Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gold
Gold
Uploaded by
huso husicOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gold
Gold
Uploaded by
huso husicCopyright:
Available Formats
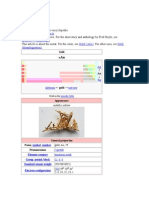
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from Latin: aurum) and atomic number 79,
making it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. In its purest form, it is
a bright, slightly reddish yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is
a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is
solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native) form, as nuggets or
grains, in rocks, in veins, and in alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native
element silver (as electrum) and also naturally alloyed with copper and palladium. Less
commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides).
Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia, a mixture of nitric
acid and hydrochloric acid, which forms a soluble tetrachloroaurate anion. Gold is insoluble
in nitric acid, which dissolves silver and base metals, a property that has long been used
to refine gold and to confirm the presence of gold in metallic objects, giving rise to the term acid
test. Gold also dissolves in alkaline solutions of cyanide, which are used
in mining and electroplating. Gold dissolves in mercury, forming amalgam alloys, but this is not
a chemical reaction.
A relatively rare element,[6][7] gold is a precious metal that has been used for coinage, jewelry, and
other arts throughout recorded history. In the past, a gold standard was often implemented as
a monetary policy, but gold coins ceased to be minted as a circulating currency in the 1930s, and
the world gold standard was abandoned for a fiat currency system after 1971.
A total of 186,700 tonnes of gold exists above ground, as of 2015.[8] The world consumption of
new gold produced is about 50% in jewelry, 40% in investments, and 10% in industry.[9] Gold's
high malleability, ductility, resistance to corrosion and most other chemical reactions, and
conductivity of electricity have led to its continued use in corrosion resistant electrical
connectors in all types of computerized devices (its chief industrial use). Gold is also used
in infrared shielding, colored-glass production, gold leafing, and tooth restoration. Certain gold
salts are still used as anti-inflammatories in medicine. As of 2017, the world's largest gold
producer by far was China with 440 tonnes per year.[10]
You might also like
- WOR8294 Assaying and Refining of GoldDocument28 pagesWOR8294 Assaying and Refining of GoldRehan Sheikh100% (2)
- Section 1 - Reading Comprehension Read The Text Carefully and Answer The Questions That Follow. Choose The Most Appropriate AnswerDocument3 pagesSection 1 - Reading Comprehension Read The Text Carefully and Answer The Questions That Follow. Choose The Most Appropriate AnswerlenakaNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy of GoldDocument8 pagesMetallurgy of GoldDeepin DotNo ratings yet
- GoldDocument1 pageGoldshubhNo ratings yet
- GoldDocument1 pageGoldHana PrasatthongNo ratings yet
- GoldDocument1 pageGoldDapoer OmaOpaNo ratings yet
- The Beauty of GoldDocument12 pagesThe Beauty of GoldDearick LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Gold in The WORLDDocument18 pagesGold in The WORLDmujib uddin siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Gold WikiDocument5 pagesGold WikigergerwgNo ratings yet
- 10 Interesting Facts About Gold - Https://egyptiansorcery - ComDocument1 page10 Interesting Facts About Gold - Https://egyptiansorcery - ComAravenaNo ratings yet
- Gold (Pronounced / Ɡoʊld/) Is A Chemical Element With The SymbolDocument20 pagesGold (Pronounced / Ɡoʊld/) Is A Chemical Element With The Symbolratish15No ratings yet
- Gold T1Document2 pagesGold T1ThunderkickNo ratings yet
- Logam MuliaDocument4 pagesLogam MuliaArif Juliari KusnandaNo ratings yet
- Silver T1Document3 pagesSilver T1Thunderkick100% (1)
- Aurum AdvisorsDocument2 pagesAurum AdvisorsaurumadvisorsusNo ratings yet
- Gold and Gold Related Investment OptionsDocument34 pagesGold and Gold Related Investment OptionsdhanvibNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table - GoldDocument2 pagesThe Periodic Table - GoldVagula SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Chemical ElementsDocument5 pagesChemical ElementsRofilR.AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Gold Iron Copper OxygenDocument3 pagesGold Iron Copper OxygenfranshuNo ratings yet
- Chemical ElementsDocument5 pagesChemical ElementsRofilR.AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Alchemy 2005Document347 pagesAlchemy 2005timop100% (4)
- SGS MIN Tech Pub 2004 03 Process Mineralogy LR en 11 09Document16 pagesSGS MIN Tech Pub 2004 03 Process Mineralogy LR en 11 09Taeu YuNo ratings yet
- Noble MetalsDocument3 pagesNoble MetalsKim Santos100% (1)
- Chemi̇cal Reacti̇ons of The Elements ...Document5 pagesChemi̇cal Reacti̇ons of The Elements ...hatice9No ratings yet
- Aurum in Latin, Is The Only Metal Except Copper: L. Kanerva Et Al. (Ed.), © Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2000Document2 pagesAurum in Latin, Is The Only Metal Except Copper: L. Kanerva Et Al. (Ed.), © Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2000AdhitaAinnurNo ratings yet
- Section 1 - Reading Comprehension Read The Text Carefully and Answer The Questions That Follow. Choose The Most Appropriate AnswerDocument3 pagesSection 1 - Reading Comprehension Read The Text Carefully and Answer The Questions That Follow. Choose The Most Appropriate AnswerlenakaNo ratings yet
- A Three Day Fasting and PrayerDocument5 pagesA Three Day Fasting and PrayerBroadsageNo ratings yet
- GoldDocument1 pageGoldaditya singhNo ratings yet
- GoldDocument5 pagesGoldMohammed Bin SayeedNo ratings yet
- Gold Process Mineralogy and Its Significance in Gold MetallurgyDocument7 pagesGold Process Mineralogy and Its Significance in Gold MetallurgyStefania HernandezNo ratings yet
- Colored Gold - WikipediaDocument30 pagesColored Gold - Wikipediashehalan nilumindaNo ratings yet
- Colored Gold.Document30 pagesColored Gold.Allah dittaNo ratings yet
- 6 GoldDocument63 pages6 GoldHoulifathNo ratings yet
- Gold - ElementDocument12 pagesGold - ElementMarion AlyssaNo ratings yet
- Gold Is A Chemical Element With The Symbol Au and Atomic Number 79Document2 pagesGold Is A Chemical Element With The Symbol Au and Atomic Number 79ic OCNo ratings yet
- NativDocument10 pagesNativHasbii PanthalassaNo ratings yet
- Crystals PDFDocument6 pagesCrystals PDFEthan ThamNo ratings yet
- Silver WikiDocument1 pageSilver Wikiwdm00No ratings yet
- Consumer Attitude Towards Gold OrnamentsDocument34 pagesConsumer Attitude Towards Gold OrnamentsDon Iz BackNo ratings yet
- Navigation Search Element 79 (Anthology) Gold (Color) Gold (Disambiguation)Document45 pagesNavigation Search Element 79 (Anthology) Gold (Color) Gold (Disambiguation)Ayaz Saa'irNo ratings yet
- Gold Is A Dense, Soft, Shiny, Malleable and Ductile Metal. It Is A Chemical Element With TheDocument2 pagesGold Is A Dense, Soft, Shiny, Malleable and Ductile Metal. It Is A Chemical Element With Theacinad_eiram10168537No ratings yet
- Kimia TranslateDocument9 pagesKimia TranslateKiswanNo ratings yet
- RhodiumDocument5 pagesRhodiumAkalatronic TunezNo ratings yet
- Aurum AdvisorsDocument2 pagesAurum AdvisorsadvisorsaurumbioNo ratings yet
- Includes Beryllium, Magnesium, Calcium, Strontium, Barium, and RadiumDocument15 pagesIncludes Beryllium, Magnesium, Calcium, Strontium, Barium, and Radiumpink_music_loveNo ratings yet
- GoldDocument3 pagesGoldapi-271680224100% (1)
- GemstoneDocument11 pagesGemstonesharma0120No ratings yet
- Recovery of Silver From X Ray Waste From Electro DepositionDocument8 pagesRecovery of Silver From X Ray Waste From Electro DepositionvenkyNo ratings yet
- Metaullargy NotesDocument14 pagesMetaullargy Noteswama ojhaNo ratings yet
- Dodo Industrial Proj FinalDocument81 pagesDodo Industrial Proj FinalShanthi ShanNo ratings yet
- Silver WikiDocument5 pagesSilver WikigergerwgNo ratings yet
- Dental Casting AlloysDocument22 pagesDental Casting AlloysSurabhi RairamNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument11 pagesChapter IMUKESH MANWANINo ratings yet
- Native Elements Sulfides SulfosaltsDocument38 pagesNative Elements Sulfides SulfosaltsChristel Batoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Dental Casting Alloys: A Seminar by Nikhil.JDocument77 pagesDental Casting Alloys: A Seminar by Nikhil.Jhotbuddy723No ratings yet
- Silver & Gold Guide Top Tips: Learn How to Quickly Invest - Build your Wealth with Gold and Silver BullionFrom EverandSilver & Gold Guide Top Tips: Learn How to Quickly Invest - Build your Wealth with Gold and Silver BullionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Gold Rush: The Uses and Importance of Gold - Chemistry Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Gold Rush: The Uses and Importance of Gold - Chemistry Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Precious Metals Investing For Beginners: The Quick Guide to Platinum and PalladiumFrom EverandPrecious Metals Investing For Beginners: The Quick Guide to Platinum and PalladiumRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)