Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 viewsConcept Map of DM
Concept Map of DM
Uploaded by
Leah GuadeThis document discusses the different types of diabetes mellitus. Type I diabetes is caused by an autoimmune destruction of the pancreatic islets resulting in little to no insulin production, most often developing at age 15. Type II diabetes involves insufficient insulin production along with the body not properly using the insulin it does produce, usually developing later in adulthood or age 40. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and involves increased insulin resistance that goes away after delivery but can lead to developing Type II diabetes later.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- DM & KomplikasiDocument98 pagesDM & KomplikasiRoby KieranNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry Reporting (Outline)Document6 pagesClinical Chemistry Reporting (Outline)Kim Lesley QuijanoNo ratings yet
- DM & KomplikasiDocument98 pagesDM & Komplikasisuho exoNo ratings yet
- Yr5 InsulinTherapyDocument61 pagesYr5 InsulinTherapyCrystel Tze JingNo ratings yet
- Diabetes 316 LecDocument6 pagesDiabetes 316 LecKatherine BautistaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes: M. Umar Aftab B.S.C (Hons) Emergency & Ict M.Phil (Physiology) PHD (Physiology)Document21 pagesDiabetes: M. Umar Aftab B.S.C (Hons) Emergency & Ict M.Phil (Physiology) PHD (Physiology)Gulzar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Insulin LisproDocument2 pagesDrug Study Insulin LisproEzron Kendrick Duran100% (1)
- Riwayat Pendidikan Riwayat PekerjaanDocument36 pagesRiwayat Pendidikan Riwayat PekerjaanRam PrototokonNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Diabetes Mellitus: Glucose RegulationDocument33 pagesPharmacology of Diabetes Mellitus: Glucose RegulationAbdullah RawashdehNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Finals ReviewerDocument11 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Finals ReviewerCzarena Ysabelle PayotNo ratings yet
- Duty Drug Study'sDocument7 pagesDuty Drug Study'sGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Hormones and Diabetes: Bantilan Borden EstreraDocument12 pagesPancreatic Hormones and Diabetes: Bantilan Borden EstreraKiarra Angelu Martinez EstreraNo ratings yet
- 1012 Endocrine Drug Table For Nurse StudyingDocument1 page1012 Endocrine Drug Table For Nurse StudyingJavier PulidoNo ratings yet
- Himawan - BPJSDocument26 pagesHimawan - BPJSAndi Upik FathurNo ratings yet
- DM & KomplikasiDocument98 pagesDM & KomplikasiAriyanaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Diabetes MellitusDocument3 pagesDrugs For Diabetes MellitusGerardLum100% (1)
- Week 7 Diabetes MellitusDocument8 pagesWeek 7 Diabetes MellitusJiro MarianoNo ratings yet
- Drug Table - EndocrineDocument6 pagesDrug Table - EndocrineVictoria DemmeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry ReviewerDocument44 pagesClinical Chemistry ReviewerMark Justin OcampoNo ratings yet
- Coass DM Mar 2010 (DR - THF)Document72 pagesCoass DM Mar 2010 (DR - THF)zayNo ratings yet
- What Is Diabetes?: Regulation of Plasma Glucose LevelDocument15 pagesWhat Is Diabetes?: Regulation of Plasma Glucose Levelمحمد القرنيNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15: Drugs For Diabetes: Introduction (ILO-1 - 2)Document38 pagesLesson 15: Drugs For Diabetes: Introduction (ILO-1 - 2)Ralp ManglicmotNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument71 pagesDiabetes Mellitusalexpharm100% (6)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studykuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and 2Document83 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Type 1 and 2ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- DPP 4Document20 pagesDPP 4Genix PharmaNo ratings yet
- Insulin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesInsulin Drug Studykuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Hormones and Antidiabetic DrugsDocument6 pagesPancreatic Hormones and Antidiabetic DrugsCas BuNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Management & Insulin InitiationDocument39 pagesDiabetes Management & Insulin InitiationTaufiqurrochman Nur AminNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 6.1 - Regulas Insulin (DR - Ali, SPPD)Document52 pagesKuliah 6.1 - Regulas Insulin (DR - Ali, SPPD)Erviana Dwi NurhidayatiNo ratings yet
- InsulinDocument2 pagesInsulinKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Insulin Detemir: (In-Su-Lin De-Te-Mir)Document2 pagesInsulin Detemir: (In-Su-Lin De-Te-Mir)FeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- StudyDocument2 pagesStudyit4728No ratings yet
- Endocrine Chart - DM MedsDocument7 pagesEndocrine Chart - DM MedsrhondaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of DiabetesDocument2 pagesPharmacology of Diabetesmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes DrugsDocument1 pageDiabetes DrugsFlowerNo ratings yet
- High Fat, Low Carb Diets and The Evidence (PDFDrive)Document160 pagesHigh Fat, Low Carb Diets and The Evidence (PDFDrive)gaetano confortoNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Written ReportDocument19 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Written ReportEros Victorino100% (2)
- Diabetes Mellitus 1Document5 pagesDiabetes Mellitus 1smurplerNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology ATI Study GuideDocument3 pagesPharmacology ATI Study Guidefaiza100% (1)
- Diabetes Drug Chart: Drug Action Use Side Effects Nursing ImplicationsDocument2 pagesDiabetes Drug Chart: Drug Action Use Side Effects Nursing ImplicationspulmonologistNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: EndocrinologyDocument6 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: EndocrinologyMiguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- Buku Diabetes MellitusDocument9 pagesBuku Diabetes MellitusanangNo ratings yet
- Antihyperglycemics DrugsDocument3 pagesAntihyperglycemics DrugsUma CrespoNo ratings yet
- Concept Map DMDocument2 pagesConcept Map DMRoshin Tejero100% (1)
- Insulin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesInsulin Drug StudyAziil Liiza100% (2)
- Endocrinology PDFDocument23 pagesEndocrinology PDFuyesNo ratings yet
- DB31 - Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus and HypoglycemiaDocument5 pagesDB31 - Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus and HypoglycemiaNeil Alcazaren かわいいNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus by DR Areef SirDocument15 pagesDiabetes Mellitus by DR Areef SirNoor HusainNo ratings yet
- Initation of Insulin - Final 2023Document27 pagesInitation of Insulin - Final 2023DEWI RIZKI AGUSTINANo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Med WardDocument13 pagesDrug Study - Med WardFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- Possible Nursing Care Plan Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Objective of Care Nursing InterventionDocument12 pagesPossible Nursing Care Plan Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Objective of Care Nursing InterventionClaire M. AuditorNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More CommonDocument2 pagesSubcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More Commonahmad ryanNo ratings yet
- Reg InsulinDocument2 pagesReg InsulinBIRIN, JEHAN KAYLE T.No ratings yet
- ApidraDocument4 pagesApidraRobert Ivan AgujarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Type 1 Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pagesPharmacology: Type 1 Diabetes MellitustabiNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Diabetes: Symptoms, Causes, and Solutions for Type 1 and 2 DiabetesFrom EverandDiabetes: Symptoms, Causes, and Solutions for Type 1 and 2 DiabetesNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Diet Plan for Diabetic Patients: Revolutionizing Diabetic NutritionFrom EverandUltimate Diet Plan for Diabetic Patients: Revolutionizing Diabetic NutritionNo ratings yet
Concept Map of DM
Concept Map of DM
Uploaded by
Leah Guade0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pagesThis document discusses the different types of diabetes mellitus. Type I diabetes is caused by an autoimmune destruction of the pancreatic islets resulting in little to no insulin production, most often developing at age 15. Type II diabetes involves insufficient insulin production along with the body not properly using the insulin it does produce, usually developing later in adulthood or age 40. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and involves increased insulin resistance that goes away after delivery but can lead to developing Type II diabetes later.
Original Description:
Original Title
77012478-Concept-Map-of-DM.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the different types of diabetes mellitus. Type I diabetes is caused by an autoimmune destruction of the pancreatic islets resulting in little to no insulin production, most often developing at age 15. Type II diabetes involves insufficient insulin production along with the body not properly using the insulin it does produce, usually developing later in adulthood or age 40. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and involves increased insulin resistance that goes away after delivery but can lead to developing Type II diabetes later.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pagesConcept Map of DM
Concept Map of DM
Uploaded by
Leah GuadeThis document discusses the different types of diabetes mellitus. Type I diabetes is caused by an autoimmune destruction of the pancreatic islets resulting in little to no insulin production, most often developing at age 15. Type II diabetes involves insufficient insulin production along with the body not properly using the insulin it does produce, usually developing later in adulthood or age 40. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and involves increased insulin resistance that goes away after delivery but can lead to developing Type II diabetes later.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
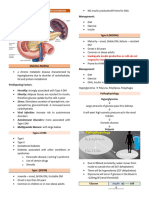
Diminished or absent insulin Insufficient insulin production
production. Ketoacidosis not common
Most often at age of 15 y.o. Classification Adult and 40 y.o. mostly
Autoimmune destruction of Type I/ IDDM Type II/NIDDM
Familial
pancreatic islets
Familial and lifelong Obesity creates insulin
demand that cannot be met
by amount of circulating
Hormone produce insulin present
Gestational
by the placenta has
May need insulin
↑ insulin resistance
4% of pregnant
women
Goes away during Diabetes
delivery
May develop Type Mellitus
3 P’s
Assessment Type I & II
II after 2 years Type I &II
Insulin Complica
Polyphagia
tions Type I: Type II: (much eating)
Hypoglycemia
Lipodystrophy
↓weight ↑weight Polydipsia
↑thirst Eye
Hormone counter T Bed problem
(↑ thirst)
Action
Poorly Controlled Diabetes R wetting Slow Polyuria
Diabetic Ketoacidosis E Rapid onset (↑urine
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemia A onset volume)
(now Ketotic Coma) T
Electrolyte Imbalance M
Long Term E
N Dx Fasting (above
T 125mg/100cc)
Angiopathy Glucose Tolerance Test
Peripheral Vascular Disease ( 2 hour value greater than
Retinopathy Insulin 200 mg/dl)
Nephropathy Glycosylated Hemoglobin
Oral
Neuropathy is ↑
Infection Hypoglycemic
Diet
↓insulin need, ↑Glucose
Exercise Submitted by: Leslie Marie D. Rendon BSN II-Beneficence
storage, ↓Glucose Fluctuation
You might also like
- DM & KomplikasiDocument98 pagesDM & KomplikasiRoby KieranNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry Reporting (Outline)Document6 pagesClinical Chemistry Reporting (Outline)Kim Lesley QuijanoNo ratings yet
- DM & KomplikasiDocument98 pagesDM & Komplikasisuho exoNo ratings yet
- Yr5 InsulinTherapyDocument61 pagesYr5 InsulinTherapyCrystel Tze JingNo ratings yet
- Diabetes 316 LecDocument6 pagesDiabetes 316 LecKatherine BautistaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes: M. Umar Aftab B.S.C (Hons) Emergency & Ict M.Phil (Physiology) PHD (Physiology)Document21 pagesDiabetes: M. Umar Aftab B.S.C (Hons) Emergency & Ict M.Phil (Physiology) PHD (Physiology)Gulzar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Insulin LisproDocument2 pagesDrug Study Insulin LisproEzron Kendrick Duran100% (1)
- Riwayat Pendidikan Riwayat PekerjaanDocument36 pagesRiwayat Pendidikan Riwayat PekerjaanRam PrototokonNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Diabetes Mellitus: Glucose RegulationDocument33 pagesPharmacology of Diabetes Mellitus: Glucose RegulationAbdullah RawashdehNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Finals ReviewerDocument11 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Finals ReviewerCzarena Ysabelle PayotNo ratings yet
- Duty Drug Study'sDocument7 pagesDuty Drug Study'sGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Hormones and Diabetes: Bantilan Borden EstreraDocument12 pagesPancreatic Hormones and Diabetes: Bantilan Borden EstreraKiarra Angelu Martinez EstreraNo ratings yet
- 1012 Endocrine Drug Table For Nurse StudyingDocument1 page1012 Endocrine Drug Table For Nurse StudyingJavier PulidoNo ratings yet
- Himawan - BPJSDocument26 pagesHimawan - BPJSAndi Upik FathurNo ratings yet
- DM & KomplikasiDocument98 pagesDM & KomplikasiAriyanaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Diabetes MellitusDocument3 pagesDrugs For Diabetes MellitusGerardLum100% (1)
- Week 7 Diabetes MellitusDocument8 pagesWeek 7 Diabetes MellitusJiro MarianoNo ratings yet
- Drug Table - EndocrineDocument6 pagesDrug Table - EndocrineVictoria DemmeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry ReviewerDocument44 pagesClinical Chemistry ReviewerMark Justin OcampoNo ratings yet
- Coass DM Mar 2010 (DR - THF)Document72 pagesCoass DM Mar 2010 (DR - THF)zayNo ratings yet
- What Is Diabetes?: Regulation of Plasma Glucose LevelDocument15 pagesWhat Is Diabetes?: Regulation of Plasma Glucose Levelمحمد القرنيNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15: Drugs For Diabetes: Introduction (ILO-1 - 2)Document38 pagesLesson 15: Drugs For Diabetes: Introduction (ILO-1 - 2)Ralp ManglicmotNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument71 pagesDiabetes Mellitusalexpharm100% (6)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studykuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and 2Document83 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Type 1 and 2ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- DPP 4Document20 pagesDPP 4Genix PharmaNo ratings yet
- Insulin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesInsulin Drug Studykuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Hormones and Antidiabetic DrugsDocument6 pagesPancreatic Hormones and Antidiabetic DrugsCas BuNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Management & Insulin InitiationDocument39 pagesDiabetes Management & Insulin InitiationTaufiqurrochman Nur AminNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 6.1 - Regulas Insulin (DR - Ali, SPPD)Document52 pagesKuliah 6.1 - Regulas Insulin (DR - Ali, SPPD)Erviana Dwi NurhidayatiNo ratings yet
- InsulinDocument2 pagesInsulinKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Insulin Detemir: (In-Su-Lin De-Te-Mir)Document2 pagesInsulin Detemir: (In-Su-Lin De-Te-Mir)FeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- StudyDocument2 pagesStudyit4728No ratings yet
- Endocrine Chart - DM MedsDocument7 pagesEndocrine Chart - DM MedsrhondaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of DiabetesDocument2 pagesPharmacology of Diabetesmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes DrugsDocument1 pageDiabetes DrugsFlowerNo ratings yet
- High Fat, Low Carb Diets and The Evidence (PDFDrive)Document160 pagesHigh Fat, Low Carb Diets and The Evidence (PDFDrive)gaetano confortoNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Written ReportDocument19 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Written ReportEros Victorino100% (2)
- Diabetes Mellitus 1Document5 pagesDiabetes Mellitus 1smurplerNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology ATI Study GuideDocument3 pagesPharmacology ATI Study Guidefaiza100% (1)
- Diabetes Drug Chart: Drug Action Use Side Effects Nursing ImplicationsDocument2 pagesDiabetes Drug Chart: Drug Action Use Side Effects Nursing ImplicationspulmonologistNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: EndocrinologyDocument6 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: EndocrinologyMiguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- Buku Diabetes MellitusDocument9 pagesBuku Diabetes MellitusanangNo ratings yet
- Antihyperglycemics DrugsDocument3 pagesAntihyperglycemics DrugsUma CrespoNo ratings yet
- Concept Map DMDocument2 pagesConcept Map DMRoshin Tejero100% (1)
- Insulin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesInsulin Drug StudyAziil Liiza100% (2)
- Endocrinology PDFDocument23 pagesEndocrinology PDFuyesNo ratings yet
- DB31 - Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus and HypoglycemiaDocument5 pagesDB31 - Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus and HypoglycemiaNeil Alcazaren かわいいNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus by DR Areef SirDocument15 pagesDiabetes Mellitus by DR Areef SirNoor HusainNo ratings yet
- Initation of Insulin - Final 2023Document27 pagesInitation of Insulin - Final 2023DEWI RIZKI AGUSTINANo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Med WardDocument13 pagesDrug Study - Med WardFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- Possible Nursing Care Plan Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Objective of Care Nursing InterventionDocument12 pagesPossible Nursing Care Plan Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Objective of Care Nursing InterventionClaire M. AuditorNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More CommonDocument2 pagesSubcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More Commonahmad ryanNo ratings yet
- Reg InsulinDocument2 pagesReg InsulinBIRIN, JEHAN KAYLE T.No ratings yet
- ApidraDocument4 pagesApidraRobert Ivan AgujarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Type 1 Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pagesPharmacology: Type 1 Diabetes MellitustabiNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Diabetes: Symptoms, Causes, and Solutions for Type 1 and 2 DiabetesFrom EverandDiabetes: Symptoms, Causes, and Solutions for Type 1 and 2 DiabetesNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Diet Plan for Diabetic Patients: Revolutionizing Diabetic NutritionFrom EverandUltimate Diet Plan for Diabetic Patients: Revolutionizing Diabetic NutritionNo ratings yet