Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fundamental Concepts
Fundamental Concepts
Uploaded by
mahepOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fundamental Concepts
Fundamental Concepts
Uploaded by
mahepCopyright:
Available Formats
www.indiabix.
com
FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS
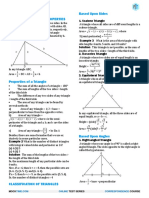
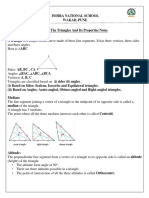
1. Results on Triangles:
i. Sum of the angles of a triangle is 180°.
ii. The sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side.
iii. Pythagoras Theorem:
In a right-angled triangle, (Hypotenuse)2 = (Base)2 + (Height)2.
iv. The line joining the mid-point of a side of a triangle to the positive vertex is called
the median.
v. The point where the three medians of a triangle meet, is called centroid. The
centroid divided each of the medians in the ratio 2 : 1.
vi. In an isosceles triangle, the altitude from the vertex bisects the base.
vii. The median of a triangle divides it into two triangles of the same area.
viii. The area of the triangle formed by joining the mid-points of the sides of a given
triangle is one-fourth of the area of the given triangle.
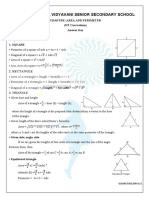
2. Results on Quadrilaterals:
i. The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
ii. Each diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into triangles of the same area.
iii. The diagonals of a rectangle are equal and bisect each other.
iv. The diagonals of a square are equal and bisect each other at right angles.
v. The diagonals of a rhombus are unequal and bisect each other at right angles.
vi. A parallelogram and a rectangle on the same base and between the same parallels
are equal in area.
vii. Of all the parallelogram of given sides, the parallelogram which is a rectangle has
the greatest area.
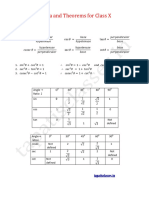
IMPORTANT FORMULAE
I. 1. Area of a rectangle = (Length x Breadth).
Area and Breadth Area
Length = .
Breadth = Length
II. 2. Perimeter of a rectangle = 2(Length + Breadth).
III. Area of a square = (side)2 = (diagonal)2.
IV. Area of 4 walls of a room = 2 (Length + Breadth) x Height.
V. 1. Area of a triangle = x Base x Height.
2. Area of a triangle = s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)
where a, b, c are the sides of the triangle and s = (a + b + c).
3. Area of an equilateral triangle 3
x (side)2.
= 4
4. Radius of incircle of an equilateral triangle of side a a
.
= 23
5. Radius of circumcircle of an equilateral triangle of side a a
.
= 3
6. Radius of incircle of a triangle of area and semi-perimeter s =
s
VI. 1. Area of parallelogram = (Base x Height).
2. Area of a rhombus = x (Product of diagonals).
3. Area of a trapezium = x (sum of parallel sides) x distance between them.
VII. 1. Area of a circle = R2, where R is the radius.
2. Circumference of a circle = 2 R.
3. Length of an arc 2 R
, where is the central angle.
= 360
4. Area of a sector 1 R2
(arc x R)= .
= 2 360
VIII. 1. Circumference of a semi-circle = R.
2. Area of semi-circle R2
.
= 2
You might also like
- Singapore Math Secondary Two Math Tutor 2BDocument472 pagesSingapore Math Secondary Two Math Tutor 2BMarie-Emmanuelle Lamelot100% (2)
- On The Desargues' Involution TheoremDocument11 pagesOn The Desargues' Involution TheoremStefy Stefan75% (4)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in CircleDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in CirclemuwahNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration FormulasDocument9 pagesSolid Mensuration Formulashenrytolentino50% (2)
- Geometry Formula SheetDocument2 pagesGeometry Formula SheetCherry DuldulaoNo ratings yet
- Area Important FormulasDocument3 pagesArea Important FormulasGopal PawarNo ratings yet
- AreasDocument4 pagesAreasvj kumarNo ratings yet
- Area, Surface Area, VolumeDocument11 pagesArea, Surface Area, VolumeSankaran Arumugam100% (1)
- Img 20210302 205750Document4 pagesImg 20210302 205750ts.hcltechbee2022No ratings yet
- Area and VolumesDocument3 pagesArea and VolumesSharon MantodeNo ratings yet
- Scan Aug 19, 2020Document1 pageScan Aug 19, 2020sandeepNo ratings yet
- Mensuration 1st ChapterDocument23 pagesMensuration 1st ChaptersanthoshNo ratings yet
- Mensuration ChapterDocument41 pagesMensuration ChapterBhumika DNo ratings yet
- 2dmensuration PDF 19 28Document10 pages2dmensuration PDF 19 28PRAKASH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Session 9 Area Volume and SurfaceDocument12 pagesSession 9 Area Volume and SurfaceRamnarayan MeenaNo ratings yet
- Img 20210302 205800Document4 pagesImg 20210302 205800Ramesh AnkathiNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes On Surface Areas and VolumesDocument11 pagesDetailed Notes On Surface Areas and VolumesVandana JohnNo ratings yet
- Important Formulas - AreaDocument7 pagesImportant Formulas - Areaharit_ecNo ratings yet
- Mensuration: Chapter - 5Document15 pagesMensuration: Chapter - 5Suvayan MohantyNo ratings yet
- S (S A) (S B) (S C) A+b+ CDocument3 pagesS (S A) (S B) (S C) A+b+ CSaideep AryalNo ratings yet
- Formulas For MensurationDocument8 pagesFormulas For MensurationMr. AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Important Formulas - Area: 3. Geometric Shapes, Solids and Important Formulas Geometric Shape Description FormulasDocument10 pagesImportant Formulas - Area: 3. Geometric Shapes, Solids and Important Formulas Geometric Shape Description FormulasAmey GudigarNo ratings yet
- Math TipsDocument5 pagesMath TipsDolly KumariNo ratings yet
- Mensuration FormulasDocument12 pagesMensuration FormulasAmey KaleNo ratings yet
- Area Wiki PDFDocument6 pagesArea Wiki PDFgooglepleckNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 FormulaDocument1 pageChapter 7 FormulaHan HtetNo ratings yet
- A KM/HR Ax: Problem On Trains KM/HR To M/s ConversionDocument7 pagesA KM/HR Ax: Problem On Trains KM/HR To M/s ConversionShiva RokaNo ratings yet
- Geometry: Triangles and Their Properties Based Upon SidesDocument34 pagesGeometry: Triangles and Their Properties Based Upon SidesVaseem Raza Mirza100% (1)
- Of Surfaces and Volumes of Solids.: DefinitionDocument7 pagesOf Surfaces and Volumes of Solids.: DefinitionSourav Kumar100% (1)
- Plane Geometry 1 & 3Document2 pagesPlane Geometry 1 & 3AhllyNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet Area and Perimeter Answer KeyDocument7 pagesGrade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet Area and Perimeter Answer Keygeetha100% (1)
- Mensuration: Basic Concepts and Important Formulas Equilateral TriangleDocument5 pagesMensuration: Basic Concepts and Important Formulas Equilateral TriangleSrinu MaddikuntlaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Concepts Results On TrianglesDocument5 pagesFundamental Concepts Results On TrianglesYellaturi Siva Kishore ReddyNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas ReviewDocument9 pagesGeometry Formulas Reviewleslybacallao305No ratings yet
- Shape Formulas For Area (A) and Circumference (C) : A BH X Base X Height A LW Length X WidthDocument16 pagesShape Formulas For Area (A) and Circumference (C) : A BH X Base X Height A LW Length X WidthDominic G. Casinto100% (1)
- Mensuration FormulasDocument6 pagesMensuration FormulasMahaveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Geometry FormulasDocument21 pagesGeometry FormulasHyma100% (1)
- Math Notes and FormulaeDocument32 pagesMath Notes and FormulaeAryaveer KumarNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Plane Geometry Introduction and Triangles 1Document7 pagesMODULE 1 Plane Geometry Introduction and Triangles 1CyndelleNo ratings yet
- Results On Triangles: Pythagoras Theorem: Median Centroid.: FormulaeDocument4 pagesResults On Triangles: Pythagoras Theorem: Median Centroid.: FormulaeKutbuddin JawadwalaNo ratings yet
- Mensuration FormulaDocument8 pagesMensuration FormulaSupratim Singh DevNo ratings yet
- Notes of The Triangles and Its PropertiesDocument3 pagesNotes of The Triangles and Its PropertiesIshanviNo ratings yet
- Geometry FormulasDocument5 pagesGeometry FormulasAlyzza Rose Pampliega LedesmaNo ratings yet
- A About Area and PerimeterDocument11 pagesA About Area and PerimeterAmiel ColanoNo ratings yet
- Plane & Solid Geometry HandoutsDocument14 pagesPlane & Solid Geometry HandoutsChristian AntonioNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet 2 Area and PerimeterDocument8 pagesGrade 9 Maths IIT Worksheet 2 Area and PerimetergeethaNo ratings yet
- Area and Perimeter: WorksheetDocument4 pagesArea and Perimeter: WorksheetTaseen TanvirNo ratings yet
- Formula and Theorems For Class XDocument12 pagesFormula and Theorems For Class XPraneel .SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1SL TRAVELERNo ratings yet
- Geometry MathDocument15 pagesGeometry Maths sekhar mahalikNo ratings yet
- Micro Project MathsDocument15 pagesMicro Project Mathsharshawardhan deshmukhNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument2 pagesGeometryKolla ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Review Sheets Geometry MATH 097: A Summary of Concepts Needed To Be Successful in MathematicsDocument10 pagesReview Sheets Geometry MATH 097: A Summary of Concepts Needed To Be Successful in Mathematicsyus accNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Maths Formula Chapter 11 PDFDocument4 pagesClass 8 Maths Formula Chapter 11 PDFmekala deevena kumariNo ratings yet
- Alsdkufashjdkfbvfkljsdghfasdhjbfvaks. Day2Document2 pagesAlsdkufashjdkfbvfkljsdghfasdhjbfvaks. Day2Jayson AlparazNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Geometry: MSJC San Jacinto CampusDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Geometry: MSJC San Jacinto Campusbonifacio gianga jrNo ratings yet
- Lateral Surface AreaDocument16 pagesLateral Surface Areafordmay100% (1)
- Mensuration FormulasDocument8 pagesMensuration FormulasRamanaReddyNo ratings yet
- Mensuration: Mensuration Is The Branch of Mathematics Which Deals WithDocument7 pagesMensuration: Mensuration Is The Branch of Mathematics Which Deals WithRekha DhanyaNo ratings yet
- Mensuration FormulasDocument9 pagesMensuration Formulasrafiqkasuri100% (1)
- Mathe Formula Grade 8Document6 pagesMathe Formula Grade 8hasan alaaNo ratings yet
- Math - 6 Module - Q4 - M1Document11 pagesMath - 6 Module - Q4 - M1Miriam Haber BarnachiaNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Section: - ScoreDocument3 pagesName: - Date: - Section: - ScoreJohn Richmond CadagNo ratings yet
- Plane & Solid Geometry HandoutsDocument14 pagesPlane & Solid Geometry HandoutsChristian Antonio100% (3)
- Heron FormulaDocument4 pagesHeron FormulakeertimmunishNo ratings yet
- Geom Unit 8 Teacher Notes 2019Document17 pagesGeom Unit 8 Teacher Notes 2019Brayden BiggsNo ratings yet
- Mensuration NotesDocument19 pagesMensuration NotesMuhammad Baig MirzaNo ratings yet
- J (UV ( - MZH$) : Series PPQQA/1 SET 2Document11 pagesJ (UV ( - MZH$) : Series PPQQA/1 SET 2R SubbaramaiahNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Cycloidal Curves - Question Bank PDFDocument2 pages1.3 Cycloidal Curves - Question Bank PDFMartin De Boras Pragash100% (3)
- Identify Solid Figure Mathematics Year 7 - GeometryDocument2 pagesIdentify Solid Figure Mathematics Year 7 - GeometryOktavianaalfNo ratings yet
- Interior and Exterior Angles of PolygonsDocument16 pagesInterior and Exterior Angles of PolygonsKENO MARTIN ADVIENTONo ratings yet
- Additional Problems For CET 2019 PDFDocument7 pagesAdditional Problems For CET 2019 PDFKenneth Ivan RamosNo ratings yet
- E5 PPTDocument77 pagesE5 PPTpkkavithaaNo ratings yet
- ProblemDescriptionBook3 NDocument78 pagesProblemDescriptionBook3 NVo Duc DienNo ratings yet
- MATHS SA - Msa Revision Package SolutionsDocument7 pagesMATHS SA - Msa Revision Package SolutionsglenlcyNo ratings yet
- CPP-Solution of Triangle SMC NEWDocument2 pagesCPP-Solution of Triangle SMC NEWtechnical yogeshNo ratings yet
- Soal Uas Kelas 1 SD Saraswati 22Document3 pagesSoal Uas Kelas 1 SD Saraswati 22Nanda RusistaNo ratings yet
- 11-Arcs and ChordsDocument4 pages11-Arcs and ChordsMichael YazonNo ratings yet
- Chapter ReviewDocument5 pagesChapter Reviewapi-232613595No ratings yet
- Computer Aided Engineering DrawingDocument136 pagesComputer Aided Engineering DrawingGuru SaranNo ratings yet
- 6 Triangle and Its Properties PDFDocument1 page6 Triangle and Its Properties PDFRamesh rajNo ratings yet
- Euclid Element's Book3 Dan 4Document35 pagesEuclid Element's Book3 Dan 4Christina SusiloNo ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical Trigonometry Refresher ModuleDocument3 pagesPlane and Spherical Trigonometry Refresher ModuleMohamad NaloNo ratings yet
- 10th Cbse Final All ChaptersDocument36 pages10th Cbse Final All ChaptersNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- Extra Problems For Jacobs Using GSPDocument21 pagesExtra Problems For Jacobs Using GSPpeter_ash_4No ratings yet
- 3.3 Further Trigonometric Equations (2. Medium) QPDocument7 pages3.3 Further Trigonometric Equations (2. Medium) QPjaiNo ratings yet
- Mensuration and Mensuration Formulas PDFDocument5 pagesMensuration and Mensuration Formulas PDFHarsh GuptaNo ratings yet