical Math 1Ardy PatawaranNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument3 pagesScienceJames Darren TadeoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Activity# 1: Break It Down!Document19 pagesUnit 3: Activity# 1: Break It Down!jules blasabasNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science: LithosphereDocument3 pagesReviewer in Science: LithosphereNatasha Loujille Collado100% (1)
- Science - 10: Name: - Date: - ScoreDocument5 pagesScience - 10: Name: - Date: - ScoreLan CeNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education: Felipe-Innocencia Deluao National High SchoolDocument6 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education: Felipe-Innocencia Deluao National High Schooljelly marie floresNo ratings yet
- Q4 Mapeh 10 ReviewerDocument4 pagesQ4 Mapeh 10 ReviewerAliah Jett Nicole BelarminoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-REVIEWERDocument8 pagesSCIENCE-REVIEWERtxm4kb4h46No ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer 3rd Quarter ExaminationDocument7 pagesBiology Reviewer 3rd Quarter ExaminationrgysabellerullNo ratings yet
- Guiruela JelianDocument3 pagesGuiruela JelianLyra LingcoranNo ratings yet
- Science 3rd Quarter ReviewerDocument19 pagesScience 3rd Quarter ReviewerErica Jane VillamorNo ratings yet
- What Is The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Nervous SystemSittie Asleah SandiganNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec Session #12 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document7 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #12 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL Biology Unit-5 January 2014 Mark SchemeDocument22 pagesEdexcel IAL Biology Unit-5 January 2014 Mark SchemeAvrinoxNo ratings yet
- Connecting Vascular and Nervous System Development: Angiogenesis and The Blood-Brain BarrierDocument32 pagesConnecting Vascular and Nervous System Development: Angiogenesis and The Blood-Brain BarrierAri CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 15Document5 pagesSample Paper 15shubhi bhangalNo ratings yet
- Sompolinsky - PhysicsToday Statistical Mechanics of Neural NetworksDocument11 pagesSompolinsky - PhysicsToday Statistical Mechanics of Neural Networksanurag sahayNo ratings yet
- Pain ControlDocument313 pagesPain ControlBlueSaga100% (1)
- Bachelor Thesis Jort BoumaDocument25 pagesBachelor Thesis Jort BoumaHari Madhavan Krishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Atlas NeuroanatomyDocument874 pagesAtlas NeuroanatomyBilge Yilmaz100% (3)
- Guillain Barre SyndromeDocument38 pagesGuillain Barre SyndromePeterson Wachira HscNo ratings yet
- Đề HSG 11 Thu-HàDocument9 pagesĐề HSG 11 Thu-HàRuby NgoNo ratings yet
- LP6 PerdevDocument6 pagesLP6 PerdevChristine Marie A Llanera-CadalloNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormoneDocument396 pagesThyroid HormoneuiliftengNo ratings yet
- International Handbook of Neuropsychological Rehabilitation PDFDocument376 pagesInternational Handbook of Neuropsychological Rehabilitation PDFFrancisco Ribeiro RachinasNo ratings yet
- Altered Cognitive-Perceptual Patterns: Clients With Neuroligic DisordersDocument96 pagesAltered Cognitive-Perceptual Patterns: Clients With Neuroligic DisordersJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- SSLC Biology Study Material Ujwalam 2023 by DIET Kollam (Eng Med)Document79 pagesSSLC Biology Study Material Ujwalam 2023 by DIET Kollam (Eng Med)adhikesh65No ratings yet
- Chennai Sahodaya Science Set 2 QP 2022-23 FOR PRACTICE ONLYDocument10 pagesChennai Sahodaya Science Set 2 QP 2022-23 FOR PRACTICE ONLYvro hamza86% (7)
- Histology of Chemical Synapses of The Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesHistology of Chemical Synapses of The Nervous SystemAhmed ZanatyNo ratings yet
- Textbook Brain Compatible Dance Education Second Editon Edition Gilbert Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Brain Compatible Dance Education Second Editon Edition Gilbert Ebook All Chapter PDFmartha.tague29695% (21)
- Coordination & Response 5 QP PDFDocument6 pagesCoordination & Response 5 QP PDFJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Sensation and PerceptionDocument40 pagesChapter 3 - Sensation and PerceptionKaiNo ratings yet
- ASA 1501-Assignment 1Document8 pagesASA 1501-Assignment 1grimsdellaNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument38 pagesArtificial IntelligenceBrent Arnold100% (3)
- Journal of Oral Biosciences: Ji Won Kim, Joo-Cheol ParkDocument7 pagesJournal of Oral Biosciences: Ji Won Kim, Joo-Cheol ParkChristina CalistaNo ratings yet
- Edgcse TTPP Cb2 SB AnswersDocument4 pagesEdgcse TTPP Cb2 SB AnswersshmuckygyalNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Sensory Neurological SystemDocument35 pagesAssessing The Sensory Neurological SystemSusan Maglaqui100% (1)
- APP Ch.3 OutlineDocument5 pagesAPP Ch.3 OutlineAlliePalmerNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Psych NotesDocument40 pagesUnit 2 Psych NotesunicornrainNo ratings yet
- Multipath Model PDFDocument10 pagesMultipath Model PDFAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet