Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 viewsPostoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres OR
Postoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres OR
Uploaded by
Krzia TehCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan (Acute Pain For Ceasarean Birth) HYPOTHETICALDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan (Acute Pain For Ceasarean Birth) HYPOTHETICALmarife84% (19)
- Nursing Care Plan For Cesarean SectionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Cesarean SectionJon Gab Paquit85% (33)
- NCP Risk For Infection Related To Postop IncisionDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For Infection Related To Postop Incisionanreilegarde80% (25)
- Nursing Care Plan of Breech PresentationDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan of Breech PresentationDr-Sanjay Singhania100% (3)
- Cesarian Section Case PresentationDocument26 pagesCesarian Section Case PresentationMae Azores86% (51)
- Cesarian Section Case PresentationDocument26 pagesCesarian Section Case PresentationMae Azores86% (51)
- NCP - Pain Related To Surgical Incision (Mark)Document4 pagesNCP - Pain Related To Surgical Incision (Mark)KM59% (22)
- Bone Marrow WashingDocument32 pagesBone Marrow WashingOjl Therapies100% (5)
- NCP-Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP-Risk For Infectioneihjay-bravo-804175% (81)
- NCP-Risk For InfectionDocument4 pagesNCP-Risk For InfectionMarianne May Loquias100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan Cesarean DeliveryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cesarean DeliveryLei Ortega50% (4)
- SP CSDocument4 pagesSP CSKhan HansNo ratings yet
- NCP NSDDocument3 pagesNCP NSDshigemasamayumi60% (5)
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Serum Status: TriglyceridesDocument1 pageLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Serum Status: TriglyceridesUpender Rao SunkishalaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation OutcomeDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation OutcomeBethel Ann Cordova100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN For Post Operative Cesarian SectionDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN For Post Operative Cesarian SectionKaren Joyce Costales Magtanong100% (3)
- NCP CSDocument9 pagesNCP CSFreida Marie PiczonNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection Related To Presence of Surgical Wounds As Evidenced by MER 2nd DegreeDocument3 pagesRisk For Infection Related To Presence of Surgical Wounds As Evidenced by MER 2nd DegreeSenyorita KHaye75% (12)
- NCP For CSDocument2 pagesNCP For CSJClaudz Pilapil50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Cesarian DeliveryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cesarian Deliveryderic97% (39)
- CS NCPDocument3 pagesCS NCPAllan VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Acute PainDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Acute PainJonette Calix Sam100% (1)
- NCP Cervical Final)Document4 pagesNCP Cervical Final)Theresa Abrillo83% (6)
- Nursing Diagnosis Background Study Inference Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis Background Study Inference Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Postpartum NCPDocument20 pagesPostpartum NCPapi-370148988% (34)
- CS NCPDocument2 pagesCS NCPElbert ViernezaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: WWW - Unp.edu - PHDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: WWW - Unp.edu - PHKrizha Angela Nicolas0% (1)
- NCP On Postpartum MotherDocument13 pagesNCP On Postpartum MotherLenjun89% (57)
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionMao71% (14)
- Normal Spontaneous Delivery NCP IncompleteDocument2 pagesNormal Spontaneous Delivery NCP IncompleteKQarlo Luis Pestaño Maniaol100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation GoalDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation GoalI Am SmilingNo ratings yet
- NCP For Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP For Acute PainEmman RamosNo ratings yet
- Assessment Cues Nursing Outcome Planning Nursing Interventions Evaluation Diagnosis Identification Interventions RationaleDocument6 pagesAssessment Cues Nursing Outcome Planning Nursing Interventions Evaluation Diagnosis Identification Interventions RationaleAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- NCP Escaran.Document3 pagesNCP Escaran.Roswell Almodiel EscaranNo ratings yet
- Case Discussion: Mayan, Mercurio, Murillo BSN 2-ADocument11 pagesCase Discussion: Mayan, Mercurio, Murillo BSN 2-ADhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Care Plan Format: Patient Is A Non-SmokerDocument2 pagesNursing Process Care Plan Format: Patient Is A Non-SmokerDavid PerezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanErica Lagsa100% (1)
- NCP and Drug Study For Ob WardDocument7 pagesNCP and Drug Study For Ob WardAce Fabrigas100% (1)
- 2nd NCPDocument4 pages2nd NCPjoidaNo ratings yet
- ViolahDocument3 pagesViolahmutjamaneNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanMariel GamaloNo ratings yet
- NCP Post Op (Impaired and Risk For Infection)Document4 pagesNCP Post Op (Impaired and Risk For Infection)Carl J.No ratings yet
- NCP NSD 2Document3 pagesNCP NSD 2Warren Bilog OleaNo ratings yet
- Copy of NCP Format)Document4 pagesCopy of NCP Format)shai raNo ratings yet
- Clinical Portrait Pertinent DataDocument9 pagesClinical Portrait Pertinent DataGermin CesaNo ratings yet
- Acute PainDocument4 pagesAcute PainIvan Jules P. PALMARESNo ratings yet
- NCP FamedDocument1 pageNCP FamedAbegail MierNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario - Nursing Care Plan (DR - Magsingal)Document1 pageCase Scenario - Nursing Care Plan (DR - Magsingal)Cristyl Shine BariaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention S Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention S Rationale EvaluationNo EulNo ratings yet
- NCP Ectopic PregnancyDocument2 pagesNCP Ectopic PregnancykatrinajhorelletillesNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJanice SolamilloNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document2 pagesNCP 2Loreily ShyreenNo ratings yet
- Nicholas Chung Ching Pui: Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNicholas Chung Ching Pui: Nursing Care PlanMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- NCP HerniaDocument4 pagesNCP HerniaLord Allen B. GomezNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument2 pagesNCP PainKimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlankingpinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute PainDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Acute PainEvet VaxbmNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Objective Data: - Well Appearing But Independent Nursing Interventions: - Review Intraoperative Desired Outcome. Goal Met. Patient Was Able ToDocument3 pagesSubjective Data: Objective Data: - Well Appearing But Independent Nursing Interventions: - Review Intraoperative Desired Outcome. Goal Met. Patient Was Able ToMariel GamaloNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationVie RahNo ratings yet
- Nursing-Care-Plan-J P VDocument8 pagesNursing-Care-Plan-J P VMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Or NCPDocument5 pagesOr NCPjelopigar921No ratings yet
- NCP PostpartumDocument6 pagesNCP PostpartumLovely Anne ArqueroNo ratings yet
- Preop Appendectomy NCPDocument3 pagesPreop Appendectomy NCPMyra AtuleNo ratings yet
- Document Tcap-Draft ALSDocument77 pagesDocument Tcap-Draft ALSMae AzoresNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment For Patient With DM Type1Document4 pagesPhysical Assessment For Patient With DM Type1Mae AzoresNo ratings yet
- Focus-Nursing Care Plan For Sleep DisordersDocument9 pagesFocus-Nursing Care Plan For Sleep DisordersMae AzoresNo ratings yet
- Sexually Connotative Disorders - ScribdDocument18 pagesSexually Connotative Disorders - ScribdMae AzoresNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument5 pagesDengue FeverMae AzoresNo ratings yet
- Status AsthmaticusDocument6 pagesStatus AsthmaticusMae Azores100% (1)
- The Learning Experience of A Student Nurse, A Critical AnalysisDocument7 pagesThe Learning Experience of A Student Nurse, A Critical AnalysisMae Azores100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationMae AzoresNo ratings yet
- Developing Work Groups For Community Health DevelopmentDocument7 pagesDeveloping Work Groups For Community Health DevelopmentMae Azores100% (1)
- Philosophy of Critical Care NursingDocument5 pagesPhilosophy of Critical Care NursingAICEL A. ABILNo ratings yet
- Psych 2AP3 - Anxiety DIsordersDocument9 pagesPsych 2AP3 - Anxiety DIsordersdeanNo ratings yet
- 14 Amazing Natural Antibiotics Mechanisms & Side EffectsDocument26 pages14 Amazing Natural Antibiotics Mechanisms & Side EffectsGuillermoNo ratings yet
- Care Pathway On NeutropeniaDocument1 pageCare Pathway On NeutropeniaShuchi RaiNo ratings yet
- Muscle RelaxantDocument33 pagesMuscle RelaxantFady Jehad ZabenNo ratings yet
- 1st PageDocument3 pages1st PageLadyAngelIgnacioValgunaNo ratings yet
- Patente Sida...Document9 pagesPatente Sida...VictorVanderFoxysNo ratings yet
- The Geography of World War ZDocument1 pageThe Geography of World War ZazuldraconNo ratings yet
- 10 Chemical Tests Fecal Occult BloodDocument11 pages10 Chemical Tests Fecal Occult BloodAdarshBijapurNo ratings yet
- Fin 1206Document8 pagesFin 1206Ajaykrishnan JayagopalNo ratings yet
- Essay 3 FGM RevisedDocument7 pagesEssay 3 FGM Revisedapi-318190162No ratings yet
- LECTURE 6 Male Reproductive System - Histology HB II 2023Document76 pagesLECTURE 6 Male Reproductive System - Histology HB II 2023Emmanuel AssopiahNo ratings yet
- The University of The West Indies Faculty of Medical Sciences Department of Clinical Medical Sciences Years 5 Medicine ClerkshipDocument4 pagesThe University of The West Indies Faculty of Medical Sciences Department of Clinical Medical Sciences Years 5 Medicine ClerkshipRyubusa HayabusaNo ratings yet
- Oral Mucous MembraneDocument71 pagesOral Mucous MembraneHarleen GrewalNo ratings yet
- Ridge AugmentationDocument109 pagesRidge AugmentationSingh Jyoti100% (3)
- Deepak Kademani - Improving Outcomes in Oral Cancer - A Clinical and Translational Update-Springer International Publishing (2020)Document189 pagesDeepak Kademani - Improving Outcomes in Oral Cancer - A Clinical and Translational Update-Springer International Publishing (2020)Shantanu DixitNo ratings yet
- Juvenile DermatomyositisDocument22 pagesJuvenile DermatomyositisEmily EresumaNo ratings yet
- American Meat Institute: Degree Hours RegulationDocument26 pagesAmerican Meat Institute: Degree Hours RegulationelataniNo ratings yet
- Common Health Problems InfancyDocument147 pagesCommon Health Problems Infancymark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary System: 1. Hair DistributionDocument9 pagesGenitourinary System: 1. Hair DistributionPaul Vincent100% (1)
- Nutritie Sportiva PDFDocument31 pagesNutritie Sportiva PDFRadu BuculeaNo ratings yet
- Sr. No. Cghs Treatment Procedure/Investigation List Non-NABH/Non - NABL Rates Nabh/Nabl RatesDocument41 pagesSr. No. Cghs Treatment Procedure/Investigation List Non-NABH/Non - NABL Rates Nabh/Nabl RatesNarayanan NMNo ratings yet
- Brain Death & Organ ProcurementDocument10 pagesBrain Death & Organ ProcurementkencheenNo ratings yet
- Prioritization of ProblemDocument2 pagesPrioritization of ProblemGenette Sy SolisNo ratings yet
- Bioteque PessaryDocument2 pagesBioteque PessaryAngelo PlataNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document11 pagesQuiz 2Ericka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Philanthrocapitalism, Past and Present - HealthDocument27 pagesPhilanthrocapitalism, Past and Present - HealthsanjnuNo ratings yet
- Patenting in BiotechnologyDocument6 pagesPatenting in BiotechnologyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
Postoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres OR
Postoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres OR
Uploaded by
Krzia Teh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pagesOriginal Title
27054577-Postoperative-Nursing-Care-Plan-for-Cesarian-Section-Patient-Case-Pres-OR.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pagesPostoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres OR
Postoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres OR
Uploaded by
Krzia TehCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
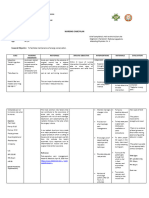
XI.
NURSING CARE PLAN
Post-operative NCP
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE OUTCOME
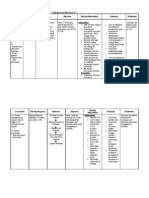
Subjective: Acute pain r/t STG: Independent: Goal met. After
“Sobrang sakit,” as disruption of skin After 1-2hr of 2hrs of nursing
verbalized by the and tissue nursing - Established rapport. -To have a good intervention, the
patient. secondary to intervention, nurse-client patient verbalized
cesarean patient will relationship pain decreased
Objective: section. verbalize - Monitored vital signs. from a scale of 8/10
-Pain scale= 8/10 decrease intensity -To establish a – 3/20 as
-Teary eyed of pain from 8/10 - Assessed quality, baseline data evidenced by
-(+) guarding to 3/10. characteristics, (-) facial grimace
behavior severity of pain. -To establish (-) guarding
-(+) facial grimace baseline data for behavior.
-Irritable comparison in Frequent small
-Pale palpebral making evaluation talks with significant
conjunctiva and to assess for others
-Skin warm to - Provided comfortable possible internal
touch environment – bleeding.
-V/S taken as changed bed linens
follows: and turned on the -Calm environment
BP= 110/80 fan. helps to decrease the
PR= 80 anxiety of the patient
RR= 22 and promote
T= 37.6 - Instructed to put pillow likelihood of
on the abdomen decreasing pain.
when coughing or
moving. - To check for
diastasis recti and
protect the area of
the incision to
improve comfort. And
to initiate
nonstressful muscle-
setting techniques
and progress as
tolerated, based on
- Instructed patient to the degree of
do deep breathing separation.
and coughing
exercise. - For pulmonary
ventilation, especially
when exercising, and
to relieve stress and
- Provided diversionary promote relaxation.
activities. Initiate
ankle pumping, - To promote
active lower circulation, prevent
extremity ROM, and venous stasis,
walking prevent pressure on
the operative site.
Collaborative:
- Administer analgesic
as per doctor’s
order. -Relieves pain felt by
the patient
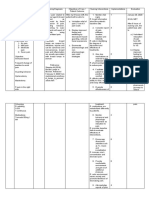
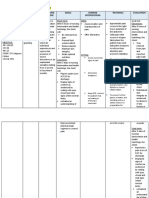
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS NURSING PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
ANALYSIS
Subjective: Risk for Due to an STG: Independent
- none infection related elective After 4 hours of -Monitor vital -To establish a Patient is
inadequate cesarean nursing signs baseline data expected to be
Objective: primary section, intervention, free of
- dressing dry defenses patient’s skin patient will be -Inspect dressing -Moist from infection, as
and intact secondary to and tissue were able to and perform drainage can be a evidenced by
-V/S taken as surgical incision mechanically understand wound care source of infection normal vital
follows: interrupted. causative signs and
T: 37.3 Thus, the factors, identify - Monitor white - Rising WBC absence of
P: 80 wound is at risk signs of blood count (WB indicates body’s purulent
R: 19 of developing infection and efforts to combat drainage from
BP: 120/80 infection. report them to pathogens; wounds,
health care normal values: incisions, and
provider 4000 to 11,000 tubes.
accordingly. mm3
LTG: - Monitor -these are signs
After 2-3 days Elevated of infection
of nursing temperature,
intervention, Redness,
patient will swelling,
achieve timely increased pain,
wound healing, or purulent
be free of drainage at
purulent incisions
drainage or
erythema, be - Wash hands -Friction and
afebrile and be and teach other running water
free of infection. caregivers to effectively remove
wash hands microorganisms
before contact from hands.
with patient and Washing between
between procedures
procedures with reduces the risk of
patient. transmitting
pathogens from
one area of the
body to another
- Encourage fluid - Fluids promote
intake of 2000 ml diluted urine and
to 3000 ml of frequent emptying
water per day of bladder;
(unless reducing stasis of
contraindicated). urine, in turn,
reduces risk of
bladder infection
or urinary tract
infection (UTI).
- Encourage - These measures
coughing and reduce stasis of
deep breathing; secretions in the
consider use of lungs and
incentive bronchial tree.
spirometer. When stasis
occurs, pathogens
can cause upper
respiratory
infections,
including
pneumonia.
Independent: -Antibiotics have
-Administer bactericidal effect
antibiotics that combats
pathogens
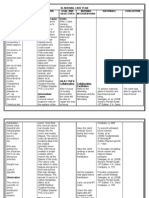
NURSING
ASSESSMENT PLANNING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS
Objective Cues:
Patient has Risk for Short Term INDEPENDENT After 8º of
not yet constipation r/t Goal: INTERVENTIONS: nursing
eliminated post pregnancy Ascertain normal This is to interventions, the
since 2° cesarean Within 8º of bowel functioning of determine the patient was able
delivery the patient, about normal bowel
section nursing to identify
Absence of how many times a pattern
bruit sounds interventions, measures to
day does she
Normal the patient will prevent infection
defecate To increase the
pattern of be able to Encourage intake of as manifested by
bulk of the
bowel has demonstrate foods rich in fiber stool and client’s
not yet behaviors or such as fruits facilitate the verbalization of:
returned lifestyle changes passage “Iinom ako ng
to prevent through the maraming tubig
developing colon at kakain ng
problem Promote adequate To promote prutas para
fluid intake. moist soft stool makadumi ako.”
Suggest drinking of
warm fluids,
especially in the
Long Term Goal:
morning to
stimulate peristalsis To stimulate
Within 3 days of Encourage contractions of
nursing ambulation such as the intestines
interventions, walking within and prevent
the patient will individual limits post operative
be able to complications
maintain usual However, since she To avoid stress
has had cesarean, on the
pattern of bowel
also encourage cesarean
functioning adequate rest incision/ wound
periods
COLLABORATIVE:
Administer bulk-
forming agents or To promote
stool softeners such defecation
as laxatives as
indicated or
prescribed by the
physician
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan (Acute Pain For Ceasarean Birth) HYPOTHETICALDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan (Acute Pain For Ceasarean Birth) HYPOTHETICALmarife84% (19)
- Nursing Care Plan For Cesarean SectionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Cesarean SectionJon Gab Paquit85% (33)
- NCP Risk For Infection Related To Postop IncisionDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For Infection Related To Postop Incisionanreilegarde80% (25)
- Nursing Care Plan of Breech PresentationDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan of Breech PresentationDr-Sanjay Singhania100% (3)
- Cesarian Section Case PresentationDocument26 pagesCesarian Section Case PresentationMae Azores86% (51)
- Cesarian Section Case PresentationDocument26 pagesCesarian Section Case PresentationMae Azores86% (51)
- NCP - Pain Related To Surgical Incision (Mark)Document4 pagesNCP - Pain Related To Surgical Incision (Mark)KM59% (22)
- Bone Marrow WashingDocument32 pagesBone Marrow WashingOjl Therapies100% (5)
- NCP-Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP-Risk For Infectioneihjay-bravo-804175% (81)
- NCP-Risk For InfectionDocument4 pagesNCP-Risk For InfectionMarianne May Loquias100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan Cesarean DeliveryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cesarean DeliveryLei Ortega50% (4)
- SP CSDocument4 pagesSP CSKhan HansNo ratings yet
- NCP NSDDocument3 pagesNCP NSDshigemasamayumi60% (5)
- Laboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Serum Status: TriglyceridesDocument1 pageLaboratory Test Report: Test Name Result Biological Reference Interval Serum Status: TriglyceridesUpender Rao SunkishalaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation OutcomeDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation OutcomeBethel Ann Cordova100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN For Post Operative Cesarian SectionDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN For Post Operative Cesarian SectionKaren Joyce Costales Magtanong100% (3)
- NCP CSDocument9 pagesNCP CSFreida Marie PiczonNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection Related To Presence of Surgical Wounds As Evidenced by MER 2nd DegreeDocument3 pagesRisk For Infection Related To Presence of Surgical Wounds As Evidenced by MER 2nd DegreeSenyorita KHaye75% (12)
- NCP For CSDocument2 pagesNCP For CSJClaudz Pilapil50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Cesarian DeliveryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cesarian Deliveryderic97% (39)
- CS NCPDocument3 pagesCS NCPAllan VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Acute PainDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Acute PainJonette Calix Sam100% (1)
- NCP Cervical Final)Document4 pagesNCP Cervical Final)Theresa Abrillo83% (6)
- Nursing Diagnosis Background Study Inference Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis Background Study Inference Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Postpartum NCPDocument20 pagesPostpartum NCPapi-370148988% (34)
- CS NCPDocument2 pagesCS NCPElbert ViernezaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: WWW - Unp.edu - PHDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: WWW - Unp.edu - PHKrizha Angela Nicolas0% (1)
- NCP On Postpartum MotherDocument13 pagesNCP On Postpartum MotherLenjun89% (57)
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionMao71% (14)
- Normal Spontaneous Delivery NCP IncompleteDocument2 pagesNormal Spontaneous Delivery NCP IncompleteKQarlo Luis Pestaño Maniaol100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation GoalDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation GoalI Am SmilingNo ratings yet
- NCP For Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP For Acute PainEmman RamosNo ratings yet
- Assessment Cues Nursing Outcome Planning Nursing Interventions Evaluation Diagnosis Identification Interventions RationaleDocument6 pagesAssessment Cues Nursing Outcome Planning Nursing Interventions Evaluation Diagnosis Identification Interventions RationaleAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- NCP Escaran.Document3 pagesNCP Escaran.Roswell Almodiel EscaranNo ratings yet
- Case Discussion: Mayan, Mercurio, Murillo BSN 2-ADocument11 pagesCase Discussion: Mayan, Mercurio, Murillo BSN 2-ADhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Care Plan Format: Patient Is A Non-SmokerDocument2 pagesNursing Process Care Plan Format: Patient Is A Non-SmokerDavid PerezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanErica Lagsa100% (1)
- NCP and Drug Study For Ob WardDocument7 pagesNCP and Drug Study For Ob WardAce Fabrigas100% (1)
- 2nd NCPDocument4 pages2nd NCPjoidaNo ratings yet
- ViolahDocument3 pagesViolahmutjamaneNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanMariel GamaloNo ratings yet
- NCP Post Op (Impaired and Risk For Infection)Document4 pagesNCP Post Op (Impaired and Risk For Infection)Carl J.No ratings yet
- NCP NSD 2Document3 pagesNCP NSD 2Warren Bilog OleaNo ratings yet
- Copy of NCP Format)Document4 pagesCopy of NCP Format)shai raNo ratings yet
- Clinical Portrait Pertinent DataDocument9 pagesClinical Portrait Pertinent DataGermin CesaNo ratings yet
- Acute PainDocument4 pagesAcute PainIvan Jules P. PALMARESNo ratings yet
- NCP FamedDocument1 pageNCP FamedAbegail MierNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario - Nursing Care Plan (DR - Magsingal)Document1 pageCase Scenario - Nursing Care Plan (DR - Magsingal)Cristyl Shine BariaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention S Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention S Rationale EvaluationNo EulNo ratings yet
- NCP Ectopic PregnancyDocument2 pagesNCP Ectopic PregnancykatrinajhorelletillesNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJanice SolamilloNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document2 pagesNCP 2Loreily ShyreenNo ratings yet
- Nicholas Chung Ching Pui: Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNicholas Chung Ching Pui: Nursing Care PlanMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- NCP HerniaDocument4 pagesNCP HerniaLord Allen B. GomezNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument2 pagesNCP PainKimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlankingpinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute PainDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Acute PainEvet VaxbmNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Objective Data: - Well Appearing But Independent Nursing Interventions: - Review Intraoperative Desired Outcome. Goal Met. Patient Was Able ToDocument3 pagesSubjective Data: Objective Data: - Well Appearing But Independent Nursing Interventions: - Review Intraoperative Desired Outcome. Goal Met. Patient Was Able ToMariel GamaloNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationVie RahNo ratings yet
- Nursing-Care-Plan-J P VDocument8 pagesNursing-Care-Plan-J P VMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Or NCPDocument5 pagesOr NCPjelopigar921No ratings yet
- NCP PostpartumDocument6 pagesNCP PostpartumLovely Anne ArqueroNo ratings yet
- Preop Appendectomy NCPDocument3 pagesPreop Appendectomy NCPMyra AtuleNo ratings yet
- Document Tcap-Draft ALSDocument77 pagesDocument Tcap-Draft ALSMae AzoresNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment For Patient With DM Type1Document4 pagesPhysical Assessment For Patient With DM Type1Mae AzoresNo ratings yet
- Focus-Nursing Care Plan For Sleep DisordersDocument9 pagesFocus-Nursing Care Plan For Sleep DisordersMae AzoresNo ratings yet
- Sexually Connotative Disorders - ScribdDocument18 pagesSexually Connotative Disorders - ScribdMae AzoresNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument5 pagesDengue FeverMae AzoresNo ratings yet
- Status AsthmaticusDocument6 pagesStatus AsthmaticusMae Azores100% (1)
- The Learning Experience of A Student Nurse, A Critical AnalysisDocument7 pagesThe Learning Experience of A Student Nurse, A Critical AnalysisMae Azores100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationMae AzoresNo ratings yet
- Developing Work Groups For Community Health DevelopmentDocument7 pagesDeveloping Work Groups For Community Health DevelopmentMae Azores100% (1)
- Philosophy of Critical Care NursingDocument5 pagesPhilosophy of Critical Care NursingAICEL A. ABILNo ratings yet
- Psych 2AP3 - Anxiety DIsordersDocument9 pagesPsych 2AP3 - Anxiety DIsordersdeanNo ratings yet
- 14 Amazing Natural Antibiotics Mechanisms & Side EffectsDocument26 pages14 Amazing Natural Antibiotics Mechanisms & Side EffectsGuillermoNo ratings yet
- Care Pathway On NeutropeniaDocument1 pageCare Pathway On NeutropeniaShuchi RaiNo ratings yet
- Muscle RelaxantDocument33 pagesMuscle RelaxantFady Jehad ZabenNo ratings yet
- 1st PageDocument3 pages1st PageLadyAngelIgnacioValgunaNo ratings yet
- Patente Sida...Document9 pagesPatente Sida...VictorVanderFoxysNo ratings yet
- The Geography of World War ZDocument1 pageThe Geography of World War ZazuldraconNo ratings yet
- 10 Chemical Tests Fecal Occult BloodDocument11 pages10 Chemical Tests Fecal Occult BloodAdarshBijapurNo ratings yet
- Fin 1206Document8 pagesFin 1206Ajaykrishnan JayagopalNo ratings yet
- Essay 3 FGM RevisedDocument7 pagesEssay 3 FGM Revisedapi-318190162No ratings yet
- LECTURE 6 Male Reproductive System - Histology HB II 2023Document76 pagesLECTURE 6 Male Reproductive System - Histology HB II 2023Emmanuel AssopiahNo ratings yet
- The University of The West Indies Faculty of Medical Sciences Department of Clinical Medical Sciences Years 5 Medicine ClerkshipDocument4 pagesThe University of The West Indies Faculty of Medical Sciences Department of Clinical Medical Sciences Years 5 Medicine ClerkshipRyubusa HayabusaNo ratings yet
- Oral Mucous MembraneDocument71 pagesOral Mucous MembraneHarleen GrewalNo ratings yet
- Ridge AugmentationDocument109 pagesRidge AugmentationSingh Jyoti100% (3)
- Deepak Kademani - Improving Outcomes in Oral Cancer - A Clinical and Translational Update-Springer International Publishing (2020)Document189 pagesDeepak Kademani - Improving Outcomes in Oral Cancer - A Clinical and Translational Update-Springer International Publishing (2020)Shantanu DixitNo ratings yet
- Juvenile DermatomyositisDocument22 pagesJuvenile DermatomyositisEmily EresumaNo ratings yet
- American Meat Institute: Degree Hours RegulationDocument26 pagesAmerican Meat Institute: Degree Hours RegulationelataniNo ratings yet
- Common Health Problems InfancyDocument147 pagesCommon Health Problems Infancymark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary System: 1. Hair DistributionDocument9 pagesGenitourinary System: 1. Hair DistributionPaul Vincent100% (1)
- Nutritie Sportiva PDFDocument31 pagesNutritie Sportiva PDFRadu BuculeaNo ratings yet
- Sr. No. Cghs Treatment Procedure/Investigation List Non-NABH/Non - NABL Rates Nabh/Nabl RatesDocument41 pagesSr. No. Cghs Treatment Procedure/Investigation List Non-NABH/Non - NABL Rates Nabh/Nabl RatesNarayanan NMNo ratings yet
- Brain Death & Organ ProcurementDocument10 pagesBrain Death & Organ ProcurementkencheenNo ratings yet
- Prioritization of ProblemDocument2 pagesPrioritization of ProblemGenette Sy SolisNo ratings yet
- Bioteque PessaryDocument2 pagesBioteque PessaryAngelo PlataNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document11 pagesQuiz 2Ericka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Philanthrocapitalism, Past and Present - HealthDocument27 pagesPhilanthrocapitalism, Past and Present - HealthsanjnuNo ratings yet
- Patenting in BiotechnologyDocument6 pagesPatenting in BiotechnologyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet