Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsCENTRALDOGMA
CENTRALDOGMA
Uploaded by
opawbunaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Principle of Animal Physiology (Christopher D. Moyes, Patricia Schulte) Principle ofDocument763 pagesPrinciple of Animal Physiology (Christopher D. Moyes, Patricia Schulte) Principle ofKing Amv88% (8)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- 3 Chemlab Expt 12 Characterization of Nucleic AcidsDocument8 pages3 Chemlab Expt 12 Characterization of Nucleic AcidsAssumpta Minette BurgosNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- BMAT Biology Notes PackDocument41 pagesBMAT Biology Notes Packzozo 55No ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chapter 2: Chemistry Comes Alive (Marieb)Document17 pagesChapter 2: Chemistry Comes Alive (Marieb)Kayte Middleton100% (1)
- PC MidtermDocument1 pagePC MidtermopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Renaissance Architecture PDFDocument53 pagesRenaissance Architecture PDFopawbuna100% (1)
- Dear God,: IF I Am Wrong, Correct Me. IF I Am Lost, Guide Me. IF I Start To Give Up, Keep Me GoingDocument33 pagesDear God,: IF I Am Wrong, Correct Me. IF I Am Lost, Guide Me. IF I Start To Give Up, Keep Me GoingopawbunaNo ratings yet
- How Are You Judged in Cyberspace?: Task #5 Quiz On Analyzing StatementsDocument1 pageHow Are You Judged in Cyberspace?: Task #5 Quiz On Analyzing StatementsopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Olivia Wilson: It Project ManagerDocument1 pageOlivia Wilson: It Project ManageropawbunaNo ratings yet
- Task #8 Recognizing The Variety and The RegisterDocument1 pageTask #8 Recognizing The Variety and The RegisteropawbunaNo ratings yet
- It Is Also Famously Known As The Land of The "Ascending Dragon" For Its Geographical Shape On The World MapDocument1 pageIt Is Also Famously Known As The Land of The "Ascending Dragon" For Its Geographical Shape On The World MapopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Professional Goals: Rosa María AguadoDocument1 pageProfessional Goals: Rosa María AguadoopawbunaNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture: Bohol Island State University - Main Campus College of Engineeering & ArchitectureDocument47 pagesHistory of Architecture: Bohol Island State University - Main Campus College of Engineeering & ArchitectureopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Rufus Stewart: Project ManagerDocument1 pageRufus Stewart: Project ManageropawbunaNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal and Psychological Skills. There Was A Significant Relationship Between The EffectsDocument2 pagesInterpersonal and Psychological Skills. There Was A Significant Relationship Between The EffectsopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Yael Amari: SpecializationsDocument1 pageYael Amari: SpecializationsopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Of A Promise KeptDocument7 pagesOf A Promise KeptopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Learning COMPETENCIES: Text Information and MediaDocument20 pagesLearning COMPETENCIES: Text Information and MediaopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Relationships of Students Driving To Academic PerformancesDocument2 pagesRelationships of Students Driving To Academic PerformancesopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Research Instrument: Students' Interpersonal Behaviour in SchoolDocument2 pagesResearch Instrument: Students' Interpersonal Behaviour in SchoolopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Hahaybuhay 2Document36 pagesHahaybuhay 2opawbuna100% (1)
- The Chemical BondDocument47 pagesThe Chemical BondopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Survival KitDocument35 pagesLife Sciences P2 Survival KitMashamba CoutinhoNo ratings yet
- Bio 206 Tutorial - 02 & 03Document26 pagesBio 206 Tutorial - 02 & 03Brian HowardNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Biomolecules Test RevisitedDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Biomolecules Test RevisitedEps SabanganNo ratings yet
- Organic MoleculesDocument5 pagesOrganic MoleculesHyung BaeNo ratings yet
- 7 - DNA StructureDocument7 pages7 - DNA Structureأمجد هيصمNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument341 pagesBIOENERGETICSAvinashNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry For Nursing (Macromolecule)Document84 pagesBiochemistry For Nursing (Macromolecule)Muhammad Na'im83% (6)
- RPT - Cdri@yahoo - Co.in RP - Tripathi@cdri - Res.in: ST STDocument30 pagesRPT - Cdri@yahoo - Co.in RP - Tripathi@cdri - Res.in: ST STDr RC MishraNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Notes-1Document5 pages2.6 Notes-1John von steinbechNo ratings yet
- Macromolecular Structure and Analysis (Semester - 1) : Reg. NoDocument6 pagesMacromolecular Structure and Analysis (Semester - 1) : Reg. NoJnanendra SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Dna, Rna, Dan Protein 1Document26 pagesDna, Rna, Dan Protein 1R yNo ratings yet
- Grade Level 9 Quarter/Domain 1 Week and Day No. Page No. 1: I. ObjectivesDocument2 pagesGrade Level 9 Quarter/Domain 1 Week and Day No. Page No. 1: I. ObjectivesCharlesNo ratings yet
- Dna Extraction: MaterialsDocument6 pagesDna Extraction: MaterialsJhayquinoxNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument7 pagesBio MoleculesJatt PandherNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Nucleic Acids - Lecture - BIOCHEMISTRYDocument13 pagesQuiz On Nucleic Acids - Lecture - BIOCHEMISTRYAlliah Turingan100% (1)
- Isolation and Characterization of Nucleic Acids From An Onion (Allium Cepa)Document3 pagesIsolation and Characterization of Nucleic Acids From An Onion (Allium Cepa)AyaAlforqueNo ratings yet
- KTP Mcat Quicksheets PDFDocument24 pagesKTP Mcat Quicksheets PDFChristine Annmarie TapawanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - BiomoleculesDocument55 pagesLecture 2 - BiomoleculesRamkiNo ratings yet
- LipidDocument36 pagesLipidSina AgataNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules (HAND WRITTEN NOTES + PYQ) - CompressedDocument154 pagesBiomolecules (HAND WRITTEN NOTES + PYQ) - Compressedabhishekbhoi2006No ratings yet
- GCE Biology Mark Scheme June 2005Document38 pagesGCE Biology Mark Scheme June 2005Kishan KatwaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Chemistry AssignmentDocument19 pagesBiomolecules Chemistry AssignmentLEGEND CjNo ratings yet
- CH 6-4 - Building Blocks of LifeDocument31 pagesCH 6-4 - Building Blocks of Lifeapi-342334216No ratings yet
- Metabolism of NucleotidesDocument24 pagesMetabolism of NucleotidesAditya NayakNo ratings yet
- Academic Handbook 0Document386 pagesAcademic Handbook 0Steven BatuboNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: C G A T G T Identification Key P Phosphate Group D A C T GDocument4 pagesDNA Replication: C G A T G T Identification Key P Phosphate Group D A C T GDanielle DavisNo ratings yet
CENTRALDOGMA
CENTRALDOGMA
Uploaded by
opawbuna0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesCENTRALDOGMA
CENTRALDOGMA
Uploaded by
opawbunaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Molecular Biology - the branch of biology that oxygen residues, two of which may be expressed
deals with the structure and function of the as a hydroxyl group
macromolecules (e.g. proteins and nucleic acids) Purine - heterocyclic aromatic organic
essential to life compound, consisting of a pyrimidine ring
Acid - chemical species that donates protons or fused to an imidazole ring
hydrogen ions and/or accepts electrons Pyrimidine - aromatic heterocyclic organic
Base - release hydroxide (OH−) ions, are slippery compound similar to pyridine
to the touch, can taste bitter if an alkali, change Adenine - It is one of the four nucleobases in
the color of indicators the nucleic acid of DNA
Molecular entity - any constitutionally or Genome - the haploid set of chromosomes in
isotopically distinct atom, molecule, ion, ion pair, a gamete or microorganism, or in each cell of
radical, radical ion, complex, conformer, etc., a multicellular organism.
identifiable as a separately distinguishable entity Genomics - the branch of molecular biology
Replication- process by which a double-stranded concerned with the structure, function,
DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical evolution, and mapping of genomes.
DNA molecules Base pairing - two complementary
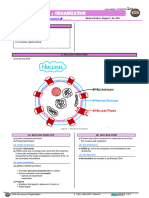
Expression - The process by which a genes coded nitrogenous molecules that are connected by
information is converted into the structures hydrogen bonds
present and operating in the cell Genetic Information - includes information
Mutation - the alteration of the nucleotide about an individual's genetic tests and the
sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or genetic tests of an individual
extrachromosomal DNA Transcription - process by which the
Molecule - a group of atoms bonded together, information in a strand of DNA is copied into a
representing the smallest fundamental unit of a new molecule of messenger RNA
chemical compound that can take part in a Translation - the process in which ribosomes
chemical reaction. in the cytoplasm or ER synthesize proteins
Genes - basic physical and functional unit of after the process of transcription of DNA to
heredity RNA in the cell's nucleus
RNA - polymeric molecule essential in various Amino acids - organic compounds that
biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation combine to form proteins
and expression of genes Proteins - macromolecules formed by amino
Nucleotides - a compound consisting of a acids
nucleoside linked to a phosphate group. Glycine - not considered an "essential amino
Nucleotides form the basic structural unit of acid" because the body can make it from
nucleic acids such as DNA other chemicals
Monomers - a molecule that can be bonded to Isoleucine - amino acid that is used in the
other identical molecules to form a polymer biosynthesis of proteins
Polynucleotides - a linear polymer whose Glutamine - important amino acid with many
molecule is composed of many nucleotide units, functions in the body
constituting a section of a nucleic acid molecule. Aliphatic - organic compound containing
Nitrogenous Base - simply a nitrogen-containing carbon and hydrogen joined together in
molecule that has the same chemical properties straight chains, branched chains, or non-
as a base aromatic rings
Pentose sugar - has five carbon atoms Polar- chemical species in which the
Phosphate group - molecule containing one distribution of electrons between the
atom of phosphorus covalently bound to four covalently bonded atoms is not even
Aromatic - property of cyclic (ring-shaped), metabolism, and ion transport as well as
planar (flat) structures with a ring of providing structural support for tissues
resonance bonds that gives increased stability Central dogma - describes the two-step
compared to other geometric or connective process, transcription and translation, by
arrangements with the same set of atoms which the information in genes flows into
Codon - sequence of three DNA or RNA proteins
nucleotides that corresponds with a specific Genetic code - the nucleotide triplets of DNA
amino acid or stop signal during protein and RNA molecules that carry genetic
synthesis information in living cells
Synthesis - production of chemical
compounds by reaction from simpler
materials
Distilled - having been purified by undergoing
heating and condensation
Cells - basic building blocks of living things
Nutrients - substance used by an organism to
survive, grow, and reproduce
Enzymes - biological molecules (typically
proteins) that significantly speed up the rate
of virtually all of the chemical reactions that
take place within cells
Ribosome - complex molecule made of
ribosomal RNA molecules and proteins that
form a factory for protein synthesis in cells
Antibodies - proteins produced and secreted
by B cells
Polymers - a substance that has a molecular
structure consisting chiefly or entirely of a
large number of similar units bonded together
Macromolecule - a molecule containing a very
large number of atoms, such as a protein,
nucleic acid, or synthetic polymer.
Hydrochloric acid- classified as strongly acidic
and can attack the skin over a wide
composition range, since the hydrogen
chloride completely dissociates in aqueous
solution.
Carbonic acid - chemical compound with the
chemical formula H₂CO₃.
Atoms - basic building blocks of ordinary
matter
Genetic blueprint - often referred to as the
blueprint for life, holds the map of your genes
Cellular function - include such basic life
processes as protein and lipid (fat) synthesis,
cell division and replication, respiration,
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Principle of Animal Physiology (Christopher D. Moyes, Patricia Schulte) Principle ofDocument763 pagesPrinciple of Animal Physiology (Christopher D. Moyes, Patricia Schulte) Principle ofKing Amv88% (8)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- 3 Chemlab Expt 12 Characterization of Nucleic AcidsDocument8 pages3 Chemlab Expt 12 Characterization of Nucleic AcidsAssumpta Minette BurgosNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- BMAT Biology Notes PackDocument41 pagesBMAT Biology Notes Packzozo 55No ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chapter 2: Chemistry Comes Alive (Marieb)Document17 pagesChapter 2: Chemistry Comes Alive (Marieb)Kayte Middleton100% (1)
- PC MidtermDocument1 pagePC MidtermopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Renaissance Architecture PDFDocument53 pagesRenaissance Architecture PDFopawbuna100% (1)
- Dear God,: IF I Am Wrong, Correct Me. IF I Am Lost, Guide Me. IF I Start To Give Up, Keep Me GoingDocument33 pagesDear God,: IF I Am Wrong, Correct Me. IF I Am Lost, Guide Me. IF I Start To Give Up, Keep Me GoingopawbunaNo ratings yet
- How Are You Judged in Cyberspace?: Task #5 Quiz On Analyzing StatementsDocument1 pageHow Are You Judged in Cyberspace?: Task #5 Quiz On Analyzing StatementsopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Olivia Wilson: It Project ManagerDocument1 pageOlivia Wilson: It Project ManageropawbunaNo ratings yet
- Task #8 Recognizing The Variety and The RegisterDocument1 pageTask #8 Recognizing The Variety and The RegisteropawbunaNo ratings yet
- It Is Also Famously Known As The Land of The "Ascending Dragon" For Its Geographical Shape On The World MapDocument1 pageIt Is Also Famously Known As The Land of The "Ascending Dragon" For Its Geographical Shape On The World MapopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Professional Goals: Rosa María AguadoDocument1 pageProfessional Goals: Rosa María AguadoopawbunaNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture: Bohol Island State University - Main Campus College of Engineeering & ArchitectureDocument47 pagesHistory of Architecture: Bohol Island State University - Main Campus College of Engineeering & ArchitectureopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Rufus Stewart: Project ManagerDocument1 pageRufus Stewart: Project ManageropawbunaNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal and Psychological Skills. There Was A Significant Relationship Between The EffectsDocument2 pagesInterpersonal and Psychological Skills. There Was A Significant Relationship Between The EffectsopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Yael Amari: SpecializationsDocument1 pageYael Amari: SpecializationsopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Of A Promise KeptDocument7 pagesOf A Promise KeptopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Learning COMPETENCIES: Text Information and MediaDocument20 pagesLearning COMPETENCIES: Text Information and MediaopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Relationships of Students Driving To Academic PerformancesDocument2 pagesRelationships of Students Driving To Academic PerformancesopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Research Instrument: Students' Interpersonal Behaviour in SchoolDocument2 pagesResearch Instrument: Students' Interpersonal Behaviour in SchoolopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Hahaybuhay 2Document36 pagesHahaybuhay 2opawbuna100% (1)
- The Chemical BondDocument47 pagesThe Chemical BondopawbunaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Survival KitDocument35 pagesLife Sciences P2 Survival KitMashamba CoutinhoNo ratings yet
- Bio 206 Tutorial - 02 & 03Document26 pagesBio 206 Tutorial - 02 & 03Brian HowardNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Biomolecules Test RevisitedDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Biomolecules Test RevisitedEps SabanganNo ratings yet
- Organic MoleculesDocument5 pagesOrganic MoleculesHyung BaeNo ratings yet
- 7 - DNA StructureDocument7 pages7 - DNA Structureأمجد هيصمNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument341 pagesBIOENERGETICSAvinashNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry For Nursing (Macromolecule)Document84 pagesBiochemistry For Nursing (Macromolecule)Muhammad Na'im83% (6)
- RPT - Cdri@yahoo - Co.in RP - Tripathi@cdri - Res.in: ST STDocument30 pagesRPT - Cdri@yahoo - Co.in RP - Tripathi@cdri - Res.in: ST STDr RC MishraNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Notes-1Document5 pages2.6 Notes-1John von steinbechNo ratings yet
- Macromolecular Structure and Analysis (Semester - 1) : Reg. NoDocument6 pagesMacromolecular Structure and Analysis (Semester - 1) : Reg. NoJnanendra SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Dna, Rna, Dan Protein 1Document26 pagesDna, Rna, Dan Protein 1R yNo ratings yet
- Grade Level 9 Quarter/Domain 1 Week and Day No. Page No. 1: I. ObjectivesDocument2 pagesGrade Level 9 Quarter/Domain 1 Week and Day No. Page No. 1: I. ObjectivesCharlesNo ratings yet
- Dna Extraction: MaterialsDocument6 pagesDna Extraction: MaterialsJhayquinoxNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument7 pagesBio MoleculesJatt PandherNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Nucleic Acids - Lecture - BIOCHEMISTRYDocument13 pagesQuiz On Nucleic Acids - Lecture - BIOCHEMISTRYAlliah Turingan100% (1)
- Isolation and Characterization of Nucleic Acids From An Onion (Allium Cepa)Document3 pagesIsolation and Characterization of Nucleic Acids From An Onion (Allium Cepa)AyaAlforqueNo ratings yet
- KTP Mcat Quicksheets PDFDocument24 pagesKTP Mcat Quicksheets PDFChristine Annmarie TapawanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - BiomoleculesDocument55 pagesLecture 2 - BiomoleculesRamkiNo ratings yet
- LipidDocument36 pagesLipidSina AgataNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules (HAND WRITTEN NOTES + PYQ) - CompressedDocument154 pagesBiomolecules (HAND WRITTEN NOTES + PYQ) - Compressedabhishekbhoi2006No ratings yet
- GCE Biology Mark Scheme June 2005Document38 pagesGCE Biology Mark Scheme June 2005Kishan KatwaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Chemistry AssignmentDocument19 pagesBiomolecules Chemistry AssignmentLEGEND CjNo ratings yet
- CH 6-4 - Building Blocks of LifeDocument31 pagesCH 6-4 - Building Blocks of Lifeapi-342334216No ratings yet
- Metabolism of NucleotidesDocument24 pagesMetabolism of NucleotidesAditya NayakNo ratings yet
- Academic Handbook 0Document386 pagesAcademic Handbook 0Steven BatuboNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: C G A T G T Identification Key P Phosphate Group D A C T GDocument4 pagesDNA Replication: C G A T G T Identification Key P Phosphate Group D A C T GDanielle DavisNo ratings yet