Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Document Music Lesson 5
Document Music Lesson 5
Uploaded by
Mhay CodnatCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- First 5 Note Chart (Tenor Sax)Document13 pagesFirst 5 Note Chart (Tenor Sax)Jeremy Williamson100% (1)
- Southeast Asian MusicDocument5 pagesSoutheast Asian MusicPRINTDESK by Dan86% (22)
- The Stradivari Viola D'amoreDocument14 pagesThe Stradivari Viola D'amoreponbohacopNo ratings yet
- The Harmonium Handbook: Owning, Playing, and Maintaining the Devotional Instrument of IndiaFrom EverandThe Harmonium Handbook: Owning, Playing, and Maintaining the Devotional Instrument of IndiaNo ratings yet
- Southeast Asian InstrumentDocument11 pagesSoutheast Asian Instrumentmuak mijarNo ratings yet
- Music of IndiaDocument7 pagesMusic of IndiaPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- MacoDocument5 pagesMacoAytona Villanueva PearlNo ratings yet
- AsiaDocument4 pagesAsiaGener LyllwynNo ratings yet
- Musical Instruments of ThailandDocument19 pagesMusical Instruments of Thailandgabrielluis08100% (8)
- Mga Instrumento Sa South East AsiaDocument11 pagesMga Instrumento Sa South East AsiaJuphilNo ratings yet
- Southeast Asian Music Grade 8Document62 pagesSoutheast Asian Music Grade 8Aina Charisse DizonNo ratings yet
- Thai InstrumentDocument13 pagesThai InstrumentJannet De Lara VergeldeDios100% (1)
- Music in Southeast Asian TheaterDocument38 pagesMusic in Southeast Asian TheaterKali GraphyNo ratings yet
- Percussion-Dominated Ensembles & String-Dominated EnsemblesDocument17 pagesPercussion-Dominated Ensembles & String-Dominated EnsemblesEdsil Jess AdalidNo ratings yet
- Gamelan: PasindhènDocument5 pagesGamelan: PasindhènMhai MabantaNo ratings yet
- q1l2 Southeast AsiaDocument76 pagesq1l2 Southeast AsiaBryan FidelNo ratings yet
- Edit-The Music of ThailandDocument50 pagesEdit-The Music of ThailandAthit ThongkumNo ratings yet
- Super HirapDocument9 pagesSuper HirapJessica Marie Borromeo DHumNo ratings yet
- Traditional Thai Musical InstrumentsDocument4 pagesTraditional Thai Musical InstrumentsJame HernaneNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument5 pagesREVIEWERaster venyzNo ratings yet
- Musical Instruments of ThailandDocument3 pagesMusical Instruments of ThailandShaira Mae CortezNo ratings yet
- Music of ThailandDocument21 pagesMusic of ThailandAmiel MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Myanmar Music SortDocument4 pagesMyanmar Music SortEjay BendoNo ratings yet
- East-Asian-Music 8 LC 2Document43 pagesEast-Asian-Music 8 LC 2Mark CantubaNo ratings yet
- Traditional Burmese MusicDocument8 pagesTraditional Burmese MusicAlvin Agonoy NovencidoNo ratings yet
- Thailand Ensemble: KHR UEA NG SAI ENS EMB LEDocument6 pagesThailand Ensemble: KHR UEA NG SAI ENS EMB LERizza Loren AcebedoNo ratings yet
- MUSIC G8 Southeast Asia Music PART 1Document56 pagesMUSIC G8 Southeast Asia Music PART 1christinaNo ratings yet
- Pin PeatDocument5 pagesPin PeatCelesteCelestePataoNo ratings yet
- The Music of Thailand PDFDocument30 pagesThe Music of Thailand PDFJanice C. Sabagay100% (3)
- The Instruments - CambodiaDocument12 pagesThe Instruments - CambodiaNeil Retiza Abay100% (1)
- MAPEHDocument11 pagesMAPEHPatrick CenaNo ratings yet
- MusicDocument20 pagesMusicJaspreet Singh WaliaNo ratings yet
- Music of CambodiaDocument7 pagesMusic of CambodiaPaulineNo ratings yet
- Desc in Music EheDocument6 pagesDesc in Music EheJayson Red SmithsonNo ratings yet
- Traditional Cambodian Musical InstrumentsDocument12 pagesTraditional Cambodian Musical InstrumentsDelve Jane C. Wenceslao100% (1)
- Korean Musical InstrumentsDocument5 pagesKorean Musical InstrumentsAndriaKimNo ratings yet
- Japan InstrumentDocument2 pagesJapan InstrumentRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Art Integration LearningDocument15 pagesArt Integration Learningkhushi guptaNo ratings yet
- MUSIC AND ARTS REVIEWER 2nd QUARTER GRADE 8Document6 pagesMUSIC AND ARTS REVIEWER 2nd QUARTER GRADE 8Grace Anne C. MercadoNo ratings yet
- TAMPURADocument5 pagesTAMPURAAbril De Gracia VeranoNo ratings yet
- Jexter MAPEH (AutoRecovered)Document9 pagesJexter MAPEH (AutoRecovered)Carlo Santos RabanalNo ratings yet
- Music of ThailandDocument44 pagesMusic of ThailandJacob BelmonteNo ratings yet
- Secondary Music 8 Q2 Week3Document18 pagesSecondary Music 8 Q2 Week3Nelson Jeff Jr. MagpaliNo ratings yet
- Korean Musical InstrumentsDocument5 pagesKorean Musical InstrumentsAndriaKim100% (1)
- Mr. Carlo Justino J. Luna: Malabanias Integrated SchoolDocument46 pagesMr. Carlo Justino J. Luna: Malabanias Integrated SchoolNeølie Abello LatúrnasNo ratings yet
- East Asian MusicDocument69 pagesEast Asian MusicClaire Montero-MasutaNo ratings yet
- Music of Indonesia 2Document2 pagesMusic of Indonesia 2Ferchris Stephen AdlawanNo ratings yet
- Southeast AsiaDocument48 pagesSoutheast AsiaLiebe Ruiz TorresNo ratings yet
- Japanese Musical InstrumentsDocument3 pagesJapanese Musical InstrumentsShanie LouNo ratings yet
- MusicDocument25 pagesMusicMjhayeNo ratings yet
- Asia Musical InstrumentsDocument11 pagesAsia Musical InstrumentsArlene NavarroNo ratings yet
- East Asian MusicDocument60 pagesEast Asian MusicDIANNE CERVANTESNo ratings yet
- Musical Instruments of India: Mary Grace Ann Valencia 3-St. Vincent de PaulDocument5 pagesMusical Instruments of India: Mary Grace Ann Valencia 3-St. Vincent de Pauljoyceannm_valenciaNo ratings yet
- Thai Music PPDocument66 pagesThai Music PPHazel Clemente CarreonNo ratings yet
- 10 Indian Plucked String InstrumentsDocument13 pages10 Indian Plucked String InstrumentsIan De La Cruz100% (1)
- Japanese and Korean Musical InstrumentDocument14 pagesJapanese and Korean Musical InstrumentNoah CofinoNo ratings yet
- 213213213213213Document3 pages213213213213213Jock ItchNo ratings yet
- CambodiaDocument5 pagesCambodiaNiel S. DefensorNo ratings yet
- MUSIC LET Asian MusicDocument13 pagesMUSIC LET Asian MusicEleomie AlipoonNo ratings yet
- Thailand Music Grade 8Document36 pagesThailand Music Grade 8Crystal RelovaNo ratings yet
- Asian MusicDocument18 pagesAsian MusicLiebe Ruiz TorresNo ratings yet
- Philippine Bamboo Instruments: AerophonesDocument13 pagesPhilippine Bamboo Instruments: AerophonesDeneb ChuaNo ratings yet
- One Common VoiceDocument20 pagesOne Common VoiceAngielyn AbardoNo ratings yet
- Gollum39s Song Sheet Music FluteDocument3 pagesGollum39s Song Sheet Music FluteEdenNo ratings yet
- Violin - Notation: Products News Music Community Company ManualsDocument1 pageViolin - Notation: Products News Music Community Company ManualsTóth ViktorNo ratings yet
- Alto Recorder Fingering Chart: Musical Instrument GuideDocument1 pageAlto Recorder Fingering Chart: Musical Instrument GuideMusic DNo ratings yet
- Great Is Thy FaithfulnessDocument1 pageGreat Is Thy FaithfulnessAaron Elias PuzenikNo ratings yet
- 2510891-Edelweiss QuartetDocument2 pages2510891-Edelweiss QuartetLeanne hilpertNo ratings yet
- Amazing Grace - PoloDocument7 pagesAmazing Grace - PoloOtávioQuartierNo ratings yet
- Yamaha Tg500Document21 pagesYamaha Tg500altaminNo ratings yet
- We Dont Talk About BrunoDocument5 pagesWe Dont Talk About Brunoapi-649553832No ratings yet
- El Condor Pasa. PartiturDocument6 pagesEl Condor Pasa. PartiturОксана РетинскаяNo ratings yet
- Slide Trombone MethodsDocument4 pagesSlide Trombone MethodsShadi Ashouri100% (1)
- 2015 Fender Custom Shop Illustrated Price List PDFDocument24 pages2015 Fender Custom Shop Illustrated Price List PDFrexNo ratings yet
- Any Kind of Dead Person Sheet MusicDocument4 pagesAny Kind of Dead Person Sheet Musicindia newtonNo ratings yet
- Nearer My God To Thee Arranged For BandDocument14 pagesNearer My God To Thee Arranged For BandElmer Patagan EsplanaNo ratings yet
- Frozen - Você Quer Brincar Na NeveDocument7 pagesFrozen - Você Quer Brincar Na NeveElias NeriNo ratings yet
- Kevin Bobo - 4 Mallet ExercisesDocument7 pagesKevin Bobo - 4 Mallet ExercisesSeth DyerNo ratings yet
- IGCSE World Focus 2020 - Arabic Music - Part 1: Instruments (Copy)Document12 pagesIGCSE World Focus 2020 - Arabic Music - Part 1: Instruments (Copy)Joshua MckayNo ratings yet
- Altissimo Fingerings For Baritone SaxophoneDocument1 pageAltissimo Fingerings For Baritone SaxophoneBruno SantosNo ratings yet
- Pickup Bartolini Wiring ConductorDocument2 pagesPickup Bartolini Wiring ConductorClau gomesNo ratings yet
- Bacchus Global Series BrochureDocument12 pagesBacchus Global Series Brochurebenja330% (1)
- Moderately: (Banda de La "Casa de La Comunidad Valenciana" en Navarra)Document73 pagesModerately: (Banda de La "Casa de La Comunidad Valenciana" en Navarra)Nuno Batista100% (2)
- Angelo ConcertinaDocument4 pagesAngelo Concertina蔡偉靖100% (1)
- Yeu Xa - Vu Cat TuongDocument2 pagesYeu Xa - Vu Cat TuongTinNo ratings yet
- Some Day My Prince Will Come: Arr. by A .BykovDocument4 pagesSome Day My Prince Will Come: Arr. by A .BykovBixente BfNo ratings yet
- Korg WavestationDocument7 pagesKorg WavestationaltaminNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Free Tech Resources GuideDocument34 pagesUltimate Free Tech Resources Guideapi-298999876100% (1)
- Bellum Belgicum: (Inspired by The Novel 'Hotse Hiddes')Document18 pagesBellum Belgicum: (Inspired by The Novel 'Hotse Hiddes')Laimonas MaseviciusNo ratings yet
Document Music Lesson 5
Document Music Lesson 5
Uploaded by
Mhay CodnatOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Document Music Lesson 5
Document Music Lesson 5
Uploaded by
Mhay CodnatCopyright:
Available Formats
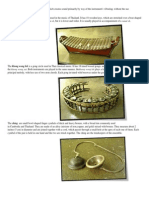
Idiophone-is any musical instrument that creates sound primarily by the
instrument as a whole vibrating—without the use of strings or membranes.
Ranat ek-is a Thai musical instrument in the percussion family that consists
of 21 wooden bars suspended by cords over a boat-shaped trough resonator
and struck by two mallets. It is used as a leading instrument in the piphat
ensemble.
Ranat lek-is a metallophone used in the classical music of Thailand. It is the
smaller of the two sizes of Thai metallophone; the larger one is called ranat
thum lek.
The ranat ek lek consists of flat metal slabs placed over a rectangular
wooden resonator. It is played with two bamboo sticks with padded ends.
The ranat ek lek is very similar to the Khmer roneat dek.
Ranat Thum- is a low pitched xylophone used in the music of Thailand. It
has 18 wooden keys, which are stretched over a boat-shaped trough
resonator. Its shape looks like a ranat ek, but it is lower and wider. It is
usually played in accompaniment of a ranat ek.
Khong wong lek-is a gong circle used in Thai classical music. It has 18
tuned bossed gongs, and is smaller and higher in pitch than the khong wong
yai. Both instruments are played in the same manner, the khong wong lek
plays a faster and more ornate variation on the principal melody, with less
use of two-note chords. Each gong is tuned with beeswax under it.
THE CHING-are finger cymbals played in Cambodian and Thai theater and
dance ensembles.[1]
THE CHAP-is a percussion instrument. It is made from bronze, as is a ching,
but is thinner.[1] The chap consists of two thin, round disks or plates with a
bulge in the center.[1] The plates are held against the hands like cymbals,
using handles made of string, passing through a hole in the center of each
plate.[1] The name comes from the sound the instrument makes when
struck directly together, "chap, chap."[1] The "timbre or tone" change when
struck at an angle. There are two kinds of chap: chap lek and chap yai. A
chap lek's diameter is 12-14 cm. A chap yai's diameter is 24-26 cm. The
Cambodian names for the two kinds of chap are chap thom (large chap) and
chap toch (small chap).
GONG WONG & GONG HUI is not information i got too.
MEMBRANOPHONE- is any musical instrument which produces sound
primarily by way of a vibrating stretched membrane. It is one of the four
main divisions of instruments in the original Hornbostel-Sachs scheme of
musical instrument classification.
THE TAPHON INSTRUMENT-is a traditional drum of Thailand. It is barrel-
shaped with two heads, and is played by the hands and fingers of both
hands, much like the more popular congas.The taphon is very similar to the
Cambodian sampho.
THE THON RAMANA- are hand drums played as a pair in Thai classical
music. It consists of two drums: the thon (โทน), a goblet drum with a
ceramic or wooden body and the rammana (รรร มะนร), a small rebana-typed
frame drum or tambourine. They are used usually in the khruang sai
ensemble. The thon gives a low pitch and the rammana gives a high pitch.
Earlier in the 20th century, the thon and rammana were sometimes played
separately.
AEROPHONE-is any musical instrument that produces sound primarily by
causing a body of air to vibrate,[1] without the use of strings or membranes,
and without the vibration of the instrument itself adding considerably to the
sound.[2] [PI &KAN ALSO AVAIL]
CHORDOPHONE-is a musical instrument that makes sound by way of a
vibrating string or strings stretched between two points. It is one of the four
main divisions of instruments in the original Hornbostel-Sachs scheme of
musical instrument classification.
SAW SAM SAI-so sam sai, also spelled saw samsai, and occasionally called
simply sam sai; literally "three stringed fiddle") is a traditional bowed string
instrument of Thailand.[1] Its body is made from a coconut that has "three
lobes".[1] The coconut is cut in half vertically and the shape is remeniscent
of the silouette of an elephant's head (from the front, not side). The coconut
bowl is covered on one end with animal skin, and it has three silk strings.[1]
Typically, the player glues a jewel onto the skin before playing, to reduce the
skin's resonance.The saw sam sai is in the saw family of Thai fiddles, which
also includes the saw u and saw duang.
CHAKEE- are a Muslim community found in the state of Gujarat in India. A
small number are also found in the city of Karachi in Pakistan.[1]The
Chakee claim to be a clan of the Soomra community of Sindh. According to
their traditions, a Soomra prince Chaneeeswar invaded Sindh with the help
of Alauddin Khalji to dethrone his younger brother Dodha. Once the Khaljis
overthrew Dodha, they expelled many of his supporters, who took refuge in
Gujarat. The local rulers in Kutch, Jamnagar and other parts of Saurashtra
gave refuge to these Soomra. A few Soomra hid with members of the Lohar
and Ghanchi community and came to be known as Chakee. They are
distributed mainly in the cities of Bhuj, Mandvi, Mundra and Moghpat in
Kutch, as well as the district of Jamnagar. The community speak the Kutchi.
In Pakistan, they are found mainly in Chakiwara area of Karachi.[1]
THREE MAIN ENSEMBLES IN THAI COURT MUSIC;
1. THE PIPHAT-is a kind of ensemble in the classical music of Thailand,
which features wind and percussion instruments. It is considered the
primary form of ensemble for the interpretation of the most sacred and
"high-class" compositions of the Thai classical repertoire, including the
Buddhist invocation entitled sathukan (Thai: สรธธ กรร) as well as the suites
called phleng rueang. It is also used to accompany traditional Thai theatrical
and dance forms including khon (Thai: โขน) (masked dance-drama), lakhon
(classical dance), and shadow puppet theater.
2.THE KHRUANG-is a musical ensemble in Thai classical music which
consists primarily of string instruments. A typical "khruang sai" ensemble
features two two-string fiddles, one high and one low ("saw duang" and
"saw ou"), a three-string zither called "jakhe", a vertical duct flute called
"khlui", hand drums, and various cymbals. Depending on the size of the
ensemble, instruments may be doubled or left out. A three-string spike
fiddle called "saw sam sai" may be added as well. The "khim" (hammered
dulcimer) has become popular and is also used in this ensemble. In the 20th
century, Western instruments such as the violin or organ have also
occasionally been integrated into "khruang sai" ensembles.
3.THE MAHORI-is a form of Cambodian and Thai classical ensemble
traditionally played in the royal courts for the purpose of secular
entertainment. It combines the xylophones and gong circles (but not the pi,
or oboe) of the piphat with the strings of the khruang sai ensemble.
Originally, the term referred only to a string ensemble, although today it
includes both string and percussion. There are three broad types of Mahori:
Mahori Khryang Lek, Mahori Khyrang Khu, and Mahori Khyrang Yai, each
differentiated by the types of instruments utilized.[1]
You might also like
- First 5 Note Chart (Tenor Sax)Document13 pagesFirst 5 Note Chart (Tenor Sax)Jeremy Williamson100% (1)
- Southeast Asian MusicDocument5 pagesSoutheast Asian MusicPRINTDESK by Dan86% (22)
- The Stradivari Viola D'amoreDocument14 pagesThe Stradivari Viola D'amoreponbohacopNo ratings yet
- The Harmonium Handbook: Owning, Playing, and Maintaining the Devotional Instrument of IndiaFrom EverandThe Harmonium Handbook: Owning, Playing, and Maintaining the Devotional Instrument of IndiaNo ratings yet
- Southeast Asian InstrumentDocument11 pagesSoutheast Asian Instrumentmuak mijarNo ratings yet
- Music of IndiaDocument7 pagesMusic of IndiaPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- MacoDocument5 pagesMacoAytona Villanueva PearlNo ratings yet
- AsiaDocument4 pagesAsiaGener LyllwynNo ratings yet
- Musical Instruments of ThailandDocument19 pagesMusical Instruments of Thailandgabrielluis08100% (8)
- Mga Instrumento Sa South East AsiaDocument11 pagesMga Instrumento Sa South East AsiaJuphilNo ratings yet
- Southeast Asian Music Grade 8Document62 pagesSoutheast Asian Music Grade 8Aina Charisse DizonNo ratings yet
- Thai InstrumentDocument13 pagesThai InstrumentJannet De Lara VergeldeDios100% (1)
- Music in Southeast Asian TheaterDocument38 pagesMusic in Southeast Asian TheaterKali GraphyNo ratings yet
- Percussion-Dominated Ensembles & String-Dominated EnsemblesDocument17 pagesPercussion-Dominated Ensembles & String-Dominated EnsemblesEdsil Jess AdalidNo ratings yet
- Gamelan: PasindhènDocument5 pagesGamelan: PasindhènMhai MabantaNo ratings yet
- q1l2 Southeast AsiaDocument76 pagesq1l2 Southeast AsiaBryan FidelNo ratings yet
- Edit-The Music of ThailandDocument50 pagesEdit-The Music of ThailandAthit ThongkumNo ratings yet
- Super HirapDocument9 pagesSuper HirapJessica Marie Borromeo DHumNo ratings yet
- Traditional Thai Musical InstrumentsDocument4 pagesTraditional Thai Musical InstrumentsJame HernaneNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument5 pagesREVIEWERaster venyzNo ratings yet
- Musical Instruments of ThailandDocument3 pagesMusical Instruments of ThailandShaira Mae CortezNo ratings yet
- Music of ThailandDocument21 pagesMusic of ThailandAmiel MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Myanmar Music SortDocument4 pagesMyanmar Music SortEjay BendoNo ratings yet
- East-Asian-Music 8 LC 2Document43 pagesEast-Asian-Music 8 LC 2Mark CantubaNo ratings yet
- Traditional Burmese MusicDocument8 pagesTraditional Burmese MusicAlvin Agonoy NovencidoNo ratings yet
- Thailand Ensemble: KHR UEA NG SAI ENS EMB LEDocument6 pagesThailand Ensemble: KHR UEA NG SAI ENS EMB LERizza Loren AcebedoNo ratings yet
- MUSIC G8 Southeast Asia Music PART 1Document56 pagesMUSIC G8 Southeast Asia Music PART 1christinaNo ratings yet
- Pin PeatDocument5 pagesPin PeatCelesteCelestePataoNo ratings yet
- The Music of Thailand PDFDocument30 pagesThe Music of Thailand PDFJanice C. Sabagay100% (3)
- The Instruments - CambodiaDocument12 pagesThe Instruments - CambodiaNeil Retiza Abay100% (1)
- MAPEHDocument11 pagesMAPEHPatrick CenaNo ratings yet
- MusicDocument20 pagesMusicJaspreet Singh WaliaNo ratings yet
- Music of CambodiaDocument7 pagesMusic of CambodiaPaulineNo ratings yet
- Desc in Music EheDocument6 pagesDesc in Music EheJayson Red SmithsonNo ratings yet
- Traditional Cambodian Musical InstrumentsDocument12 pagesTraditional Cambodian Musical InstrumentsDelve Jane C. Wenceslao100% (1)
- Korean Musical InstrumentsDocument5 pagesKorean Musical InstrumentsAndriaKimNo ratings yet
- Japan InstrumentDocument2 pagesJapan InstrumentRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Art Integration LearningDocument15 pagesArt Integration Learningkhushi guptaNo ratings yet
- MUSIC AND ARTS REVIEWER 2nd QUARTER GRADE 8Document6 pagesMUSIC AND ARTS REVIEWER 2nd QUARTER GRADE 8Grace Anne C. MercadoNo ratings yet
- TAMPURADocument5 pagesTAMPURAAbril De Gracia VeranoNo ratings yet
- Jexter MAPEH (AutoRecovered)Document9 pagesJexter MAPEH (AutoRecovered)Carlo Santos RabanalNo ratings yet
- Music of ThailandDocument44 pagesMusic of ThailandJacob BelmonteNo ratings yet
- Secondary Music 8 Q2 Week3Document18 pagesSecondary Music 8 Q2 Week3Nelson Jeff Jr. MagpaliNo ratings yet
- Korean Musical InstrumentsDocument5 pagesKorean Musical InstrumentsAndriaKim100% (1)
- Mr. Carlo Justino J. Luna: Malabanias Integrated SchoolDocument46 pagesMr. Carlo Justino J. Luna: Malabanias Integrated SchoolNeølie Abello LatúrnasNo ratings yet
- East Asian MusicDocument69 pagesEast Asian MusicClaire Montero-MasutaNo ratings yet
- Music of Indonesia 2Document2 pagesMusic of Indonesia 2Ferchris Stephen AdlawanNo ratings yet
- Southeast AsiaDocument48 pagesSoutheast AsiaLiebe Ruiz TorresNo ratings yet
- Japanese Musical InstrumentsDocument3 pagesJapanese Musical InstrumentsShanie LouNo ratings yet
- MusicDocument25 pagesMusicMjhayeNo ratings yet
- Asia Musical InstrumentsDocument11 pagesAsia Musical InstrumentsArlene NavarroNo ratings yet
- East Asian MusicDocument60 pagesEast Asian MusicDIANNE CERVANTESNo ratings yet
- Musical Instruments of India: Mary Grace Ann Valencia 3-St. Vincent de PaulDocument5 pagesMusical Instruments of India: Mary Grace Ann Valencia 3-St. Vincent de Pauljoyceannm_valenciaNo ratings yet
- Thai Music PPDocument66 pagesThai Music PPHazel Clemente CarreonNo ratings yet
- 10 Indian Plucked String InstrumentsDocument13 pages10 Indian Plucked String InstrumentsIan De La Cruz100% (1)
- Japanese and Korean Musical InstrumentDocument14 pagesJapanese and Korean Musical InstrumentNoah CofinoNo ratings yet
- 213213213213213Document3 pages213213213213213Jock ItchNo ratings yet
- CambodiaDocument5 pagesCambodiaNiel S. DefensorNo ratings yet
- MUSIC LET Asian MusicDocument13 pagesMUSIC LET Asian MusicEleomie AlipoonNo ratings yet
- Thailand Music Grade 8Document36 pagesThailand Music Grade 8Crystal RelovaNo ratings yet
- Asian MusicDocument18 pagesAsian MusicLiebe Ruiz TorresNo ratings yet
- Philippine Bamboo Instruments: AerophonesDocument13 pagesPhilippine Bamboo Instruments: AerophonesDeneb ChuaNo ratings yet
- One Common VoiceDocument20 pagesOne Common VoiceAngielyn AbardoNo ratings yet
- Gollum39s Song Sheet Music FluteDocument3 pagesGollum39s Song Sheet Music FluteEdenNo ratings yet
- Violin - Notation: Products News Music Community Company ManualsDocument1 pageViolin - Notation: Products News Music Community Company ManualsTóth ViktorNo ratings yet
- Alto Recorder Fingering Chart: Musical Instrument GuideDocument1 pageAlto Recorder Fingering Chart: Musical Instrument GuideMusic DNo ratings yet
- Great Is Thy FaithfulnessDocument1 pageGreat Is Thy FaithfulnessAaron Elias PuzenikNo ratings yet
- 2510891-Edelweiss QuartetDocument2 pages2510891-Edelweiss QuartetLeanne hilpertNo ratings yet
- Amazing Grace - PoloDocument7 pagesAmazing Grace - PoloOtávioQuartierNo ratings yet
- Yamaha Tg500Document21 pagesYamaha Tg500altaminNo ratings yet
- We Dont Talk About BrunoDocument5 pagesWe Dont Talk About Brunoapi-649553832No ratings yet
- El Condor Pasa. PartiturDocument6 pagesEl Condor Pasa. PartiturОксана РетинскаяNo ratings yet
- Slide Trombone MethodsDocument4 pagesSlide Trombone MethodsShadi Ashouri100% (1)
- 2015 Fender Custom Shop Illustrated Price List PDFDocument24 pages2015 Fender Custom Shop Illustrated Price List PDFrexNo ratings yet
- Any Kind of Dead Person Sheet MusicDocument4 pagesAny Kind of Dead Person Sheet Musicindia newtonNo ratings yet
- Nearer My God To Thee Arranged For BandDocument14 pagesNearer My God To Thee Arranged For BandElmer Patagan EsplanaNo ratings yet
- Frozen - Você Quer Brincar Na NeveDocument7 pagesFrozen - Você Quer Brincar Na NeveElias NeriNo ratings yet
- Kevin Bobo - 4 Mallet ExercisesDocument7 pagesKevin Bobo - 4 Mallet ExercisesSeth DyerNo ratings yet
- IGCSE World Focus 2020 - Arabic Music - Part 1: Instruments (Copy)Document12 pagesIGCSE World Focus 2020 - Arabic Music - Part 1: Instruments (Copy)Joshua MckayNo ratings yet
- Altissimo Fingerings For Baritone SaxophoneDocument1 pageAltissimo Fingerings For Baritone SaxophoneBruno SantosNo ratings yet
- Pickup Bartolini Wiring ConductorDocument2 pagesPickup Bartolini Wiring ConductorClau gomesNo ratings yet
- Bacchus Global Series BrochureDocument12 pagesBacchus Global Series Brochurebenja330% (1)
- Moderately: (Banda de La "Casa de La Comunidad Valenciana" en Navarra)Document73 pagesModerately: (Banda de La "Casa de La Comunidad Valenciana" en Navarra)Nuno Batista100% (2)
- Angelo ConcertinaDocument4 pagesAngelo Concertina蔡偉靖100% (1)
- Yeu Xa - Vu Cat TuongDocument2 pagesYeu Xa - Vu Cat TuongTinNo ratings yet
- Some Day My Prince Will Come: Arr. by A .BykovDocument4 pagesSome Day My Prince Will Come: Arr. by A .BykovBixente BfNo ratings yet
- Korg WavestationDocument7 pagesKorg WavestationaltaminNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Free Tech Resources GuideDocument34 pagesUltimate Free Tech Resources Guideapi-298999876100% (1)
- Bellum Belgicum: (Inspired by The Novel 'Hotse Hiddes')Document18 pagesBellum Belgicum: (Inspired by The Novel 'Hotse Hiddes')Laimonas MaseviciusNo ratings yet