Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genetics and Developmental Biology 2018 Module B
Genetics and Developmental Biology 2018 Module B
Uploaded by
CatCopyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGenetics and Developmental Biology 2018 Module B
Genetics and Developmental Biology 2018 Module B
Uploaded by
Cat1
NMAT REVIEW 2018 5. Mendel crossed peas having round green seeds with
GENETICS MODULE B peas having wrinkled yellow seeds. All F1 plants had seeds
that were round and yellow. Predict the genotype of the
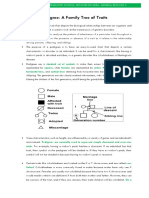
1. Hemophilia is an X-linked recessive genetic disorder in offspring resulting from a testcross of the F1 plants. Note:
which blood fails to clot properly due to gene mutations. A Yellow is dominant over green; round is dominant over
person with hemophilia may experience easy bruising and wrinkled.
sudden bleeding. The pedigree diagram below shows the a. Rryy, rrYy, and rryy
inheritance of hemophilia. b. RRYy, RrYy, rrYy, and rryy
c. RrYy, Rryy, rrYy, and rryy
d. RrYy, Rryy, and rrYy
6. In peas, a gene for tall plants (T) is dominant over its
allele for short plants (t). The gene for smooth peas (S) is
dominant over its allele for wrinkled peas (s). The genes
are not linked. Calculate the phenotypic ratio for the
results of a cross between TtSs x TtSs.
a. 9 short and smooth : 3 tall and wrinkled : 3 tall and
smooth : 1 short and wrinkled
b. 9 tall and wrinkled : 3 tall and smooth : 3 short and
smooth : 1 short and wrinkled
c. 9 tall and smooth : 3 tall and wrinkled : 3 short and
smooth : 1 short and wrinkled
d. 9 short and wrinkled : 3 short and smooth : 3 tall and
smooth : 1 tall and wrinkled
What could be the possible genotypes and phenotypes of
the parents? 7. How many phenotypic classes are produced by a
a. XY (normal male) and XXh (female carrier) dihybrid test-cross where one parent is heterozygous for
b. XhY (hemophilic male) and XX (normal female) both pairs of genes?
c. XhY (hemophilic male) and XhXh (hemophilic female) a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4
d. XhY (hemophilic male) and XXh (female carrier)
8. It has long been known in the field of human genetics
2. Cleft chin in humans is inherited as a simple recessive that wavy hair is the expression of a heterozygous
trait. Determine the genotypes of the parents who have genotype in which the allele for straight hair is paired with
five children, four normal and one with cleft chin. the allele for curly hair. Lucinda Lovelee married Larry
a. Heterozygous mother and heterozygous father Legg. Both have wavy hair. What is the probability that
b. Homozygous mother and heterozygous father their offspring, the littlest Legg, will have wavy hair?
c. Heterozygous mother and homozygous father a. 25% b. 33% c. 50% d. 66%
d. Homozygous mother and homozygous father
9. A woman with blood type IAIi and a man with blood
3. A woman heterozygous for polydactyly (extra fingers genotype IBIi have two children, both type AB. What is the
and toes), a dominant trait, is married to a normal man. probability that a third child will be blood type AB?
What is the probability of producing an offspring that has a. 25% b. 33% c. 50% d. 66%
extra fingers or toes?
a. 100% b. 75% c. 50% d. 25% 10. Morty has type B blood. His wife Jessica is unsure of
her blood type. If their first child, Morty Jr., is type A,
4. In Coleus, some plants have shallowly crenated edges their second offspring, Rick, is AB and the twins, Beth and
and others have deeply incised leaves. A cross is made Summer, are B. Determine the genotypes of Morty and
between homozygous deep and shallow individuals. The Jessica?
shallow trait is dominant. What is the genotype of the F2 a. Morty is IBIi and Jessica is IAIB
generation? b. Morty is IBIB and Jessica is IAIi
a. All heterozygous shallow c. Morty is IBIB and Jessica is either IAIA or IAIi
b. All homozygous shallow d. Morty is IBIi and Jessica is either IAIB or IAIi
c. 3 shallowly crenated : 1 deeply crenated
d. 1 homozygous shallow : 2 heterozygous shallow : 1 11. Albinism in corn plants is caused by a recessive lethal
homozygous deep gene that results in death before maturity. What will the
adult phenotypic ratio be for the F1 generation of
heterozygous parents?
a. 3 Normal : 1 Albino
b. 2 Normal : 2 Albino
c. All are normal
d. No offspring will reach adulthood
LEARNFAST REVIEW AND TUTORIAL HUB – NMAT REVIEWER
2
12. Huntington's chorea is a dominant lethal in humans. 19. What is the major difference between messenger RNA
The disease does not appear until later in life, so that molecules and the transfer RNA molecules?
afflicted individuals may already have produced children. a. Messenger RNA molecules contains ribose while transfer
What is the F1 phenotypic ratio of parents who are RNA molecules contains deoxyribose
homozygous dominant and heterozygous? b. Messenger RNA molecules carry coded information to
a. All are normal the ribosomes while transfer RNA molecules carry amino
b. All have Huntington’s chorea acids to the ribosomes
c. 50% of the children have Huntington’s chorea c. Messenger RNA molecules contain thymine while
d. Cannot be determined transfer RNA molecules contain uracil
d. Messenger RNA molecules function when they are
13. Red-green color blindness is inherited as a X-linked double-stranded while transfer RNA molecules function
recessive. If a color-blind woman marries a man who has when they are single-stranded.
normal vision, what would be the expected phenotypes of
their children with reference to this character? 20. A DNA strand with a sequence of 5’-ATGCCGGAT-3’
a. All have normal vision was used to synthesize new protein molecules. It
b. All boys are color blind while all girls have normal vision underwent transcription and produced an mRNA strand
c. All girls are color blind while all boys have normal vision that will proceed to translation. What is the nucleotide
d. All are color blind sequence of the complementary mRNA strand of the DNA
strand?
14. Suppose that gene b is sex-linked, recessive, and a. 5’-ATGCCGGAT-3’
embryonic lethal. A man marries a woman who is b. 5’-TACGGCCTA-3’
heterozygous for this gene. If this couple had many c. 5’-UACGGCCUA-3’
normal children, what would be the predicted sex ratio of d. 5’-AUGCCGGAU-3’
these children?
a. 2 female : 1 male c. 1 female : 2 male 21. What is the nucleotide sequence of the
b. 1 female : 1 male d. 3 female : 2 male complementary tRNA strand of the DNA strand found in
number 20?
15. In rabbits, a series of multiple alleles controls coat a. 5’-ATGCCGGAT-3’
color in the following way: C is dominant to all other b. 5’-TACGGCCTA-3’
alleles and causes full color. The chinchilla phenotype is c. 3’-UACGGCCUA-5’
due to the cch allele, which is dominant to all alleles other d. 3’-AUGCCGGAU-5’
than C. The ch allele, dominant only to ca (albino), results
in the Himalayan coat color. Thus, the order of dominance 22. The mRNA sequence CGUUUACACCGUCAC codes for
is C > cch > ch > ca. A cross has been made between two how many amino acids?
rabbits with a coat color of chinchilla with the genotype a. 5 b. 6 c. 3 d. more than 6
cchca and Himalayan with the genotype chca. Predict the
phenotypic ratio of the F1 generation. For numbers 23 to 25, refer to the figure below.
a. 1 chinchilla : 1 Himalayan
b. 2 chinchilla : 1 Himalayan : 1 albino
c. 1 chinchilla : 2 Himalayan : 1 albino
d. 3 chinchilla: 1 Himalayan
16. Replication of DNA:
a. Takes place in a “conservative” manner
b. Takes place in a “dispersive” manner
c. Takes place in a “semi-conservative” manner
d. Usually involves one origin of replication per
chromosome in eukaryotes
17. Given the following single strand of DNA sequence
- 5’-GAATTG-3’ – what is the sequence of the opposite
strand?
a. 5’-CAATTC-3’ c. 5’-CTTAAG-3’
b. 5’-CTTAAC-3’ d. 5’-GAATTG-3’
18. If a DNA stand has a nitrogenous base sequence of
AATGC, what is its complimentary RNA strand?
a. AAUGC b. CGUAA c. UUACG d. TTACG 23. Shown here is a hypothetical viral mRNA sequence:
5’-AUGCAUACCUAUGAGACCCUUGGA-3’
How many different polypeptide sequences can be
produced?
a. 5 b. 6 c. 7 d. 8
LEARNFAST REVIEW AND TUTORIAL HUB – NMAT REVIEWER
3
24. What is the polypeptide sequence produced by the 7. Below the neurocoel is a structure called the notochord
mRNA sequence found in number 23? which helps support the development of the embryo.
a. histidine – threonine – tyrosine – glutamic acid – What is the fate of the notochord in adult organisms?
threonine – leucine – glycine a. Spinal cord
b. methionine – histidine – threonine – glutamic acid – b. Spinal column
leucine – serine c. Becomes part of the dorsal musculature
c. glutamine – histidine – arginine – leucine – valine – d. Degenerates
alanine
d. alanine – tyrosine – tryptophan – glycine – serine – 8. The segmented blocks of tissue that develop on each
proline side of the notochord are called the
a. Neural tube c. Adrenal medulla
25. Predict the amino acid sequence produced during b. Somites d. Rubella
translation by the short hypothetical mRNA sequence:
5’-AUGCCGGAUUAUUGA-3’ 9. There are three primordial germ layers found in
a. methionine – proline – aspartic acid – tyrosine – stop embryos, namely, ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
b. proline – aspartic acid – tyrosine Each germ layer gives rise to distinct organs and parts in
c. methionine – alanine – proline – glutamic acid an animal’s body. Which of the following was derived from
d. serine – glutamic acid – cysteine the mesoderm?
I. Skeletal muscles
DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY II. Lungs
III. Lining of the stomach
IV. Cranium
1. During internal fertilization, the sperm cell fuses with
V. Cornea
the egg cell in the fallopian tube. From there, the a. I and III c. III and V
developing zygote will implant itself in the uterus. The
b. II and IV d. I only
zygote will undergo extensive mitotic divisions in order to
give rise to a multicellular organism. How many sets of cell
For numbers 10 and 11, match the following animals with
division are there between the zygote stage and the eight-
the correct egg classifications.
cell embryonic stage?
a. Micolecithal c. Megalecithal
a. 3 b. 4 c. 6 d. 8
b. Mesolecithal d. Isolecithal
2. As the embryo increases in cell number, it also exhibits
B 10. Rana sp.
different cell movements, namely invagination, involution,
C 11. Sus scrofa domestica
and epiboly. These cell movements give rise to different
structures in the embryo. What do you call the embryonic
12. Strictly speaking, “ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny”
stage wherein the first embryonic cavity appears?
means
a. Morula c. Gastrula
a. embryonic stages of an animal resemble adult ancestors
b. Blastula d. Neurula
b. adults of an animal resemble embryonic stages of its
ancestors
3. The second embryonic cavity gives rise to the future
c. adult animals resemble adult ancestors
gastrointestinal tract of the organism. Which of the d. embryonic stages of an animal resemble embryonic
following cavities refers to the second embryonic cavity?
stages of its ancestors
a. Blastocoel c. Neurocoel
b. Archenteron d. Coelom
13. Which of the following is a feature in fetal
development?
4. Which of the following is not associated with the site of
I. Ductus arteriosus
invagination during gastrulation?
II. Foramen ovale
a. Dorsal lip c. All of the following
III. Fetal haemoglobin with a higher affinity for
b. Blastopore d. None of the following
oxygen than adult haemoglobin
a. I only
5. During neurulation, the neural tube is formed after the
b. II only
_________ stage.
c. I and III only
a. Neural plate c. Neural fold
d. All of the following
b. Neural crest d. Neural thickening
14. A female animal that forms eggs, hatches in the body,
6. The first truly vertebrate phase of development is
and then younglings are born alive is known as what type
marked by the formation of the
of offspring production?
a. Archenteron c. Neural crest
a. Oviparous c. Ovoviviparous
b. Coccyx d. Primitive streak
b. Viviparous d. Marsupials
LEARNFAST REVIEW AND TUTORIAL HUB – NMAT REVIEWER
4
15. Which is likely to happen if the amphibian zygote is For numbers 23 to 25, pair the following plant embryonic
experimentally manipulated so that the first cleavage structures with its fate in an adult plant.
plane misses the gray crescent instead of bisecting it? a. Cotyledon c. Epicotyl
a. There will be 2 undifferentiated ball of cells b. Hypocotyl d. Radicle
b. 2 normal tadpoles will develop
c. 2 abnormal tadpoles will develop C 23. Embryonic structure that eventually develops into
d. Only the blastomere that gets the grey crescent will the leaves of the plant
develop into normal tadpole D 24. Embryonic structure that eventually develops into
the main root of the plant
16. An amphibian embryo, a band of cells called the B 25. Embryonic structure that eventually becomes part of
neural crest… the plant stem
a. Rolls up to form the neural tube
b. Develops into the main section of the brain
c. Produces amoeboid cells that migrate to form teeth,
skull bones, and other structures in the embryo
d. Induces the formation of the embryo
17. Which embryonic membrane is closest to the shell in a
bird egg?
a. Allantois c. Amnion
b. Chorion d. Yolk Sac
18. What is the function of the chorion in terrestrial
vertebrate embryos?
a. To keep the embryo moist
b. To exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide with the
environment
c. To absorb nutrients stored in yolk
d. To store nitrogenous waste
19. In macrolecithal eggs, normal cleavage is not possible
because of the presence of a dense, concentrated yolk
mass. Instead of a distinct mass of blastomeres, a
__________ is found in the egg.
a. Primitive streak c. Area pellucida
b. Area opaca d. Hensen’s node
20. Which of the following is true for fraternal twins?
a. They are derived from a single egg cell
b. There can only be one gender, either both male and
both female
c. They are derived from a single sperm cell
d. None of the following
21. Which is the best statement regarding the role of the
embryo in hormone production?
a. The embryo breaks down proteins in the endospermal
cells to produce auxins
b. The embryo converts tryptophan into indoleacetic acid
c. The embryo releases gibberellin which triggers the
synthesis of enzymes that break down the endosperm
d. The embryo produces enzymes which break down
the endosperm cells
22. Growth pattern in pollen tube is similar to that of
fungal hyphae or root hairs in exhibiting
a. Oscillated elongation of tube
b. Tip-oriented growth
c. Multiple-oriented growth
d. Predetermined path of growth
LEARNFAST REVIEW AND TUTORIAL HUB – NMAT REVIEWER
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- International Baccalaureate (IB) Database Questions Biology HLDocument20 pagesInternational Baccalaureate (IB) Database Questions Biology HLTonia von HugoNo ratings yet
- Jacob Gutierrez - Gizmos DNAAnalysisDocument4 pagesJacob Gutierrez - Gizmos DNAAnalysisJacob GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic PharmacologyDocument17 pagesAdrenergic PharmacologyCatNo ratings yet
- I Na's C Upcakes I Na's C Upcakes I Na's C UpcakesDocument1 pageI Na's C Upcakes I Na's C Upcakes I Na's C UpcakesCatNo ratings yet
- Task 3 CoachingDocument1 pageTask 3 CoachingCatNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal: State Your Primary Reasons of Organizing This ActivityDocument6 pagesProject Proposal: State Your Primary Reasons of Organizing This ActivityCatNo ratings yet
- Badminton Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesBadminton Lesson PlanCatNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal: State Your Primary Reasons of Organizing This ActivityDocument7 pagesProject Proposal: State Your Primary Reasons of Organizing This ActivityCatNo ratings yet
- Certificate For Catrina Dimayacyac For "Evaluation For KKK-COVID19 Mahirap Maging Mahirap - How Are The Poor Coping With COVID-19?"Document1 pageCertificate For Catrina Dimayacyac For "Evaluation For KKK-COVID19 Mahirap Maging Mahirap - How Are The Poor Coping With COVID-19?"CatNo ratings yet
- Topics For Reporting and ReportersDocument1 pageTopics For Reporting and ReportersCatNo ratings yet
- Delerio, Janel O. Resistance Training ActivityDocument2 pagesDelerio, Janel O. Resistance Training ActivityCatNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument3 pagesExercisesCatNo ratings yet
- August 6 September 30docxDocument2 pagesAugust 6 September 30docxCatNo ratings yet
- Pedigree Analysis Hand-OutDocument4 pagesPedigree Analysis Hand-OutCatNo ratings yet
- Pedagology ApproachesDocument1 pagePedagology ApproachesCatNo ratings yet
- SPC Crude Drugs CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesSPC Crude Drugs CarbohydratesCatNo ratings yet
- Must To Know Formulas (NMAT)Document2 pagesMust To Know Formulas (NMAT)CatNo ratings yet
- Cvs (Diuretics)Document2 pagesCvs (Diuretics)CatNo ratings yet
- Tablets: Tablets Characteristics of Ideal TabletDocument4 pagesTablets: Tablets Characteristics of Ideal TabletCatNo ratings yet
- Statistical Assistance Certification Form: This Is To Certify That The Statistical Data For This Manuscript EntitledDocument1 pageStatistical Assistance Certification Form: This Is To Certify That The Statistical Data For This Manuscript EntitledCatNo ratings yet
- Bay Leaves Group 2 Plant Material Data SheetDocument7 pagesBay Leaves Group 2 Plant Material Data SheetCat100% (1)
- Experiment 4 RecrystallizationDocument17 pagesExperiment 4 RecrystallizationCatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Genetics Brain and Personali - 2016 - Neuroimaging Personality SoDocument20 pagesChapter 4 - Genetics Brain and Personali - 2016 - Neuroimaging Personality Somi_shareNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Evolutionary Psychology The New Science of The Mind 4 e 4th Edition David BussDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Evolutionary Psychology The New Science of The Mind 4 e 4th Edition David Busskeelratlakzk100% (46)
- Final CodesDocument77 pagesFinal Codesprakhar agrawalNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce Revision NotesDocument28 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce Revision NotesInnama FatimaNo ratings yet
- 4C Factors of Behaviour Based On The Reaserch of William MarstonDocument4 pages4C Factors of Behaviour Based On The Reaserch of William Marstonnishantu_2255705@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Basis of Major Depressive Disorder: Molecular PsychiatryDocument12 pagesThe Genetic Basis of Major Depressive Disorder: Molecular PsychiatryLilla Laura KisNo ratings yet
- MSC Dissertation Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesMSC Dissertation Literature Reviewc5nqw54q100% (1)
- Lamarck Vs DarwinDocument2 pagesLamarck Vs DarwinRoberto FiorilloNo ratings yet
- Genome Editing Using Crispr-Cas9: Doctoral SeminarDocument35 pagesGenome Editing Using Crispr-Cas9: Doctoral Seminarjajati keshari nayakNo ratings yet
- Technical Standards and Guidelines For The Diagnosis of Biotinidase DeficiencyDocument7 pagesTechnical Standards and Guidelines For The Diagnosis of Biotinidase DeficiencySaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Plant Morpho-Anatomy Intro PDFDocument113 pagesLecture 1 Plant Morpho-Anatomy Intro PDFLance CarandangNo ratings yet
- COURSE Syllabus: The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance CenterDocument10 pagesCOURSE Syllabus: The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance CenterlanaNo ratings yet
- Test 01 GrammarDocument9 pagesTest 01 GrammarRiandi HartartoNo ratings yet
- Lenv v202 ExamDocument32 pagesLenv v202 ExamHenry LanguisanNo ratings yet
- Maths For Biologists Student BookDocument43 pagesMaths For Biologists Student Booknitede4580No ratings yet
- Human Blood DNA Isolation: Lab Report 4Document5 pagesHuman Blood DNA Isolation: Lab Report 4Omar Mohsen SarhanNo ratings yet
- The New TaxonomyDocument258 pagesThe New TaxonomyMichelNo ratings yet
- BLAST: An Introductory Tool For Students To Bioinformatics ApplicationsDocument11 pagesBLAST: An Introductory Tool For Students To Bioinformatics ApplicationsAbdul jNo ratings yet
- 2021-Review-CRISPR Technologies and PAM-free NucleaseDocument12 pages2021-Review-CRISPR Technologies and PAM-free NucleaseCristian Felipe Sandoval QuiñonezNo ratings yet
- Introduction of DNA Into Living Cells: GBE310, Spring 2015Document33 pagesIntroduction of DNA Into Living Cells: GBE310, Spring 2015Shahriar ShamimNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics For MSC Medical MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesThesis Topics For MSC Medical Microbiologychristinasantospaterson100% (2)
- SHERLOCK: Nucleic Acid Detection With CRISPR Nucleases: ProtocolDocument29 pagesSHERLOCK: Nucleic Acid Detection With CRISPR Nucleases: ProtocolShreya PrakashNo ratings yet
- السيرة الذاتية للدكتور احمد محمد علوان البوحمدDocument10 pagesالسيرة الذاتية للدكتور احمد محمد علوان البوحمدahmedNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument14 pagesBiology ReviewerMarianne Tiffany RegalaNo ratings yet
- 2 Ultra Structure of CellsDocument49 pages2 Ultra Structure of CellsYousef WardatNo ratings yet
- Character of Sunflower PollinationDocument6 pagesCharacter of Sunflower PollinationZain JawadNo ratings yet
- Fact or Assumption - Rivera DennisseDocument8 pagesFact or Assumption - Rivera DennisseFrancisca MuñozNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Guide 2Document3 pagesCell Cycle Guide 2api-318387471No ratings yet