Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab Values Table PedSAP
Lab Values Table PedSAP
Uploaded by
nikoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab Values Table PedSAP
Lab Values Table PedSAP
Uploaded by
nikoCopyright:
Available Formats
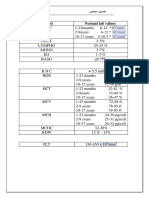
Chloride (Cl) All ages 95–108 mEq/L
C-reactive protein (CRP) All ages < 0.8 mg/dL
Creatin kinase (CK) Cord blood 70 380 units/L
REFERENCE VALUES FOR COMMON LABORATORY TESTS Creatinine (clearance) (CrCl) All ages 90–140 mL/minute/1.73 m2
Serum Chemistries Reference Range γ-Glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) Newborn– < 2 months 12–147 units/L
Albumin Premature 1 day 1.8–3 g/dL 2– < 4 months 8–90 units/L
Full-term < 6 days 2.5–3.9 g/dL 4 months – 19 years 5–32 units/L
8 days–1 year 1.9–4.9 g/dL Adult 7-49 units/L
1–3 years 3.4–5.2 g/dL Glucose, serum Cord blood 45–96 mg/dL
4–19 years 3.5–5.6 g/dL Premature 20–60 mg/dL
Ammonia Newborn – Child 29-150 mcg/dL Newborn 1 day 40–60 mg/dL
Adult 15–60 mcg/dL Newborn > 1 day 50–90 mg/dL
Amylase 1–19 years 30–100 units/L Child 60–100 mg/dL
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) ≤ 7 days 6–40 units/L Adult 70–105 mg/dL
8–30 days: Hemoglobin A1C (A1C) All ages 4%–6%
Male 10 to 40 units/L Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) Newborn 180–2000 units/L
Female 8–32 units/L 1 month – < 1 year 170–580 units/L
1–12 months 12–45 units/L Lipase 1–18 years
1–9 years 3–216
110–500units/L
units/L
1–19 years 5–55 units/L Magnesium All agesyears
10–19 1.5–2.5
100–330 mEq/L
units/L
Alkaline phosphatase (ALK) 1-12 months 150-420 units/L Osmolality,
Lipase serum All
1–18ages
years 266–295 mOsm/kg
3–216 units/L
1–9 years 100–420 units/L Phosphorus
Magnesium (inorganic) (PO4) Newborn
All ages 0–5 days 4.5–9 mg/dL
1.5–2.5 mEq/L
10–11 years 140–560 units/L Osmolality, serum 1–3 years
All ages 3.8–6.5
266–295mg/dL
mOsm/kg
12–13 years: Phosphorus (inorganic) (PO4) 4–11 years0–5 days
Newborn 3.2–5.8 mg/dL
4.5–9 mg/dL
Male 100–495 units/L 12–15 years
1–3 years 2.9–5.4 mg/dL
3.8–6.5 mg/dL
Female 100–420 units/L 16–19 years
4–11 years 2.4–4.7
3.2–5.8mg/dL
mg/dL
14–15 years: Potassium (K) Newborn
12–15 years 3.7–7.2
2.9–5.4mEq/L
mg/dL
Male 100–525 units/L 1– < 3 months
16–19 years 4.0–6.2 mEq/L
2.4–4.7 mg/dL
Female 70–320 units/L Potassium (K) 3Newborn
months–1 year 3.4–5.6 mEq/L
3.7–7.2 mEq/L
16–19 years: 1–16 years
1– < 3 months 3.5–5.1
4.0–6.2mEq/L
mEq/L
Male 65–260 units/L Prealbumin >3 1months–1
month year 8–42 mg/dL
3.4–5.6 mEq/L
Female 50–320 units/L Sodium (Na) All
1–16ages
years 130–147 mEq/L
3.5–5.1 mEq/L
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) Newborn ≤ 7 days: Transferrin
Prealbuminsaturation All
> 1 ages
month 10–50%
8–42 mg/dL
Male 30–150 units/L Uric acid,(Na)
Sodium serum Newborn–14
All ages years 1–7 mg/dLmEq/L
130–147
Female 24–150 units/L Transferrin saturation All ages 10–50%
8 days – < 12 months 9–80 units/L Uric acid, serum Newborn–14 years 1–7 mg/dL
Hematology
1–3 years 20–60 units/L
3–9 years 15–50 units/L
Age Hemoglobin Hematocrit RBC MCV MCH MCHC Plt WBC
10–15 years 10–40 units/L Hematology
(g/dL) (%) (× 106 (fL) (pg/cell) (g/dL) (mm3) (× 103
16–19 years: 3 cells/mm3)
Male 15–45 units/L Age Hemoglobin Hematocrit cells/mm
RBC ) MCV MCH MCHC Plt WBC
≤ 30 15–24
(g/dL) 44–70
(%) 4–5.5 6 99–
(fL) 33–39 30–36
(pg/cell) (g/dL) (mm 84– 3 9.1–34
) (× 103
Female 5 to 30 units/L (× 10
days 3 115 478a cells/mm3)
Bilirubin, direct Newborn < 0.6 mg/dL cells/mm )
1–23 10.5–14 32–42 72– 24–30 150– 6–17
≥ 1 month < 0.2 mg/dL ≤ 30 15–24 44–70 4–5.5 99– 33–39 30–36 84– 9.1–34
mo 88 450 a
Bilirubin, total Cord blood < 2 mg/dL days 115 478
2–9 yr 11.5–14.5 33–43 76– 25–31 4–15.5
Premature < 6 days < 16 mg/dL 1–23 10.5–14 32–42 72– 24–30 150– 6–17
90
Full-term < 6 days < 12 mg/dL mo 88 450
10–17 12.5–16.1 36–47 78– 26–32 4–13.5
1 month– < 12 months < 2 mg/dL 2–9 yr 11.5–14.5 33–43 76– 25–31 4–15.5
yr 95
1–19 years < 1.5 mg/dL 90
(male)
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) All ages 2–20 mg/dL 10–17 12.5–16.1 36–47 78– 26–32 4–13.5
10–17 12–15 35–45 78– 26–32
yr 95
yr 95
Calcium, ionized Cord blood 5–6 mg/dL (male)
(female)
Newborn 3–24 hours 4.3–5.1 mg/dL 10–17 12–15 35–45 78– 26–32
≥ 18 yr 13.5–18 42–52 78– 27–31
Newborn 24–38 hours 4–4.7 mg/dL yr 95
(male) 100
≥ 2 days 4.8–4.92 mg/dL (female)
≥ 18 yr 12.5–16 37–47 78– 27–31
Calcium, total serum Cord blood 9.5–11.5 mg/dL ≥ 18 yr 13.5–18 42–52 78– 27–31
(female) 100
Newborn 3–24 hours 9–10.6 mg/dL a (male) 100
Value for ages 0–7 days; for age > 7 days, similar to range for all patient ages.
Newborn 24–48 hours 7–12 mg/dL ≥ 18 yr 12.5–16 37–47 78– 27–31
4–7 days 6.7–10.9 mg/dL (female) 100
aBlood Gases
Child 8.8–10.8 mg/dL Value for ages 0–7 days; for age > 7 days, similar to range for all patient ages.
Arterial Capillary Venous
Adolescent–Adult 8.4–10.2 mg/dL
pH 7.35–7.45 7.35–7.45 7.32–7.42
Carbon dioxide (venous) (CO2) All ages 20–30 mEq/L
Partial pressure of 32–48 mm Hg 35–45 mm Hg 38–52 mm Hg
Chloride (Cl) All ages 95–108 mEq/L carbon dioxide
C-reactive protein (CRP) All ages < 0.8 mg/dL (PCO2)
Creatine kinase (CK) Cord blood 70–380 units/L Partial pressure of 70–108 mm Hg 60–80 mm Hg 24–48 mm Hg
Newborn 5–8 hours 214–1175 units/L oxygen (PO2)
Newborn 24–33 hours 130–1200 units/L Oxygen saturation 90–95% 90–95% 40–70%
Newborn 72–100 hours 87–1578 units/L (SaO2)
Adult 5–200 units/L Serum bicarbonate 19–28 mEq/L 19–25 mEq/L 19–25 mEq/L
Creatinine, serum (SCr) Cord blood 0.6–1.2 mg/dL (HCO3)
Newborn 0.3–1 mg/dL a
Values given in this table are commonly accepted reference ranges compiled from many sources. Patient-specific
Child 0.3–0.7 mg/dL goals may
aValues differ
given depending
in this on age, sex,
table are commonly clinical
accepted condition,
reference and
ranges the laboratory
compiled from manymethodology used to perform
sources. Patient-specific the
goals may
Adolescent 0.5–1 mg/dL differ
assay.depending on age, sex, clinical condition, and the laboratory methodology used to perform the assay.
Adult male 0.9–1.2 mg/dL Informationfrom:
Information from: Pediatric
Pediatric and and Neonatal
Neonatal Dosage Dosage Handbook,
Handbook, 21st ed. 21st ed. Ohio:
Hudson, Hudson, Ohio: Lexicomp,
Lexicomp, 2014; AMA2014;
Manual AMA Man-
of Style,
Adult female 0.6-1.1 mg/dL 10th ed.Style,
ual of New York: Oxford
10th ed. NewUniversity Press,University
York: Oxford 2007; AyersPress,
P, Warrington L. Diagnosis
2007; Ayers and treatment
P, Warrington of simple
L. Diagnosis andacid-base
treatment
Creatinine (clearance) (CrCl) All ages 90–140 mL/minute/1.73 m2 disorders. Nutr Clin Pract 2008;23:122-7; DiPiro JT, Talbert RL, Yee GC, et al., eds. Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic
of simple acid-base disorders. Nutr Clin Pract 2008;23:122-7; DiPiro JT, Talbert RL, Yee GC, et al., eds. Pharma-
Approach, 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical, 2011; Lee M. Basic Skills in Interpreting Laboratory Data, 4th ed.
cotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach, 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical, 2011; Lee M. Basic Skills in
γ-Glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) Newborn– < 2 months 12–147 units/L Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, 2009; and MUSC Health, Laboratory Services. Test Directory
Interpreting
and Specimen Laboratory Data, 4thCharleston,
Collection Handbook. ed. Bethesda, MD: American
SC: MUSC Pathology Society of Health-System
and Laboratory Pharmacists,
Services, 2008–2009; 2009; Lane
The Harriet and
2– < 4 months 8–90 units/L MUSC Health, Laboratory Services. Test Directory
Handbook, 21st ed. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: Elsevier,and Specimen Collection Handbook. Charleston, SC: MUSC
2018.
4 months – 19 years 5–32 units/L Pathology and Laboratory Services, 2008–2009; The Harriet Lane Handbook, 21st ed. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania:
You might also like
- Normal Paediatric Lab ValuesDocument6 pagesNormal Paediatric Lab ValuesRITESH SINGH100% (1)
- Blank Lab Work ReportsDocument8 pagesBlank Lab Work ReportsPamTremble100% (4)
- Laboratory Critical - Panic Value List - Stanford Health CareDocument4 pagesLaboratory Critical - Panic Value List - Stanford Health CareLABNo ratings yet
- Lab Values Table PedSAP PDFDocument1 pageLab Values Table PedSAP PDFdrmanoj13No ratings yet
- Panic (Critical) Values 06-14-2021 0Document2 pagesPanic (Critical) Values 06-14-2021 0JorgeNo ratings yet
- III YEAR Paed Reference RangesDocument5 pagesIII YEAR Paed Reference RangesEllen AngelNo ratings yet
- Normal Laboratory Values For ChildrenDocument6 pagesNormal Laboratory Values For ChildrenWilsonNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Normal Reference Ranges: Children's Hospital and Health Center - San DiegoDocument6 pagesLaboratory Normal Reference Ranges: Children's Hospital and Health Center - San Diegoوليد. وفي الروحNo ratings yet
- Reference Values For ChildrenDocument3 pagesReference Values For ChildrenHussein MohsenNo ratings yet
- Blood Test Reference Ranges For ChildrenDocument1 pageBlood Test Reference Ranges For ChildrenBrandon FedynichNo ratings yet
- NR 446 Week 5 ATI Weekly Tips PediatricsDocument18 pagesNR 446 Week 5 ATI Weekly Tips PediatricsChristine LansdownNo ratings yet
- Pathology Normal ValuseDocument1 pagePathology Normal ValuseDISTRICT HOSPITAL LABNo ratings yet
- 2017 April, Aljazi Pediatric Nutritional AssessmentDocument19 pages2017 April, Aljazi Pediatric Nutritional AssessmentEleaNo ratings yet
- Valores de Laboratorio Harriet LaneDocument14 pagesValores de Laboratorio Harriet LaneRonald MoralesNo ratings yet
- PL Diagnostics: M.V.P.Lane PLOT 39-SEC-3Document8 pagesPL Diagnostics: M.V.P.Lane PLOT 39-SEC-3JabuuPLayzNo ratings yet
- G. SatyavathiDocument11 pagesG. SatyavathiJabuuPLayzNo ratings yet
- PL Diagnostics: M.V.P.Lane PLOT 39-SEC-3Document11 pagesPL Diagnostics: M.V.P.Lane PLOT 39-SEC-3JabuuPLayzNo ratings yet
- Normal Blood Values Arterial Blood Gas Electrolytes/Blood ChemDocument1 pageNormal Blood Values Arterial Blood Gas Electrolytes/Blood ChemHazel Grace GuNo ratings yet
- L. Bhagya LakshmiDocument14 pagesL. Bhagya LakshmiJabuuPLayzNo ratings yet
- Harriet LaneDocument14 pagesHarriet LaneTony DawaNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Function PanelDocument3 pagesHepatic Function PanelMajeed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Labs Harriet LaneDocument18 pagesLabs Harriet LaneRodrigo SandovalNo ratings yet
- Normal ValuesDocument12 pagesNormal ValuessweetyjonasNo ratings yet
- Tests SI Units Traditional Units: Clinical Laboratory Tests - Normal ValuesDocument2 pagesTests SI Units Traditional Units: Clinical Laboratory Tests - Normal ValuesAnonymous OvwqAMyrWxNo ratings yet
- Chemical Pathology Reference Range 2017Document19 pagesChemical Pathology Reference Range 2017Shobana RaveendranNo ratings yet
- Viewing Online Investiagation ResultDocument2 pagesViewing Online Investiagation ResultLOKESH KUMAR MEENANo ratings yet
- Gregory S Pediatric Anesthesia - 2011 - GregoryDocument15 pagesGregory S Pediatric Anesthesia - 2011 - GregoryANISA RIFKA RIDHONo ratings yet
- Vasavi Diagnostic Laboratory: Church Road, Chitradurga - 577501Document2 pagesVasavi Diagnostic Laboratory: Church Road, Chitradurga - 577501ksnchitradurgaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Normal Laboratory ValuesDocument15 pagesPediatric Normal Laboratory ValuesAkhmad Dani AwaludinNo ratings yet
- Normal Values e PDFDocument2 pagesNormal Values e PDFManishNo ratings yet
- Reference Value TersacoDocument2 pagesReference Value TersacoSud007jbNo ratings yet
- Mayo Clinic Laboratories Critical Values / Critical Results ListDocument4 pagesMayo Clinic Laboratories Critical Values / Critical Results Listlab adjidarmoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Normal CBC Ranges: W.El Gendy MD Prof. Clinical Pathology Alexandria UniversityDocument24 pagesPediatric Normal CBC Ranges: W.El Gendy MD Prof. Clinical Pathology Alexandria Universitywaramlah ramlanNo ratings yet
- Erythrocytes (RBCS) Platelets (Cellular Fragments) Leukocytes (WBCS) I) Neutrophils Ii) Eosinophils Iii) Basophils Lymphocytes MonocytesDocument4 pagesErythrocytes (RBCS) Platelets (Cellular Fragments) Leukocytes (WBCS) I) Neutrophils Ii) Eosinophils Iii) Basophils Lymphocytes MonocytesGenera Rose Radaza VillaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Values DocumentDocument5 pagesLaboratory Values Documentbfqbn4zbyrNo ratings yet
- HCN 148-12 - Pept Helpful Hints - r3Document2 pagesHCN 148-12 - Pept Helpful Hints - r3Rastia AlimmattabrinaNo ratings yet
- Reference Ranges Feb 18 FINALDocument5 pagesReference Ranges Feb 18 FINALNAMPEWO ELIZABETHNo ratings yet
- Form HSL Pemeriksaan TernewDocument3 pagesForm HSL Pemeriksaan Ternewvika eenNo ratings yet
- Cifras de Refer en CIA de Laboratorio - Harriet LaneDocument18 pagesCifras de Refer en CIA de Laboratorio - Harriet LaneLicea Bco JoseNo ratings yet
- Critical Result List Mayo ClinicDocument4 pagesCritical Result List Mayo ClinicODH LaboratoryNo ratings yet
- YAsh Report Dec PDFDocument2 pagesYAsh Report Dec PDFyashNo ratings yet
- Valori NormaleDocument4 pagesValori NormaleDragomirescu Ana-cristinaNo ratings yet
- Adult (Post Pubescent) Range Paediatric (Age If Applicable) RangeDocument9 pagesAdult (Post Pubescent) Range Paediatric (Age If Applicable) RangeKoas bedahNo ratings yet
- Buletin Lp.3Document2 pagesBuletin Lp.3Joana B. NikolovaNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Reference Ranges Jan 18Document5 pagesPaediatric Reference Ranges Jan 18Rajesh BaluNo ratings yet
- Https:Jetmapp - orbundsis.com:Einstein-freshair:Videos::102793DigitalDownload LabValues NurseInTheMaking 2pagesDocument5 pagesHttps:Jetmapp - orbundsis.com:Einstein-freshair:Videos::102793DigitalDownload LabValues NurseInTheMaking 2pagesamazonian005100% (1)