Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PG Organic Unit - II
PG Organic Unit - II
Uploaded by
Elakkiya shankar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views4 pagesThis document contains 53 multiple choice questions related to organic chemistry topics including reaction intermediates, carbenes, carbanions, carbocations, and free radicals. The questions assess understanding of hybridization, stability, formal charge, and reaction names.
Original Description:
Original Title
PG Organic Unit -II
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains 53 multiple choice questions related to organic chemistry topics including reaction intermediates, carbenes, carbanions, carbocations, and free radicals. The questions assess understanding of hybridization, stability, formal charge, and reaction names.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views4 pagesPG Organic Unit - II
PG Organic Unit - II
Uploaded by
Elakkiya shankarThis document contains 53 multiple choice questions related to organic chemistry topics including reaction intermediates, carbenes, carbanions, carbocations, and free radicals. The questions assess understanding of hybridization, stability, formal charge, and reaction names.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
SRI VIJAY VIDYALAYA COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE,
NALLAMPALLI
Accredited with ‘A’ grade by NAAC
M.Sc. ORGANIC CHEMISTRY –I
UNIT II
REACTION INTERMEDIATES, STRUCTURE AND REACTIVITY
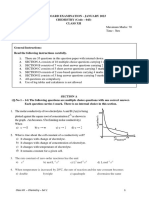
1. Which one is hybridization of carbenes?
(a) Sp2 singlet & Sp2 triplet b) Sp2 Doublet& Sp2 triplet c) Sp2 Doublet &Sp2 singlet
d) Sp2 singlet& Sp2 singlet
2. The order of decreasing stability of the following cations is:
(I) CH3C+HCH3 (II) CH3C+HOCH3 (III) CH3C+HCOCH3
a) III > II > I b) I > II > III c) II > I > III d) I > III > II
3. The hybridization of carbanion is
a) Sp b) Sp2 c) Sp3 d) Sp3d
4. What is the known name of the given reaction?
C6H5N+2 + CuX → C6H5X + N2 + Cu+
a) Gattermanns reaction b) Sandmeyers reaction c) Dehydrogenation reaction
d) Esterification reaction
5. What is the known name of the given reaction?
a) Gattermanns reaction b) Sandmeyers reaction c) Dehydrogenation reaction
d) Ullmann reaction
6. Select the correct statement from the following option.
a) Carbanion is the intermediate compound
b) In carbanion, central carbon atom carries negative charge
c) It possess an unshared pair of electron
d) All of the mentioned
7. The hybridisation of carbanion is
a) Sp b) Sp2 c) Sp3 d) Sp3d
8. The formal charge at the carbanion is
a) +1 b) -1 c) 0 d) +2
9. The geometry of carbanion is
a) Pyramidal b) Linear c) Tetrahedral d) Trigonal planar
10. The structure of carbanion is pyramidal but it undergoes rapid inversion similar to those of
amines.
a) True b) False
11. Negative charge of carbanion can be dispersed by
a) (+I) effect and resonance b) (-I) effect and resonance c) Hyper conjugation
d) (+M) effect and resonance
12. Which of the following carbanion is least stable?
a) 10 b) 20 c) 30 d) CH3
13. Which of the following carbanions is most stable?
a) 10 b) 20 c) 30 d) CH3
14. On increasing the number of alkyl groups, the stability of carbanions
a) Increases b) Decreases c) Remains same d) None of the mentioned
14. Due to (+I) effect, the methyl groups are electron accepting in nature.
a) True b) False
15. Stability of free radicals can be explained on the basis of
a) Inductive effect b) Electromeric effect c) Hyper conjugation d) Mesomeric effect
16. The hybridisation of carbocation is
a) Sp b) Sp2 c) Sp3 d) Sp3d
17. Arrange the following carbocations in the order of increasing stability.
a) Benzyl > 30 > 20 > 10 b) Benzyl > 10 > 20 > 30 c) 30 > 20 > 10 > Benzyl
0 0 0
d) 1 > 2 > 3 > Benzyl
18. The shape of carbocation is
a) Pyramidal b) Bent c) Linear d) Trigonal planar
19. Carbonium ions are the intermediates in which the positive charge is carried by the carbon
atom with ___________ electrons in the valence shell.
a) 6 b) 5 c) 4 d) 3
20. Positive charge of carbocations can be dispersed by
a) (+I) effect of alkyl group b) Resonance in allyl or benzyl carbocation
c) Hyperconjugation in 1 , 2 and 30 carbocations
0 0
d) All of the mentioned
21. Alkyl substitution at the carbon bearing positive charge stabilizes carbocations.
a) True b) False
22. The formal charge at the carbocation is equal to
a) -1 b) 0 c) +1 d) +2
23. The homolytic bond dissociation energy is inversely proportional to the
a) Bond length b) Ease of formation c) Dipole moment d) All of the mentioned
24. Which of the following free radical has the maximum ease of formation?
a) 10 b) 20 c) 30 d) CH3
25. Which one is stability of carbenes
a) Triplet carbene > Singlet carbene b) Singlet carbene >Triplet carbene c) Triplet carbene >
Triplet carbene d) None of these
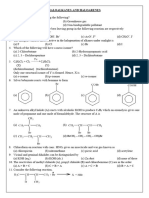
26. What do we get by chlorinating hydroxy or methoxybiphenyl?
a) Hydroxy hypochlorite b) Aniline c) Alkali hypochlorite d) None of the mentioned
27. What is the name of the following reaction: C6H5-NH2-HCL + HF —–> C6H5-NH2-HF +
HCl?
a) Addition reaction b) Substitution reaction c) Sandmeyer’s reaction d) None of the
mentioned
28. In Sandmeyer reaction, what is the intermediate compound formed before adding cuprous
halide?
a) Alcohol halide b) Diazonium halide c) Aqueous halide d) None of the mentioned
29. What is the general formula of Diazonium salt?
a) RN2+X– b) RN+ c) RXI d) RN2+HSO–2
30. What is the known name of the given reaction?
C6H5N+2 + CuCl → C6H5Cl + N2 + Cu+
a) Gattermanns reaction b) Sandmeyers reaction c) Dehydrogenation reaction
d) Esterification reaction
31. What is the known name of the given reaction?
[C6H5N+2]BF−4 → C6H5F + BF3 + N2
a) Gattermanns reaction b) Sandmeyers reaction c) Dehydrogenation reaction
d) Balz-Schiemann reaction
32. What do we get by chlorinating hydroxy or methoxybiphenyl?
a) Hydroxy hypochlorite b) Aniline c) Alkali hypochlorite d) None of the mentioned
Explanatiion: Ans C
Chlorinating Alkali hypochlorite we get hydroxy or methoxybiphenyl, the reaction is as
follows: C6H5-C6H5-OH ————–> C6H5-C6H5-Cl-OH.
33. What is the name of the following reaction: C6H5-NH2-HCL + HF —–> C6H5-NH2-HF + HCl?
a) Addition reaction b) Substitution reaction c) Sandmeyer’s reaction d) None of the
mentioned
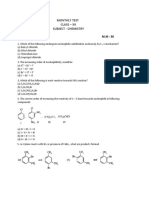
34. What is the known name of the given reaction?
[C6H5N+2]Cl− + C6H6 → C6H5−C6H5 + N2 + HCl
a) Gattermanns reactionb) Sandmeyers reaction c ) Gomberg–Bachmann reaction
d) Esterification reaction
35. What is the known name of the given reaction?
[C6H5N+2]Cl− + ArCH=CHCO2H → ArC=C−C6H5 + N2 + CO2 + HCl
a) Gattermanns reaction b) Sandmeyers reaction c) Meerwein reaction d) Balz-Schiemann
reaction
36. What is the known name of the given reaction?
a) Gattermanns reactionb) Sandmeyers reaction
c ) Pschorr Reaction d) Esterification reaction
37. What is the known name of the given reaction?
a) Gattermanns reactionb) Sandmeyers reaction
c ) Pschorr Reaction d) Esterification reaction
38. Which of the following is a permanent electron displacement effect?
a) Inductomeric b) Electromeric c) Inductive d) All of the mentioned
39. Arrange the following groups in the order of decreasing (+I) effect.
a) C6H5O– > COO– > CR3 > CHR2 > H b) C6H5O– > H > CR3 > CHR2 > COO–
c) CR3 > C6H5O– > H > COO– > CHR2 d) C6H5O– > COO– > CHR2 > CR3 > H
40. Arrange the following groups in the order of decreasing (-I) effect.
a) CN > F > Br > Cl > COOH > I > H b) COOH > CN > F > Br > Cl > I > H
c) H > COOH > CN > I > Cl > F > Cl d) CN > COOH > F > Cl > Br > I > H
41. Due to presence of C – X polar bond in alkyl halide, alkyl halides are
a) More reactive than corresponding alkane b) Less reactive than corresponding alkane
c) Equally reactive as corresponding alkane d) None of the mentioned
42. Identify the correct sequence according to electronegativity
a) F> NH2> CH3>OH` b) NH2`> F`>CH3`> OH` c) NH2`>OH`> CH3`>F`
d) F`> OH`>NH2`>CH3`
43. Identify the correct sequence according to electro negativity
a) F> NH2> CH3>OH` b) NH2`> F`>CH3`> OH` c) NH2`>OH`> CH3`>F`
d) F`> OH`>NH2`>CH3`
44. Which one is Hammett equation liner free energy relationship?
𝑲𝒑𝑨 𝐾0𝑝𝐴 𝐾𝑝𝐴 𝐾𝑝𝐴
a) log 𝑲𝟎𝒑𝑨 = σ b) log = σ# c) log 𝐾0𝑝𝐴 = σν d) log 𝐾0𝑝𝐴 = σл
𝐾𝑝𝐴
45. What is the known name of the given reaction?
a)Gomberg-Bachmann reaction b) Pschorr reaction c)Ullmann reaction d)Hunsdiecker
reaction
46. What is the known name of the given reaction?
a)Gomberg-Bachmann reaction b) Pschorr reaction c)Ullmann reaction d)Hunsdiecker
reaction
47. Which one is Taft Equation?
𝐾𝑝𝐴
a) Log10k=log10k0+ρ* σ*+δ Es b) og10k0= log10k l+ρ* σ*+δ Es c) log 𝐾0𝑝𝐴 = σ
𝐾0𝑝𝐴
d) log = σ#
𝐾𝑝𝐴
48. What is an equilibrium state?
a) Extent of reaction b) Optimum condition c) Least value product d) All of the mentioned
49. What is the driving force in a reaction?
a) Energy given b) Energy released c) Free energy d) None of the mentioned
50. What is ‘transition-state theory’ related to?
a) Free energy b) Activated complex c) Transition state d) All of the mentioned
51. Hydrolysis of ester is catalyzed by what?
a) Hydroxyl ion b) Nitrite ion c) Halogen d) All of the mentioned
52. Hydrolysis of alkyl halide is possible in which type of mechanism?
a) Unimolecular b) Bimolecular c) Both unimolecular and bimolecular d) None the
mentioned
53. Why is controlled oxidation needed?
a) High energy b) Loss of products c) Temperature d) All of the mentioned
You might also like
- SELF STUDY PAPER PT4TC Final 27.12.2017 DeboldDocument36 pagesSELF STUDY PAPER PT4TC Final 27.12.2017 Deboldakilchem1919No ratings yet
- TimidDocument13 pagesTimid公孫堂傲100% (2)
- Organic Sem III P 1Document10 pagesOrganic Sem III P 1Karamdev NishadNo ratings yet
- Radicals PDFDocument34 pagesRadicals PDFadelNo ratings yet
- Model Paper-4Document4 pagesModel Paper-4mkrishna collegeNo ratings yet
- Grade12Pre Boardexamination QPChemistryQPSET1Document7 pagesGrade12Pre Boardexamination QPChemistryQPSET1BigsmokeNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument6 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenespayoNo ratings yet
- MCQ, Case-Case Study and Assertion Reason Question Bank For Periodic Assessment 1Document42 pagesMCQ, Case-Case Study and Assertion Reason Question Bank For Periodic Assessment 1Mohammed AmmaarNo ratings yet
- 15 CHEMISTRY Some Basic Principles & Techniques HydrocarbonsDocument3 pages15 CHEMISTRY Some Basic Principles & Techniques HydrocarbonsHasan shaikhNo ratings yet
- Kcet Chemistry 2017 Key AnswersDocument7 pagesKcet Chemistry 2017 Key AnswersKumar HanumanthaiahNo ratings yet
- MCQ Module V Btech 2nd SemDocument6 pagesMCQ Module V Btech 2nd SemUttam NeelapureddyNo ratings yet
- Haloalkane and HaloareneDocument8 pagesHaloalkane and HaloareneSaransh KumarNo ratings yet
- Xi Chemistry Full Portion One Marks 1Document3 pagesXi Chemistry Full Portion One Marks 1ssanthoshjs47No ratings yet
- Xi Term 1 ChemistryDocument11 pagesXi Term 1 ChemistryBenson BennyNo ratings yet
- II PUCmid Term 23Document4 pagesII PUCmid Term 23Varun. B. CNo ratings yet
- DPT-48 Chem & Zoo Neet 01.03.24Document13 pagesDPT-48 Chem & Zoo Neet 01.03.24pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument4 pagesChemqzglsefafNo ratings yet
- HaloDocument17 pagesHaloadityakatariya157No ratings yet
- Halogen Derivetives of Alkane MCQDocument11 pagesHalogen Derivetives of Alkane MCQParshantKumarBajaj92% (13)
- MCQS of Inorganic BS6THDocument12 pagesMCQS of Inorganic BS6THPhoton Online Science AcademyNo ratings yet
- This Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingDocument8 pagesThis Test Contains A Total of 15 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingvarunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Chemistry MCQs PDFDocument33 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Chemistry MCQs PDFSanjana Sanjay100% (1)
- Ii Puc Chemistry 6 JanDocument4 pagesIi Puc Chemistry 6 JanAshok KalleppanavarNo ratings yet
- XI Chemistry QPDocument6 pagesXI Chemistry QPuddyan TripathiNo ratings yet
- Trial Exam DCS Che 12 2022 Final (MA)Document19 pagesTrial Exam DCS Che 12 2022 Final (MA)navin chhetriNo ratings yet
- 12thchemistrysamplepaper1 291223044313Document9 pages12thchemistrysamplepaper1 291223044313aditikharb2020No ratings yet
- Chemistry - Class XI - Question PaperDocument7 pagesChemistry - Class XI - Question PaperKnvigneshwarNo ratings yet
- Chemsitry Exclusive Sample PapersDocument9 pagesChemsitry Exclusive Sample Papersvdevant2006No ratings yet
- Dec 2013Document90 pagesDec 2013sridharR hahahaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Model Paper 5 (23-24) (2003 VERSION)Document4 pagesChemistry Model Paper 5 (23-24) (2003 VERSION)qzglsefafNo ratings yet
- Class 11sc 2021 PaperDocument10 pagesClass 11sc 2021 PaperAman KumarNo ratings yet
- 11th Chemistry Annual Exam ReappearDocument5 pages11th Chemistry Annual Exam ReappearGPS MAP UpdatesNo ratings yet
- ChemistryTestfinal - LASTDocument30 pagesChemistryTestfinal - LASTpurpleasma64No ratings yet
- I Preparatory I PU Chemistry QPDocument3 pagesI Preparatory I PU Chemistry QPadityahegde1122No ratings yet
- 11th - Chemistry MaterialDocument12 pages11th - Chemistry Materialprathiksha6660No ratings yet
- Neet Sample 1Document24 pagesNeet Sample 1iamniteshgargNo ratings yet
- NEET Sample Paper Model-1Document36 pagesNEET Sample Paper Model-1Shyamala GopinathNo ratings yet
- SINGLES Alkyl and Aryl Halides For Adv PDFDocument15 pagesSINGLES Alkyl and Aryl Halides For Adv PDFSahilNo ratings yet
- Set 2Document6 pagesSet 2sanjith4arisNo ratings yet
- Xii Chem QPDocument6 pagesXii Chem QPnrusinghsamal2006No ratings yet
- Xii Chemistry Practice Test - 16-10-2021Document9 pagesXii Chemistry Practice Test - 16-10-2021Manoj RacerNo ratings yet
- GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 60 QuestionsDocument67 pagesGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 60 Questionssradhasreeni68No ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Revision Test Question Papers EM 221210Document10 pagesNamma Kalvi 11th Chemistry Revision Test Question Papers EM 221210forever gamersNo ratings yet
- Review Final Exam. April. 2023Document24 pagesReview Final Exam. April. 2023Mohammad SaimonNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument8 pagesChemistryAmit MishraNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument5 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloareneskavitha2511977No ratings yet
- Monthly Test Class - Xii Subject - ChemistryDocument10 pagesMonthly Test Class - Xii Subject - ChemistryHîмanî JayasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Model-2, Nov-2021Document14 pagesChemistry Model-2, Nov-2021Elsa HarryNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC20CHEMISTRY20POST20TESTDocument13 pagesORGANIC20CHEMISTRY20POST20TESTJan Mill100% (1)
- Chem 001Document22 pagesChem 001Yashveer RaiNo ratings yet
- Pre Mid Term Examination (2022 - 23) Subject:Chemistry Class: Xiith Time: 1 Hour 30 Min M.M - 35Document3 pagesPre Mid Term Examination (2022 - 23) Subject:Chemistry Class: Xiith Time: 1 Hour 30 Min M.M - 35VatsalyaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Preboard Chemistry Answer KeyDocument7 pagesClass 12 Preboard Chemistry Answer KeyDiksha TNo ratings yet
- Chem Test No. 4 (Alkyl Halides, Alcohol and Phenols)Document4 pagesChem Test No. 4 (Alkyl Halides, Alcohol and Phenols)fahadmustafa100% (1)
- Term 1 Model Examination 2021-22 Chemistry (043) : General InstructionsDocument14 pagesTerm 1 Model Examination 2021-22 Chemistry (043) : General InstructionsAngelina SelinNo ratings yet
- Trial Exam DCS Che 12 2022 FinalDocument11 pagesTrial Exam DCS Che 12 2022 Finalnavin chhetriNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question BankDocument16 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Question BankBrown HustlerNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-03-05 at 12.32.19 AMDocument8 pagesScreenshot 2023-03-05 at 12.32.19 AMAnushka ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet