Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Measurements Question Bank
Electrical Measurements Question Bank
Uploaded by
Harish B. M.Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Electrical Machinery PS BimbhraDocument1,000 pagesElectrical Machinery PS BimbhraNiranjan Taware83% (18)
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Linear and Digital Integrated Circuits Question BankDocument8 pagesLinear and Digital Integrated Circuits Question Bankdhanaram100% (1)
- Course Outcome Eds PDFDocument12 pagesCourse Outcome Eds PDFDileep VarmaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-III Question BankDocument9 pagesElectrical Machines-III Question BanksanthiNo ratings yet
- Iare Emi Emie Question BankDocument13 pagesIare Emi Emie Question BankRsandeep GupthaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation QBDocument9 pagesElectronic Measurements and Instrumentation QBSridhar Koneru VenkkatNo ratings yet
- MWEDocument13 pagesMWEsruthigummadiNo ratings yet
- QuestionBank Power QualityDocument7 pagesQuestionBank Power QualityramNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields Question BankDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Fields Question Bankbhanuc3No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields Question Bank PDFDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Fields Question Bank PDFsravanti kanuguNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Question Bank - PDF JntuDocument18 pagesElectrical Circuits Question Bank - PDF Jntudivya sakhamuriNo ratings yet
- Pulse and Digital Circuits (PDC) QB PDFDocument15 pagesPulse and Digital Circuits (PDC) QB PDFlakshmanNo ratings yet
- SS Jntu HydDocument19 pagesSS Jntu HydgiribabukandeNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Question Bank On Short Answer QuestionsDocument12 pagesObjectives: Question Bank On Short Answer QuestionsTahseen AnjumNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines - III PDFDocument9 pagesElectrical Machines - III PDFAliya MahaboobNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Question Bank PDFDocument15 pagesDigital Signal Processing Question Bank PDFsruthigummadiNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design Question BankDocument10 pagesVLSI Design Question Bankbooks babuNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor Drives Question BankDocument16 pagesPower Semiconductor Drives Question BankSaileela Reddy GangasaniNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-I Question BankDocument12 pagesElectrical Machines-I Question BankimmadiuttejNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Electrical Energy Question Bank PDFDocument17 pagesUtilization of Electrical Energy Question Bank PDFKranthi Kumar100% (1)
- Group - A (Short Answer Questions) : S.No Blooms Taxonomy Level Course OutcomesDocument15 pagesGroup - A (Short Answer Questions) : S.No Blooms Taxonomy Level Course OutcomesRama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Institute of Aeronautical Engineering: Short Answer QuestionsDocument11 pagesInstitute of Aeronautical Engineering: Short Answer Questionsmighty statusNo ratings yet
- 12 FDP 11 Ec 306 Electronics Circuits Lab TotalDocument459 pages12 FDP 11 Ec 306 Electronics Circuits Lab Totalkrish104411No ratings yet
- Electrical Machines - IIDocument9 pagesElectrical Machines - IIvenkat0% (1)
- Structural Analysis - I Question Bank PDFDocument16 pagesStructural Analysis - I Question Bank PDFSayed Urooj AbbasNo ratings yet
- CIVIL EngineeringDocument16 pagesCIVIL EngineeringSasala RajuNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Question BankDocument8 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Question BankdhruvNo ratings yet
- Bioelectric Signals and Electrodes Part-ADocument7 pagesBioelectric Signals and Electrodes Part-Alakshmi shreeNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - II Question Bank PDFDocument11 pagesStrength of Materials - II Question Bank PDFpavanNo ratings yet
- EEC 249 PracticalDocument66 pagesEEC 249 Practicalsanialiu2711No ratings yet
- Tutorial Bank: Unit-I The Cellular Concept-System Design FundamentalsDocument7 pagesTutorial Bank: Unit-I The Cellular Concept-System Design Fundamentalsvictor kNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Propulsion - I Question BankDocument5 pagesAerospace Propulsion - I Question BankGanesh Natarajan SNo ratings yet
- Eca - QBDocument13 pagesEca - QBAnil kumarNo ratings yet
- EC8094 Satellite Communication Qustion BankDocument12 pagesEC8094 Satellite Communication Qustion Bankkumar chitraNo ratings yet
- EDS CourseDocument18 pagesEDS CourseSaikumarNo ratings yet
- Ee - Sec-C-Lesson PlanDocument14 pagesEe - Sec-C-Lesson PlanAmarabalan NarasingamNo ratings yet
- EE1451 RES 2 Mark Q & ADocument8 pagesEE1451 RES 2 Mark Q & AparameshNo ratings yet
- Kiit University: Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesKiit University: Lesson Plan012ANTARA DUBEYNo ratings yet
- FEM Question Bank PDFDocument23 pagesFEM Question Bank PDFedla rajuNo ratings yet
- Group - A (Short Answer Questions) : S. No Blooms Taxonomy Level Course OutcomeDocument15 pagesGroup - A (Short Answer Questions) : S. No Blooms Taxonomy Level Course OutcomeIshani JhaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electrical Engineering Question BankDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Electrical Engineering Question BankUpender Rao SunkishalaNo ratings yet
- EE6701 High Voltage EngineeringDocument15 pagesEE6701 High Voltage EngineeringKRISHNA KUMAR ANo ratings yet
- EDS CourseDocument18 pagesEDS CourseSaikumarNo ratings yet
- 15ee72 QBDocument3 pages15ee72 QBCma CmaNo ratings yet
- CS QBDocument14 pagesCS QBSanjana RoyyapallyNo ratings yet
- Electronic Measurements & InstrumentationDocument9 pagesElectronic Measurements & InstrumentationSumanth NaniNo ratings yet
- BE3251 BEEE QB 01 - by WWW - Learnengineering.inDocument101 pagesBE3251 BEEE QB 01 - by WWW - Learnengineering.inrd gamingNo ratings yet
- EE8702-Power System Operation and Control - by WWW - Learnengineering.inDocument20 pagesEE8702-Power System Operation and Control - by WWW - Learnengineering.inhari vigneshNo ratings yet
- Signals & SystemsDocument19 pagesSignals & SystemsManish KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Power Quality (Rev. Feb 2018)Document3 pagesPower Quality (Rev. Feb 2018)Chai Jia JieNo ratings yet
- ENC10 Tamping Depth TransducerDocument4 pagesENC10 Tamping Depth Transducerbravi14141No ratings yet
- WWW - Universityquestions.in: Question BankDocument5 pagesWWW - Universityquestions.in: Question BankRojaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument15 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsAnonymous V3C7DYwKlv100% (1)
- TP6261 ConsiderUsingHarmonic 20061019 PDFDocument17 pagesTP6261 ConsiderUsingHarmonic 20061019 PDFmubarakkirkoNo ratings yet
- STLDDocument8 pagesSTLDsasi kiran sNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument4 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringpraveenaNo ratings yet
- 3-Fault AnalysisDocument104 pages3-Fault AnalysismubarakkirkoNo ratings yet
- Marks CO BL PI: BE B CDocument2 pagesMarks CO BL PI: BE B CV Nagaraj ECE KIOTNo ratings yet
- High Efficiency RF and Microwave Solid State Power AmplifiersFrom EverandHigh Efficiency RF and Microwave Solid State Power AmplifiersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- A Paper Presentation On: Nuclear Fusion ReactorDocument19 pagesA Paper Presentation On: Nuclear Fusion ReactorHarish B. M.100% (1)
- What Is TCP and Udp - Difference Between TCP and Udp - Types of Ip Address - Classes of Ipv4 - What Is SubnettingDocument12 pagesWhat Is TCP and Udp - Difference Between TCP and Udp - Types of Ip Address - Classes of Ipv4 - What Is SubnettingHarish B. M.No ratings yet
- 223-Statcom Seminar ReportDocument24 pages223-Statcom Seminar ReportHarish B. M.100% (1)
- Analysis of Overcurrent Protection Relay Settings of A Commercial Building-ReferencesDocument1 pageAnalysis of Overcurrent Protection Relay Settings of A Commercial Building-ReferencesHarish B. M.No ratings yet
- Seminar Topics PDFDocument8 pagesSeminar Topics PDFHarish B. M.No ratings yet
- Different Types of Electricity Markets Modelled Using PLEXOS Integrated Energy Model - The UK Balancing Market ExampleDocument7 pagesDifferent Types of Electricity Markets Modelled Using PLEXOS Integrated Energy Model - The UK Balancing Market ExampleHarish B. M.No ratings yet
- Prof. Ch. SAI BABU: Online Gate Coaching ClassesDocument103 pagesProf. Ch. SAI BABU: Online Gate Coaching ClassesHarish B. M.100% (1)
- New Doc 2019-08-23 19.44.18Document16 pagesNew Doc 2019-08-23 19.44.18Harish B. M.No ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-07-12 16.27.02Document4 pagesNew Doc 2019-07-12 16.27.02Harish B. M.No ratings yet
- Epgs 2maxDocument22 pagesEpgs 2maxHarish B. M.No ratings yet
- Onservation of Electrical Energy: Presentation by A.Reshma P. Lavanya G.sowjanya B.M.Harish B.sainath ReddyDocument19 pagesOnservation of Electrical Energy: Presentation by A.Reshma P. Lavanya G.sowjanya B.M.Harish B.sainath ReddyHarish B. M.No ratings yet
- 4 Eee Ii IiDocument15 pages4 Eee Ii IiHarish B. M.No ratings yet
- Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity: CtivityDocument5 pagesActivity Activity Activity Activity Activity: CtivityHarsh ShahNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Physics 2015-2016 PDFDocument22 pagesCBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Physics 2015-2016 PDFHrithik RajNo ratings yet
- CPP (Current Electricity (OBJ) B.Document18 pagesCPP (Current Electricity (OBJ) B.Falgun SoniNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Current Electricity Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Current Electricity Frequently Asked QuestionsNaveen rajNo ratings yet
- CST-02 With Answer Key PDFDocument17 pagesCST-02 With Answer Key PDFkavyareddyNo ratings yet
- Ei6301-Electrical Measurements Question PDFDocument13 pagesEi6301-Electrical Measurements Question PDFVIKRAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Current Electricity Practice QuestionsDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Current Electricity Practice QuestionsSmitha ThomasNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument63 pagesPhysicsprisha4No ratings yet
- Investigatory Project For PhysicsDocument21 pagesInvestigatory Project For PhysicsSiby GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurement Lab ManualDocument57 pagesElectrical Measurement Lab Manualckrishna625100% (1)
- Current Electricity Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGDocument20 pagesCurrent Electricity Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGRavi YadavNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Sheet SolnsDocument95 pagesCurrent Electricity Sheet SolnsHarsh WardhnNo ratings yet
- Derivations IDocument53 pagesDerivations IGG100% (2)
- Assertion and Reason QuestionsDocument13 pagesAssertion and Reason QuestionsGokul M PNo ratings yet
- PalmSens4 BrochureDocument17 pagesPalmSens4 BrochureKhalid ZghearNo ratings yet
- GSS-Physics PU2 Viva-Voce QuestionsDocument4 pagesGSS-Physics PU2 Viva-Voce Questions331Sachin KiragiNo ratings yet
- Time Electronics: 1007 DC Millivolt Potentiometer and CalibratorDocument2 pagesTime Electronics: 1007 DC Millivolt Potentiometer and CalibratorLi-ly AcostaNo ratings yet
- Radiometer ABL 700 SerieDocument234 pagesRadiometer ABL 700 SerieMuhamad AfidinNo ratings yet
- A & R Type Questions G-12 - PhysicsDocument13 pagesA & R Type Questions G-12 - PhysicsAbhiram VetchaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document19 pagesChapter 1Aira Shaynon GasNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity (QB)Document20 pagesCurrent Electricity (QB)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Meter BridgeDocument5 pagesMeter BridgeSandhya67% (9)
- 62dfade9dbe3f100116c0e27 - ## - Current Electricity - Short Notes - (Only PDFDocument35 pages62dfade9dbe3f100116c0e27 - ## - Current Electricity - Short Notes - (Only PDFYuvraj TripathiNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 12 Physics NotesDocument150 pagesCbse Class 12 Physics Notescrickjohn71% (17)
- Physics EM Model Question PaperDocument16 pagesPhysics EM Model Question Paperedukondalubonthu805No ratings yet
- Meter Bridge Experiment Using Wheatstone Bridge PrincipleDocument12 pagesMeter Bridge Experiment Using Wheatstone Bridge PrincipletahsNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry TheoryDocument198 pagesBiochemistry TheorysgajendranNo ratings yet
- 2023-24 - SR - Super60 (Incoming) - STERLING - Batch - PHYSICS - Teaching & Test Schedule - Code@03-04-2023Document9 pages2023-24 - SR - Super60 (Incoming) - STERLING - Batch - PHYSICS - Teaching & Test Schedule - Code@03-04-2023Geetha NNo ratings yet
- 2current Electricity PDFDocument43 pages2current Electricity PDFrabinNo ratings yet
Electrical Measurements Question Bank
Electrical Measurements Question Bank
Uploaded by
Harish B. M.Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Measurements Question Bank
Electrical Measurements Question Bank
Uploaded by
Harish B. M.Copyright:
Available Formats
www.alljntuworld.
in JNTU World
ld
or
OBJECTIVES
This course deals with measuring instruments mainly indicating instruments and the associated torques, instrument
transformers, power factor meter, frequency meter , synchro scopes, wattmeter, energy meter, potentiometer
,resistance measuring methods, ac bridges, ballistic galvanometer, flux meter, extension range of indicating
instruments.
W
QUESTION BANK ON SHORT ANSWER QUESTION
S. No Question Blooms Course
Taxonomy Level Outcome
UNIT -1
MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
1 Give the main classifications of electrical instruments. Understand 1
TU
2 Define the absolute instruments. Remember 1
3 Define the secondary instrument. Remember 1
4 Define the recording instruments. Remember 1
5 State the principle of magnetic effect. Remember 2
6 State the principle of electro-static effect. Remember 2
7 State the principle of electro-induction effect. Remember 2
8 What the different types are of associated with secondary instruments? Remember 4
9 What are the different arrangements to provide damping torque? Remember 1
JN
10 What is the different control torques? Remember 1
11 What is the importance of spring control torque? Understand 1
12 What is the importance of gravity control torque? Understand 1
13 What is the importance of MC instruments? Understand 1
14 What is the importance of MI instruments? Understand 1
15 Give two differences between MC and MI instruments. Understand 1
UNIT – II
1 Define instrument transformer. Remember 1
2 Give the importance of instrument transformer. Understand 1
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
S. No Question Blooms Course
Taxonomy Level Outcome
3 What is the main two instrument transformer? Create 4
4 Define transformation ratio. Remember 1
5 Define turns ratio. Remember 1
6 Define nominal ratio. Remember 1
7 Define ratio correction factor. Remember 1
8 Define the ratio error. Remember 1
9 Define the phase angle error. Remember 1
ld
10 Define the burden on secondary winding of instrument transformer. Remember 1
11 What is the limitation on operation of current transformer? Understand 4
12 Write the expression for ratio and phase angle error of potential Understand 2
Transformer.
13 Write the expression for ratio and phase angle error of current Understand 2
Transformer.
or
14 Suggest the different methods to reduce the ratio and phase angle Evaluate 3
Error of potential transformer.
15 Suggest the different methods to reduce the ratio and phase angle Evaluate 3
error of current transformer.
UNIT – III
(MEASUREMENT OF POWER)
1 Define power. Remember 1
2
W
Define power in DC circuits. Remember 1
3 Define power in AC circuits. Remember 1
4 Write the expression for torque in electro-dynamometer type Understand 2
wattmeter.
5 What are the main two coils in wattmeter? Remember 1
6 Define element in wattmeter/. Remember 1
7 Define the nature of resistance in pressure and current coil in Remember 1
wattmeter.
TU
8 How the pressure and control coil of wattmeter are connected in circuit/ Analyse 2
9 What is the principle of ferro-dynamic type wattmeter? Remember 2
10 How the low power factor is different from regular wattmeter? Analyse 2
11 Name the power measured by wattmeter. Remember 1
12 Suggest the type of connection of wattmeter into circuit under different Evaluate 3
conditions.
13 What is the importance of instrument transformer in collaboration with Analyse 2
wattmeter?
JN
14 Give the expression for three phase power using instrument transformer. Understand 2
15 Define double element. Remember 1
UNIT – IV
(MESUREMENT OF ENERGY)
1 Define energy. Remember 1
2 Define energy in DC circuits. Remember 1
3 Define energy in AC circuits. Remember 1
4 Write the expression for driving torque in single-phase induction type 2
energy meter. Understand
5 What are the main two coils in energy meter? Remember 1
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
S. No Question Blooms Course
Taxonomy Level Outcome
6 Define element in energy meter. Remember 1
7 Define the nature of resistance in pressure and current coil in energy Remember 1
meter.
8 How the pressure and control coil of energy meter are connected in 2
Analyze
circuit?
9 What is the different type of registering system of energy meter? Remember 3
10 What is the importance of braking system in energy meter? Understand 2
11 Give the arrangement to provide braking torque. Understand 3
ld
12 Suggest the type of connection of energy meter into circuit under Analyze 3
different conditions.
13 Define the static and running frictions in energy meter. Remember 1
14 Give the expression for braking torque in energy meter. Understand 2
15 Define double element. Remember 1
or
UNIT –V
(POTENTIOMETER)
1 Define potentiometer. Remember 1
2 What are the different types of potentiometer? Remember 3
3 Draw the DC Crompton potentiometer. Remember 1
4 What is the importance standard cell in DC Crompton potentiometer? Understand 1
5 What is the importance of volt-ratio box in collaboration with DC Understand 1
W
Crompton potentiometer?
6 Draw the circuit diagram for calibration of ammeter using DC Crompton Remember 1
potentiometer.
7 Draw the circuit diagram for calibration of voltmeter using DC Remember 1
Crompton potentiometer.
8 Draw the circuit diagram for measurement of resistance using DC Remember 1
Crompton potentiometer.
9 Draw the circuit diagram for measurement of power using DC Crompton 1
potentiometer. Remember
TU
10 Write the classification of AC potentiometer. Remember 3
11 Define polar type potentiometer. Remember 1
12 Define co-ordinate type potentiometer. Remember 1
13 Name the polar type potentiometer. Remember 1
14 Name the co-ordinate type potentiometer Remember 1
15 Draw the drysdale type potentiometer. Remember 1
UNIT –VI
(RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS)
JN
1 Define the resistance. Remember 1
2 What are different ranges of unknown resistance? Remember 3
3 Draw the wheat stone bridge for measurement of unknown resistance. Remember 1
4 Draw the volt-amp method circuit for measurement of unknown Remember 1
resistance.
5 Draw the amp-volt method circuit for measurement of unknown Remember 1
resistance.
6 Define the sensitivity of wheat stone bridge. Remember 1
7 Define the sensitivity galvanometer. Remember 1
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
S. No Question Blooms Course
Taxonomy Level Outcome
8 What is the importance of carey foster bridge? Evaluate 2
9 What is the importance of kelvin’s double bridge? Evaluate 2
10 Draw the Kelvin’s double bridge. Remember 1
11 Compare wheat stone bridge and substitution method to measure Evaluate 2
unknown resistance.
12 Write the expression for sensitivity of wheat stone bridge. Understand 2
13 Write the expression for sensitivity of galvanometer. Understand 2
ld
14 What is the importance of meggar circuit? Evaluate 2
15 Draw the circuit of substitution method. Remember 1
UNIT –VII
A.C BRIDGES
1 What are the main classifications of bridge? Remember 3
2 What is the condition for balance of bridge in DC bridges? Analyze 4
or
3 What is the condition for balance of bridge in AC bridges? Analyze 4
4 Write the condition for balance in terms of magnitude and phase for AC Analyze 4
bridges.
5 Draw the circuit diagram of wheat stone bridge. Remember 1
6 Draw the circuit diagram of Maxwell’s inductance bridge. Remember 1
7 Draw the circuit diagram of Maxwell’s inductance-capacitance bridge. Remember 1
8
9
W
Draw the circuit diagram of Anderson bridge.
Draw the circuit diagram of Owen bridge.
Remember
Remember
1
1
10 Draw the circuit diagram of Campbell bridge. Remember 1
11 Draw the circuit diagram of de-sauté’s bridge. Remember 1
12 Draw the circuit diagram of Schering bridge. Remember 1
13 What are the different types of sources for AC bridges? Remember 3
14 What are the different types of detectors in AC bridges? Remember 3
TU
15 Write the advantages and disadvantages of wheat stone bridge. Understand 2
UNIT –VIII
MAGNETIC MEASUREMENTS
1 State the principle on which ballistic galvanometer. Remember 2
2 State the principle on which flux meter. Remember 2
3 What is the importance of ballistic galvanometer? Understand 2
4 What is the importance of flux meter? Understand 2
5 Draw the ballistic galvanometer. Remember 1
JN
6 Draw the flux meter. Remember 1
7 Write the expression for torque governing ballistic galvanometer. Understand 2
8 Write the expression for torque governing flux meter. Understand 2
9 Write the applications of ballistic galvanometer. Understand 3
10 Write the applications of flux meter. Understand 3
11 Write the expression for equation of motion. Understand 2
12 Write the advantage and disadvantages of ballistic galvanometer. Understand 2
13 Write the advantage and disadvantages of flux meter. Understand 2
14 Compare the ballistic galvanometer and flux meter. Evaluate 3
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
S. No Question Blooms Course
Taxonomy Level Outcome
15 Define ballistic galvanometer. Remember 1
Group – II LONG ASNWERS QUASTIONS
S. No Question Blooms Course
Taxonomy Level Outcome
UNIT -1
ld
MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
1 Draw and explain the PMMC instrument construction along with Remember 1
operation
2 Draw and explain the MI attraction instrument construction along with Remember 1
operation.
3 Derive the expression for value of shunt in the universal aryton ammeter. Create 2
4 Derive the expression for value of multiplier in the universal aryton Create 2
or
voltmeter.
5 Draw and explain the idio static instrument construction along with Remember 1
operation.
6 Derive the torque equation of MI instruments. Create 2
7 What is loading effect? Explain with an example. Remember 3
8 Give the main classifications of electrical instruments along with the Understand 3
definitions with relevant examples.
9
W
Define magnetic effect, electro-static effect, heat effect, chemical effect, Remember 2
induction effect.
10 Derive the expression for value of multiplier in the multi-range Create 2
voltmeter.
UNIT –II
(INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMER)
1 Give the construction of current transformer and explain its operation. Understand 1
2 Give the construction of potential transformer and explain its operation. Understand 1
TU
3 Draw and explain the construction and operation of 1-phase power factor 1,2
meter. Remember
4 Draw and explain the construction and operation of 3-phase power factor Remember 1,2
meter.
5 Draw and explain the construction and operation of weston type Remember 1,2
frequency meter.
6 Draw and explain the construction and operation of resonant type Remember 1,2
frequency meter.
7 Draw and explain the construction and operation of Weston type Remember 1,2
synchroscope.
JN
8 Draw and explain the construction and operation of moving iron type Remember 1,2
frequency meter.
9 Draw and explain the construction and operation of moving iron type Remember 1,2
suynchroscopes.
10 Explain the difference between construction of 1-phase and 3-phase Create 3
power factor meter and why?
UNIT –III
(MEASUREMENT OF POWER)
1 Draw and explain the construction and operation of electro- Remember 1,2
dynamometer wattmeter.
2 Derive the expression for correction factor of wattmeter. Create 2
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
S. No Question Blooms Course
Taxonomy Level Outcome
3 Draw and explain the construction and operation of ferrodynamic Remember 1,2
wattmeter.
4 State the blondel’s theorem and explain with an example. Remember 2
5 Derive the expression for power factor angle in two wattmeter method Create 2
for measurement of power.
6 Draw and explain the construction and operation of 2 element wattmeter. Remember 1,2
7 Draw and explain the construction and operation of var meter. Remember 1,2
8 Explain the procedure to test whether the wattmeter measures exact Understand 4
ld
power or not.
9 Prove the power statement in three-phase circuits using two wattmeter Create 4
methods for unbalanced load.
10 Prove the power statement in three-phase circuits using two wattmeter Create Iv
method.
UNIT –IV
or
(MESUREMENT OF ENERGY)
1 Draw and explain the operation induction type energy meter. Remember 1,2
2 What is phantom loading, explain with an example? Remember 2
3 Explain the test-A procedure for testing of energy-meter. Understand 4
4 Explain the test-B procedure for testing of energy-meter. Understand 4
5 Explain the test-C procedure for testing of energy-meter. Understand 4
6 Draw and explain the operation of maximum demand meter. Remember 1,2
7
W
Explain the different type adjustments made for smooth working of Understand 3
energy-meter.
8 Draw and explain the two element energy-meter Remember 1
9 Suggest the different methods to reduce the errors which effect the Understand 3
measurement of energy.
10 Compare the 1-phase and 3-phase induction type energy meter. Understand 2
UNIT –V
(POTENTIOMETER)
TU
1 Define potentiometer and explain the operation of DC Crompton Remember 1
potentiometer with neat sketch.
2 Draw and explain the operation of drysdale potentiometer. Remember 1,2
3 Draw and explain the operation of gal tinsley potentiometer. Remember 1,2
4 Give and explain the applications of DC Crompton potentiometer. Understand 2
5 Give and explain the applications of AC Crompton potentiometer. Understand 2
6 Distinguish between DC and AC potentiometer. Understand 3
7 Explain the process of standardization for DC Crompton potentiometer. Understand 2
JN
8 Write different types of errors effecting the operation of DC Crompton Understand 4
potentiometer.
9 Explain the measurement of resistance and power using DC Crompton Understand 2
potentiometer.
10 Explain the measurement of voltage and current using DC Crompton Understand 2
potentiometer.
UNIT –VI
(RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS)
1 Explain the method of volt-amp for measurement of resistance. Understand 2
2 Explain the method of substitution method for measurement of Understand 2
resistance
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
S. No Question Blooms Course
Taxonomy Level Outcome
3 Draw and derive the expressions for unknown resistance using wheat Remember 1,2
stone bridge.
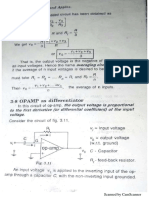
4 In the wheatstonebridge p= 1000 ohms, q = 100 ohms, r = 2005 ohms Apply 3
and s = 200 ohms.the battery has an emf of 5v. The galvanometer has a
current sensitivity of 100mm/ micro amp andinternal resistanec of 100
ohms. Calculate the current through galvanometer and sensitivity of
bridge
5 Draw and derive the expression for unknown resistance using Kelvin Remember 1,2
ld
double bridge
6 Draw and explain the operation of megger circuit. Remember 1,2
7 In a carey foster bridge a resistance of 1.0125 ohms is compared with Apply 3
standard resistance of 1.0000 ohms, the slide wire has a resistance of
0.250 ohms in 100 divisions. the ratio arms nominally each 10 ohms, are
actually 10.05 and 9.95 ohms. Slide wire is of 100 cm. find the position
of balance.
or
8 Draw and explain loss of charge method. Remember 2
9 Compare the advantages and disadvantages of carey foster bridge, Evaluate 3
Kelvin’s double bridge and wheat stone bridge.
10 Give the classifications of different ranges of resistance suggesting the Understand 3
best methods to measure.
UNIT –VII
(A.C BRIDGES)
1
2
W
Explain the basic construction of bridge.
Draw and derive the known parameters from Maxwell’s inductance-
Understand
Remember
1,2
1,2
capacitance bridge.
3 Draw and derive the known parameters from HAY’S bridge. Remember 1,2
4 Draw and derive the known parameters from ANDERSON’S bridge. Remember 1,2
5 Draw and derive the known parameters from OWEN’S bridge. Remember 1,2
6 Draw and derive the known parameters from DE-SAUTY’S bridge. Remember 1,2
7 Draw and derive the known parameters from CAMPBELL’S bridge. Remember 1,2
TU
8 Draw and derive the known parameters from WEIN’S bridge. Remember 1,2
9 Draw and derive the known parameters from SCHERING bridge. Remember 1,2
10 Draw and derive the known parameters from MAXWELL’S Remember 1,2
INDUCTANCE bridge.
UNIT –VIII
(MAGNETIC MEASUREMENTS)
1 Distinguish between d’arsonal and ballistic galvanometer. Understand 3
2 Derive the expression for torque equation of galvanometer. Create 2
JN
3 Draw the construction and explain the operation of ballistic Remember 1,2
galvanometer.
4 Write the advantages and disadvantages of ballistic galvanometer. Understand 3
5 What are the different types of errors effecting measurement by ballistic Understand 3
galvanometer and how?
6 Suggest the different methods for reducing the errors effecting Analyse iii
measurement by galvanometer.
7 Derive the expression for torque equation of flux meter. Create 3
8 Draw the construction and explain the operation of flux meter. Remember 1,2
9 Write the advantages and disadvantages of flux meter. Understanfd 3
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
S. No Question Blooms Course
Taxonomy Level Outcome
10 What are the different types of errors effecting measurement by flux Understand 3
meter and how?
11 Suggest the different methods for reducing the errors effecting Analyse 3
measurement by flux meter.
12 Derive the expression for equation of motion flux meter. Create 2
13 Compare the ballastic galvanometer and flux meter. Evaluate 3
ld
GROUP – III ANALYTICAL QUESTIONS
S. No Question Blooms Course
Taxonomy Level Outcome
UNIT -1
MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
1 A moving-coil instrument gives a full scale deflection. When the current Apply 3
or
is 40 mA and its resistance is 25. Calculate the value of the shunt to be
connected in parallel with the meter to enable it to be used as an
ammeter for measuring currents up to 50 A.
2 A moving-coil instrument having a resistance of 10 ohms, gives a full Apply 3
scale deflection. When the current is 8 mA. Calculate the value of the
multiplier to be connected in series with the instrument so that it can be
used as a voltmeter for measuring full scale deflection up to 100 V
3
W
A moving-coil instrument gives full.scale.deflection. For a current of 10
mA. Neglecting the resistance of the instrument, calculate the
Apply 3
approximate value of series resistance needed to enable the instrument to
measure up to (a) 20 V (b) 100 V(c) 250 V
4 A meter of resistance 50 ohms has a full scale deflection of 4 mA. Apply 3
Determine the value of shunt resistance required in order that full scale
deflection should be (a) 15 mA (b) 20 A (c) 100 A
5 A moving-coil instrument having a resistance of 20, gives af.s.d. when Apply 3
the current is5 mA. Calculate the value of the multiplier to be connected
TU
in series with the instrument so that it can be used as a voltmeter for
measuring full. Scale. deflection up to 200 V
6 A moving-coil instrument has a full scale deflection of 20 mA and a Apply 3
resistance of 25 . Calculate the values of resistance required to enable
the instrument to be used (a) as a 0–10 A ammeter and (b) as a 0–100 V
voltmeter. State the mode of resistance connection in each case.
7 A meter has a resistance of 40 and registers a maximum deflection when Apply 3
a current of 15 mA flows. Calculate the value of resistance that converts
the movement into(a) an ammeter with a maximum deflection of50 A
(b) a voltmeter with a range 0–250 V
JN
8 An ammeter has a full. Scale deflection. Of100 mA and a resistance of Apply 3
50. The ammeter is used to measure the current in a load of resistance
500 when the supply voltage is 10 V. Calculate (a) the ammeter reading
expected (neglecting its resistance)(b) the actual current in the circuit,
(c) the power dissipated in the ammeter, and (d) the power dissipated in
the load.
9 A voltage of 240 V is applied to a circuit consisting of an 800 resistor in Apply 3
series with a 1.6 k resistor. What is the voltage across the 1.6 k resistor?
The potential differences across the 1.6k resistor is measured by a
voltmeter of f.s.d.250 V and sensitivity 100 /V. Determine the voltage
indicated
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
S. No Question Blooms Course
Taxonomy Level Outcome
10 A 0–1 A ammeter having a resistance of 50is used to measure the Apply 3
current flowing in 1 k resistor when the supply voltage is 250
V.Calculate: (a) the approximate value of current (neglecting the
ammeter resistance), (b) the actual current in the circuit, (c) the power
dissipated in the ammeter, (d) the power dissipated in the 1 k resistor.
11 (a) A current of 15 A flows through a load having a resistance of 4. Apply 3
Determine the power dissipated in the load. (b) A wattmeter, whose
current coil has a resistance of 0.02 is connected (as shown in Fig.
10.13) to measure the power in the load. Determine the wattmeter
ld
reading assuming the current in the load is still15 A.
12 A PMMC instrument has a coil dimensions 15mm*12mm. the flux Apply 3
density in the air gap is 1.8 mWb/m*m and the spring constant
0.14micro N-m/rad. Determine the number of turns required to produce
an angular deflection of 90degrees when a current of 5mA is flowing
through the coil.
or
13 A PMMC instrument has a coil dimensions 15mm*12mm. the flux Apply 3
density in the air gap is 1.8 mWb/m*m and the spring constant
0.14micro N-m/rad. Determine the number of turns required to produce
an angular deflection of 90degrees when a current of 5mA is flowing
through the coil.
UNIT – II
INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMER
1 A current transformer has a single turn primary and a 200 turn’s Apply 3
W
secondary winding. The secondary winding supplies a current of 5a to a
non-inductive burden of 1 ohm resistance. The requisite flux set up in
the core by an mmf of 80a.the frequency is 50hz and the net cross-
section of the core is 1000mm2.calculate the ratio and phase angle error.
2 The exciting current of a ring core current transformer, of ratio 1000/5a Apply 3
when operating at full primmary.current and with a secondary burden of
non-inductive resistance of 1ohm is 1a, at a power factor of 0.4.calculate
phase and ratio error.
3 a 1000/5a 50 hz current transformer has a secondary burden comprising Apply 3
TU
of non-inductive impedance of 1.6 ohms .the primary winding has one
turn .calculate the flux in the core and ratio error at full load. Neglect
leakage reactance and assume the iron loss in core to be 105w at full
load. the magnetizing mmf is 100
4 a potential transformer ratio 1000/100v has the following constants: Apply 3
Primary resistance = 945 ohms, secondary resistance = 0.86 ohm,
primary reactance = 66.2 ohms, total equivalent reactance = 110 ohms,
no-load current at 0.4 power factor. calculate phase and ratio error
UNIT – III
(MEASUREMENT OF POWER)
JN
1 the indication on a110v, 5a wattmeter used in conjunction with potential Apply 3
and current transformer of nominal ratio 100/1 and 20/1 respectively
350w.if the resistance and reactance of pressure coil is 362ohms and
100mh and the ratio and phase angle error of pt and ct are 0.8%, -45 deg
and -0.2%, 90deg.what is the actual power measured, the load phase
angle is 50deg and 500 hz.
2 In the two wattmeter method readings are 2000w and 500w respectively. Apply 3
Find the power factor of circuit.
when the both the readings are positive
If one of the wattmeter is obtained by interchanging terminals.
3 In the two wattmeter method readings are 7500w and-1500w Apply 3
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
S. No Question Blooms Course
Taxonomy Level Outcome
respectively. Find the power factor of circuit.
find the power factor of the circuit
If the voltage is 400v, what is the capacitance must be added
such that only one wattmeter reads total power.
4 A 3-ph motor load has power factor of 0.4. The reading of total input is Apply 3
3-kw. Hence calculate reading of each wattmeter.
5 A wattmeter has a cc of 0.1ohm resistance resistance and pc of 6500 Apply 3
ohms resistance. Calculate the percentage in measurement.
12a, 250v with unity power factor.
ld
12a, 250v with 0.4 power factor.
6 The cc of wattmeter connected in series with ammeter and inductive Apply 3
load .An voltmeter and pc are connected in parallel with 100hz supply.
The readings are 4.5a, 240v and 23w.pc is of r = 2000 ohms and l =
10mh. What is the error in the measurement?
7 A wattmeter is rated at 10a 25v the cc is of (0.06+0.02j). The pc is Apply 3
or
purely resistive of 6250 ohms. Find the error due to two different types
of connections. The load is 10a at apower factor of 0.174 lagging. the
voltage across load is 25v
8 The cc of wattmeter connected in series with ammeter and inductive Apply 3
load. A voltmeter and pc are connected in parallel with 100hz supply.
the readings are 4.5a, 240v and 23w.pc is of r = 2000 ohms and l =
10mh
UNIT –IV
1
W (MESUREMENT OF ENERGY)
Explain the phantom loading for the wattmeter with cc of 0.1 ohm and Apply iii
pc of 8800 ohms and dc source of 6v and 5A.
2 The readings from the TEST A are RX = 10 RS = 10 KX= 1000 Apply 3
KS= 1200 find the error in the measurements.
3 The readings from the TEST B are Apply 3
nx = 10o within time of 10 sec rs = 10
kx= 150 within tome of 15 sec ks= 1200
TU
Find the error in the Measurements.
4 The readings from the TEST C are Apply 3
RX = 5 T = 100 SEC KX= 100 V = 230 V I = 2A
Find the error in the measurements.
5 The readings from the TEST C are Apply 3
RX = 5 T = 90 SEC KX= 1000 V = 230 V I = 4A
Find the error in the measurements.
6 The readings from the TEST C are Apply 3
RX = 5 T = 60 SEC KX= 1000 V = 230 V I = 6A
JN
Find the error in the measurements.
7 The readings from the TEST C are Apply 3
RX = 5 T = 300 SEC KX= 1000 V = 230 V I = 8A find the error in the
measurements
8 The readings from the TEST C are RX = 5 T = 20 SEC KX= 1000 Apply 3
V = 230 V I = 10A find the error in the measurements.
UNIT –V
(POTENTIOMETER)
1 The potentiometer is operated in conjunction with volt-ratio box; the Apply 3
voltage measured by potentiometer is 0.86 with full scale deflection of
1.6 v. Determine the reading of potentiometer for the range of 75v, 150v,
300v.
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
S. No Question Blooms Course
Taxonomy Level Outcome
2 A simple slide wire is used for measurement of current in the circuit. the Apply 3
voltage across standard resistor of 0.1 ohm is at 75cm. Find the
magnitude of current if the standard cell emf if 1.45v is balanced at 50
cm.
3 For the volt-ratio the input and output voltages are 100v and 2v. If the Apply 3
volt-ratio box is of (r1+r2) with 10m ohms. Determine the r1 and r2
values.
4 Calculate the inductance of coil from the following measurement of ac Apply 3
ld
potentiometer. Voltage across 0.1 ohm standard resistor in series with
coil is 0.613 with 12.6 deg.
Voltage drop across test coil through 100/1 volt-ratio box is 0.718 with
50.48 deg.
5 Calculate the impedance of the coil voltage across 1 ohm standard Apply 3
resistor in series with coil is 0.238v and -0.085 v are in phase and
quadrature voltage respectively
Voltage drop across test coil through 10/1 volt-ratio box is 0.3375 and
or
0.232v are in phase and quadrature voltage respectively
UNIT –VI
(RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS)
1 In the volt-ampere method the voltmeter and ammeter readings are 180V Apply 3
and 2A for the second type of connections. Find the error in the
measurement.
2 A resistance of approximately 3000 ohms needed to balance the bridge. Apply 3
W
It is obtain on the 5 dial resistance box of 1000, 100, 10, 1, 0.1 ohms.
The measuring is to be guaranteed to 0.1%.
3 In the Wheatstone bridge p= 1000 ohms, q = 100 ohms, r = 2005 ohms Apply 3
and s = 200 ohms. The battery has an emf of 5v. the galvanometer has a
current sensitivity of 100mm/ micro amp and internal resistance of 100
ohms. Calculate the current through galvanometer and sensitivity of
bridge.
4 A wheat stone bridge has ratio arm of 1000/100 ohms. to measure Apply 3
unknown resistance of 25 ohms. Two galvanometers are used –
TU
Galvanometer A - resistance of 50 ohms and sensitivity
of 200
Galvanometer B - resistance of 600 ohms and
sensitivity of 500
5 The values of resistors in wheat stone bridge are P = R = 1k ohms, S == Apply 3
5k ohms, G = 100 ohms, derive the bridge
6 In a carey foster bridge a resistance of 1.0125 ohms is compared with Apply 3
standard resistance of 1.0000 ohms, the slide wire has a resistance of
0.250 ohms in 100 divisions. the ratio arms nominally each 10 ohms, are
actually 10.05 and 9.95 ohms. Slide wire is of 100 cm. find the position
JN
of balance.
UNIT –VII
(A.C BRIDGES)
1 In the given bridge Apply 3
ARM AB = L1 WITH r1 IN SERIES WITH R1
ARM AD = 47.8 Mh in series with 32.7 ohms
ARM BC = 100 OHMS
ARM CD = 100 OHMS
IF BALANCE IS OBTAINED FOR R1 = 1.36 OHMS
CALCULATE L1 AND r1.
2 In the given bridge Apply 3
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
S. No Question Blooms Course
Taxonomy Level Outcome
ARM AB = L1 IN SERIES WITH R1
ARM AD = 2410 OHMS
ARM BC = 750 OHMS
ARM CD = 0.35 MICRO F WITH 64.5 OHMS
FIND THE UNKNOWN PARAMETERS.
3 In the given bridge Apply 3
ARM AB = L1 WITH r1= 43.1 OHMS IN SERIES WITH R1
ARM AD = 250 OHMS
ARM BC = 100 OHMS
ld
ARM CD = 200 OHMS
ARM DE = 229.7 OHMS
ARM CE = 1 MICRO F.
THE UNKNOWN PARAMETERS.
4 In the given bridge Apply 3
ARM AB = 200 OHMS IN PARALLEL 1 MICRO F
or
ARM AD = R2 IN SERIES WITH 2 MICRO F.
ARM BC = 400 OHMS
ARM CD = 1000 OHMS
FIND THE UNKNOWN PARAMETERS.
5 In the given bridge Apply 3
ARM AB = C1 IN SERIES WITH R1
ARM AD = 5.2 OHMS IN SERIES WITH 0.5 MICRO F
ARM BC = 2000 OHMS
W
ARM CD = 2850 OHMS
FIND THE UNKNOWN PARAMETERS.
TU
JN
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
You might also like
- Electrical Machinery PS BimbhraDocument1,000 pagesElectrical Machinery PS BimbhraNiranjan Taware83% (18)
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Linear and Digital Integrated Circuits Question BankDocument8 pagesLinear and Digital Integrated Circuits Question Bankdhanaram100% (1)
- Course Outcome Eds PDFDocument12 pagesCourse Outcome Eds PDFDileep VarmaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-III Question BankDocument9 pagesElectrical Machines-III Question BanksanthiNo ratings yet
- Iare Emi Emie Question BankDocument13 pagesIare Emi Emie Question BankRsandeep GupthaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation QBDocument9 pagesElectronic Measurements and Instrumentation QBSridhar Koneru VenkkatNo ratings yet
- MWEDocument13 pagesMWEsruthigummadiNo ratings yet
- QuestionBank Power QualityDocument7 pagesQuestionBank Power QualityramNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields Question BankDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Fields Question Bankbhanuc3No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Fields Question Bank PDFDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Fields Question Bank PDFsravanti kanuguNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Question Bank - PDF JntuDocument18 pagesElectrical Circuits Question Bank - PDF Jntudivya sakhamuriNo ratings yet
- Pulse and Digital Circuits (PDC) QB PDFDocument15 pagesPulse and Digital Circuits (PDC) QB PDFlakshmanNo ratings yet
- SS Jntu HydDocument19 pagesSS Jntu HydgiribabukandeNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Question Bank On Short Answer QuestionsDocument12 pagesObjectives: Question Bank On Short Answer QuestionsTahseen AnjumNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines - III PDFDocument9 pagesElectrical Machines - III PDFAliya MahaboobNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Question Bank PDFDocument15 pagesDigital Signal Processing Question Bank PDFsruthigummadiNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design Question BankDocument10 pagesVLSI Design Question Bankbooks babuNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor Drives Question BankDocument16 pagesPower Semiconductor Drives Question BankSaileela Reddy GangasaniNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-I Question BankDocument12 pagesElectrical Machines-I Question BankimmadiuttejNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Electrical Energy Question Bank PDFDocument17 pagesUtilization of Electrical Energy Question Bank PDFKranthi Kumar100% (1)
- Group - A (Short Answer Questions) : S.No Blooms Taxonomy Level Course OutcomesDocument15 pagesGroup - A (Short Answer Questions) : S.No Blooms Taxonomy Level Course OutcomesRama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Institute of Aeronautical Engineering: Short Answer QuestionsDocument11 pagesInstitute of Aeronautical Engineering: Short Answer Questionsmighty statusNo ratings yet
- 12 FDP 11 Ec 306 Electronics Circuits Lab TotalDocument459 pages12 FDP 11 Ec 306 Electronics Circuits Lab Totalkrish104411No ratings yet
- Electrical Machines - IIDocument9 pagesElectrical Machines - IIvenkat0% (1)
- Structural Analysis - I Question Bank PDFDocument16 pagesStructural Analysis - I Question Bank PDFSayed Urooj AbbasNo ratings yet
- CIVIL EngineeringDocument16 pagesCIVIL EngineeringSasala RajuNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Question BankDocument8 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Question BankdhruvNo ratings yet
- Bioelectric Signals and Electrodes Part-ADocument7 pagesBioelectric Signals and Electrodes Part-Alakshmi shreeNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - II Question Bank PDFDocument11 pagesStrength of Materials - II Question Bank PDFpavanNo ratings yet
- EEC 249 PracticalDocument66 pagesEEC 249 Practicalsanialiu2711No ratings yet
- Tutorial Bank: Unit-I The Cellular Concept-System Design FundamentalsDocument7 pagesTutorial Bank: Unit-I The Cellular Concept-System Design Fundamentalsvictor kNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Propulsion - I Question BankDocument5 pagesAerospace Propulsion - I Question BankGanesh Natarajan SNo ratings yet
- Eca - QBDocument13 pagesEca - QBAnil kumarNo ratings yet
- EC8094 Satellite Communication Qustion BankDocument12 pagesEC8094 Satellite Communication Qustion Bankkumar chitraNo ratings yet
- EDS CourseDocument18 pagesEDS CourseSaikumarNo ratings yet
- Ee - Sec-C-Lesson PlanDocument14 pagesEe - Sec-C-Lesson PlanAmarabalan NarasingamNo ratings yet
- EE1451 RES 2 Mark Q & ADocument8 pagesEE1451 RES 2 Mark Q & AparameshNo ratings yet
- Kiit University: Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesKiit University: Lesson Plan012ANTARA DUBEYNo ratings yet
- FEM Question Bank PDFDocument23 pagesFEM Question Bank PDFedla rajuNo ratings yet
- Group - A (Short Answer Questions) : S. No Blooms Taxonomy Level Course OutcomeDocument15 pagesGroup - A (Short Answer Questions) : S. No Blooms Taxonomy Level Course OutcomeIshani JhaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electrical Engineering Question BankDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Electrical Engineering Question BankUpender Rao SunkishalaNo ratings yet
- EE6701 High Voltage EngineeringDocument15 pagesEE6701 High Voltage EngineeringKRISHNA KUMAR ANo ratings yet
- EDS CourseDocument18 pagesEDS CourseSaikumarNo ratings yet
- 15ee72 QBDocument3 pages15ee72 QBCma CmaNo ratings yet
- CS QBDocument14 pagesCS QBSanjana RoyyapallyNo ratings yet
- Electronic Measurements & InstrumentationDocument9 pagesElectronic Measurements & InstrumentationSumanth NaniNo ratings yet
- BE3251 BEEE QB 01 - by WWW - Learnengineering.inDocument101 pagesBE3251 BEEE QB 01 - by WWW - Learnengineering.inrd gamingNo ratings yet
- EE8702-Power System Operation and Control - by WWW - Learnengineering.inDocument20 pagesEE8702-Power System Operation and Control - by WWW - Learnengineering.inhari vigneshNo ratings yet
- Signals & SystemsDocument19 pagesSignals & SystemsManish KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Power Quality (Rev. Feb 2018)Document3 pagesPower Quality (Rev. Feb 2018)Chai Jia JieNo ratings yet
- ENC10 Tamping Depth TransducerDocument4 pagesENC10 Tamping Depth Transducerbravi14141No ratings yet
- WWW - Universityquestions.in: Question BankDocument5 pagesWWW - Universityquestions.in: Question BankRojaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument15 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsAnonymous V3C7DYwKlv100% (1)
- TP6261 ConsiderUsingHarmonic 20061019 PDFDocument17 pagesTP6261 ConsiderUsingHarmonic 20061019 PDFmubarakkirkoNo ratings yet
- STLDDocument8 pagesSTLDsasi kiran sNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument4 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringpraveenaNo ratings yet
- 3-Fault AnalysisDocument104 pages3-Fault AnalysismubarakkirkoNo ratings yet
- Marks CO BL PI: BE B CDocument2 pagesMarks CO BL PI: BE B CV Nagaraj ECE KIOTNo ratings yet
- High Efficiency RF and Microwave Solid State Power AmplifiersFrom EverandHigh Efficiency RF and Microwave Solid State Power AmplifiersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- A Paper Presentation On: Nuclear Fusion ReactorDocument19 pagesA Paper Presentation On: Nuclear Fusion ReactorHarish B. M.100% (1)
- What Is TCP and Udp - Difference Between TCP and Udp - Types of Ip Address - Classes of Ipv4 - What Is SubnettingDocument12 pagesWhat Is TCP and Udp - Difference Between TCP and Udp - Types of Ip Address - Classes of Ipv4 - What Is SubnettingHarish B. M.No ratings yet
- 223-Statcom Seminar ReportDocument24 pages223-Statcom Seminar ReportHarish B. M.100% (1)
- Analysis of Overcurrent Protection Relay Settings of A Commercial Building-ReferencesDocument1 pageAnalysis of Overcurrent Protection Relay Settings of A Commercial Building-ReferencesHarish B. M.No ratings yet
- Seminar Topics PDFDocument8 pagesSeminar Topics PDFHarish B. M.No ratings yet
- Different Types of Electricity Markets Modelled Using PLEXOS Integrated Energy Model - The UK Balancing Market ExampleDocument7 pagesDifferent Types of Electricity Markets Modelled Using PLEXOS Integrated Energy Model - The UK Balancing Market ExampleHarish B. M.No ratings yet
- Prof. Ch. SAI BABU: Online Gate Coaching ClassesDocument103 pagesProf. Ch. SAI BABU: Online Gate Coaching ClassesHarish B. M.100% (1)
- New Doc 2019-08-23 19.44.18Document16 pagesNew Doc 2019-08-23 19.44.18Harish B. M.No ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-07-12 16.27.02Document4 pagesNew Doc 2019-07-12 16.27.02Harish B. M.No ratings yet
- Epgs 2maxDocument22 pagesEpgs 2maxHarish B. M.No ratings yet
- Onservation of Electrical Energy: Presentation by A.Reshma P. Lavanya G.sowjanya B.M.Harish B.sainath ReddyDocument19 pagesOnservation of Electrical Energy: Presentation by A.Reshma P. Lavanya G.sowjanya B.M.Harish B.sainath ReddyHarish B. M.No ratings yet
- 4 Eee Ii IiDocument15 pages4 Eee Ii IiHarish B. M.No ratings yet
- Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity: CtivityDocument5 pagesActivity Activity Activity Activity Activity: CtivityHarsh ShahNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Physics 2015-2016 PDFDocument22 pagesCBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12 Physics 2015-2016 PDFHrithik RajNo ratings yet
- CPP (Current Electricity (OBJ) B.Document18 pagesCPP (Current Electricity (OBJ) B.Falgun SoniNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Current Electricity Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Current Electricity Frequently Asked QuestionsNaveen rajNo ratings yet
- CST-02 With Answer Key PDFDocument17 pagesCST-02 With Answer Key PDFkavyareddyNo ratings yet
- Ei6301-Electrical Measurements Question PDFDocument13 pagesEi6301-Electrical Measurements Question PDFVIKRAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Current Electricity Practice QuestionsDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Current Electricity Practice QuestionsSmitha ThomasNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument63 pagesPhysicsprisha4No ratings yet
- Investigatory Project For PhysicsDocument21 pagesInvestigatory Project For PhysicsSiby GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurement Lab ManualDocument57 pagesElectrical Measurement Lab Manualckrishna625100% (1)
- Current Electricity Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGDocument20 pagesCurrent Electricity Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGRavi YadavNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Sheet SolnsDocument95 pagesCurrent Electricity Sheet SolnsHarsh WardhnNo ratings yet
- Derivations IDocument53 pagesDerivations IGG100% (2)
- Assertion and Reason QuestionsDocument13 pagesAssertion and Reason QuestionsGokul M PNo ratings yet
- PalmSens4 BrochureDocument17 pagesPalmSens4 BrochureKhalid ZghearNo ratings yet
- GSS-Physics PU2 Viva-Voce QuestionsDocument4 pagesGSS-Physics PU2 Viva-Voce Questions331Sachin KiragiNo ratings yet
- Time Electronics: 1007 DC Millivolt Potentiometer and CalibratorDocument2 pagesTime Electronics: 1007 DC Millivolt Potentiometer and CalibratorLi-ly AcostaNo ratings yet
- Radiometer ABL 700 SerieDocument234 pagesRadiometer ABL 700 SerieMuhamad AfidinNo ratings yet
- A & R Type Questions G-12 - PhysicsDocument13 pagesA & R Type Questions G-12 - PhysicsAbhiram VetchaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document19 pagesChapter 1Aira Shaynon GasNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity (QB)Document20 pagesCurrent Electricity (QB)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Meter BridgeDocument5 pagesMeter BridgeSandhya67% (9)
- 62dfade9dbe3f100116c0e27 - ## - Current Electricity - Short Notes - (Only PDFDocument35 pages62dfade9dbe3f100116c0e27 - ## - Current Electricity - Short Notes - (Only PDFYuvraj TripathiNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 12 Physics NotesDocument150 pagesCbse Class 12 Physics Notescrickjohn71% (17)
- Physics EM Model Question PaperDocument16 pagesPhysics EM Model Question Paperedukondalubonthu805No ratings yet
- Meter Bridge Experiment Using Wheatstone Bridge PrincipleDocument12 pagesMeter Bridge Experiment Using Wheatstone Bridge PrincipletahsNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry TheoryDocument198 pagesBiochemistry TheorysgajendranNo ratings yet
- 2023-24 - SR - Super60 (Incoming) - STERLING - Batch - PHYSICS - Teaching & Test Schedule - Code@03-04-2023Document9 pages2023-24 - SR - Super60 (Incoming) - STERLING - Batch - PHYSICS - Teaching & Test Schedule - Code@03-04-2023Geetha NNo ratings yet
- 2current Electricity PDFDocument43 pages2current Electricity PDFrabinNo ratings yet