Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Informatii Seismice
Informatii Seismice
Uploaded by
MuresanAnna-KarinaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- MCAT Physics Formula SheetDocument3 pagesMCAT Physics Formula Sheetemma_reese100% (2)
- Week 6 - Fluid MechanicsDocument24 pagesWeek 6 - Fluid MechanicsHaze BlehNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Momentum Equation and Its ApplicationsDocument33 pagesChapter 5 - Momentum Equation and Its ApplicationsmapasabcNo ratings yet
- Earthquake AnalysisDocument11 pagesEarthquake AnalysisKhalid CaliNo ratings yet
- Trying To Pull A Boulder Up A Hill Working Vectors: W + F + N + P oDocument4 pagesTrying To Pull A Boulder Up A Hill Working Vectors: W + F + N + P odjbhetaNo ratings yet
- 6 MomentumjDocument19 pages6 MomentumjSoon LeeNo ratings yet
- ME 221 - Impulse & Momentum PrinciplesDocument47 pagesME 221 - Impulse & Momentum PrinciplesRakib HossainNo ratings yet
- GroundDocument40 pagesGroundc885ffmfrrNo ratings yet
- Practica 6 MFDocument3 pagesPractica 6 MFPedro LozanoNo ratings yet
- ME 2201-Lecture 8 - Shear and Bending Moment in Beams-Graphical MethodsDocument16 pagesME 2201-Lecture 8 - Shear and Bending Moment in Beams-Graphical Methodsfontawesome111No ratings yet
- Dynamic Earth Pressure PDFDocument38 pagesDynamic Earth Pressure PDFSadaf QasimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15 Stress TransformationDocument6 pagesLesson 15 Stress TransformationJoshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Earth Pressure Coefficient For Earthquake Analysis (Mononobe-Okabe)Document4 pagesDynamic Earth Pressure Coefficient For Earthquake Analysis (Mononobe-Okabe)chidsalazarNo ratings yet
- Impulse - MomentumDocument15 pagesImpulse - MomentumVijay Mohan SettiNo ratings yet
- Stress Distribution Trough SoilDocument5 pagesStress Distribution Trough Soilsam jandaliNo ratings yet
- Navier Stokes Eq NDocument12 pagesNavier Stokes Eq NSarath Chandra100% (1)
- CH 4 - Principles of Power SystemDocument19 pagesCH 4 - Principles of Power SystemAqsa KhanamNo ratings yet
- FM 6 Momentum AnalysisDocument29 pagesFM 6 Momentum Analysisالياس يونس مرغلانيNo ratings yet
- Impluse and MomentumDocument24 pagesImpluse and MomentumDenden Den100% (1)
- Comprehensive Step by Step Calculations For Retaining Wall Analysis Are Provided BelowDocument15 pagesComprehensive Step by Step Calculations For Retaining Wall Analysis Are Provided BelowLakshmiWijayasiriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Static Forces On SurfacesDocument54 pagesLecture 3 - Static Forces On Surfacesisrael moizo dintsiNo ratings yet
- Chapter V - Momentum EquationDocument16 pagesChapter V - Momentum EquationOmar Ashraf 3amerNo ratings yet
- Teoría M-ODocument3 pagesTeoría M-OAlonso PolarNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Mechanical SystemDocument33 pagesLec 3 Mechanical SystemFelopateer EmadNo ratings yet
- 16ME206T - Fluid Mechanics and Fluid MachineryDocument41 pages16ME206T - Fluid Mechanics and Fluid MachineryAbhinaya SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Force in ANGLE AND INCLINESDocument39 pagesForce in ANGLE AND INCLINESJoseph SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Physics As NotesDocument28 pagesPhysics As NotesShyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics: ExampleDocument13 pagesDynamics: ExampleAnonymous ZUaUz1wwNo ratings yet
- More Applications of Momentum - 2Document8 pagesMore Applications of Momentum - 2Alexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Revisão Bibliográfica de AerodinâmicaDocument31 pagesRevisão Bibliográfica de AerodinâmicaRodrigo PenaNo ratings yet
- V V Q ( V) V: 14.1 Der Satz Von Der Erhaltung Der Elektrischen LadungDocument4 pagesV V Q ( V) V: 14.1 Der Satz Von Der Erhaltung Der Elektrischen LadungSlaven IvanovicNo ratings yet
- Momentum Principle and Flow Analysis (6 Hours)Document17 pagesMomentum Principle and Flow Analysis (6 Hours)Ramdeo YadavNo ratings yet
- Fluid Pressure FullDocument5 pagesFluid Pressure FullBranded HackerNo ratings yet
- Fluids Ebook - Linear Momentum EquationDocument3 pagesFluids Ebook - Linear Momentum EquationYim Hoe YenNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Momentum Analysis of Flow SystemsDocument38 pagesTopic 2 Momentum Analysis of Flow Systemsethandleon4No ratings yet
- Study of Impact of Jet On Flat PlateDocument6 pagesStudy of Impact of Jet On Flat PlateMohan Ganesh100% (4)
- Stress DistributionDocument25 pagesStress DistributionMoyukh De100% (2)
- Jca DynamicsDocument16 pagesJca DynamicsDanica DevezaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Equivalent Static or Dynamic AnalysisDocument8 pagesBasics of Equivalent Static or Dynamic AnalysisSaikat Das Gupta100% (1)
- Euler Equations in Fluid DynamicsDocument11 pagesEuler Equations in Fluid Dynamicsshyamal_ranjan4474No ratings yet
- NatuurkundeII SamenvattingDocument43 pagesNatuurkundeII SamenvattingThibo VerstryngeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 1-Meng 215 Lecture 2 With TutorialsDocument55 pagesFluid Mechanics 1-Meng 215 Lecture 2 With TutorialsJoseph Wilson JuniorNo ratings yet
- Stresses in SoilDocument18 pagesStresses in SoilAliNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Meteorology 2Document16 pagesDynamic Meteorology 2ADNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I Impact of Jet On VanesDocument8 pagesUNIT-I Impact of Jet On VanesAjeet Kumar75% (4)
- HSC Physics PDFDocument202 pagesHSC Physics PDFLawrence Lim Ah Kow100% (1)
- Pressure On Plane SurfaceDocument6 pagesPressure On Plane SurfacetalatbilalNo ratings yet
- Ans No. 4-Conservation of Mass Equation-: + Known As Continuity EquationDocument4 pagesAns No. 4-Conservation of Mass Equation-: + Known As Continuity EquationHimanshu TrivediNo ratings yet
- Forces Acting On Gravity DamsDocument6 pagesForces Acting On Gravity DamsRama Sagar Naik100% (3)
- Unit 4 Stress DistributionDocument10 pagesUnit 4 Stress DistributionDIVYA NATHNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Analysis On Motion of Charged Particles in Electric FieldDocument25 pagesA Detailed Analysis On Motion of Charged Particles in Electric FieldRakesh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Work and EnergyDocument32 pagesWork and Energycreative dudeNo ratings yet
- End Term Lab Reports TOMDocument26 pagesEnd Term Lab Reports TOMSabtain AbbasNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionsDocument11 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionsMarianne Kristelle FactorNo ratings yet
- Module I HMDocument23 pagesModule I HMAnilkumar GopiNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Intensity of Electromagnetic Waves as a Function of Frequency, Source Distance and Aperture AngleFrom EverandIntensity of Electromagnetic Waves as a Function of Frequency, Source Distance and Aperture AngleNo ratings yet
- Pamanturi NecoeziveDocument2 pagesPamanturi NecoeziveMuresanAnna-KarinaNo ratings yet
- Dddddddddddddddddddddawdse Rdfreawdlf Grekfse The Concrete Mix With 4% Endura-600 Macro Synthetic Polypropylene Fiber Shows That Concrete Was More Slippery and Difficult To Compact. IDocument1 pageDddddddddddddddddddddawdse Rdfreawdlf Grekfse The Concrete Mix With 4% Endura-600 Macro Synthetic Polypropylene Fiber Shows That Concrete Was More Slippery and Difficult To Compact. IMuresanAnna-KarinaNo ratings yet
- LINDEN 16LC220-10tDocument4 pagesLINDEN 16LC220-10tMuresanAnna-KarinaNo ratings yet
- Design Applications of Raft Foundations-John Hemsley-Thomas Telford PDFDocument642 pagesDesign Applications of Raft Foundations-John Hemsley-Thomas Telford PDFMuresanAnna-KarinaNo ratings yet
- Acces Steel - Design of Portal Frame Eaves Connections PDFDocument23 pagesAcces Steel - Design of Portal Frame Eaves Connections PDFMuresanAnna-KarinaNo ratings yet
- 2011 - Retaining Wall Design Guide USFS - Mohney - 5 - LVR - Slope Stability PDFDocument559 pages2011 - Retaining Wall Design Guide USFS - Mohney - 5 - LVR - Slope Stability PDFMuresanAnna-Karina67% (3)
Informatii Seismice
Informatii Seismice
Uploaded by
MuresanAnna-KarinaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Informatii Seismice
Informatii Seismice
Uploaded by
MuresanAnna-KarinaCopyright:
Available Formats
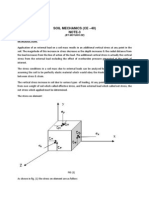
Earthquake increases the effect of active pressure and reduces the effect of passive
pressure. The theories used in our programs (Mononobe-Okabe, Arrango, JTJ 004-
89, JTS 146-2012, SL 203-97, NCMA-SRW) are derived assuming cohesionless soils
without influence of water. Therefore, all input soils are assumed cohesionless when
employing these theories to address the earthquake effects. Earthquake effects due to
surcharge are not considered in the program - the user may introduce these effects
(depending on the type of surcharge) as "Applied forces".
The coefficient kh is assumed always positive and such that its effect is always
unfavorable. The coefficient kv may receive both positive and negative value. If the
equivalent acceleration av acts downwards (from the ground surface) the inertia
forces kv Ws will be exerted on the soil wedge in the opposite direction (lifting the wedge
up). The values of equivalent acceleration av (and thus also the coefficient kv) and inertia
forces kv Ws are assumed as positive. It is clearly evident that the inertia forces act in the
direction opposite to acceleration (if the acceleration is assumed upwards - av = -
kv g then the inertia force presses the soil wedge downwards: - kv Ws. The direction with
most unfavorable effects on a structure is assumed when examining the seismic effects.
For sheeting structures it is possible to neglect the effect of vertical equivalent
acceleration kv Ws and input kv = 0.
You might also like
- MCAT Physics Formula SheetDocument3 pagesMCAT Physics Formula Sheetemma_reese100% (2)
- Week 6 - Fluid MechanicsDocument24 pagesWeek 6 - Fluid MechanicsHaze BlehNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Momentum Equation and Its ApplicationsDocument33 pagesChapter 5 - Momentum Equation and Its ApplicationsmapasabcNo ratings yet
- Earthquake AnalysisDocument11 pagesEarthquake AnalysisKhalid CaliNo ratings yet
- Trying To Pull A Boulder Up A Hill Working Vectors: W + F + N + P oDocument4 pagesTrying To Pull A Boulder Up A Hill Working Vectors: W + F + N + P odjbhetaNo ratings yet
- 6 MomentumjDocument19 pages6 MomentumjSoon LeeNo ratings yet
- ME 221 - Impulse & Momentum PrinciplesDocument47 pagesME 221 - Impulse & Momentum PrinciplesRakib HossainNo ratings yet
- GroundDocument40 pagesGroundc885ffmfrrNo ratings yet
- Practica 6 MFDocument3 pagesPractica 6 MFPedro LozanoNo ratings yet
- ME 2201-Lecture 8 - Shear and Bending Moment in Beams-Graphical MethodsDocument16 pagesME 2201-Lecture 8 - Shear and Bending Moment in Beams-Graphical Methodsfontawesome111No ratings yet
- Dynamic Earth Pressure PDFDocument38 pagesDynamic Earth Pressure PDFSadaf QasimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15 Stress TransformationDocument6 pagesLesson 15 Stress TransformationJoshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Earth Pressure Coefficient For Earthquake Analysis (Mononobe-Okabe)Document4 pagesDynamic Earth Pressure Coefficient For Earthquake Analysis (Mononobe-Okabe)chidsalazarNo ratings yet
- Impulse - MomentumDocument15 pagesImpulse - MomentumVijay Mohan SettiNo ratings yet
- Stress Distribution Trough SoilDocument5 pagesStress Distribution Trough Soilsam jandaliNo ratings yet
- Navier Stokes Eq NDocument12 pagesNavier Stokes Eq NSarath Chandra100% (1)
- CH 4 - Principles of Power SystemDocument19 pagesCH 4 - Principles of Power SystemAqsa KhanamNo ratings yet
- FM 6 Momentum AnalysisDocument29 pagesFM 6 Momentum Analysisالياس يونس مرغلانيNo ratings yet
- Impluse and MomentumDocument24 pagesImpluse and MomentumDenden Den100% (1)
- Comprehensive Step by Step Calculations For Retaining Wall Analysis Are Provided BelowDocument15 pagesComprehensive Step by Step Calculations For Retaining Wall Analysis Are Provided BelowLakshmiWijayasiriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Static Forces On SurfacesDocument54 pagesLecture 3 - Static Forces On Surfacesisrael moizo dintsiNo ratings yet
- Chapter V - Momentum EquationDocument16 pagesChapter V - Momentum EquationOmar Ashraf 3amerNo ratings yet
- Teoría M-ODocument3 pagesTeoría M-OAlonso PolarNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Mechanical SystemDocument33 pagesLec 3 Mechanical SystemFelopateer EmadNo ratings yet
- 16ME206T - Fluid Mechanics and Fluid MachineryDocument41 pages16ME206T - Fluid Mechanics and Fluid MachineryAbhinaya SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Force in ANGLE AND INCLINESDocument39 pagesForce in ANGLE AND INCLINESJoseph SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Physics As NotesDocument28 pagesPhysics As NotesShyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics: ExampleDocument13 pagesDynamics: ExampleAnonymous ZUaUz1wwNo ratings yet
- More Applications of Momentum - 2Document8 pagesMore Applications of Momentum - 2Alexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Revisão Bibliográfica de AerodinâmicaDocument31 pagesRevisão Bibliográfica de AerodinâmicaRodrigo PenaNo ratings yet
- V V Q ( V) V: 14.1 Der Satz Von Der Erhaltung Der Elektrischen LadungDocument4 pagesV V Q ( V) V: 14.1 Der Satz Von Der Erhaltung Der Elektrischen LadungSlaven IvanovicNo ratings yet
- Momentum Principle and Flow Analysis (6 Hours)Document17 pagesMomentum Principle and Flow Analysis (6 Hours)Ramdeo YadavNo ratings yet
- Fluid Pressure FullDocument5 pagesFluid Pressure FullBranded HackerNo ratings yet
- Fluids Ebook - Linear Momentum EquationDocument3 pagesFluids Ebook - Linear Momentum EquationYim Hoe YenNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Momentum Analysis of Flow SystemsDocument38 pagesTopic 2 Momentum Analysis of Flow Systemsethandleon4No ratings yet
- Study of Impact of Jet On Flat PlateDocument6 pagesStudy of Impact of Jet On Flat PlateMohan Ganesh100% (4)
- Stress DistributionDocument25 pagesStress DistributionMoyukh De100% (2)
- Jca DynamicsDocument16 pagesJca DynamicsDanica DevezaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Equivalent Static or Dynamic AnalysisDocument8 pagesBasics of Equivalent Static or Dynamic AnalysisSaikat Das Gupta100% (1)
- Euler Equations in Fluid DynamicsDocument11 pagesEuler Equations in Fluid Dynamicsshyamal_ranjan4474No ratings yet
- NatuurkundeII SamenvattingDocument43 pagesNatuurkundeII SamenvattingThibo VerstryngeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 1-Meng 215 Lecture 2 With TutorialsDocument55 pagesFluid Mechanics 1-Meng 215 Lecture 2 With TutorialsJoseph Wilson JuniorNo ratings yet
- Stresses in SoilDocument18 pagesStresses in SoilAliNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Meteorology 2Document16 pagesDynamic Meteorology 2ADNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I Impact of Jet On VanesDocument8 pagesUNIT-I Impact of Jet On VanesAjeet Kumar75% (4)
- HSC Physics PDFDocument202 pagesHSC Physics PDFLawrence Lim Ah Kow100% (1)
- Pressure On Plane SurfaceDocument6 pagesPressure On Plane SurfacetalatbilalNo ratings yet
- Ans No. 4-Conservation of Mass Equation-: + Known As Continuity EquationDocument4 pagesAns No. 4-Conservation of Mass Equation-: + Known As Continuity EquationHimanshu TrivediNo ratings yet
- Forces Acting On Gravity DamsDocument6 pagesForces Acting On Gravity DamsRama Sagar Naik100% (3)
- Unit 4 Stress DistributionDocument10 pagesUnit 4 Stress DistributionDIVYA NATHNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Analysis On Motion of Charged Particles in Electric FieldDocument25 pagesA Detailed Analysis On Motion of Charged Particles in Electric FieldRakesh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Work and EnergyDocument32 pagesWork and Energycreative dudeNo ratings yet
- End Term Lab Reports TOMDocument26 pagesEnd Term Lab Reports TOMSabtain AbbasNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionsDocument11 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionsMarianne Kristelle FactorNo ratings yet
- Module I HMDocument23 pagesModule I HMAnilkumar GopiNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Intensity of Electromagnetic Waves as a Function of Frequency, Source Distance and Aperture AngleFrom EverandIntensity of Electromagnetic Waves as a Function of Frequency, Source Distance and Aperture AngleNo ratings yet
- Pamanturi NecoeziveDocument2 pagesPamanturi NecoeziveMuresanAnna-KarinaNo ratings yet
- Dddddddddddddddddddddawdse Rdfreawdlf Grekfse The Concrete Mix With 4% Endura-600 Macro Synthetic Polypropylene Fiber Shows That Concrete Was More Slippery and Difficult To Compact. IDocument1 pageDddddddddddddddddddddawdse Rdfreawdlf Grekfse The Concrete Mix With 4% Endura-600 Macro Synthetic Polypropylene Fiber Shows That Concrete Was More Slippery and Difficult To Compact. IMuresanAnna-KarinaNo ratings yet
- LINDEN 16LC220-10tDocument4 pagesLINDEN 16LC220-10tMuresanAnna-KarinaNo ratings yet
- Design Applications of Raft Foundations-John Hemsley-Thomas Telford PDFDocument642 pagesDesign Applications of Raft Foundations-John Hemsley-Thomas Telford PDFMuresanAnna-KarinaNo ratings yet
- Acces Steel - Design of Portal Frame Eaves Connections PDFDocument23 pagesAcces Steel - Design of Portal Frame Eaves Connections PDFMuresanAnna-KarinaNo ratings yet
- 2011 - Retaining Wall Design Guide USFS - Mohney - 5 - LVR - Slope Stability PDFDocument559 pages2011 - Retaining Wall Design Guide USFS - Mohney - 5 - LVR - Slope Stability PDFMuresanAnna-Karina67% (3)