Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial 2
Tutorial 2
Uploaded by
Kishore KumarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial 2
Tutorial 2
Uploaded by
Kishore KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
PYL 114
TUTORIAL SHEET – 2
11/01/2020
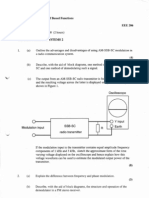
1. (a) Give a schematic drawing of the X-ray spectrum emitted from a molybdenum (Mo)
target and identify on it with appropriate symbols all characteristic wavelengths.
(b) Explain the origin of all characteristic “λ’s” on a schematic drawing and an energy
diagram respectively.
(c) Assuming the X-ray unit is operated with an accelerating voltage of 40 kV, what is the
shortest X-ray wavelength (λ) obtained from it?
2. An X-ray generator operates with a deficient power supply which can only deliver an
accelerating voltage of 6.8 kV.
(a) Will you be able to obtain CuKα radiation (λ = 1.542 Å) from this generator?
(b) What is the shortest λ of X-radiation obtainable?
(c) Assuming the shortest λ obtainable through Bremsstrahlung (λSWL) were 1.380 Å,
which is the same wavelength as that of CuKβ, could CuKα radiation be obtained under
these conditions?
3. What is the smallest acceleration potential that must be applied to an X-ray generator so as
to still achieve diffraction in solid potassium (at room temperature)?
4. An X-ray generator with an unknown target material yields Kα radiation with which the
smallest diffraction peak (2θ1) in tantalum (Ta) is found to be at 58.7°. What is the target
material in the X-ray generator?
5. Do you expect the first diffraction peak in Pd to be shifted to a larger or smaller θ value
(operating with Kα, monochromatic X-rays) if you change the target in an X-ray tube from
Cu to Mo? Explain.
You might also like
- Anne Frank's Diary - The Graphic - Anne FrankDocument155 pagesAnne Frank's Diary - The Graphic - Anne FrankKishore Kumar100% (4)
- MIT5 111F14 Lec04SolnDocument2 pagesMIT5 111F14 Lec04SolnFaiza Jan IftikharNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic ExercisesDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic ExercisesDineo Pampier100% (2)
- MPS201 X Ray - Production Draft - NotesDocument8 pagesMPS201 X Ray - Production Draft - NotesPatrick SibandaNo ratings yet
- AL Essays (Radioactivity, Light & Electrons) - 1Document7 pagesAL Essays (Radioactivity, Light & Electrons) - 1umpc1248No ratings yet
- 1982 YearDocument7 pages1982 YearTamizh E STNo ratings yet
- RF Nov2016Document2 pagesRF Nov2016rameshdurairajNo ratings yet
- 27. ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND X-RAYSDocument5 pages27. ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND X-RAYSShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- ModernPhysics HomeWorkSheet-2Document1 pageModernPhysics HomeWorkSheet-2Rishi KumarNo ratings yet
- 256d98b22018 MID SEMDocument2 pages256d98b22018 MID SEMAnkit BishtNo ratings yet
- r05220405 Analog CommunicationsDocument7 pagesr05220405 Analog CommunicationsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Questions 2015-2016 CorrectedDocument3 pagesQuestions 2015-2016 CorrectedVictor ImehNo ratings yet
- (681533) 2. Particles and Waves RevisionDocument7 pages(681533) 2. Particles and Waves RevisionTriple M Guider NephaweNo ratings yet
- Ect305 Analog and Digital Communication, December 2022Document3 pagesEct305 Analog and Digital Communication, December 2022Dinil DhananjayanNo ratings yet
- L-4/T-2/EEE Date: 18/12/2012: Section Four ThreeDocument56 pagesL-4/T-2/EEE Date: 18/12/2012: Section Four ThreeALI-EMAM- AL-BADINo ratings yet
- Kuk Analog Communication Paper 2022Document3 pagesKuk Analog Communication Paper 2022ankurNo ratings yet
- Section C Physics Paper 1 Revision Questions For A LevelDocument24 pagesSection C Physics Paper 1 Revision Questions For A LevelzakNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological Universitykn patelNo ratings yet
- Minimum Learning Material (XII)Document6 pagesMinimum Learning Material (XII)Abhi VarnaNo ratings yet
- Stucor QP Ec8701Document6 pagesStucor QP Ec8701diamond puppyNo ratings yet
- EC403 Microwave & Radar Engineering, May 2019Document2 pagesEC403 Microwave & Radar Engineering, May 2019Vishnu prasad SNo ratings yet
- 15A04501 Antennas and Wave Propagation - QP - Dec 2017 PDFDocument2 pages15A04501 Antennas and Wave Propagation - QP - Dec 2017 PDFPallavi ChNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem PHY Assignment Que 2023 24.Document4 pages2nd Sem PHY Assignment Que 2023 24.Sai AdarshNo ratings yet
- Hpha042 Exercise (1st)Document3 pagesHpha042 Exercise (1st)piletjo phaladiNo ratings yet
- (00000000 00000000) Final ANSWER OPTO-ELECTRONICS ECE 532 Spring 2016 PDFDocument16 pages(00000000 00000000) Final ANSWER OPTO-ELECTRONICS ECE 532 Spring 2016 PDFOmar Abdelrehim Ibrahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ec7105-Microwave EngineeringDocument9 pagesEc7105-Microwave EngineeringKushal GellaNo ratings yet
- School of Physics & Materials Science: Thapar University, PatialaDocument1 pageSchool of Physics & Materials Science: Thapar University, PatialaPRADYUMAN PRATAP CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Btech 2 Sem Engineering Physics Kas201t 2022Document2 pagesBtech 2 Sem Engineering Physics Kas201t 2022Neelam SinghNo ratings yet
- PhotonsDocument56 pagesPhotonsbob jizzleNo ratings yet
- NTDocument3 pagesNTlkNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1: Swarnandhra College of Engineering & Technology Deparment of Ece Mid-1 Question Bank For AwpDocument2 pagesUNIT-1: Swarnandhra College of Engineering & Technology Deparment of Ece Mid-1 Question Bank For Awpgirija12No ratings yet
- PBL (Chapter 2) 2022Document3 pagesPBL (Chapter 2) 2022MUHAMMAD ALIF BIN MOHD ROAIMNo ratings yet
- Physics: Rapid Crash CourseDocument12 pagesPhysics: Rapid Crash CourseHudsun HornetNo ratings yet
- Phy 1071 - Phy-1071 - Engineering Physics-2Document2 pagesPhy 1071 - Phy-1071 - Engineering Physics-2Challa SaiNo ratings yet
- S.S.Dav Public School, Khunti Sub:-Physics Second Mock Test Fm:-70Document4 pagesS.S.Dav Public School, Khunti Sub:-Physics Second Mock Test Fm:-70sharique alamNo ratings yet
- E3-282 Basics of Semiconductor Devices & Technology Assignment 1: Quantum MechanicsDocument12 pagesE3-282 Basics of Semiconductor Devices & Technology Assignment 1: Quantum MechanicsWiluam Rutherford Bond0% (1)
- Lesson 1 X Rays and DiffractionDocument44 pagesLesson 1 X Rays and Diffractioniordache100% (1)
- 9Document4 pages9Bùi Hữu Đức0% (1)
- Eee206 2000Document2 pagesEee206 2000api-3819098No ratings yet
- Parul Institute Engineering & Technology Electronics and Communication) Class: M. E 2 SemecDocument4 pagesParul Institute Engineering & Technology Electronics and Communication) Class: M. E 2 SemecDonika MarkandeNo ratings yet
- Assignment PH 101 SCDocument3 pagesAssignment PH 101 SCAbhishekBhowmickNo ratings yet
- Characteristic Xraysof CopperDocument4 pagesCharacteristic Xraysof CopperAmmar QasimNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment 12-07-2020 - PDFDocument2 pagesHomework Assignment 12-07-2020 - PDFUtkarsh Bhauji Kannake ep19b014No ratings yet
- Final Exam Spectroscopy 2022 23 RepeatDocument17 pagesFinal Exam Spectroscopy 2022 23 RepeatIris BenardeteNo ratings yet
- QP Ec8701Document6 pagesQP Ec8701sruthiga kNo ratings yet
- 2014 光電子學Document2 pages2014 光電子學廖宇庭No ratings yet
- 107 B.tech Engg - PhysicsDocument5 pages107 B.tech Engg - Physicsrhq4w5hgm7No ratings yet
- UPH004Document2 pagesUPH004tjainbe23No ratings yet
- Quest PDFDocument2 pagesQuest PDFpramilaNo ratings yet
- Uec401 2017Document2 pagesUec401 2017g SinghNo ratings yet
- FON Question BankDocument1 pageFON Question BankLohit PNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Photoelectric 91-10Document12 pages3.3 Photoelectric 91-10Murray PhysicsNo ratings yet
- The People's University of Bangladesh Summer 2016 - Final Examination Optoelectronics ETE - 313Document1 pageThe People's University of Bangladesh Summer 2016 - Final Examination Optoelectronics ETE - 313mahmoodNo ratings yet
- Ete 313 PDFDocument1 pageEte 313 PDFmahmoodNo ratings yet
- Tarea Moderna 2dp Sol.Document2 pagesTarea Moderna 2dp Sol.Salma PerezNo ratings yet
- MIT3 091SCF09 hw3Document3 pagesMIT3 091SCF09 hw3Jesús MartínezNo ratings yet
- (PHT100) Phy A, Dec 2020Document3 pages(PHT100) Phy A, Dec 2020adithyan sreeniNo ratings yet
- Ac 1Document8 pagesAc 1andhracollegesNo ratings yet
- PHY pp2 QNS 2021Document11 pagesPHY pp2 QNS 2021Kevin KiplangatNo ratings yet
- X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesFrom EverandX-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation: Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandAn Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation: Techniques and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Assignment Week6Document2 pagesAssignment Week6Kishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment Week5Document2 pagesAssignment Week5Kishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6 AnswersDocument4 pagesAssignment 6 AnswersKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 AnswersDocument6 pagesAssignment 2 AnswersKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 AnswersDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 AnswersKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 AnswersDocument2 pagesAssignment 4 AnswersKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Courses OfferedDocument43 pagesCourses OfferedKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Waveguidance: TIR at Two Parallel InterfacesDocument2 pagesWaveguidance: TIR at Two Parallel InterfacesKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- 8 Essential Tips To Nourish Your Meditation Practice: 1. Practice Daily, Even If For A Short TimeDocument3 pages8 Essential Tips To Nourish Your Meditation Practice: 1. Practice Daily, Even If For A Short TimeKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Em 1Document34 pagesEm 1Kishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Undergraduate Core (UC) Undergraduate Elective (UE) Category Credits Category CreditsDocument5 pagesUndergraduate Core (UC) Undergraduate Elective (UE) Category Credits Category CreditsKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Edge DetectionDocument7 pagesAdvanced Edge DetectionKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction Electrodynamics Griffiths SolutionsDocument2 pagesIntroduction Electrodynamics Griffiths SolutionsKishore Kumar50% (4)
- PH 1180854Document5 pagesPH 1180854Kishore KumarNo ratings yet