Professional Documents
Culture Documents
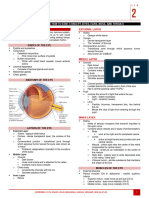
A. Eye Balls D. Lacrimal Glands: 1. External Structures of The Eye
A. Eye Balls D. Lacrimal Glands: 1. External Structures of The Eye
Uploaded by
beayapCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Aesthetic Facial Anatomy Essentials For Injections-CRC Press (2020)Document259 pagesAesthetic Facial Anatomy Essentials For Injections-CRC Press (2020)stella95% (22)
- Injectable Fillers in Aesthetic MedicineDocument192 pagesInjectable Fillers in Aesthetic MedicineHuyền Ngọc Lường100% (7)
- How To Best Utilize The Line of Ligaments and The Surface Volume Coefficient in Facial Soft Tissue Filler InjectionsDocument9 pagesHow To Best Utilize The Line of Ligaments and The Surface Volume Coefficient in Facial Soft Tissue Filler InjectionsArcelino FariasNo ratings yet
- Neurological Exam Lecture NotesDocument26 pagesNeurological Exam Lecture NotesNaveen KovalNo ratings yet
- Gemp3 Paediatric Clinical Examination SkillsDocument13 pagesGemp3 Paediatric Clinical Examination SkillsAnna-Tammy HumanNo ratings yet
- Case Study Cesarean SectionDocument17 pagesCase Study Cesarean SectionWeng Maesa MontemayorNo ratings yet
- IA. Background of The StudyDocument50 pagesIA. Background of The StudyAnonymous ijwkaZsuyNo ratings yet
- Family Case Analysis 2Document98 pagesFamily Case Analysis 2Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- Physical Diagnosis Information OverviewDocument119 pagesPhysical Diagnosis Information OverviewNarcis PopaNo ratings yet
- Ocular EmergenciesDocument4 pagesOcular EmergenciesJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Enls v4 0 Sah Slides FinalDocument40 pagesEnls v4 0 Sah Slides FinalTariku GelesheNo ratings yet
- Introduction To OrthopedicsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To OrthopedicsSalman MajidNo ratings yet
- Etiology and Clinical Profile of Pericardial Effusion PatientsDocument4 pagesEtiology and Clinical Profile of Pericardial Effusion PatientsIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Clinical Hematology Prof DR Gamal AbdulDocument260 pagesClinical Hematology Prof DR Gamal AbdulNabila UsmanNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Case of DiplopiaDocument63 pagesApproach To A Case of DiplopiaSriniwasNo ratings yet
- Heartsound MurmurDocument2 pagesHeartsound MurmurDya AndryanNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Revision LectureDocument80 pagesOphthalmology Revision LectureCarla LaniganNo ratings yet
- General Diagnosis Board Review NotesDocument16 pagesGeneral Diagnosis Board Review NotesmaeydakhalidNo ratings yet
- Enls v4 0 Ais Slides FinalDocument38 pagesEnls v4 0 Ais Slides FinalAndrio GultomNo ratings yet
- Common Eye Problems and DiagnosisDocument84 pagesCommon Eye Problems and Diagnosisvivekrajbhilai5850No ratings yet
- YEAR 1 and 2 OSCE Revision: Author: DR Thomas PayneDocument30 pagesYEAR 1 and 2 OSCE Revision: Author: DR Thomas Payneminayoki100% (1)
- Peripheral Vascular (PVS) Examination OSCE Station GuideDocument4 pagesPeripheral Vascular (PVS) Examination OSCE Station GuideNikita JacobsNo ratings yet
- Rosh NeuroDocument11 pagesRosh NeuroSoni AliNo ratings yet
- Orthopedics - Brodno: TraumatologyDocument29 pagesOrthopedics - Brodno: TraumatologyKamila Anna JakubowiczNo ratings yet
- Ring Enhancing LesionsDocument50 pagesRing Enhancing LesionsVivek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Patient Care: University of California, San Francisco School of MedicineDocument41 pagesFoundations of Patient Care: University of California, San Francisco School of MedicinePaul Carty SorianoNo ratings yet
- JI RevalidaDocument61 pagesJI RevalidaAren LingadNo ratings yet
- Head To Toe AssessmentDocument22 pagesHead To Toe AssessmentNessa Layos MorilloNo ratings yet
- Neurology - Saif.wesmosis.2013 104907Document68 pagesNeurology - Saif.wesmosis.2013 104907Helene AlawamiNo ratings yet
- (APJ) Common ENT CasesDocument31 pages(APJ) Common ENT CasesApryl Phyllis JimenezNo ratings yet
- Headache: Rosen's Chapters 17 and 105 November 9, 2006 by George FiliadisDocument45 pagesHeadache: Rosen's Chapters 17 and 105 November 9, 2006 by George Filiadishemanthshah2801No ratings yet
- Neurological Examination SummaryDocument90 pagesNeurological Examination SummaryAlida Taranu TernströmNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience I - Neurologic History Taking and Examination (POBLETE)Document9 pagesNeuroscience I - Neurologic History Taking and Examination (POBLETE)Johanna Hamnia PobleteNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmologic Exam PDFDocument70 pagesOphthalmologic Exam PDFSamsam Almarez BacaltosNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Peripheral Neurological SystemDocument2 pagesExamination of The Peripheral Neurological Systemkenners100% (12)
- Neuro 1 and 2 LabDocument3 pagesNeuro 1 and 2 LabHardikPatelNo ratings yet
- Migraine 2Document23 pagesMigraine 2danish sultanNo ratings yet
- Methods of ExaminationDocument53 pagesMethods of ExaminationTeodor ŞişianuNo ratings yet
- Causes Obstruction Causes CSF To Build Up in The Brain. If The Cause Is Congenital, Symptoms Such As AnDocument22 pagesCauses Obstruction Causes CSF To Build Up in The Brain. If The Cause Is Congenital, Symptoms Such As Anmhelandie100% (1)
- Review Slides OphthaDocument14 pagesReview Slides OphthaSUSHMITA MAE ROSE CONTRERASNo ratings yet
- Neurology Exam Checklist1Document6 pagesNeurology Exam Checklist1Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Medrano Neuro Notes 2.0Document22 pagesMedrano Neuro Notes 2.0roldan pantojaNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics: The Eyes Have ItDocument14 pagesPediatrics: The Eyes Have ItDrSyed Rahil IqbalNo ratings yet
- PEDIA Handouts 2010Document17 pagesPEDIA Handouts 2010Jannine Marie EmpasisNo ratings yet
- 4.1d - Pathology of The Pituitary - Nov.10 - Dr. GalangDocument4 pages4.1d - Pathology of The Pituitary - Nov.10 - Dr. GalangMiel Raphael AranillaNo ratings yet
- Neurology Shifting Exam: CnvandcnviiDocument9 pagesNeurology Shifting Exam: CnvandcnviicarlosNo ratings yet
- Review Lectures Forlu6: Basic Eye Exam Common Opd Complaints Common Er Cases PharmacologyDocument110 pagesReview Lectures Forlu6: Basic Eye Exam Common Opd Complaints Common Er Cases Pharmacologyupmed2012block9No ratings yet
- PRES (Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome) and Eclampsia-ReviewDocument5 pagesPRES (Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome) and Eclampsia-ReviewAvicena M IqbalNo ratings yet
- Seizure: Focal/partial SeizuresDocument7 pagesSeizure: Focal/partial SeizuresMauren DazaNo ratings yet
- Neurology in TableDocument93 pagesNeurology in TableHassan Bani SaeidNo ratings yet
- 4 ConvulsionDocument40 pages4 ConvulsionMohamed Na3eemNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing A Review of Neurologic Concepts: Nurse Licensure Examination ReviewDocument251 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing A Review of Neurologic Concepts: Nurse Licensure Examination ReviewJovelle AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- X Ray SchemeDocument6 pagesX Ray SchemeIdiAmadouNo ratings yet
- MIS-C: Clinic-Diagnostic/Dispo Recs For Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in ChildrenDocument8 pagesMIS-C: Clinic-Diagnostic/Dispo Recs For Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in ChildrenJosselle Sempio CalientaNo ratings yet
- Slides For SeizureDocument15 pagesSlides For SeizureBryan Mae H. Degorio100% (3)
- 2-Physical Examination and SkillsDocument48 pages2-Physical Examination and SkillsHari ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Hereditary DystrophiesDocument51 pagesHereditary Dystrophiesoctober1998No ratings yet
- Best Aid To Ophthalmology - Pramod TK - 318Document3 pagesBest Aid To Ophthalmology - Pramod TK - 318Danielle SangalangNo ratings yet
- DD Nyeri Kepala Skenario 1Document8 pagesDD Nyeri Kepala Skenario 1Ika Putri YulianiNo ratings yet
- Abdominal PXDocument60 pagesAbdominal PXabinadivegaNo ratings yet
- Cerebellar LesionsDocument3 pagesCerebellar LesionsMary100% (1)
- Neuro AssessmentDocument3 pagesNeuro AssessmentTori RolandNo ratings yet
- OSCE Neurologic Examination - 3Document13 pagesOSCE Neurologic Examination - 3Nana BananaNo ratings yet
- Neurology NotesDocument1 pageNeurology NotesTharaniNo ratings yet
- Eent CompiledDocument15 pagesEent CompiledAlthea Franz DuoNo ratings yet
- The Eye Is Made Up of THREE LayersDocument2 pagesThe Eye Is Made Up of THREE LayersMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- Eye Instillation Procedure Guide NursingDocument3 pagesEye Instillation Procedure Guide NursingTrisha ApillanesNo ratings yet
- Anatomia FeteiDocument32 pagesAnatomia FeteiPascalau AndreiNo ratings yet
- Eye, Orbit, Orbital Region, andDocument72 pagesEye, Orbit, Orbital Region, andSmartyna Sophia100% (1)
- By Komal Sharma Assistant ProfessorDocument14 pagesBy Komal Sharma Assistant ProfessorOphthalmology DiscussionNo ratings yet
- Facial Anatomy View For Aesthetic Botulinum Toxin Injection: Bhertha Miyuki TamuraDocument225 pagesFacial Anatomy View For Aesthetic Botulinum Toxin Injection: Bhertha Miyuki Tamurahesham0% (1)
- Script For Head To NeckDocument7 pagesScript For Head To NeckRhelina MinNo ratings yet
- Craniofacial MalformationsDocument162 pagesCraniofacial MalformationsDiana Lora ParvuNo ratings yet
- Patient AssessmentDocument5 pagesPatient AssessmentMary Janine Joy RimanoNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR On Eyelid Echi 3rd YearDocument93 pagesSEMINAR On Eyelid Echi 3rd Yearsushmitabiswas052No ratings yet
- Assessing Eye Structure and Visual AcuityDocument4 pagesAssessing Eye Structure and Visual AcuityRoldan BalangyaoNo ratings yet
- DoubleEyelids by William P Chen MDDocument36 pagesDoubleEyelids by William P Chen MDAnonymous 8hVpaQdCtrNo ratings yet
- Ocular Quiz 1Document16 pagesOcular Quiz 1Antwi EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment Guide EYES AND VISUAL ACUITYDocument12 pagesPhysical Assessment Guide EYES AND VISUAL ACUITYPauline HidlaoNo ratings yet
- Lipoenxertia PeriorbitalDocument31 pagesLipoenxertia PeriorbitalIvoNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka DaniDocument3 pagesDaftar Pustaka Danidokter linggauNo ratings yet
- Jarvis: Physical Examination & Health Assessment, 3rd Canadian EditionDocument3 pagesJarvis: Physical Examination & Health Assessment, 3rd Canadian EditionkekeNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Penguatan Kompetensi Perawat Mata Tahun 2023Document10 pagesJadwal Penguatan Kompetensi Perawat Mata Tahun 2023ThabutiNo ratings yet
- Botulinum Toxin in Facial ReanimationDocument13 pagesBotulinum Toxin in Facial ReanimationAna Caroline Ramirez de AndradeNo ratings yet
- Kyle Gwyn Apanto Mascariña - PE-DOCUMENTATION-Final-revisionDocument8 pagesKyle Gwyn Apanto Mascariña - PE-DOCUMENTATION-Final-revisionKylie Gwyn100% (1)
- Basic Sciences in Ophthalmology - 9788184486087-EmailDocument446 pagesBasic Sciences in Ophthalmology - 9788184486087-EmailwulanfarichahNo ratings yet
- Clinical Ophthalmology Made Easy®Document419 pagesClinical Ophthalmology Made Easy®Uzair Akhter100% (2)
- Head To Toe AssessmentDocument21 pagesHead To Toe AssessmentZahra jane A.100% (1)
- Patient Assesment 1Document23 pagesPatient Assesment 1luckyNo ratings yet
- Effective Small-Incision Surgery For Involutional Lower Eyelid EntropionDocument7 pagesEffective Small-Incision Surgery For Involutional Lower Eyelid EntropiondoctorbanNo ratings yet
A. Eye Balls D. Lacrimal Glands: 1. External Structures of The Eye
A. Eye Balls D. Lacrimal Glands: 1. External Structures of The Eye
Uploaded by
beayapOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A. Eye Balls D. Lacrimal Glands: 1. External Structures of The Eye
A. Eye Balls D. Lacrimal Glands: 1. External Structures of The Eye
Uploaded by
beayapCopyright:
Available Formats
Eye
d. LACRIMAL GLANDS
1. External Structures of the eye It is within the upper eyelids,
a. EYE BALLS outer canthus of the eyes
Coordinated by 6 muscles Production of tears
4 Rectus Muscles (lateral,
medial, superior, inferior)
2. Inner Structures of the eye
Responsible for the
movement of the eye
horizontally and vertically a. CONJUNCTIVA
2 Oblique Muscles (superior, Not inner or outer
inferior) It is a transparent mucus
Responsible for the membrane that lines the lower
movement of the eyes in all eyelids
direction Outer Layer (support and protection)
b. OCULAR ADNEXIA a. SCLERA
The accessory organ of the eyes More of a fibrous protective
for support and protection coating which changes according
Muscles to age
Bony orbit (bony
structure which protect Newborn Light blue (cause of
the eyes) hypopigmentation)
Toddler- Whitish
middle
c. EYELIDS
adult
Upper and lower eyelids
Adult Slightly yellow or
A thin layer, elastic folds of skin
dirty white
which protects the eyes
Tear Film Protective in nature
- Produce moisture in the
eyes b. CORNEA
Posterior part of the sclera
Palpebral Fissure It is the refractory medium
-the space between the which is govern by contraction
upper and lower eyelids or relaxation of ciliary muscle
when the eyes are close Refraction
Bending of light govern
Canthi (Canthus) by contraction and
- At the corner of palpibral relaxation of ciliary
fissure muscle
- Inner (nasal) canthus
- Outer (lateral) canthus
1 Eye Lecture | [Type the company name]
Middle Layer (Blood Supply)
E. VITREOUS BODY
a. UVEAL TRACT Produce vitreous humor
Vascular in nature which A jelly like substance,
contains a lot of blood vessel thick in consistency
Supply the retina responsible for maintain
the shape of the eye
A. IRIS F. LENS
It is black and highly pigmented Biconvex, clear
wherein pupil is in the center Main function is to focus vision
B. PUPIL on retina
At the center Innnermost Layer
Constriction and dilatation is
caused by interaction of 2 iris a. RETINA
muscle Contains different sensory receptors
responsible for transmission of light
Bright Constriction
objects/ Near RODS For night time
objects CONES For day time
Dark objects/ Dilation For better Imaging
Far objects
C. CILIARY BODY Normal pathway of Vision
E xactly responsible for
Production of Aqueous Humor Outside
Clear and thin in Cornea
consistency which is
found at anterior Aqueous Humor
chamber of the eye
Lens
D. CHOROID
Also produce aqueous humor Vitreous Humor
It is found in the posterior/ end
portion of Uveal tract between Retina
Sclera and Retina
Posterior portion of uveal tract Occipital Lobe
which is located between sclera
and retina. Vision
Should have continuous flow of vision
2 Eye Lecture | [Type the company name]
Blindness 3. Image processing (retina to occipital
Damage on retina, optic nerve, lobe)
occipital nerve. Start when pick up from retina
Central Blindness to occipital lobe
Tumor in brain cause blindness Normally 2 visions are seen but
registered as one
Diplopia is abnormal
Govern by 3 steps:
1. Transmission of light (outside to
retina) Assessment of the eyes
Power of Accommodation History
-ability of eye to see/focus at 1. Biographical & demographic data
near and far object 2. Current health
Conduction of Ciliary muscle a. CC
- Pupils constricted b. Symptoms Analysis
Relaxed Ciliary Muscle Abnormal Vision
- Pupils dilate Causes
2. Visceral receptors of retina -poor refraction
-interference from entry
Fovea of light
-A part of retina which has -claudicating of cornea/
the highest level of visual opacity of lens
acuity - malfunctioning of nerve
- Both cones and rod are Common Visual Changes
located Glare of halos
-cones are more than rods Flashing of light
Floating spots
Dark Adaptation Diplopia
-From bright place to dark Abnormal Appearance
place pupil dilates to get as Red eye
much light as possible (infection,
-After 20-30 mins. The eyes trauma, bleeding)
are adjusted to dark place. Growth or lesion
- Rods work (sty)
Edema
Light Adaptation (inflammatory
- Dark place to bright place process/ allergic
- Cones work conditions)
- Too much exposure to
light will bleach
photopigment
3 Eye Lecture | [Type the company name]
Abnormal sensation Physical Examination
Eye pain
Hearing/lacrimati 1. External Eye
on a. Eye Position
Increase ocular >symmetrical with one another and
secretion at the same level
>assess in side view for presence of
3. Past Health History exopthalmus (protrusion of the eye)
a. Childhood disorders and
infectious diseases (history b. Eyebrows
of eye trauma) >equal hair distribution
>let the patient smile the eyebrows
should be at the same level
b. Major illness and
hospitalization
c. Eyelids & Eyelashes
Systemic diseases >ask the patient to close the eyes
(DM, HTN) >N= no space
Ocular Diseases
(Instances of blurring d. Blinking Reflex
of vision) >N=blinks 20x/ min.
With glasses or >Ab = frequent blinking
contact lens
Hospitalization r/t e. Eyeballs
>let the patient close the eyes then
eye and brain
palpate for symmetry and firmness
History of head
> N= not hard, not soft
trauma (e.g bad fall, > IOP = hard or with eye pain
vehicular accident)
f. Lacrimal Apparatus
c. Medications( Prescribed OTC >check for edema and secretions
drugs since when it is used)
g. Conjunctiva and Sclera
d. Allergies >pinkish red
4. Family Health History h. Corneal Reflex
>cotton wisp
a. Familial eye disorder
b. Systemic diseases
i. Cornea
>with the use of penlight it should
5. Psychosocial Factors be shiny
a. Nature of work
b. Leisure activities j. Anterior Chamber
c. Health management k. Iris & Pupil
behaviors r/t the eye l. Ocular Motility
>functioning of ciliary muscles
4 Eye Lecture | [Type the company name]
CORNEAL LIGHT REFLEX OR
HIRSCHBERG TEST Diagnostic Procedures
>12- 15” away, penlight is 1. Fundus Photography
directed to nose bridge Visualization of internal aspect
>N = reflection to cornea is of eye
equal
>Ab = unequal
2. Exopthalmometry
COVER-UNCOVER TEST Measure the degree of forward
>covering one eye with a protrusion of the eyes
board, then instructed the
patient to look straight . 3. Opthalmic Radiography
>patient eye should be fixed Any procedure that will outline
on one location the eyes with dye/ radioisotopes
and will use magnetic waves
m. Vision
>Visual acuity 4. Electroretonography
>visual field testing Like a contact lens attached to
the eyeball and monitor the
n. Special testing for vision electrical activity of the eyes
5. Fluorescein Angiography
2. Internal Eye Visualization of blood vessels that supplies
the eyes with the use of radio opaque dye/
a. Ophthamoscopy fluorescein dye and put under green light
Assessment of internal eye with
the use of ophthalmoscope (a
hand piece device) which
magnifies all the things that are ERRORS OF REFRACTION
seen inside the eyes 15- 20x
Refractive Errors
b. Tonometry The image is not focused in the
A process of measuring the IOP retina
with the use of tonometer
Patient should lie down/ sit with Refractometry
head reclining and instill an Process of measuring refractive
ophthalmic anesthetic agent and errors
then the tonometer is placed
above the eye ball Refraction
Normal IOP = 8- 21 mmHg Process of determining what lens will
benefit the client.
5 Eye Lecture | [Type the company name]
EMMETROPIA Normal refractory state, can see
the image/ refractory to retina at Bifocal Lens Progressive
20 ft Lens
Errors of Definition Correcte
Refraction d by Far vision Far vision
HYPEROPIA >What you see Convex
(farsighted) clearly is far objects lens Intermediate
>Brought about by Near vision Near vision
short antero
posterior diameter of
the lens
>The image is not
reflected in the
retina but at the back
SURGERY
of retina
1. Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK)
MYOPIA >What you see Concave
The light will pass through the
(nearsighted) clearly is near objects Lens
cornea and flattened it (myopia)
>Brought about by
or make it steeper (hyperopia)
long antero posterior
diameter of the lens
2. Laser In Situ Keratomileusis (LASIKs)
>The image is not
Peel the outermost layer of the
reflected in the
cornea, flattened it (myopia) or
retina but at the
make it steeper (hyperopia),
front of retina
then return the layer
>Familial in nature
PRESBYOPIA Associated by aging 1.Bifocal
Lens
2.Progres
Optometrist
sive Lens
Identify error of refraction and
ASTIGMATISM Because of the Cylindri- prescribe lens
unequal curvature of cal Lens
cornea the light is Optician
not properly focused Makes the eyeglasses
in retina
Ophthalmologist/ Oculist
Doctor of medicine who
diagnosed eye disorder and treat
6 Eye Lecture | [Type the company name]
CATARACT 3. Intumescent Cataract
The lens which used to be transparent The lens absorbs more water
becomes opaque/ decreases or loosens
transparency; light will not focus in retina 4. Hypermature
>complete vision but blured Protein starts to breakdown in lens
3 types **Important component of lens
>>Water
1. Congenital >>Protein
Brought about by pregnant mother
in the first trimester who is exposed
to radiation (xray) or communicable Management
diseases (german measles) 1. Cataract extraction
If you have a client in the a. Intracapsular cataract extraction
reproductive stage identify if Removal of lens and capsule
pregnant or not
b. Extracapsular cataract extraction
2. Acquired Removal of lens
Ask the patient if he had an eye
trauma **Phaecoemulsification
May be cause by increase in blood Probe under the lens which vibrates
glucose, BP, or trauma and remove the opaque lens
3. Senile 2. Intraocular Lens Implantation
Associated with aging process Replace the opaque lens with
synthetic lens
Clinical Manifestations
1. Blurring of vision Post-op Directions
Gradual, can be corrected by 1. Cannot stoop forward
means of glasses 2. No straining
2. Diplopia 3. No coughing
Double vision 4. No vomiting
3. Photophobia 5. No lifting of objects more than 15 lbs
High sensitivity to light 6. Lie down on unaffected side @ low
fowler’s position
7. Wear eye shield for 1 month; wear it
Stages
during night time or nap time
1. Immature type of cataract
8. If have to wear eye patch, cover both
Not all portion of the lens is opaque eyes instead of one
Reduction of vision but adegquate
vision remainin
Glaucoma
>>Tunnel Vision
2. Mature cataract >>can only see center
Practically the whole lens is opaque
Very poor vision probably light
perception is available
Retina Detachment
>> Curtain light vision
7 Eye Lecture | [Type the company name]
You might also like
- Aesthetic Facial Anatomy Essentials For Injections-CRC Press (2020)Document259 pagesAesthetic Facial Anatomy Essentials For Injections-CRC Press (2020)stella95% (22)
- Injectable Fillers in Aesthetic MedicineDocument192 pagesInjectable Fillers in Aesthetic MedicineHuyền Ngọc Lường100% (7)
- How To Best Utilize The Line of Ligaments and The Surface Volume Coefficient in Facial Soft Tissue Filler InjectionsDocument9 pagesHow To Best Utilize The Line of Ligaments and The Surface Volume Coefficient in Facial Soft Tissue Filler InjectionsArcelino FariasNo ratings yet
- Neurological Exam Lecture NotesDocument26 pagesNeurological Exam Lecture NotesNaveen KovalNo ratings yet
- Gemp3 Paediatric Clinical Examination SkillsDocument13 pagesGemp3 Paediatric Clinical Examination SkillsAnna-Tammy HumanNo ratings yet
- Case Study Cesarean SectionDocument17 pagesCase Study Cesarean SectionWeng Maesa MontemayorNo ratings yet
- IA. Background of The StudyDocument50 pagesIA. Background of The StudyAnonymous ijwkaZsuyNo ratings yet
- Family Case Analysis 2Document98 pagesFamily Case Analysis 2Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- Physical Diagnosis Information OverviewDocument119 pagesPhysical Diagnosis Information OverviewNarcis PopaNo ratings yet
- Ocular EmergenciesDocument4 pagesOcular EmergenciesJim Jose AntonyNo ratings yet
- Enls v4 0 Sah Slides FinalDocument40 pagesEnls v4 0 Sah Slides FinalTariku GelesheNo ratings yet
- Introduction To OrthopedicsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To OrthopedicsSalman MajidNo ratings yet
- Etiology and Clinical Profile of Pericardial Effusion PatientsDocument4 pagesEtiology and Clinical Profile of Pericardial Effusion PatientsIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Clinical Hematology Prof DR Gamal AbdulDocument260 pagesClinical Hematology Prof DR Gamal AbdulNabila UsmanNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Case of DiplopiaDocument63 pagesApproach To A Case of DiplopiaSriniwasNo ratings yet
- Heartsound MurmurDocument2 pagesHeartsound MurmurDya AndryanNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Revision LectureDocument80 pagesOphthalmology Revision LectureCarla LaniganNo ratings yet
- General Diagnosis Board Review NotesDocument16 pagesGeneral Diagnosis Board Review NotesmaeydakhalidNo ratings yet
- Enls v4 0 Ais Slides FinalDocument38 pagesEnls v4 0 Ais Slides FinalAndrio GultomNo ratings yet
- Common Eye Problems and DiagnosisDocument84 pagesCommon Eye Problems and Diagnosisvivekrajbhilai5850No ratings yet
- YEAR 1 and 2 OSCE Revision: Author: DR Thomas PayneDocument30 pagesYEAR 1 and 2 OSCE Revision: Author: DR Thomas Payneminayoki100% (1)
- Peripheral Vascular (PVS) Examination OSCE Station GuideDocument4 pagesPeripheral Vascular (PVS) Examination OSCE Station GuideNikita JacobsNo ratings yet
- Rosh NeuroDocument11 pagesRosh NeuroSoni AliNo ratings yet
- Orthopedics - Brodno: TraumatologyDocument29 pagesOrthopedics - Brodno: TraumatologyKamila Anna JakubowiczNo ratings yet
- Ring Enhancing LesionsDocument50 pagesRing Enhancing LesionsVivek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Patient Care: University of California, San Francisco School of MedicineDocument41 pagesFoundations of Patient Care: University of California, San Francisco School of MedicinePaul Carty SorianoNo ratings yet
- JI RevalidaDocument61 pagesJI RevalidaAren LingadNo ratings yet
- Head To Toe AssessmentDocument22 pagesHead To Toe AssessmentNessa Layos MorilloNo ratings yet
- Neurology - Saif.wesmosis.2013 104907Document68 pagesNeurology - Saif.wesmosis.2013 104907Helene AlawamiNo ratings yet
- (APJ) Common ENT CasesDocument31 pages(APJ) Common ENT CasesApryl Phyllis JimenezNo ratings yet
- Headache: Rosen's Chapters 17 and 105 November 9, 2006 by George FiliadisDocument45 pagesHeadache: Rosen's Chapters 17 and 105 November 9, 2006 by George Filiadishemanthshah2801No ratings yet
- Neurological Examination SummaryDocument90 pagesNeurological Examination SummaryAlida Taranu TernströmNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience I - Neurologic History Taking and Examination (POBLETE)Document9 pagesNeuroscience I - Neurologic History Taking and Examination (POBLETE)Johanna Hamnia PobleteNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmologic Exam PDFDocument70 pagesOphthalmologic Exam PDFSamsam Almarez BacaltosNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Peripheral Neurological SystemDocument2 pagesExamination of The Peripheral Neurological Systemkenners100% (12)
- Neuro 1 and 2 LabDocument3 pagesNeuro 1 and 2 LabHardikPatelNo ratings yet
- Migraine 2Document23 pagesMigraine 2danish sultanNo ratings yet
- Methods of ExaminationDocument53 pagesMethods of ExaminationTeodor ŞişianuNo ratings yet
- Causes Obstruction Causes CSF To Build Up in The Brain. If The Cause Is Congenital, Symptoms Such As AnDocument22 pagesCauses Obstruction Causes CSF To Build Up in The Brain. If The Cause Is Congenital, Symptoms Such As Anmhelandie100% (1)
- Review Slides OphthaDocument14 pagesReview Slides OphthaSUSHMITA MAE ROSE CONTRERASNo ratings yet
- Neurology Exam Checklist1Document6 pagesNeurology Exam Checklist1Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Medrano Neuro Notes 2.0Document22 pagesMedrano Neuro Notes 2.0roldan pantojaNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics: The Eyes Have ItDocument14 pagesPediatrics: The Eyes Have ItDrSyed Rahil IqbalNo ratings yet
- PEDIA Handouts 2010Document17 pagesPEDIA Handouts 2010Jannine Marie EmpasisNo ratings yet
- 4.1d - Pathology of The Pituitary - Nov.10 - Dr. GalangDocument4 pages4.1d - Pathology of The Pituitary - Nov.10 - Dr. GalangMiel Raphael AranillaNo ratings yet
- Neurology Shifting Exam: CnvandcnviiDocument9 pagesNeurology Shifting Exam: CnvandcnviicarlosNo ratings yet
- Review Lectures Forlu6: Basic Eye Exam Common Opd Complaints Common Er Cases PharmacologyDocument110 pagesReview Lectures Forlu6: Basic Eye Exam Common Opd Complaints Common Er Cases Pharmacologyupmed2012block9No ratings yet
- PRES (Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome) and Eclampsia-ReviewDocument5 pagesPRES (Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome) and Eclampsia-ReviewAvicena M IqbalNo ratings yet
- Seizure: Focal/partial SeizuresDocument7 pagesSeizure: Focal/partial SeizuresMauren DazaNo ratings yet
- Neurology in TableDocument93 pagesNeurology in TableHassan Bani SaeidNo ratings yet
- 4 ConvulsionDocument40 pages4 ConvulsionMohamed Na3eemNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing A Review of Neurologic Concepts: Nurse Licensure Examination ReviewDocument251 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing A Review of Neurologic Concepts: Nurse Licensure Examination ReviewJovelle AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- X Ray SchemeDocument6 pagesX Ray SchemeIdiAmadouNo ratings yet
- MIS-C: Clinic-Diagnostic/Dispo Recs For Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in ChildrenDocument8 pagesMIS-C: Clinic-Diagnostic/Dispo Recs For Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in ChildrenJosselle Sempio CalientaNo ratings yet
- Slides For SeizureDocument15 pagesSlides For SeizureBryan Mae H. Degorio100% (3)
- 2-Physical Examination and SkillsDocument48 pages2-Physical Examination and SkillsHari ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Hereditary DystrophiesDocument51 pagesHereditary Dystrophiesoctober1998No ratings yet
- Best Aid To Ophthalmology - Pramod TK - 318Document3 pagesBest Aid To Ophthalmology - Pramod TK - 318Danielle SangalangNo ratings yet
- DD Nyeri Kepala Skenario 1Document8 pagesDD Nyeri Kepala Skenario 1Ika Putri YulianiNo ratings yet
- Abdominal PXDocument60 pagesAbdominal PXabinadivegaNo ratings yet
- Cerebellar LesionsDocument3 pagesCerebellar LesionsMary100% (1)
- Neuro AssessmentDocument3 pagesNeuro AssessmentTori RolandNo ratings yet
- OSCE Neurologic Examination - 3Document13 pagesOSCE Neurologic Examination - 3Nana BananaNo ratings yet
- Neurology NotesDocument1 pageNeurology NotesTharaniNo ratings yet
- Eent CompiledDocument15 pagesEent CompiledAlthea Franz DuoNo ratings yet
- The Eye Is Made Up of THREE LayersDocument2 pagesThe Eye Is Made Up of THREE LayersMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- Eye Instillation Procedure Guide NursingDocument3 pagesEye Instillation Procedure Guide NursingTrisha ApillanesNo ratings yet
- Anatomia FeteiDocument32 pagesAnatomia FeteiPascalau AndreiNo ratings yet
- Eye, Orbit, Orbital Region, andDocument72 pagesEye, Orbit, Orbital Region, andSmartyna Sophia100% (1)
- By Komal Sharma Assistant ProfessorDocument14 pagesBy Komal Sharma Assistant ProfessorOphthalmology DiscussionNo ratings yet
- Facial Anatomy View For Aesthetic Botulinum Toxin Injection: Bhertha Miyuki TamuraDocument225 pagesFacial Anatomy View For Aesthetic Botulinum Toxin Injection: Bhertha Miyuki Tamurahesham0% (1)
- Script For Head To NeckDocument7 pagesScript For Head To NeckRhelina MinNo ratings yet
- Craniofacial MalformationsDocument162 pagesCraniofacial MalformationsDiana Lora ParvuNo ratings yet
- Patient AssessmentDocument5 pagesPatient AssessmentMary Janine Joy RimanoNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR On Eyelid Echi 3rd YearDocument93 pagesSEMINAR On Eyelid Echi 3rd Yearsushmitabiswas052No ratings yet
- Assessing Eye Structure and Visual AcuityDocument4 pagesAssessing Eye Structure and Visual AcuityRoldan BalangyaoNo ratings yet
- DoubleEyelids by William P Chen MDDocument36 pagesDoubleEyelids by William P Chen MDAnonymous 8hVpaQdCtrNo ratings yet
- Ocular Quiz 1Document16 pagesOcular Quiz 1Antwi EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment Guide EYES AND VISUAL ACUITYDocument12 pagesPhysical Assessment Guide EYES AND VISUAL ACUITYPauline HidlaoNo ratings yet
- Lipoenxertia PeriorbitalDocument31 pagesLipoenxertia PeriorbitalIvoNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka DaniDocument3 pagesDaftar Pustaka Danidokter linggauNo ratings yet
- Jarvis: Physical Examination & Health Assessment, 3rd Canadian EditionDocument3 pagesJarvis: Physical Examination & Health Assessment, 3rd Canadian EditionkekeNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Penguatan Kompetensi Perawat Mata Tahun 2023Document10 pagesJadwal Penguatan Kompetensi Perawat Mata Tahun 2023ThabutiNo ratings yet
- Botulinum Toxin in Facial ReanimationDocument13 pagesBotulinum Toxin in Facial ReanimationAna Caroline Ramirez de AndradeNo ratings yet
- Kyle Gwyn Apanto Mascariña - PE-DOCUMENTATION-Final-revisionDocument8 pagesKyle Gwyn Apanto Mascariña - PE-DOCUMENTATION-Final-revisionKylie Gwyn100% (1)
- Basic Sciences in Ophthalmology - 9788184486087-EmailDocument446 pagesBasic Sciences in Ophthalmology - 9788184486087-EmailwulanfarichahNo ratings yet
- Clinical Ophthalmology Made Easy®Document419 pagesClinical Ophthalmology Made Easy®Uzair Akhter100% (2)
- Head To Toe AssessmentDocument21 pagesHead To Toe AssessmentZahra jane A.100% (1)
- Patient Assesment 1Document23 pagesPatient Assesment 1luckyNo ratings yet
- Effective Small-Incision Surgery For Involutional Lower Eyelid EntropionDocument7 pagesEffective Small-Incision Surgery For Involutional Lower Eyelid EntropiondoctorbanNo ratings yet