Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cervix Information
Cervix Information
Uploaded by
Edrea Aquino MendezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cervix Information
Cervix Information
Uploaded by
Edrea Aquino MendezCopyright:
Available Formats
The cervix is the lower portion of the uterus, an
organ of the female reproductive tract. It connects
the vagina with the main body of the uterus,
acting as a gateway between them.
Anatomically and histologically, the cervix
is distinct from the uterus, and hence we
consider it as a separate anatomical structure.
In this article, we shall look at the structure of the
cervix, its vasculature, innervation, functions, and
any clinical relevance.
Anatomical Structure Clinical Relevance: Disorders of the Cervix
The cervix is composed of two regions;
the ectocervix and the endocervical canal. Cervicitis
The ectocervix is the portion of the cervix
that projects into the vagina. It is lined by Cervicitis is chronic inflammation and infection
stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium. of the cervix, most commonly caused
The opening in the ectocervix, the external os, by Chlamydia
marks the transition from the ectocervix to the trachomatis or Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
endocervical canal.
The endocervical canal (or endocervix) is the
It is usually asymptomatic although pelvic pain,
more proximal, and ‘inner’ part of the cervix. It is vaginal discharge, postcoital bleeding and
lined by a mucus-secreting simple columnar
dyspareunia may be present. Complications of
epithelium. The endocervical canal ends, and the cervicitis include PID, whilst the potential
uterine cavity begins, at a narrowing called blockage of mucus ducts and cyst formation
the internal os. increases the risk of infertility by increasing the
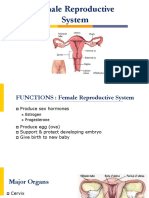
Functions hostility of the environment for sperm.
The cervix performs two main functions:
It facilitates the passage of sperm into the
uterine cavity. This is achieved via dilation of the Cervical Cancer
external and internal os.
Maintains sterility of the upper female Cancer of the cervix is the most common cancer
reproductive tract. The cervix, and all structures affecting the female reproductive tract. There are
superior to it, are sterile. This ultimately protects two main classifications of cervical cancer:
the uterine cavity and the upper genital tract by
preventing bacterial invasion. This environment is Squamous cell carcinoma – cancer of the
maintained by the frequent shedding of the epithelial lining of the ectocervix.
endometrium, thick cervical mucus and a narrow Adenocarcinoma – cancer of the glands found
external os. within the lining of the cervix.
Vascular Supply and Lymphatics
The blood supply to the uterus is via the uterine Infection of the female genitalia with human
artery. Venous drainage is via a plexus in the papilloma virus (HPV), is widely known as the
broad ligament that drains into the uterine cause of the majority of cervical cancers. Latest
veins. vaccinations against cervical cancer are, in
Lymphatic drainage of the uterus is via the iliac, essence, a vaccination against HPV.
sacral, aortic and inguinal lymph nodes.
of your menstrual cycle. At the point of greatest
fertility, the cervix produces a good deal of clear
mucus which helps to promote pregnancy.
During pregnancy, the mucus produced by the
cervix thickens to create a cervical "plug." This
shields the growing embryo from infection. The
cervical plug thins and is expelled when birth is
imminent.
The cervix is the lower third portion of the uterus.
It forms the neck of the uterus and opens into During menstruation, the cervix opens a small
the vagina (which is also called the endocervical amount to permit passage of menstrual flow.
canal). It is a little over an inch long, and just During pregnancy, the cervical os closes to help
about an inch wide. Made up largely of muscle keep the fetus in the uterus until birth. Another
tissue, it plays a minor role except during important function of the cervix occurs during
pregnancy or if a medical problem emerges. labor when the cervix dilates (widens), to allow
the passage of the fetus from the uterus to the
Because of its location between the uterus and vagina.2
the vagina, the cervix is rarely seen. To see
one's own cervix requires a mirror and bright Conditions and Problems
light. It is possible to feel the cervix with your
finger; if you do so you'll notice that it changes There are a number of issues that can affect the
texture over the course of your cycle. cervix. These include injury and infection
(especially during pregnancy and birth), cancer,
Anatomy genital warts, and various types of venereal
disease. The cervix can cause issues during
The narrow opening of the cervix is called pregnancy and birth, as well. For example,
the os. The cervical os allows menstrual blood to cervical insufficiency occurs when the cervix is
flow out from the vagina during menstruation. too weak to maintain a pregnancy.3
The cervix is covered by the epithelium which is Having regular Pap smears is imperative to
made of a thin layer of cells. Epithelial cells are detect early changes to the cervical cells which
either squamous or columnar (also called may lead to cervical cancer. You should know,
glandular cells). Squamous cells are flat and however, that the majority of abnormal Pap
scaly, while columnar cells appear, as indicated smears are due to inflammation or infection.
by their name, column-like.
--- (Web MD
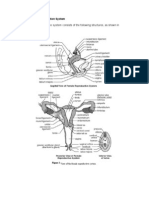
There are three parts of the cervix:1 https://www.webmd.com/women/picture-of-the-
cervix#1
1. The lowest part, which can only be seen The cervix is a cylinder-shaped neck of tissue
from inside the vagina, is called the that connects the vagina and uterus. Located at
ectocervix. The center of the ectocervix the lowermost portion of the uterus, the cervix is
can open, creating a passage between composed primarily of fibromuscular tissue.
the uterus and vagina. There are two main portions of the cervix:
2. The endocervix, also called the
endocervical canal, is the passage
between ectocervix and the uterus. The part of the cervix that can be seen
3. The point at which the endocervix and from inside the vagina during a
ectocervix meet is called the gynecologic examination is known as
transformation zone. the ectocervix. An opening in the center
of the ectocervix, known as the external
os, opens to allow passage between the
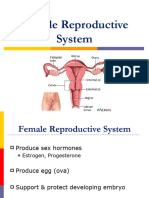
Functions
uterus and vagina.
The cervix produces cervical mucus. Cervical
mucus changes in consistency over the course
The endocervix, or endocervical canal, the internal os. The endocervical canal
is a tunnel through the cervix, from the transports sperm into the uterine cavity, allows
external os into the uterus. the escape of blood from the uterus
during menstruation, and supplies mucus (a
The overlapping border between the endocervix thick lubricating protein) to the female
and ectocervix is called the transformation zone. reproductive tract. During childbirth the canal is
greatly stretched
The cervix produces cervical mucus that
changes in consistency during the menstrual The endocervical canal is lined with a
cycle to prevent or promote pregnancy. moist mucous membrane. Cells within this tissue
layer secrete fluids and project minute hairlike
During childbirth, the cervix dilates widely to
structures called cilia that help to move sperm
allow the baby to pass through. During
through the canal. The fluids given off consist
menstruation, the cervix opens a small amount
mainly of water, sugars, starches, and proteins.
to permit passage of menstrual flow.
During ovulation (when the ovaries release an
egg) the mucous secretions are plentiful and
watery; before and after ovulation the secretions
(health line) are thick and relatively scant. The mucus is
arranged in a meshlike pattern of filaments and
The cervix of the uterus, also known as the spaces. During ovulation the openings in the
cervix or uterine cervix, attaches the vagina to meshwork of filaments become larger so that
the uterus. sperm may freely pass through. Lysozyme, also
It is approximately four centimeters long, present in cervical mucus, is an enzyme that
approximately half of which extends into the helps to destroy certain types of bacteria and
vaginal canal; however, the length of the cervix acts as a defense against infections.
can be affected by age and childbirth, along with Covering the mucous membrane is a thick layer
individual (genetic) variations. of collagen and elastic fibres. There is also some
The uterine cervix produces a mucus that aids in muscle tissue, but the quantity is considerably
carrying sperm from the vagina to the uterus, less than in the rest of the uterus. The cervix is
where it can fertilize an egg if the woman is densely fibrous and, consequently, more rigid
ovulating. When the woman isn't ovulating, the than the other uterine tissue.
cervical mucus thickens and serves as a barrier During pregnancy the cervix is the only part of
to keep sperm out of the uterus. the uterus that does not expand to house the
During childbirth, the cervix thins out and developing child; the mucus inside the
eventually dilates (expands) to 10 centimeters to endocervical canal becomes very thick at this
allow the baby to pass through the birth canal. time and acts as a plug that helps to seal off the
Once the baby is born and the placenta is rest of the uterus from infection. Shortly before
expelled, the cervix begins to thicken and close. childbirth, the mucus thins, and the cervical walls
Cancer sometimes develops in the cervix of relax to permit delivery.
uterus. Dysplasia is a fully treatable pre-cancer
condition of the cervix diagnosed via a pap
smear. If dysplasia isn't diagnosed and treated,
cervical cancer, which is usually caused by the
human papilloma virus, begins to spread.
-
Cervix, lowest region of the uterus; it attaches
the uterus to the vagina and provides a passage
between the vaginal cavity and the uterine
cavity. The cervix, only about 4 centimetres (1.6
inches) long, projects about 2 centimetres into
the upper vaginal cavity. The cervical opening
into the vagina is called the external os; the
cavity running the length of the cervix is
the endocervical canal; the opening of the
endocervical canal into the uterine cavity,
You might also like
- FC OB July 2021Document13 pagesFC OB July 2021Johnmer Avelino100% (1)
- Complications With The Power of LaborDocument8 pagesComplications With The Power of LaborEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Review of Anaphy 109Document3 pagesReview of Anaphy 109Erika BacarroNo ratings yet
- Caesarean Section: Advanced Maternal and Child Health Nursing NSC504Document60 pagesCaesarean Section: Advanced Maternal and Child Health Nursing NSC504tsega tilahunNo ratings yet
- A Case Study About Cervical PolypsDocument8 pagesA Case Study About Cervical PolypsJisel-Apple BulanNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument75 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemProf Lina Ramli67% (3)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiologybadgurl08No ratings yet
- Uterus AnatomyDocument7 pagesUterus AnatomyJoseph RadislaoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKristine Alejandro100% (1)
- Operative ReviewCSDocument8 pagesOperative ReviewCSmarkie917No ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesReview of Anatomy and PhysiologyRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Final Module in M101 1Document54 pagesFinal Module in M101 1J. TSNo ratings yet
- Final Module in M101Document56 pagesFinal Module in M101J. TSNo ratings yet
- 41 Female Reproductive AnatomyDocument14 pages41 Female Reproductive Anatomyruaa firasNo ratings yet
- Ana Physio ReprodDocument8 pagesAna Physio ReprodTeodoro Lemuel Ramos Gaela100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyAlano S. LimgasNo ratings yet
- Cervix: 1 StructureDocument9 pagesCervix: 1 StructurenathanNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument60 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemjeenath justin dossNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Functions of The UterusDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Functions of The UterusAnthony jesusNo ratings yet
- Session 4 Lecture 1 Part 1Document25 pagesSession 4 Lecture 1 Part 1avin xsroNo ratings yet
- Particularitatile Aparatului Reproducator La IapaDocument6 pagesParticularitatile Aparatului Reproducator La IapaGiorgiana DanielaNo ratings yet
- Part, Function and Process of Reproduction SystemDocument31 pagesPart, Function and Process of Reproduction SystemSavia NaldiNo ratings yet
- Ana 5.3 Female Reproductive System (Gross) - QuijanoDocument10 pagesAna 5.3 Female Reproductive System (Gross) - Quijanolovelots1234No ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument78 pagesREPRODUCTIONglaizaNo ratings yet
- Reporting EPDocument48 pagesReporting EPMaine YukiNo ratings yet
- Femalereproductivesystem 120329125448 Phpapp02Document18 pagesFemalereproductivesystem 120329125448 Phpapp02Crapster GamingNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyAironne ManguilimotanNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Organ in MammalsDocument11 pagesReproductive Organ in MammalstajudeenabdullahaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemjonaNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproduction SystemDocument10 pagesThe Female Reproduction Systemrafaelvillacorta100% (1)
- Case Study About Cervical CancerDocument11 pagesCase Study About Cervical CancerJisel-Apple Bulan100% (1)
- Reproductive System For ReviewerDocument50 pagesReproductive System For Reviewerzyrle (zayrieeo)No ratings yet
- 4NUR-8.1 Case 4 - Gynecologic Nursing (Written Report)Document30 pages4NUR-8.1 Case 4 - Gynecologic Nursing (Written Report)lhedavenNo ratings yet
- Case Study Cephal-TransDocument7 pagesCase Study Cephal-TransAldjen SetiasNo ratings yet
- About VaginaDocument13 pagesAbout VaginaRazend Muhd0% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology Reproductive SystemDocument91 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Reproductive SystemApril BenaventeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Document49 pagesAnatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Humraz100% (1)
- Mayo MaDocument23 pagesMayo Madextroid12No ratings yet
- Reporductive SystemDocument31 pagesReporductive SystemEmma Joel OtaiNo ratings yet
- Female RSystemDocument71 pagesFemale RSystemicliftonguytonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Embryology and Uterine AnomailesDocument45 pagesAnatomy, Embryology and Uterine AnomailesMesk BanatNo ratings yet
- Case Study-Cesarean BirthDocument5 pagesCase Study-Cesarean BirthDada Malicsi Landicho100% (2)
- UterusDocument3 pagesUterusBernadette FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Cervix AnatomyDocument3 pagesCervix AnatomyEunice FernandezNo ratings yet
- 178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemDocument25 pages178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemJUVY ANN PATOSANo ratings yet
- REWIEW OF FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NewDocument49 pagesREWIEW OF FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM NewnamitaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Female Reproductive SystemDocument54 pagesPresentation On: Female Reproductive SystemLetsShop BbsrNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument6 pagesBIOLOGYCLANSIE BUXTON CHIKUMBENo ratings yet
- Operative Review TAHBSODocument22 pagesOperative Review TAHBSOGinger Enireht HTaibNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyLouie Kem Anthony BabaranNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Reproductive SystemDocument93 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Reproductive SystemMelizza Fajardo BañanoNo ratings yet
- Student Name: ALI HASSAN RAZA STUDENT I D: 2018304027Document6 pagesStudent Name: ALI HASSAN RAZA STUDENT I D: 2018304027Sayed AsifNo ratings yet
- Case Study 7Document29 pagesCase Study 7Hanniel MontecalboNo ratings yet
- Female RSsystem 2Document90 pagesFemale RSsystem 2icliftonguytonNo ratings yet
- ANA 222 Female Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesANA 222 Female Reproductive SystemprincessmakklisNo ratings yet
- Female Genital Tract and The Pelvic BonesDocument37 pagesFemale Genital Tract and The Pelvic Bonesعبد الله الحربيNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy of Female Reproductive SystemseongeokNo ratings yet
- Discussion of The Diseases ProcessDocument4 pagesDiscussion of The Diseases ProcessMica CoveyNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System: Edward Vallejo Ganggang, RN, LPTDocument26 pagesFemale Reproductive System: Edward Vallejo Ganggang, RN, LPTJosephine AcioNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: An account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes, and the method of preventing itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: An account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes, and the method of preventing itNo ratings yet
- MCN MnemonicDocument3 pagesMCN MnemonicEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- LinksDocument1 pageLinksEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Four Rights in Food SafetyDocument1 pageFour Rights in Food SafetyEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- The Four Stages of LaborDocument12 pagesThe Four Stages of LaborEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Volleyball CourtDocument1 pageVolleyball CourtEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesSkeletal SystemEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Grief, Stages of Grief and Grief ProcessDocument6 pagesGrief, Stages of Grief and Grief ProcessEdrea Aquino Mendez100% (2)
- An Example of Resource AllocationDocument16 pagesAn Example of Resource AllocationEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Nightingale Became A Figure of Public Admiration Come To Be Viewed As An Honorable VocationDocument3 pagesNightingale Became A Figure of Public Admiration Come To Be Viewed As An Honorable VocationEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: CompositionDocument3 pagesUrinary System: CompositionEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Anaphy LecDocument2 pagesAnaphy LecEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Ramon BagatsingDocument7 pagesRamon BagatsingEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- At A Glance: The Philippine Health Care System: MedicinesDocument15 pagesAt A Glance: The Philippine Health Care System: MedicinesEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Arnis InfoDocument34 pagesArnis InfoEdrea Aquino MendezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: MDH Ob/GyneDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan: MDH Ob/GyneTrisha Dianne RaquenioNo ratings yet
- Tosoh Series 2147Document3 pagesTosoh Series 2147ShahinNo ratings yet
- Induction of LabourDocument62 pagesInduction of LabourSam christenNo ratings yet
- Uterine InvolutionDocument19 pagesUterine InvolutionvetlakshmiNo ratings yet
- Case Report Iufd - RashifDocument32 pagesCase Report Iufd - RashifM Nur MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Act, 2021Document5 pagesMedical Termination of Pregnancy (Amendment) Act, 2021Hrishav Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- 534-Article Text-925-1-10-20190304 PDFDocument5 pages534-Article Text-925-1-10-20190304 PDFAsghar KhanNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Breastfeeding For Better Health Outcomes The Way ForwardDocument4 pagesOptimizing Breastfeeding For Better Health Outcomes The Way ForwardEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Rle mooore-2-Week-2-Packet-2Document12 pagesRle mooore-2-Week-2-Packet-2Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- 2019 Bookmatter BlausteinSPathologyOfTheFemaleDocument40 pages2019 Bookmatter BlausteinSPathologyOfTheFemaleKazuto Kath TorresNo ratings yet
- On Nursing Responsibilities of Drugs in ObstetricsDocument117 pagesOn Nursing Responsibilities of Drugs in ObstetricsSanjita Kumari PanditNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Utilisation of Antenatal Care Services Among Pregnant Women Attending Kitagata Hospital, Sheema District UgandaDocument8 pagesFactors Affecting Utilisation of Antenatal Care Services Among Pregnant Women Attending Kitagata Hospital, Sheema District UgandaKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Ebook Emery and Rimoins Principles and Practice of Medical Genetics and Genomics Perinatal and Reproductive Genetics PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument68 pagesEbook Emery and Rimoins Principles and Practice of Medical Genetics and Genomics Perinatal and Reproductive Genetics PDF Full Chapter PDFwilliam.nugent910100% (34)
- Materi WS EWS 2018 - Dr. Dedi - PEWS MEWS OBSEWSDocument59 pagesMateri WS EWS 2018 - Dr. Dedi - PEWS MEWS OBSEWSIndrati TRNo ratings yet
- MCN Doc PacabisDocument18 pagesMCN Doc PacabisSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- In Defense of AbortionDocument4 pagesIn Defense of Abortiondaniel maingiNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Child Marriage: Presented By: Class: X'BDocument17 pagesPresentation On Child Marriage: Presented By: Class: X'BAkash Kumar100% (1)
- NUR2460L Teaching PlanDocument4 pagesNUR2460L Teaching PlanCherie L. MilburnNo ratings yet
- Met Coff 1994Document17 pagesMet Coff 1994ShamNo ratings yet
- Lange Qa Mammography Examination 5Th Edition Olive Peart Full ChapterDocument47 pagesLange Qa Mammography Examination 5Th Edition Olive Peart Full Chapterjennifer.miller203100% (7)
- PubLSIS II Survey Finding Report June 2018Document620 pagesPubLSIS II Survey Finding Report June 2018Mao udangNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument95 pagesReproductionSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- 6i. Male Reproduction - OnPRC Module 2-Student HandoutDocument12 pages6i. Male Reproduction - OnPRC Module 2-Student HandoutAkash ShawNo ratings yet
- Embryology of HeartDocument6 pagesEmbryology of HeartWidelmark FarrelNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Scientific Research: AnesthesiologyDocument2 pagesInternational Journal of Scientific Research: AnesthesiologyALfuNo ratings yet
- 2 Drug Study - PanganadamanDocument5 pages2 Drug Study - PanganadamanNornisah H. PangandamanNo ratings yet
- Control of The Estrous Cycle in Guinea-Pig (Cavia Porcellus)Document6 pagesControl of The Estrous Cycle in Guinea-Pig (Cavia Porcellus)EveAriNo ratings yet
- Case Summary FamilyMedicine30 27-YDocument8 pagesCase Summary FamilyMedicine30 27-YAndrea Kristin OrigenesNo ratings yet
- Puerperal PyrexiaDocument20 pagesPuerperal Pyrexiaهلا اكرم عقل طميزهNo ratings yet