Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cisco Router and Switch Configuration PDF
Cisco Router and Switch Configuration PDF
Uploaded by
Juan Pablo AragonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cisco Router and Switch Configuration PDF
Cisco Router and Switch Configuration PDF
Uploaded by
Juan Pablo AragonCopyright:
Available Formats
Cisco Router and Switch Configuration (ver 1.
2)
Name(s)______________________________
CIN__________________________________
(when in doubt, use command line interface ? character) Date________________
Group# ______________
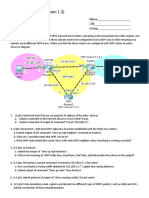
Connect your router to the network as shown in the ETB106 network topology drawing. Connect a rollover cable from
the console port of the Cisco 1600 (or 2500) router to a 9-pin RS-232 serial port on a computer. Download Putty or
Teraterm communication software from Internet onto your computer and configure the terminal emulation software to
9600 bps, 8 data bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit. From the software program, verify that you can connect to the router’s
console and get into enable mode (Router#). Reset the router to its factory default state by executing “erase startup-
config” and “reload” commands. If you are not able to log into the router, see step-by-step instructions for resetting the
password at http://cs3.calstatela.edu/~egean/cs4471/cisco-router-password-reset.pdf . Configure the Ethernet interface on
the router with IP address specified in network topology drawing. Your router’s default gateway address and default route
should be set to 10.86.44.1. Change the hostname of your router to RouterX (where X is your group number). Change
the default router gateway of a virtual machine (VM) instance running on your computer from 10.86.44.1 to the IP
address of the Ethernet interface of your Cisco 1600 (2500) router. From a command prompt on the VM instance, verify
that you can ping the Cisco 1600 router’s Ethernet interface and have connectivity to the Internet.
1. Simulate a wide-area-network connection by connecting the WAN ports of two Cisco routers together via two V.35
serial cables (or one crossover serial cable). DCE side needs clock rate set. Configure the IP address of the WAN
serial port (s0) with IP address specified in network topology drawing. Netmask should be 255.255.255.0. From a
command prompt on your VM instance, verify that you can ping your own WAN interface (192.168.x.y) on your
Cisco 1600 (or 2500) router. Verify that you can ping the other endpoint (192.168.x.z on your neighbor’s s0) of
your WAN connection. Submit a screen capture of the output of a successful traceroute command from your
computer’s command prompt to the other WAN endpoint (192.168.x.z) of your router’s WAN connection.
2. Turn on RIP version 2 so that your router will learn how to reach other indirectly connected networks in the lab.
a. Submit a screenshot of your router’s routing table. It should contain RIP routes advertised by five other networks
(192.168.x.0) in the lab. Work with your fellow classmates if needed.
b. From your computer’s command prompt, do a traceroute to the serial WAN interface of another group’s router
whose network was learned by your router via RIP version 2. Submit a screenshot of the result of the traceroute.
3. From your computer, capture and decode RIP version 2 packets advertised by your router.
a. What UDP port number is used by RIP advertisement packets?
b. Print out a screenshot from Wireshark packet analyzer that shows the decoded network routes being advertised by
your router. You will need to expand and drill down into the packet decodes to see this information.
4. Save the router’s current configuration from main memory to NVRAM.
a. What Cisco command did you use to accomplish this?
b. Print out a copy of this configuration file.
5. Connect your console cable from your computer’s serial port to the console port of your Ethernet switch and
configure its hostname to SwitchX ( where X is your group number). Also configure the IP address of your switch to
the value shown in the network topology drawing. Verify that you can ping the IP address of your switch from the
command prompt of your computer.
a. submit a screenshot of output of “show cdp neighbors” and “show mac address-table” from your switch.
b. Submit a copy of the configuration file of your Ethernet switch.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5824)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Cisco Packet Tracer IntroductionDocument2 pagesCisco Packet Tracer IntroductionJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- Ribbon Microphone: User ManualDocument16 pagesRibbon Microphone: User ManualJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- 8 Ways To Biohack Your HealthDocument5 pages8 Ways To Biohack Your HealthJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- The Time: Over Just 7 Days, Lenovo Wraps Up Two Deals Totaling $5 BillionsDocument6 pagesThe Time: Over Just 7 Days, Lenovo Wraps Up Two Deals Totaling $5 BillionsJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- 03 CCNA 200-301 Chapter 3-Fundamentals of WANs and IP RoutingDocument19 pages03 CCNA 200-301 Chapter 3-Fundamentals of WANs and IP RoutingJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- cs4471 Lab&read Assignments - 2020 SpringDocument3 pagescs4471 Lab&read Assignments - 2020 SpringJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- 01 CCNA 200-301 Chapter 1-Introduction To TCP IP NetworkingDocument21 pages01 CCNA 200-301 Chapter 1-Introduction To TCP IP NetworkingJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- 02 CCNA 200-301 Chapter 2-Fundamentals of Ethernet LansDocument31 pages02 CCNA 200-301 Chapter 2-Fundamentals of Ethernet LansJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- cs4471 Lab&read Assignments - 2019 SpringDocument1 pagecs4471 Lab&read Assignments - 2019 SpringJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- cs4471 OSPF LabDocument1 pagecs4471 OSPF LabJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- Wireshark Packet Capture and DecodeDocument1 pageWireshark Packet Capture and DecodeJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- cs4471 Access Contol List LabDocument1 pagecs4471 Access Contol List LabJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- cs4471 NAT LabDocument1 pagecs4471 NAT LabJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- DZRDocument11 pagesDZRJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- Vapcap M Vaporizer Manual Planet of The VapesDocument1 pageVapcap M Vaporizer Manual Planet of The VapesJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- Davinci Iq Vaporizer ManualDocument4 pagesDavinci Iq Vaporizer ManualJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- Miqro Vaporizer Owners ManualDocument36 pagesMiqro Vaporizer Owners ManualJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- Cisco Network Admission Control, Volume I NAC Framework Architecture and Design PDFDocument263 pagesCisco Network Admission Control, Volume I NAC Framework Architecture and Design PDFJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- Boundless Tera Vaporizer Manual English Planet of The VapesDocument31 pagesBoundless Tera Vaporizer Manual English Planet of The VapesJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- Fp-30 Midi Imple E01 WDocument38 pagesFp-30 Midi Imple E01 WJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- README OsxDocument4 pagesREADME OsxJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet
- DemystifyingtheChineseEconomy AuERDocument11 pagesDemystifyingtheChineseEconomy AuERJuan Pablo AragonNo ratings yet