Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acetazolamide
Acetazolamide
Uploaded by
Alexandra Antondy0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
591 views2 pagesDiamox (acetazolamide) is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor used to treat glaucoma and seizures by inhibiting carbonic anhydrase and reducing fluid production. It can cause side effects involving multiple body systems like the CNS, GI, renal, and metabolic systems. Nurses monitor for signs of hypokalemia and adverse reactions when assessing patients taking acetazolamide and teach them about reporting side effects and following dosage instructions. The goals of treatment are to decrease intraocular pressure for glaucoma, reduce seizure frequency, and prevent conditions like altitude sickness.
Original Description:
Original Title
acetazolamide
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDiamox (acetazolamide) is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor used to treat glaucoma and seizures by inhibiting carbonic anhydrase and reducing fluid production. It can cause side effects involving multiple body systems like the CNS, GI, renal, and metabolic systems. Nurses monitor for signs of hypokalemia and adverse reactions when assessing patients taking acetazolamide and teach them about reporting side effects and following dosage instructions. The goals of treatment are to decrease intraocular pressure for glaucoma, reduce seizure frequency, and prevent conditions like altitude sickness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
591 views2 pagesAcetazolamide
Acetazolamide
Uploaded by
Alexandra AntondyDiamox (acetazolamide) is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor used to treat glaucoma and seizures by inhibiting carbonic anhydrase and reducing fluid production. It can cause side effects involving multiple body systems like the CNS, GI, renal, and metabolic systems. Nurses monitor for signs of hypokalemia and adverse reactions when assessing patients taking acetazolamide and teach them about reporting side effects and following dosage instructions. The goals of treatment are to decrease intraocular pressure for glaucoma, reduce seizure frequency, and prevent conditions like altitude sickness.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
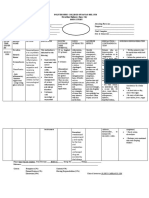
Mindanao State University – Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Bianca Mikaela F.
Dosdos
Block: 262
PHARMACOLOGY
DRUG STUDY
Brand Name: Diamox Generic Name: Acetazolamide Drug Classification: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
Dosage, Route & Frequency
Drug-Drug & Drug-Food Side Effects Adverse Reactions (By
Recommende Drug Action Indications Contraindications
Prescribed Interactions (By System) System)
d
IV (Adults): Inhibition of Drug-Drug: Lowering of Hypersensitiv CNS: depression, CNS: depression,
Glaucoma carbonic Excretion of barbiturates, intraocular ity or cross- fatigue, weakness, fatigue, weakness,
(closed anhydrase in aspirin, and lithium isqand pressure in the sensitivity drowsiness. drowsiness.
angle)—250– the eye results may lead topeffectiveness. treatment of with EENT: transient EENT: transient
500 mg, may in decreased Excretion of amphetamine, glaucoma. sulfonamides nearsightedness. nearsightedness.
repeat in 2– 4 secretion of quinidine, procainamide, Management of may occur; GI: anorexia, metallic GI: anorexia, metallic
hr to a aqueous and possibly tricyclic acute altitude Hepatic taste, nausea, vomiting, taste, nausea,
maximum of 1 humor. antidepressantsispand may sickness. Edema disease or melena. vomiting, melena.
g/day. Inhibition of lead to toxicity. due to HF. insufficiency; GU: crystalluria, renal GU: crystalluria, renal
Edema—250– renal carbonic Mayqcyclosporine levels Adjunct to the Concurrent calculi. Derm: STEVENS- calculi. Derm:
375 mg/day. IV anhydrase, treatment of use with JOHNSON SYNDROME, STEVENS-JOHNSON
(Children): resulting in refractory ophthalmic rashes. SYNDROME, rashes.
Glaucoma—5– self-limiting seizures. carbonic Endo: hyperglycemia. F Endo: hyperglycemia. F
10 mg/kg q 6 urinary Unlabeled Use: anhydrase and E: hyperchloremic and E: hyperchloremic
hr, not to excretion of Reduce inhibitors acidosis, hypokalemia, acidosis, hypokalemia,
exceed 1 sodium, cerebrospinal (brinzolamid growth retardation (in growth retardation (in
g/day. potassium, fluid production e, children receiving children receiving
Edema— 5 bicarbonate, in hydrocephalus. dorzolamide) chronic therapy). chronic therapy).
mg/kg/dose and water. CNS Prevention of is not Hemat: APLASTIC Hemat: APLASTIC
once daily. IV inhibition of renal calculi recommende ANEMIA, HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA, HEMOLYTIC
(Neonates): carbonic composed of uric d; OB: Avoid ANEMIA, LEUKOPENIA. ANEMIA, LEUKOPENIA.
Hydrocephalus anhydrase and acid or cystine. during first Metab: weight loss, Metab: weight loss,
—5 resultant trimester of hyperuricemia. hyperuricemia.
mg/kg/dose q diuresis pregnancy.. Neuro: paresthesias. Neuro: paresthesias.
6 hrqby 25 maypabnormal Misc:allergic reactions Misc:allergic reactions
mg/kg/day up neuronal firing. including ANAPHYLAXIS. including
to a maximum Alkaline ANAPHYLAXIS.
of 100 diuresis
mg/kg/day prevents
precipitation of
uric acid or
cystine in the
urinary tract.
Responsibilities in the Nursing Process (ADPIE) Responsibilities in the Nursing Process (ADPIE)
Assessment Patient/Family Teaching
● Observe for signs of hypokalemia (muscle weakness, malaise, fatigue, ECG changes, ● Instruct patient to take as directed. Take missed doses as soon as possible unless almost time for next
vomiting). dose. Do not double doses. Patients on anticonvulsant therapy may need to gradually withdraw
● Assess for allergy to sulfonamides. medication.
● Intraocular Pressure: Assess for eye discomfort or decrease in visual acuity. ● Advise patient to report numbness or tingling of extremities, weakness, rash, sore throat, unusual
● Seizures: Monitor neurologic status in patients receiving acetazolamide for seizures. bleeding or bruising, fever, or signs/symptoms of a sulfonamide adverse reaction (Stevens-Johnson
Initiate seizure precautions syndrome [flu-like symptoms, spreading red rash, or skin/mucous membrane blistering], toxic epidermal
Potential Nursing Diagnoses necrolysis [widespread peeling/blistering of skin]) to health care professional. If hematopoietic reactions,
Disturbed sensory perception (visual) (Indications) fever, rash, hepatic, or renal problems occur, acetazolamide should be discontinued.
Implementation Evaluation/Desired Outcomes
● Do not confuse acetazolamide with acetohexamide. Do not confuse Diamox with ● Decrease in intraocular pressure when used for glaucoma. If therapy is not effective or patient is
Diabinese. unable to tolerate one carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, using another may be effective and more tolerable.
● Encourage fluids to 2000– 3000 mL/day, unless contraindicated, to prevent ● Decrease in the frequency of seizures.
crystalluria and stone formation. ● Reduction of edema.
● A potassium supplement without chloride should be administered concurrently with ● Prevention of altitude sickness.
acetazolamide. ● Prevention of uric acid or cystine stones in the urinary tract.
Sources:
https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-6755/acetazolamide-oral/details
https://www.rxlist.com/acetazolamide-side-effects-drug-center.htm
https://davisplus.fadavis.com/3976/meddeck/pdf/acetazolamide.pdf
You might also like
- Tm1 Caregiving Nina 2.1Document85 pagesTm1 Caregiving Nina 2.1Nina Oaip75% (24)
- M Test (Meridian Test) MukainoDocument11 pagesM Test (Meridian Test) MukainoVicente Acosta100% (1)
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NewDocument4 pagesDrug Study NewJehannah Dayanara Berdan HayudiniNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Oraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardDocument1 pageOraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardJamie LeeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study BISACODYLDocument1 pageDrug Study BISACODYLAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Drug SDocument2 pagesDrug SJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY LevetiracetamMaria Althea NajorraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study QIDocument8 pagesDrug Study QImaeDonitaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolDocument1 pageDrug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolmikErlh100% (2)
- DS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Document2 pagesDS - Oral Rehydration Salts (ORS)Celline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- OxcarbazepineDocument4 pagesOxcarbazepineahmad_makhtarNo ratings yet
- Check The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutDocument2 pagesCheck The Physician's Observe and Follow The 14 Warn The Mother AboutJust nowNo ratings yet
- Atenolol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 pagesAtenolol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- BNP (C)Document2 pagesBNP (C)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CaseDocument3 pagesDrug Study CaseKatrina Ponce100% (1)
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNifedipine Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTramadol Drug StudyTipey Segismundo0% (1)
- Stugeron® TabletsDocument3 pagesStugeron® TabletsmahgadNo ratings yet
- Furosemid Citicoline Clexane, LevofloxacinDocument9 pagesFurosemid Citicoline Clexane, Levofloxacincotyboy50% (2)
- Drug Study 2Document1 pageDrug Study 2Blitz KriegNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAbby BorabienNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ferrous Sulfate + FADocument3 pagesDrug Study Ferrous Sulfate + FAKristine ChampnessNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument4 pagesDrugVANNEZA TRIXZY TAMPARONGNo ratings yet
- Epirubicin 10Document1 pageEpirubicin 10PdianghunNo ratings yet
- Hydrocortisone Ointment-Drug StudyDocument1 pageHydrocortisone Ointment-Drug StudyTrisha CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDexamethasone Drug StudyVIDMENTON PHNo ratings yet
- MannitolDocument1 pageMannitolAina HaravataNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFINAL Drug StudycasedraftNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TemplateDocument6 pagesDrug Study TemplateUDDE-E MARISABELNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY-LidocaineDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY-LidocaineCarissa Mae Tapec Estrada100% (1)
- IsoketDocument2 pagesIsoketJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- UROKINASE (Kinlytic)Document4 pagesUROKINASE (Kinlytic)Mikaela Gabrielle GeraliNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Bsn3aDocument3 pagesDrug Study Bsn3aEmuelle GanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - OB WardDocument8 pagesDrug Study - OB WardCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GabapentinDocument3 pagesDrug Study Gabapentinbridget.badiang001No ratings yet
- Drugstudy PotassiumchlorideDocument3 pagesDrugstudy Potassiumchloridetrina412No ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument1 pageCEFUROXIMEJose Luis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - ParacetamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study - ParacetamolNE TdrNo ratings yet
- MedroxyprogesteroneDocument5 pagesMedroxyprogesteroneunkown userNo ratings yet
- Formoterol Gonzaga.Document2 pagesFormoterol Gonzaga.Sheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NCP Appendicitis Medix CADocument3 pagesDrug Study NCP Appendicitis Medix CABel CortezNo ratings yet
- NCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingDocument3 pagesNCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingVerajoy DaanNo ratings yet
- Tramadol (Dolcet)Document1 pageTramadol (Dolcet)Beverly Ann de LeonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SulfasalazineDocument2 pagesDrug Study SulfasalazineBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 04-21-09Document2 pagesDrug Study 04-21-09obietobiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study. GeamhDocument5 pagesDrug Study. GeamhMacky RobentaNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Oxide (Antacid, Anti-Convulsant, Electrolyte, Laxative)Document1 pageMagnesium Oxide (Antacid, Anti-Convulsant, Electrolyte, Laxative)Danielle Marie SamblacenoNo ratings yet
- Carboprost TromethamineDocument2 pagesCarboprost TromethamineDeathDefying DonutNo ratings yet
- Darbepoetin AlfaDocument3 pagesDarbepoetin Alfaapi-3797941No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Dextromethorphan)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Dextromethorphan)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - KetoprofenDocument3 pagesDrug Study - KetoprofenThalia UyNo ratings yet
- Duty Drug Study'sDocument7 pagesDuty Drug Study'sGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Carved I LolDocument2 pagesCarved I LolmariaclaramutyaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: MontelukastDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Montelukastunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis FelodipineDocument2 pagesDrug Analysis FelodipineNika LoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument5 pagesDrug Study ICUEcko MoawiaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DoxycylineDocument3 pagesDrug Study DoxycylineMethaGod GameNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- MannitolDocument3 pagesMannitolAlexandra AntondyNo ratings yet
- Case Study Analysis Garcia FamilyDocument1 pageCase Study Analysis Garcia FamilyAlexandra AntondyNo ratings yet
- FlecainideDocument3 pagesFlecainideAlexandra AntondyNo ratings yet
- College of Nusrsing: Mindanao State University Iligan Institute of Technology Iligan City, 9200 PhilippinesDocument6 pagesCollege of Nusrsing: Mindanao State University Iligan Institute of Technology Iligan City, 9200 PhilippinesAlexandra AntondyNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: ALEXA MURIEL L. MOZAR Section: BLOCK 261Document2 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: ALEXA MURIEL L. MOZAR Section: BLOCK 261Alexandra AntondyNo ratings yet
- Indian Nutraceutical IndustryDocument64 pagesIndian Nutraceutical Industryhariom100% (2)
- Treatment in Epileptic Encephalopathy With ESES and Landau-Kleffner SyndromeDocument6 pagesTreatment in Epileptic Encephalopathy With ESES and Landau-Kleffner SyndromeDaniela TapiaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7 2overcrowding ED - Edited.editedDocument41 pagesAssignment 7 2overcrowding ED - Edited.editedLetisha PooranNo ratings yet
- 07 DR Ismat Mohd SulaimanDocument21 pages07 DR Ismat Mohd SulaimanGiles Ching100% (1)
- Kinesiology Taping Theory and ApplicationDocument8 pagesKinesiology Taping Theory and Applicationtaxel00% (1)
- HLT37215 Cert III Pathology Collection Brochure v1 2022Document7 pagesHLT37215 Cert III Pathology Collection Brochure v1 2022aman_grewal03mNo ratings yet
- Hospital and Clinical Pharmacy CH 1 Hospital Pharmacy NotesDocument12 pagesHospital and Clinical Pharmacy CH 1 Hospital Pharmacy Notesmaharachandana18No ratings yet
- Sairui E-Commerce Product CatalogueDocument23 pagesSairui E-Commerce Product CatalogueCanaan GamelifeNo ratings yet
- Kellgren and Lawrence Grading For Osteoartritis RadiographsDocument6 pagesKellgren and Lawrence Grading For Osteoartritis Radiographsnitu73100% (1)
- CastrationDocument22 pagesCastrationಮನೋಜ್ ಭಾರದ್ವಾಜ್No ratings yet
- Dr. Michael Tarver Emergency Suspension ComplaintDocument10 pagesDr. Michael Tarver Emergency Suspension ComplaintDentist The MenaceNo ratings yet
- Skill Instr Mod 5 JunioDocument5 pagesSkill Instr Mod 5 JunioSae TumNo ratings yet
- 2016 UpToDate Sepsis Syndromes in Adults: Epidemiology, Definitions, Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Prognosis - UpToDateDocument20 pages2016 UpToDate Sepsis Syndromes in Adults: Epidemiology, Definitions, Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Prognosis - UpToDateCinthia Karina ValarezoNo ratings yet
- Analytical Exposition Text: By: Ariful SukronDocument8 pagesAnalytical Exposition Text: By: Ariful SukronAriful SukronNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument4 pagesDefinitionhujjathNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous Abscess Furuncles and CarbuclesDocument25 pagesCutaneous Abscess Furuncles and Carbuclesazmmatgowher_1219266No ratings yet
- February 19, 2014Document12 pagesFebruary 19, 2014Maple Lake MessengerNo ratings yet
- Cellular Aberration Reviewer 5-6Document9 pagesCellular Aberration Reviewer 5-6Jessica A. BurgosNo ratings yet
- Test Health and DiseasesDocument4 pagesTest Health and DiseasesAndrea Anderson-HydeNo ratings yet
- Childhood Traumatic GriefDocument85 pagesChildhood Traumatic Griefmoi5566No ratings yet
- Unit Plan-Health Healthy Eating and Habits January 5th-31stDocument22 pagesUnit Plan-Health Healthy Eating and Habits January 5th-31stapi-534505202No ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Essentials of Nursing Leadership Management 3rd Edition Kelly Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Essentials of Nursing Leadership Management 3rd Edition Kelly Test Bank PDFphaethon.meak0ka6o100% (10)
- CASR Part 67 Ed. 1 Amdt 0 - Medical Standard and CertificationDocument43 pagesCASR Part 67 Ed. 1 Amdt 0 - Medical Standard and CertificationR SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Gen Z and Mental Health in The US - February 2022 ReportDocument26 pagesGen Z and Mental Health in The US - February 2022 ReportT VyNo ratings yet
- Nestle India & Its Resililent SpiritDocument15 pagesNestle India & Its Resililent SpiritPrerna RathiNo ratings yet
- Public Perception of Mental Health in Iraq: Research Open AccessDocument11 pagesPublic Perception of Mental Health in Iraq: Research Open AccessSri HariNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroductionPaul OrbinoNo ratings yet
- Disaster Drill JournalDocument3 pagesDisaster Drill Journalapi-508765756No ratings yet