Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nabl News 46 Apr 2007
Nabl News 46 Apr 2007
Uploaded by
Gagan SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- JHA - Unloading of Sheet PileDocument3 pagesJHA - Unloading of Sheet PileJensen Sunga100% (1)
- Astm F-1962 PDFDocument18 pagesAstm F-1962 PDFKenNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Quality/Management: A Workbook with an Eye on AccreditationFrom EverandLaboratory Quality/Management: A Workbook with an Eye on AccreditationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Laboratory Accreditation - Procedural GuidelinesDocument3 pagesLaboratory Accreditation - Procedural Guidelinesshk76No ratings yet
- A.S .Kanagasabapathy and Pragna Rao: Kamineni Hospitals LTD., L.B. Nagar, Hyderabad - 500 068Document3 pagesA.S .Kanagasabapathy and Pragna Rao: Kamineni Hospitals LTD., L.B. Nagar, Hyderabad - 500 068A RahmanNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Improvin Quality and Standards of LaboratoriesDocument3 pagesGuidelines For Improvin Quality and Standards of LaboratoriesBodhraj singh solankiNo ratings yet
- SAC-SINGLAS 002 (JUNE 2018) : Guidelines For The Application of ISO/IEC 17025: 2017Document8 pagesSAC-SINGLAS 002 (JUNE 2018) : Guidelines For The Application of ISO/IEC 17025: 2017Michael AngNo ratings yet
- Newsletter May 2022Document30 pagesNewsletter May 2022Geo Globe ConsultantsNo ratings yet
- General Information Brochure: National Accreditation Board For Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL)Document44 pagesGeneral Information Brochure: National Accreditation Board For Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL)Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- Nabl 100Document45 pagesNabl 100Mirza Abdul Wali BaigNo ratings yet
- Nabl 143 PDFDocument11 pagesNabl 143 PDFavmrNo ratings yet
- NABL Accreditation Principle & ProcedureDocument3 pagesNABL Accreditation Principle & ProcedureVishnu Prabhu100% (2)
- 8 NablDocument8 pages8 NablAnushkaManiTripathiNo ratings yet
- NABL 100, 07-May-2018Document49 pagesNABL 100, 07-May-2018sriram0% (1)
- NABL 100 General Information Brochure-1045599101Document7 pagesNABL 100 General Information Brochure-1045599101Pampana V Rao0% (1)
- 100 PDFDocument49 pages100 PDFDigvijay ShindeNo ratings yet
- NABL AccreditationDocument2 pagesNABL AccreditationVishal MahireNo ratings yet
- NABL 164 - Guidelines For Inter-Laboratory Comparison For Calibration Laboratories Where Formal PT Programs Are Not Available PDFDocument7 pagesNABL 164 - Guidelines For Inter-Laboratory Comparison For Calibration Laboratories Where Formal PT Programs Are Not Available PDFzilangamba_s4535No ratings yet
- NABLDocument18 pagesNABLAditya Kumar Dubey100% (1)
- Nabl 142Document9 pagesNabl 142karthikkandaNo ratings yet
- Nabl 142 PDFDocument6 pagesNabl 142 PDFavmrNo ratings yet
- Nabl 125 PDFDocument28 pagesNabl 125 PDFavmrNo ratings yet
- NABLDocument2 pagesNABLvermadevanjNo ratings yet
- Notes On NablDocument13 pagesNotes On Nablearth metallurgical services pvt.ltd.No ratings yet
- Nabl 142Document11 pagesNabl 142MCS TechnologyNo ratings yet
- p19 Caeal Unce Pol Rev 1-4Document39 pagesp19 Caeal Unce Pol Rev 1-4Januusz RuizNo ratings yet
- SAC SINGLAS 001 (29 March 2019)Document17 pagesSAC SINGLAS 001 (29 March 2019)MC KongNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Interlaboratory Comparison ResulDocument7 pagesInterpretation of Interlaboratory Comparison Resullab icNo ratings yet
- Nabl 123 PDFDocument23 pagesNabl 123 PDFavmrNo ratings yet
- NABL 100-21-Jul-2016Document46 pagesNABL 100-21-Jul-2016sahaNo ratings yet
- Awareness Training On ISO 17025 and Linkgae With ISO 9000 (Autosaved)Document43 pagesAwareness Training On ISO 17025 and Linkgae With ISO 9000 (Autosaved)IlinaRoy100% (1)
- Nabl 100Document46 pagesNabl 100Mayur JadhavNo ratings yet
- CALIBRATION INTERVAL - HOW TO INCREASE THE CALIBRATION FREQUENCY OF INSTRUMENTS - Calibration AwarenessDocument24 pagesCALIBRATION INTERVAL - HOW TO INCREASE THE CALIBRATION FREQUENCY OF INSTRUMENTS - Calibration AwarenessGordinhorsNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Interlaboratory Comparison ResulDocument7 pagesInterpretation of Interlaboratory Comparison ResulMarco Latosa100% (1)
- Nabl 122 PDFDocument39 pagesNabl 122 PDFavmrNo ratings yet
- Condrete Testing Solutions LTD Rev 1: 1. PurposeDocument6 pagesCondrete Testing Solutions LTD Rev 1: 1. PurposeAnonymous TvM4DyNo ratings yet
- Nabl 124 PDFDocument39 pagesNabl 124 PDFavmr100% (1)
- 06 - KAN - RLK - 01 Requirements For Calibration Laboratory (En)Document22 pages06 - KAN - RLK - 01 Requirements For Calibration Laboratory (En)Ali ZafarNo ratings yet
- Calibration Interval: How To Increase The Calibration Frequency of InstrumentsDocument10 pagesCalibration Interval: How To Increase The Calibration Frequency of InstrumentsINSTRUCAL CALIBRATION SERVICESNo ratings yet
- Why Laboratory Accreditation?Document2 pagesWhy Laboratory Accreditation?Samiksha SarafNo ratings yet
- 4 Egac SystemDocument55 pages4 Egac SystemWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- KAN - RLK-01-requirements-for-calibration-laboratoryDocument22 pagesKAN - RLK-01-requirements-for-calibration-laboratoryNurul RochmawatiNo ratings yet
- Sac-Singlas 001, Oct 10Document15 pagesSac-Singlas 001, Oct 10Yash PennaNo ratings yet
- Proficiency Testing RequirementsDocument5 pagesProficiency Testing RequirementssanjaydgNo ratings yet
- Laboraoty Accreditation & Implementation of Qms As Per Is/Iso/Iec 17025Document30 pagesLaboraoty Accreditation & Implementation of Qms As Per Is/Iso/Iec 17025nirmal_gcetNo ratings yet
- A2LA General Requirements For Proficiency TestingDocument7 pagesA2LA General Requirements For Proficiency Testingcinvehbi711No ratings yet
- Laboratory Scope: Heyco Metals, Inc. Quality Assurance Test Facility Manual and Laboratory ScopeDocument9 pagesLaboratory Scope: Heyco Metals, Inc. Quality Assurance Test Facility Manual and Laboratory ScopeAbhishek ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visser2006 Article InterpretationOfInterlaboratorDocument6 pagesVisser2006 Article InterpretationOfInterlaboratorRiki Effendi AlKhawarizmiNo ratings yet
- Nabl 122 09 PDFDocument19 pagesNabl 122 09 PDFmaheshNo ratings yet
- EA 4 16 EA Guidelines On The Expression of Uncertainty in Quantitative TestingDocument27 pagesEA 4 16 EA Guidelines On The Expression of Uncertainty in Quantitative TestingBercamUSCNo ratings yet
- Nabl 100Document39 pagesNabl 100Vishal Sharma67% (3)
- NABL CronologyDocument3 pagesNABL CronologyvermadevanjNo ratings yet
- Proficiency Testing CheatsheetDocument1 pageProficiency Testing CheatsheetRafael GarzónNo ratings yet
- NABL 163 - Policy For Participation in Proficiency Testing Activities PDFDocument8 pagesNABL 163 - Policy For Participation in Proficiency Testing Activities PDFzilangamba_s4535No ratings yet
- BCB 110 (IB) - NABCB Accreditation Criteria For IBs - Mar 2017 PDFDocument8 pagesBCB 110 (IB) - NABCB Accreditation Criteria For IBs - Mar 2017 PDFMani Rathinam RajamaniNo ratings yet
- Application Form For For Testing Labs ISO17025Document14 pagesApplication Form For For Testing Labs ISO17025PK Jha100% (2)
- 61a0264109a87c7fd5dfd0f09b14ddbb (1).pptDocument183 pages61a0264109a87c7fd5dfd0f09b14ddbb (1).pptANISH KHAITANNo ratings yet
- SP2 PDFDocument8 pagesSP2 PDFaridaconceptNo ratings yet
- Faq - OngcDocument7 pagesFaq - Ongcamitgh91No ratings yet
- Accreditation of Laboratories: A General ApproachDocument65 pagesAccreditation of Laboratories: A General ApproachkuttiNo ratings yet
- The Concise Calibration & Test Equipment Management Guide: The Concise Collection, #1From EverandThe Concise Calibration & Test Equipment Management Guide: The Concise Collection, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- BioethicsDocument32 pagesBioethicsJireh RiveraNo ratings yet
- AR1810.00-PRO-REP-004 Rev 00 - HAZID TERMS OF REFERENCE PDFDocument10 pagesAR1810.00-PRO-REP-004 Rev 00 - HAZID TERMS OF REFERENCE PDFYaakoubi FethiNo ratings yet
- DLL Health 2 Q3 W5 8Document7 pagesDLL Health 2 Q3 W5 8Brenda GenelazoNo ratings yet
- Safety Officer1Document5 pagesSafety Officer1Noryati AbdullahNo ratings yet
- PESTEL AnalysisDocument14 pagesPESTEL Analysisp943272882% (11)
- Childcare Application FormDocument2 pagesChildcare Application Formapi-655739915No ratings yet
- Paracetamol CalpolDocument1 pageParacetamol Calpolunkown userNo ratings yet
- Approved SystemsDocument25 pagesApproved SystemsadrianrrccNo ratings yet
- Applied Pharmacology For The Dental Hygienist 7th Edition Haveles Solutions ManualDocument34 pagesApplied Pharmacology For The Dental Hygienist 7th Edition Haveles Solutions Manualatop.remiped25zad100% (16)
- B Meg Integra - Multi Max - Multi Vitamins + Minerals + Amino Acids - Gamecock Apparel and SuppliesDocument3 pagesB Meg Integra - Multi Max - Multi Vitamins + Minerals + Amino Acids - Gamecock Apparel and SuppliesCu AgNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Toxic Positivity To The Purpose in Life and Environmental Mastery of Laid-Off Young Adult Workers During PandemicDocument189 pagesThe Influence of Toxic Positivity To The Purpose in Life and Environmental Mastery of Laid-Off Young Adult Workers During PandemicRolando Balgos IIINo ratings yet
- OEKO-TEX Quality Assurance SystemDocument3 pagesOEKO-TEX Quality Assurance Systemzman99No ratings yet
- Stock GDL-CDMX 26-09-22Document3 pagesStock GDL-CDMX 26-09-22Ivan Domínguez LopezNo ratings yet
- Freud's Structural and Topographical Models of PersonalityDocument3 pagesFreud's Structural and Topographical Models of PersonalityWajiha Asad KiyaniNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 9 Respiratory System PhysiologyDocument5 pagesLab Exercise 9 Respiratory System PhysiologySophia Nicole RosalesNo ratings yet
- PT1A - Salvadora, N. Assignment 1Document2 pagesPT1A - Salvadora, N. Assignment 1N.No ratings yet
- 06 Offline Module CourseDocument15 pages06 Offline Module CourseDylan Angelo AndresNo ratings yet
- Products Medicine WarehouseDocument54 pagesProducts Medicine WarehouseksdmksdmNo ratings yet
- MSDS Blasocut: Blaser Swisslube IncDocument4 pagesMSDS Blasocut: Blaser Swisslube InczaqNo ratings yet
- Transes Tra - PediaDocument9 pagesTranses Tra - PediaJoshua DelantarNo ratings yet
- Inclusiveness - Chapter OneDocument22 pagesInclusiveness - Chapter OneFena Ad100% (1)
- Emergence Delirium in Pediatric PatientsDocument6 pagesEmergence Delirium in Pediatric PatientsJZ100% (1)
- Alteraciones Cromosomicas Molecular GeneticsDocument14 pagesAlteraciones Cromosomicas Molecular GeneticsChristian AguirreNo ratings yet
- Rko Obat Agustus 2023Document40 pagesRko Obat Agustus 2023Adi IsnawanNo ratings yet
- Snowflakes FactsDocument13 pagesSnowflakes FactsAbigail LorenzanaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On The Benefits of ExerciseDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On The Benefits of Exercisegxuqjkhkf100% (1)
- Prothrombin Time (Protime) : Activity #9Document20 pagesProthrombin Time (Protime) : Activity #9Kei Ef SiNo ratings yet
- Nejmoa 2304146Document13 pagesNejmoa 2304146Njeodo VignyNo ratings yet
Nabl News 46 Apr 2007
Nabl News 46 Apr 2007
Uploaded by
Gagan SinghOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nabl News 46 Apr 2007
Nabl News 46 Apr 2007
Uploaded by
Gagan SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
NABL NEWS
Memorandum of Understanding between
NABL and ESMA
NABL has signed a Memorandum of Understanding 3. To set up a special program for the inter-laboratory
(MoU) with Emirates Authority for Standardization comparisons for the laboratories between the two
& Metrology (ESMA), Abu Dhabi, UAE for countries in order to build mutual confidence in test
technical co-operation in accreditation activities. results.
This MoU was signed on 26th March 2007 in New 4. Exchange visits of experts and trainees.
Delhi by Director NABL and Director General of
ESMA. This MoU has been signed with an objective 5. Exchange of information including bulletins, training
to serve the interests of both NABL and ESMA, and courses, studies and statistics and information related
to facilitate trade. to the interpretation of accreditation & conformity
assessment requirements.
The cooperation shall include the common fields of
work between NABL & ESMA, particularly with 6. Common organizing of the training courses,
respect to: conferences and meetings that are related to
accreditation fields.
1. Developing mutual recognition of laboratory
accreditations granted by both NABL & ESMA in 7. Exchange of experience between assessors,
accordance with the standards, guides and accreditation and technical committees of both
documents of the specialized international parties.
organizations 8. Study visits for staff to NABL and ESMA.
2. Use of assessors approved by NABL & ESMA in Any activity to be undertaken under this MoU is to be agreed
carrying out assessments to grant accreditation in by NABL and ESMA in advance before commencement of the
UAE and in India as required. activity.
NABL Secretariat shifts to new premises
NABL Secretariat has shifted to a new premises and address for any communication is:
NABL
3rd Floor, NISCAIR
14, Satsang Vihar Marg
New Mehrauli Road
New Delhi - 110067
The telephone / fax numbers remains unchanged.
Tel: +91 - 11 - 26529718 - 20 / 26526864
Fax: +91 - 11 - 26529716
E-mail: info@nabl-india.org
NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007 1
Validation of Calibration Result and Generation of Stability Data of
Reference Standard using Control Chart Method
An approach for implementation
Introduction view of recently published 'NABL Policies and
Guidelines for Electro-Technical Calibration
Reference standards are the most critical instruments Laboratories', the stability data shall be generated by
for a calibration agency. Most of the activities of preparation of control / trend chart based on successive
every calibration lab are centered upon reference calibration of standard(s)/ master(s). The same is to be
standards. Calibration of the reference standard
established by laboratories within two years from the
through an external calibration agency requires the
date of application. Hence, all the laboratories have to
selection of calibration agency that can provide
use some or other method for generating stability data.
reliable calibration results and decision on re-
calibration interval. However, in most of the cases Present Criteria for selection of a Calibration
the decision to select a Calibration Lab for calibration
Lab and need of Validation of Results
of standard is guided by the financial factors i.e.
calibration charges and overhead charges for Scope of accreditation
calibration.
Every calibration lab is audited by the NABL assessors
There is a possibility that the calibration results for implementation of Quality system based on
reported by calibration agency are unreliable and do ISO/IEC17025:2005 and outcome of NABL assessment
not match with true value of standard. Hence, criteria is the scope of accreditation awarded by NABL. Scope of
to validate the calibration results are needed so that accreditation of a calibration lab is the best measurement
unreliable results, if any, may be identified & capability of that lab for the respective range/parameters.
removed. Otherwise, it will continue to harm even Although scope of accreditation is one of the very
after the expiry of validity period of the certificate by important criteria for the selection of calibration lab, but
creating doubts on the integrity standard. it is extremely difficult to make an assessment of
Manufacturer provides initial information on competence of a lab just by looking at the scope of
calibration interval. However, this information is not accreditation and knowing about best measurement
exactly based on stability of the particular standard capability of the lab.
but on the past stability data of same model of other Performance of lab in Proficiency Testing/Inter-
standards. As each standard is different from other laboratory comparison
standard, after few years of use, each standard should
be characterized by its own stability data. As per the guidelines of NABL, a NABL accredited lab
has to demonstrates its proficiency by participation in
Lot of literature is available for providing guidelines Proficiency Testing (PT) program to cover its entire
for recommendation on calibration interval. But it is scope in a period of four years. Due to lack of sufficient
very difficult to implement the guidelines available number of PT programs, NABL has now introduced
in these literatures. Hence, most of the labs are Inter-laboratory Comparison Programs for this. Most of
prompted to follow the recommendation of the the laboratories are lacking in implementation of these
manufacturer or they are requesting the calibration programs. But, at present customer does not have access
agencies to give their opinion for the same. But, in to results of PT or Inter-laboratory comparison program.
2 NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007
Data of Internal Quality Checks Determination of calibration interval of reference
standard
The data generated by labs as a part of internal quality
checks to demonstrate the implementation of quality Also as per the norms of ISO/IEC 17025:2005, a NABL
system is also not shared with the customers. accredited calibration lab can't give recommendation on
calibration interval on its own. It is the responsibility of
Even though a customer might select a calibration lab
for calibration of its standards using any criteria, the user lab to decide the calibration-interval with the
including above-mentioned criteria, to assess the help of some supporting data. Calibration interval of a
proficiency of the lab. But, there exist a possibility of standard is a time period where the value of the standard
unreliable results being given in the calibration remains within specified accuracy limits. Calibration
certificate. If results of calibration are not validated interval recommended by a calibrating agency can be
to remove erroneous results, traceability chain may validated or a user can on its own decide optimum
be broken. Hence, it is ultimately up to the customer calibration interval using stability data of standard.
to validate the received calibration result or be Generation of stability data using control
prepared to bear the consequences related with poor
results. In fact, even a single unidentified erroneous
charts
result, can continue to create doubts in the integrity of Description of approach
the standard.
In this paper Linear regression (Curve fitting) has been
Role of Stability Data of reference used to draw a control chart with the help of history of
standard calibration data of the instrument.
NABL has also made it mandatory for the labs to The basic requirement for this approach is the 5 to 6 data
generate the stability data of all their reference of previous calibration results from a good recognized
standards and to use it as one of the type 'B' lab, preferably the results shall be from National Physical
contribution in place of accuracy of standard. Laboratory.
Calibration data of the standard can be used to draw a Linear regression establishes a relationship between
control chart/ trend line to generate stability data of two parameters, one considered the independent and
the standard. the other the dependent parameter. The independent
Stability data as important Type 'B' contributions parameter is the time and dependent parameter is the
towards overall measurement uncertainty of value of a given parameter. From this we are able to
calibration compute the value at times past and to predict its
value in the future.
When a calibration agency uses the reference
standard for the calibration of working standards or An uncertainty can be assigned to those values,
any other instrument, it has to decide upon the provided the assumptions are met: points normally
significant contributors for overall measurement distributed around the regression line, white noise,
uncertainty. Stability data is one of the influencing and the underlying function really is linear. A
factors for Type 'B' calculation. Till now, most of the regression line, which describes a standard's
calibration labs take accuracy provided by behavior over time, provides a better value for the
manufacturer for this. However, after recent NABL standard than any individual measurements or
guidelines, all the calibration labs need to use calibrations that have been made.
stability data in place of accuracy in type 'B' Following assumptions are being made for the presented
uncertainty calculations. approach.
NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007 3
* It has been assumed that the standards follow a The standard error of the regression coefficient (slope) is
relatively linear drift. Sy|x
* It has been assumed that calibration results of Sb =
standards over the years follow normal Sx Ö( n-1)
distribution.
and at a given confidence level, confidence interval for
* As the data are finite, this approach takes in to the true slope 'b' is
consideration the Student's t function. This
function is widely used in type 'A' calculation of b= ± ts b
measurement uncertainty with limited data. Where 't' is 'student's t function' for desired confidence
This approach has been explained in the following level and n-2 degree of freedom.
paragraphs. Confidence interval for intercept is
For a fixed standard, record 'n' number of data for tSy|x
calibration results (y) and calibration dates (x). Draw ±
a regression line on the basis of least square method. Ön
This line can be expressed with following equation. Use of statistical data generated through control chart
Y = bX + a For calculation of Calibration Interval
In above formula 'b' is the slope of line; The slope of Calibration interval of a standard can be calculated
the regression line (also called "Regression using stability data:
Coefficient") can be given by (Microsoft Excel
Worksheet has a built in function called 'Slope' which Accuracy - Uncertainty of calibration as per Cal. Cer.
directly returns value of slope for a set of paired data) Slope + |Uncertainty of slope |
nS xy - S x S y In above-mentioned formula 'slope' and 'uncertainty of
b= slope' are the stability data generated from control chart.
2 2
nS x - (S x) For use of Type 'B' contribution
'a' being termed as intercept at 0, is the value of Y at As per the recent guidelines NABL, stability data ('slope'
X = 0, is given by (Microsoft Excel Worksheet has a and 'uncertainty of slope') can be used as Type 'B'
built in function called 'Intercept' which directly contribution in place of accuracy of standard.
returns value of Intercept for a set of paired data) For validation of calibration data
Sy-b Sx For this purpose, the results reported in recent calibration
a= certificate and its associated uncertainty is validated
n with reference to 'value of intercept' & 'its associated
uncertainty' on the date of calibration by assessment of
The variance of points about the line is given by 'En value' derived using following formula..
n-1
Sy|x2 = (sy2-b2sx2 ) Value reported in calibration certificate -
n-2 value of intercept on the date of calibration.
En =
Where 'sy' and 'sx' are the standard deviations of the Ö{(Uncertainty reported in calibration
'y' (calibration value) and 'x' (date of calibration) certificate)2 + (uncertainty of intercept)2}
values, respectively.
4 NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007
This approach has already been successfully applied It also gave us confidence that we can provide good
in Cal Lab, ITI Limited, Naini for following types of services to the external customer. We can now help
standards. customers by providing a value added service of giving
statistically appropriate calibration interval of their
1. Fixed Capacitors. instruments.
2. Fixed Inductors.
3. Fixed Resistors. Case Studies
4. Current Shunt.
5. Time Mark Generators. 1. Identification of an erroneous calibration value of
6. Attenuators. 1mH Inductor used as reference standard
7. DC Voltage Sources. We have participated in a PT program for 1mH inductor.
8. Multi-function Calibrators. Our reference standard and a stable LCR meter were used
9. Leveled Sine Wave Generator. to calibrate the artifact for PT by comparison method.
10. Calibration Generator.
Calibration values were calculated using apparent values
In most of the cases the results have been found to be of DUC & STD and actual value of reference standard as
encouraging. The use of this method has already reported by the calibration agency. Uncertainty
resulted in the following benefits for the lab. calculations were done considering Type 'A' and
1. Stability data of the most of the standard sources following type 'B' contributions.
have been generated. (a) Stability of standard as given by manufacturer.
2. Stability data of the standards has been used to (b) Uncertainty as reported in calibration certificate.
decide Calibration Periodicity of the most of the
standards. (c) Short term stability of LCR meter.
3. For most of the standards Long-term drift has Results of calibration of artifact of PT were sent to nodal
been brought down. Long-term drift of Time lab. When interim findings of PT were reported to us, it
mark generator has been brought down from was informed that our results were not satisfactory and
20 ppm to 6 ppm. we were asked to identify the cause of non-conformance
and report back the corrected results.
4. Estimated value of intercept & its associated
uncertainty is being used as an effective basis for At the time of participation in above-mentioned PT, the
validation of calibration results. Results are validation of calibration results and generation of
satisfactory in all cases. In case of doubtful stability data was not done as per presently used
results, we were able to convince the calibration technique in Calibration Lab of ITI Ltd. Naini. Our 1 mH
agency that results obtained by them during the reference inductor was procured in July 1982 and has
calibration of our standards are not satisfactory. been regularly calibrated through National Physical
5. Use of control charts also gave us lot of Laboratory, except in the last calibration when it was sent
confidence due to which many reference to one of the NABL accredited calibration lab.
standards which were earlier sent to external After thorough analysis of previous calibration results of
agency for routine calibration are now being kept the reference standards using statistical techniques, it
as working standards and are being calibrated in- was concluded that cause of non-conformance might be
house. due to erroneous results of last calibration, which was
All above factors have resulted into significant performed by a NABL accredited Lab. Calculation were
savings towards periodic calibration charges of the again carried out using revised Stability Data and
standards of our lab. It has also improved our best estimated value of reference inductor on the date of PT.
measurement capability in almost all the parameters. Estimated value of the inductance standard was
NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007 5
projected using calibration data of all available data Control chart was prepared and which is shown in Fig I.
except data of last calibration. Corrected result,
1000.06 -
which was within the limits, was again sent to nodal
lab and identified cause of non-conformance was V
1000.04 -
also informed. Afterwards the same reference al 1000.02 -
ue
standard was again sent to NPL and our doubts were 1000.00 -
proved correct. Thus we were able to remove an In 998-98 -
erroneous calibration result by using presented p 999.96 -
statistical technique. F
999.94 -
2. Deciding calibration interval of 1000 pF 999.92 -
standard capacitor 999.90 -
We are having GR's 1404 series Reference capacitor.
82 84 86 88 90 92 94 96 98 00 02 04 06 08
These are mostly calibrated from NPL. NPL used to
report a calibration interval of two years that was still
more than calibration interval of one year normally Accuracy - Uncertainty of
calibration as per Cal. Cer.
reported by other NABL accredited labs. Estimated calibration - interval =
Slope + |Uncertainty of slope |
Approach used in this paper as applied to this
capacitor is being presented herewith. The previous
calibration data as on July 2002 are as follows: 20 - 10
= ----------- = 6.5 years
Date of Cal (x) Jul-82 Apr-85 Sep-90 Jul-97 Apr-00 Jul-02
1.53
VALUE_obs (y) 999.998 999.995 999.995 999.997 999.99 1000.006
It was felt that estimated value of 6.5 years is too long and
After step by step calculation as explained above,
lot of risk is associated if standard changes its
stability data obtained is summarized below:
characteristics during this period. So a reduced period of
b(slope) 1.3170E-04 3.5 years was decided as calibration interval.
a(intercept at 0) 999.99807 Conclusion
sy/x 0.0058 It may be concluded that projected value of standard &
t factor for n-2,99% 4.60 stability data is quite useful for validation of calibration
conf_int_slope(tsb) 1.4431E-03 results, for deciding calibration interval and as important
type 'B' contribution for drift' to implement recent
ci for intercept 1.0828E-02
guidelines of NABL regarding stability data. Thus it
A close observation of above data will reflect that helps to improve the reliability of results of a calibration
resultant value of drift per year (i.e.0.13 ppm ± 1.4 lab, improves best measurement capability of lab and
ppm) is much lower than the value provided by results in saving on expenditure towards calibration.
manufacturer (20 ppm).
Disclaimer
For a target accuracy of approximately 20 ppm,
revised calibration interval was calculated for Mr. S. K. Gupta from ITI Limited, Naini, Allahabad has
uncertainty of calibration as 10 ppm reported during written this article and is being published for the benefit
last calibration as below: of calibration laboratories. This article reflects the
views of the author and is not a NABL Guideline.
6 NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007
NABL PROFICIENCY TESTING PROVIDER
ACCREDITATION PROGRAM
Proficiency Testing (PT) is the use of inter-laboratory New Delhi, which was attended by 70 participants from
comparison to provide quality assurance for various sectors. This workshop was also used to sensitize
determination of performance by individual potential Proficiency Testing Providers on requirements
laboratories for specific tests and measurements. All for accreditation of Proficiency Testing Schemes.
accredited laboratories have to participate in
To train assessors to evaluate the competence of the
proficiency testing activity once in four years for all
organization for this scheme, NABL invited faculty
major disciplines to satisfy International Laboratory
members from United Kingdom Accreditation Scheme
Accreditation Co-operation (ILAC) requirement.
(UKAS) as this is a new activity for NABL in view of
ILAC is considering revision in this requirement by
UKAS long experience in this area. The training program
enhancing the frequency of Proficiency Testing
for assessors as per ILAC G:13 and ISO/IEC Guide 43:
Participation. Presently NABL offers PT Schemes nd rd
Part 1, 1997 was organized by NABL on 2 - 3 April
for testing and calibration laboratories in cooperation
2007. Twenty assessors from various discipline of
with accredited testing laboratories or the national
Testing, Calibration and Medical fields were trained to
meteorological institute (NPL, India). There is a
assess applicant organization as per ILAC G:13 and
progressive increase in the number of accredited
ISO/IEC Guide 43: Part 1,1997.
laboratories with increased diversity in fields of
accreditation. There is thus increase in the demand to NABL has also prepared necessary documents for this
fulfill the number of PT Schemes needed to cover PT scheme, which will be uploaded on NABL website by 1st
participation requirements of laboratories. Keeping June 2007. Interested Organizations are requested to
this in view, NABL proposes to start the program for download these documents and submit application form
accreditation of Proficiency Testing Scheme and Quality Manual (as per ILAC G: 13 and ISO/IEC
Providers (PT Providers) as per ILAC G: 13 and Guide 43: Part 1,1997) to NABL.
ISO/IEC Guide 43: Part 1,1997.
In case of any clarifications / queries / comments or
To find out interest of different organizations in feedback related to the documents, organizations may
accreditation as Proficiency Testing Providers, contact Dr. Aparna Dhawan, Accreditation Officer
th
NABL conducted a workshop on 9 Oct 2006 at NPL, (aparna@nabl-india.org).
7 NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007
NEWBORN SCREENING QUALITY ASSURANCE
PROGRAM (NSQAP) in India
A major public health responsibility, newborn Quality Assurance and Proficiency Testing for
screening for detection of treatable, inherited Newborn Screening
metabolic diseases is a system consisting of six parts:
education, screening, follow-up, diagnosis, For more than 26 years, Centers for Disease Control and
management, and evaluation. Effective screening of Prevention (CDC), Atlanta, Georgia, USA has been the
newborns using dried-blood-spot (DBS) specimens only comprehensive source in the world for quality
collected at birth, combined with follow-up assurance and proficiency testing involving the testing of
newborns for preventable diseases, the Newborn
diagnostic studies and treatment, helps prevent
Screening Quality Assurance Program (NSQAP). The
mental retardation and premature death. If these
program started in November 1979 with DBS specimens
diseases are not accurately diagnosed and treated, for T4 and TSH. CDC's Newborn Screening Laboratory
they cause mental retardation, severe illness, and Branch evaluates the performance of all participating
premature deaths in newborns. laboratories (73 domestic and one or more laboratories in
53 other nations), ensuring that they analyze the blood
Within 48 hours of a child's birth, a sample of blood is spots correctly and providing technical assistance to
obtained from a "heel stick," and the blood is resolve any diagnostic problems.
analyzed for treatable diseases, including
phenylketonuria, sickle cell disease, and Thousands of children are living healthy and productive
hypothyroidism. The sample, called a "blood spot," lives as a result of newborn screening and the Newborn
is tested at a laboratory. Accurate screening ensures Screening Laboratory's quality assurance and
proficiency testing program. The QA program consists of
that-
materials for quarterly (4 times each year) proficiency
testing (PT). Six DBS proficiency testing programs are
Affected babies are identified quickly.
offered for metabolic disorders, tandem mass
spectrometry (MS/MS) measured analytes, sickle cell
Cases of disease are not missed.
disease & other hemoglobinopathies, cystic fibrosis,
The number of false-positive results is Type I diabetes mellitus and anti-HIV-1.
minimized. The PT program provides laboratories with quarterly
panels of blind-coded DBS specimens and gives the
Early treatment can begin that will prevent laboratory an independent external assessment of its
negative and irreversible health outcomes for performance. Each year several laboratories misclassify
affected newborns. at least one PT specimen and are provided immediate
consultation to resolve the analytical problem.
NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007 8
The NSQAP is designed to help screening These parameters cover following diseases:
laboratories achieve excellent technical proficiency
and maintain confidence in their performance. Congenital hypothyroidism
Through the interactive efforts with the program's Phenylketonuria
participants, the program strives to grow and evolve
with the changing needs. Galactosemia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia, Maple syrup urine
Program Operations disease
NSQAP's purpose is to improve interlaboratory Homocystinuria
comparability and to work toward interlaboratory
Biotinidase deficiency
harmonization of newborn screening tests that use
DBSs. Participants may include newborn screening Galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GALT)
laboratories, confirmatory testing laboratories, diet deficiency
monitoring laboratories, and manufacturers.
Cystic fibrosis (CF)
NSQAP prepares PT quarterly reports that show the Hemoglobinopathies
distributions of analytical values and qualitative
assessments reported by participants. NSQAP offers Toxoplasmosis
PT programs for the following parameters:
(Currently, the PT panels for SCDs and other
T4 hemoglobinopathies are limited to specimens containing
hemoglobins related to SCDs, alpha-thalassemia,
TSH hemoglobin E-related disorders, and hemoglobins
representative of beta-thalassemia in
17-OHP combination with a structural variant). This program has
limited enrollment because of the availability of
Total Galactose quantities of pre-screened cord blood.
Biotinidase At the end of each year, a summary of all PT and QC data
Galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase reported for that year will be prepared and distributed to
all participants. Distributions of PT panels occur in
Amino acids (Phe, Leu, Met, Tyr, Val, Cit) January, April, July, and October. There is no cost to the
participant for products or shipping.
Acylcarnitines (C3, C4, C5, C5DC, C6, C8,
C10, C14, C16) Filter Paper
Sickle cell disease (SCD) and other The paper disk punched to aliquot DBS specimens is a
hemoglobinopathies volumetric measurement and requires degree of
uniformity among and within production lots. As a part
Immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT) and
of the QA program, an isotopic method developed at
mutations
CDC's Newborn Screening Laboratory is used to
Antibodies( IgG and IgM) to toxoplasmosis evaluate and compare different lots of filter paper.
9 NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007
Mean counts per minute of added isotopic- labeled Proficiency Testing
thyroxine (T4) within a 1/8- inch disk are equated
with the serum volume of the disks from the dried All PT panels contain 5 blind coded 75µl or 100µl DBS
whole blood specimens. In comparing production specimens. Specimens in the PT panels contained either
lots, statistical analyses of the counting data used to endogenous levels or are enriched with predetermined
determine values for homogeneity and serum levels of T4, TSH, Phe, Gal, 17-OHP, Leu, Met, and
absorption of the disks. acylcarnitines. Specimens for the CF panel are prepared
with IRT enriched blood. Special separate panels for
For historical reference and for maintaining biotinidase deficiency and for GALT deficiency are
uniformity of testing on all the paper production lots, prepared with purchased blood from donors with enzyme
lysed- cell procedure is used. Performance is also deficiencies. Specimens for the hemoglobinopathies
panel are prepared from umbilical cord blood. Specimen
measured with intact cell preparations. The
sets are packaged in a zip-closed metallized plastic bag
published & standardized acceptable volumes per
with desiccant, instructions for analysis, and data report
1/8-inch disc are 1.30 ± 0.19 l (mean value & 95% forms for those labs that did not report data by internet.
confidence interval) for lysed-cell blood and 1.54 ±
0.17l for intact-cell blood. Reports are prepared and distributed quarterly of all
results that are received by the cutoff dates. The PT
Specimen Preparation and Data Handling quantitative results are grouped by kit or method to
illustrate any method-related differences.
The total concentration of each specimen or lot is
equal to the sum of the enriched concentration and NSQAP in India
the endogenous concentration (nonenriched). Some
Association of Clinical Biochemists of India (ACBI) in
specimens were enriched above the endogenous T4 collaboration with Newborn Screening Branch at the
concentration and some were enriched with T4 after Centers for Disease Control (CDC), Atlanta, Georgia,
T4 depletion of the base serum. Except for USA has launched the Newborn Screening Quality
biotinidase and GALT, all DBS specimens in the PT Assurance Program (NSQAP) in India from January
surveys were prepared from whole blood of 55% 2007 as detailed above.
hematocrit. Purified analytes or natural donor blood,
except for TSH, which uses the Second International The laboratories preforming newborn sceening can
Reference Preparation (80/558), are used for all enroll in this international program. The laboratory
must use neonatal screening kits for performing the
enrichments. For galactosemia, enrichments are
above mentioned tests and sampling should be done
made with galactose, galactose-1- phosphate, or both
on dried blood spots (DBS).
so that both free galactose and total galactose (free
galactose plus galactose present as galactose-1- The program comes at NO COST TO THE LAB.
phosphate) could be measured. For biotinidase and
GALT, individual case donor blood was used. All For details contact:
reported analytic values outside the 99% confidence Dr. Puneet K. Nigam
limits are excluded from the summaries of Head, NSQAP ACBI
quantitative results. Email: nsqap2007@gmail.com
NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007 10
TRAINING ACTIVITIES
NABL has discontinued conducting training program on Laboratory Quality Management System and Internal Audit
for ISO/IEC 7025:2005. However for the benefit of the laboratories, NABL publishes information on training
programs offered by other established training Institutes. It may please be noted that NABL is not involved in design
or conduct of these courses. NABL will however conduct training programs based on ISO 15189 for the benefit of
medical laboratories and schedule of these courses will be available on NABL website.
Training Schedules
S. Date
No. Program Name Venue Contact Person
From To
1. Measurement Centre for Electronics Test Ms. Veena S. Kamath 09/04/07 11/04/07
Uncertainty (Chemical Engineering, ETDC [cetebg@etdcbg.org]
Parameters) for Campus, 100 Feet Road,
Laboratories Peenya Industrial Estate,
Bangalore
2. Measurement Indian Institute of Quality Mr. B. Singh 16/04/07 18/04/07
Uncertainty (Electro- Management, Malviya [iiqmetdc@sancharnet.in]
technical & Mechanical Industrial Area, Jaipur.
Parameters) for
Laboratories
3. Laboratory Quality Indian Institute of Quality Mr. B. Singh 07/05/07 10/05/07
Management System & Management, Malviya [iiqmetdc@sancharnet.in]
Internal Audit as per Industrial Area, Jaipur.
ISO/IEC 17025:2005
4. General Requirements Institute for Design of Mr. S. G. Khaladkar 08/05/07 11/05/07
for the Competence of Electrical Measuring [info@idemi.org]
Testing & Calibration Instruments (IDEMI),
Laboratories and Eastern Express Highway,
Internal Audit as per Opposite Everard Nagar,
ISO/IEC 17025:2005 Sion, Chunabhatti,
Mumbai - 400 022.
5. RF Measurements Centre for Electronics Test Ms. Veena S. Kamath 09/05/07 11/05/07
Engineering, ETDC Campus, [cetebg@etdcbg.org]
100 Feet Road, Peenya
Industrial Estate, Bangalore
11 NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007
6. Measurement Centre for Electronics Test Ms. Veena S. Kamath 09/05/07 11/05/07
Uncertainty (Electro- Engineering, ETDC Campus, [cetebg@etdcbg.org]
technical & Mechanical 100 Feet Road, Peenya
Parameters) for Industrial Estate, Bangalore
Laboratories
7. Laboratory Quality Centre for Electronics Test Ms. Veena S. Kamath 22/05/07 25/05/07
System, Management Engineering, ETDC Campus, [cetebg@etdcbg.org]
and Internal Audit as 100 Feet Road, Peenya
per ISO/IEC 17025:2005 Industrial Estate, Bangalore
8. Workshop on Institute for Design of Electrical Mr. S. G. Khaladkar 24/05/07 25/05/07
Estimation & Evaluation Measuring Instruments (IDEMI), [info@idemi.org]
of Total Uncertainty in Eastern Express Highway,
Measurement as per Opposite Everard Nagar,
NABL 141. Sion, Chunabhatti,
Mumbai - 400 022.
9. Certified Calibration Centre for Electronics Test Ms. Veena S. Kamath 11/06/07 16/06/07
Professional Engineering, ETDC Campus, [cetebg@etdcbg.org]
100 Feet Road, Peenya
Industrial Estate, Bangalore.
10. Measurement Indian Institute of Quality Mr. B. Singh 18/06/07 20/06/07
Uncertainty (Chemical Management, Malviya [iiqmetdc@sancharnet.in]
Parameters) for Industrial Area, Jaipur.
Laboratories
11. Laboratory Quality Indian Institute of Quality Mr. B. Singh 16/07/07 19/07/07
Management System & Management, Malviya [iiqmetdc@sancharnet.in]
Internal Audit as per Industrial Area, Jaipur.
ISO/IEC 17025:2005
12. Laboratory Quality Centre for Electronics Test Ms. Veena S. Kamath 24/07/07 27/07/07
System, Management Engineering, ETDC Campus, [cetebg@etdcbg.org]
and Internal Audit as per 100 Feet Road, Peenya
ISO/IEC 17025:2005 Industrial Estate, Bangalore
13. Measurement Uncertainty Indian Institute of Quality Mr. B. Singh 06/08/07 08/08/07
(Electro-technical & Management, Malviya [iiqmetdc@sancharnet.in]
Mechanical Parameters) Industrial Area, Jaipur.
for Laboratories
14. General Requirements Institute for Design of Electrical Mr. S. G. Khaladkar 07/08/07 10/08/07
for the Competence of Measuring Instruments (IDEMI), [info@idemi.org]
Testing & Calibration Eastern Express Highway,
Laboratories and Opposite Everard Nagar,
Internal Audit as per Sion, Chunabhatti,
ISO/IEC 17025:2005 Mumbai - 400 022.
15. Measurement Centre for Electronics Test Ms. Veena S. Kamath 20/08/07 22/08/07
Uncertainty (Electro- Engineering, ETDC [cetebg@etdcbg.org]
technical & Mechanical Campus, 100 Ft Road,
Parameters) for Peenya Industrial Estate,
Laboratories Bangalore
NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007 12
NABL Laboratory Assessors Training Course
NABL is currently looking for experts in the following areas to train as NABL Assessors:
Calibration Laboratories: Dimension, Mass, Density, 1. Educational qualification:
Volume, Force, Torque, Hardness, Pressure, Vacuum,
l For Testing and Calibration laboratories: Post
Electro-technical, Thermal, Optical, Fluid Flow
graduation in Science or Graduate in Engineering
with 5 years post qualifacation experience in Testing
Testing Laboratories: Plastics, Petroleum & / Calibration laboratory
Petrochemicals, Pigments, inks & dyes, Pesticides
Microbiology, Drugs & Pharmaceuticals, Pollution & l For Medical Laboratories: M.D. (Pathology), M.D.
environment, Food, Explosives, Ores & minerals, Metals, (Microbiology) / Ph.D. (Microbiology) with M.Sc.
Fertilizers, Gold assaying, Forensic science and NDT (Medical Microbiology), M.D. (Biochemistry) /
Ph.D. (Biochemistry) with M. Sc. (Biochemistry),
M.S. (Anatomy) / Ph.D. with M. Sc. (Human
Medical Laboratories: Clinical Biochemistry, Clinical
Anatomy) / Ph.D. (Genetics) / Ph.D. (Applied
Pathology, Haematology and Immunohaematology,
Biology) with experience in genetics, M.D. in Lab
Microbiology and Seerology, Histopathology, Medicine with 5 years post qualification experience
Cytopathology, Genetics. in Medical Laboratory
Experts must have experience in both the management l DCP with 7 years post qualification experience in
and operation of testing & calibration laboratories and be medical laboratory
technically knowledgeable in one or more areas of testing 2. Should be currently working in the laboratory.
and calibration. The criteria for the selection of experts to
be trained as assessors are as follows : 3. Should have good communication skills.
Interested candidates may send their bio-data in the format given in document no. NABL - 221
(document can be downloaded from NABL website) to :
Mr. M.V.N. Mohan, In-charge (Training)
National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories,
3rd Floor, NISCAIR, 14, Satsang Vihar Marg
New Mehrauli Road, New Delhi - 110067
Phone: 011- 26529718- 20, 26526864
Fax: 011- 26529716
E-mail: training@nabl-india.org
Assessor training course is a five-day residential training programme and the course fees is Rs 7,500/- per participant.
This fee shall be paid on receipt of invitation for participation
(For updated information on schedules of NABL training courses,
you are requested to visit NABL web-site: www.nabl-india.org)
14 NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007
NEW ACCREDITATION GRANTED
( JANUARY – MARCH 2007 )
Testing Laboratories
S. No. Laboratory Name Field (s)
1. Coal Testing Lab, Panipat Thermal Power Station, Panipat C
2. Consumer Testing Services-Laboratory, SGS India Private Limited, Bangalore B
3. Electronics and Quality Development Centre, Gandhinagar FF
4. Electronics and Quality Development Centre, Vadodara E
5. Export Inspection Agency - Kochi Laboratory, Kochi C, B
6. Fertiliser Testing Laboratory, Aurangabad C
7. Fertilizer Testing Laboratory, Pune C
8. Haryana Test House & Consultancy Services, Panipat M
9. Indian Institute of Packaging, Mumbai P
10. Indian Oil Corporation Limited - Kandla Laboratory, Kutch, Gujarat C
11. Quality Control Testing Laboratory, Sanghi Industries Ltd., Sanghipuram, Kutch, Gujarat C, M
12. Radiotech - NDT Laboratory, Ahmedabad NDT
13. Regional Laboratory, Textiles Committee, Guntur M
14. S.N. Metallurgical Services, Aurangabad C, M
15. SGS India Private Limited, Karur C, M
16. SQAE (ME) Testing Laboratory, Itarsi C, M
17. Sunflag Laboratory, Bhandara C, M
18. Superintendence Company of India (P) Ltd., Kolkata C
19. Susira Industries Limited Calibration and Testing Laboratory, Chennai M
20. Testtex India Analytical Laboratory, Mumbai C, M
21. Wool Research Association - Textile Lab, Thane C, M
NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007 14
Calibration Laboratories
S. No. Laboratory Name Field (s)
1. A. A. Calibration Pvt. Ltd., Ghaziabad T
2. Aar Gee Engineering, Chennai M
3. Acumen Measurements & Consultancy Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi T
4. Belz Calibration Laboratory, Faridabad T
5. Calibration Laboratory, Jain Scientific Glass Works, Ambala Cantt. M
6. Cal-Tech Calibration Services Pvt. Ltd., Pune M
7. Cross Calibration Center, Faridabad M
8. Electrometer Corporation, Kolkata FF
9. Electronics Regional Test Laboratory (E), Kolkata FF
10. Madhya Pradesh State Electronics Development Corporation Ltd., Bhopal ET
11. Material Testing Department-Calibration Lab, Vehicle Factory, Jabalpur M
12. Metrological Testing & Calibration Centre, Bangalore ET
13. Sadbhav Calibration Services, Vadodara M
14. Vashisth Calibration Centre, Ballabgarh ET, T
Medical Laboratories
S. No. Laboratory Name Field(s)
1. APL Diagnostic Expert - Clinical Biochemistry,
Ashish Pathology Laboratory, Ahmedabad Haematology & Immunohaematology
2. Apollo Hospitals, Chennai Clinical Biochemistry,
Clinical Pathology,
Haematology & Immunohaematology,
Microbiology & Serology,
Histopathology,
Cytopathology,
Genetics
3. Divine Diagnosis Centre Private Limited, Clinical Biochemistry,
Kolkata Clinical Pathology,
Haematology & Immunohaematology
15 NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007
S. No. Laboratory Name Fields
4. Eastern Diagnostics & Clinical Biochemistry,
Medical Centre Ltd., Kolkata Clinical Pathology,
Haematology & Immunohaematology
5. Final Diagnosis Pvt. Ltd., Noida Clinical Biochemistry,
Haematology & Immunohaematology
6. Green Cross Pathology & Clinical Biochemistry,
R.I.A. Laboratory, Ahmedabad Clinical Pathology,
Haematology & Immunohaematology,
Microbiology & Serology
7. St. John's Laboratory Services, Bangalore Clinical Biochemistry,
Clinical Pathology,
Microbiology & Serology,
Genetics
8. Star Imaging & Path Lab, New Delhi Clinical Biochemistry,
Clinical Pathology,
Haematology & Immunohaematology,
Microbiology & Serology,
Cytopathology
Abbreviations used : C-Chemical, M-Mechanical, E-Electrical, T-Thermal, B-Biological, FF-Fluid Flow,
P-Photometry, L-Electronics, F-Forensic Testing, NDT-Non Destructive Testing,
R-Radiological, ET-Electrotechnical, O-Optical, T&O-Thermal & Optical
Scope of Accreditation and other details of all Accredited Laboratories are available on
NABL web site “www.nabl-india.org” under ‘Laboratory Search’
Accreditation Withdrawn & Accreditation Voluntary
Laboratory Debarred Withdrawn
NABL has withdrawn accreditation of Standard KBM Engineering Research Laboratory,
Analytical Laboratory, Delhi in the fields of Ahmedabad has voluntarily withdrawn from
Biological testing (Certificate No. T-0781) and NABL accreditation in the field of Mechanical
Chemical testing (Certificate No. T-0780) w.e.f. testing (Certificate No. T-0476 valid till 25-08-
2nd March 2007 for misuse of NABL 2008) w.e.f. 4th April 2007.
accreditation. NABL has also debarred the
laboratory from applying for accreditation for a
period of two years.
NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007 16
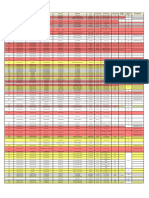
MASTER LIST OF NABL DOCUMENTS
S.No. Document Title Issue Issue Amend. Amend.
No. No. Date No. Date
1. NABL 100 General Information - 01.05.2006 00 -
Brochure
2. NABL 102 Specific Criteria for Biological 02 06.02.2007 00 -
Testing laboratories
3. NABL 103 Specific Guidelines for 02 28.02.2003 01 05.07.2005
Chemical Testing laboratories
4. NABL 104 Specific Criteria for Electrical 02 02.04.2003 01 05.07.2005
Testing laboratories
5. NABL 105 Specific Criteria for Electronics 01 1995 02 05.07.2005
Testing laboratories
6. NABL 106 Specific Criteria for Fluid Flow 01 1994 02 05.07.2005
Testing laboratories
7. NABL 107 Guidelines and Specific 02 01.11.1999 02 05.07.2005
Criteria for Accreditation of
Mechanical Testing laboratories
8. NABL 108 Specific Criteria for Non- 01 01.01.1994 02 05.07.2005
Destructive Testing laboratories
9. NABL 109 Specific Criteria for Photometry 01 01.04.1998 02 05.07.2005
Testing laboratories
10. NABL 110 Specific Criteria for Radiological 01 01.01.1994 02 05.07.2005
Testing laboratories
11. NABL 112 Specific Criteria for Accreditation 02 11.05.2005 04 16.01.2007
of Medical laboratories
12. NABL 113 Specific Guidelines for Accreditation 01 18.06.1998 02 05.07.2005
of Forensic Science Laboratories
& Checklist for Assessors
13. NABL 113 A Specific Guidelines for Accreditation 01 29.12.1999 02 21.10.2003
of DNA Fingerprinting Laboratories
& Checklist for Assessor
17 NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007
S.No. Document Title Issue Issue Amend. Amend.
No. No. Date No. Date
14. NABL 114 NABL Guidelines for 02 05.07.2005 00 -
Food Testing Laboratories
15. NABL 121 Specific Criteria for Calibration 03 08.10.2002 01 05.07.2005
Laboratories in Electro-Technical
Discipline
16. NABL 122 Specific Criteria for Calibration 03 08.10.2002 01 05.07.2005
Laboratories in Mechanical
Discipline
17. NABL 123 Specific Criteria for Calibration 03 08.10.2002 01 05.07.2005
Laboratories in Radiological
Discipline
18. NABL 124 Specific Criteria for Calibration 03 08.10. 2002 02 05.07.2005
Laboratories in Thermal &
Optical Discipline
19. NABL 125 Specific Criteria for Calibration 03 08.10. 2002 01 05.07.2005
Laboratories in Fluid Flow Discipline
20. NABL 130 Specific Criteria for Site Testing 02 13.08. 2002 01 05.07.2005
and Site Calibration Laboratories
21. NABL 131 Terms and Conditions for 05 02.11.2005 02 08.02.2007
Maintaining NABL Accreditation
22. NABL 132 Procedure for Dealing with 02 20.02.2006 00 -
Complaints
23. NABL 133 NABL Guidelines to Accredited 03 20.01.2006 00 -
Laboratories for use of NABL Symbol
24. NABL 134 Procedure for Dealing with Appeals 01 20.02.2006 00 -
Against Adverse Decisions Taken
by NABL
25. NABL 141 Guidelines for Estimation & 02 02.04.2000 03 18.08.2000
Expression of Uncertainty in
Measurement
26. NABL 142 Policy on Calibration and 03 18.10.2004 02 05.07.2005
Traceability of Measurements
NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007 18
S.No. Document Title Issue Issue Amend. Amend.
No. No. Date No. Date
27. NABL 151 Application Form for Testing 10 14.02.2006 00 -
Laboratories
28. NABL 152 Application Form for 10 14.02.2006 00 -
Calibration Laboratories
29. NABL 153 Application Form for Medical 01 14.02.2006 00 -
Testing Laboratories
30. NABL 160 Guide for preparing a Quality Manual 03 05.07.2005 00 -
31. NABL 161 Guide for Internal Audit and 02 02.04.2002 02 05.07.2005
Management Review for Laboratories
32. NABL 162 Guidelines for Proficiency Testing 03 04.04.2001 01 05.07.2005
Programme for Testing &
Calibration Laboratories
33. NABL 163 Policies & Procedures for Inter- 04 13.08.2002 04 18.10.2004
laboratory comparisons and/or
Proficiency Testing
34. NABL 164 Guidelines for Inter-Laboratory 01 28.04.2005 00 -
Comparison for Calibration
Laboratories where formal PT
programmes are not available
35. NABL 174 Sample Calculations for 02 04.10.2004 01 05.07.2005
Uncertainty of Measurement
in Electrical Testing
36. NABL 209 Pre-Assessment Guidelines and Forms 01 02.12.2002 01 05.07.05
37. NABL 210 NABL Assessor Guide 03 01.05.2002 03 05.07.05
40. NABL 215 Assessment Forms & Checklists 03 05.07.2005 04 13.02.07
(Based on ISO/IEC 17025)
19 NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007
S.No. Document Title Issue Issue Amend. Amend.
No. No. Date No. Date
41. NABL 216 Procedures for Dealing with Adverse 03 21.02.2006 00 –
Decisions
42. NABL 217 Assessment Forms and Checklist 01 16.01.2007 00 –
(Based on ISO 15189: 2003)
43. NABL 221 Bio-data of Assessors 01 02.08.2004 00 --
44. NABL 400 Directory of Accredited Testing - 01.02.2007 00 –
Laboratories
45. NABL 500 Directory of Accredited Calibration - 01.02.2007 00 –
Laboratories
46. NABL 600 Directory of Accredited Medical - 01.02.2007 00 –
Testing Laboratories
WITHDRAWN DOCUMENTS
S. Document Name Doc. Last Last Withdrawn Reasons
No. No. Issue No. Amend No. w.e.f.
1. Policy and Procedures for Assessment, NABL Included in
Surveillance & Re-Assessment of Laboratories 214 03 05 14.02.07 NABL 100
Note : 1. All NABL documents can be downloaded free of cost from NABL website :www.nabl-india.org
2. The Master list is updated on a regular basis and is also available on NABL website.
Editorial Board
Rajesh Maheshwari - Member
R. Srikanth - Member
NABL NEWS is quarterly published by
National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL)
3rd Floor, NISCAIR, 14, Satsang Vihar Marg
New Mehrauli Road, New Delhi - 110067
Tel.: 011-26529718-20, 26526864, Fax: 011-26529716
E-mail: info@nabl-india.org, Website: www.nabl-india.org
Registered Office : Department of Science & Technology
Technology Bhavan, New Mehrauli Road, New Delhi-110016
NABL NEWS, ISSUE NO. 46, APRIL 2007 20
You might also like
- JHA - Unloading of Sheet PileDocument3 pagesJHA - Unloading of Sheet PileJensen Sunga100% (1)
- Astm F-1962 PDFDocument18 pagesAstm F-1962 PDFKenNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Quality/Management: A Workbook with an Eye on AccreditationFrom EverandLaboratory Quality/Management: A Workbook with an Eye on AccreditationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Laboratory Accreditation - Procedural GuidelinesDocument3 pagesLaboratory Accreditation - Procedural Guidelinesshk76No ratings yet
- A.S .Kanagasabapathy and Pragna Rao: Kamineni Hospitals LTD., L.B. Nagar, Hyderabad - 500 068Document3 pagesA.S .Kanagasabapathy and Pragna Rao: Kamineni Hospitals LTD., L.B. Nagar, Hyderabad - 500 068A RahmanNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Improvin Quality and Standards of LaboratoriesDocument3 pagesGuidelines For Improvin Quality and Standards of LaboratoriesBodhraj singh solankiNo ratings yet
- SAC-SINGLAS 002 (JUNE 2018) : Guidelines For The Application of ISO/IEC 17025: 2017Document8 pagesSAC-SINGLAS 002 (JUNE 2018) : Guidelines For The Application of ISO/IEC 17025: 2017Michael AngNo ratings yet
- Newsletter May 2022Document30 pagesNewsletter May 2022Geo Globe ConsultantsNo ratings yet
- General Information Brochure: National Accreditation Board For Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL)Document44 pagesGeneral Information Brochure: National Accreditation Board For Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL)Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- Nabl 100Document45 pagesNabl 100Mirza Abdul Wali BaigNo ratings yet
- Nabl 143 PDFDocument11 pagesNabl 143 PDFavmrNo ratings yet
- NABL Accreditation Principle & ProcedureDocument3 pagesNABL Accreditation Principle & ProcedureVishnu Prabhu100% (2)
- 8 NablDocument8 pages8 NablAnushkaManiTripathiNo ratings yet
- NABL 100, 07-May-2018Document49 pagesNABL 100, 07-May-2018sriram0% (1)
- NABL 100 General Information Brochure-1045599101Document7 pagesNABL 100 General Information Brochure-1045599101Pampana V Rao0% (1)
- 100 PDFDocument49 pages100 PDFDigvijay ShindeNo ratings yet
- NABL AccreditationDocument2 pagesNABL AccreditationVishal MahireNo ratings yet
- NABL 164 - Guidelines For Inter-Laboratory Comparison For Calibration Laboratories Where Formal PT Programs Are Not Available PDFDocument7 pagesNABL 164 - Guidelines For Inter-Laboratory Comparison For Calibration Laboratories Where Formal PT Programs Are Not Available PDFzilangamba_s4535No ratings yet
- NABLDocument18 pagesNABLAditya Kumar Dubey100% (1)
- Nabl 142Document9 pagesNabl 142karthikkandaNo ratings yet
- Nabl 142 PDFDocument6 pagesNabl 142 PDFavmrNo ratings yet
- Nabl 125 PDFDocument28 pagesNabl 125 PDFavmrNo ratings yet
- NABLDocument2 pagesNABLvermadevanjNo ratings yet
- Notes On NablDocument13 pagesNotes On Nablearth metallurgical services pvt.ltd.No ratings yet
- Nabl 142Document11 pagesNabl 142MCS TechnologyNo ratings yet
- p19 Caeal Unce Pol Rev 1-4Document39 pagesp19 Caeal Unce Pol Rev 1-4Januusz RuizNo ratings yet
- SAC SINGLAS 001 (29 March 2019)Document17 pagesSAC SINGLAS 001 (29 March 2019)MC KongNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Interlaboratory Comparison ResulDocument7 pagesInterpretation of Interlaboratory Comparison Resullab icNo ratings yet
- Nabl 123 PDFDocument23 pagesNabl 123 PDFavmrNo ratings yet
- NABL 100-21-Jul-2016Document46 pagesNABL 100-21-Jul-2016sahaNo ratings yet
- Awareness Training On ISO 17025 and Linkgae With ISO 9000 (Autosaved)Document43 pagesAwareness Training On ISO 17025 and Linkgae With ISO 9000 (Autosaved)IlinaRoy100% (1)
- Nabl 100Document46 pagesNabl 100Mayur JadhavNo ratings yet
- CALIBRATION INTERVAL - HOW TO INCREASE THE CALIBRATION FREQUENCY OF INSTRUMENTS - Calibration AwarenessDocument24 pagesCALIBRATION INTERVAL - HOW TO INCREASE THE CALIBRATION FREQUENCY OF INSTRUMENTS - Calibration AwarenessGordinhorsNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Interlaboratory Comparison ResulDocument7 pagesInterpretation of Interlaboratory Comparison ResulMarco Latosa100% (1)
- Nabl 122 PDFDocument39 pagesNabl 122 PDFavmrNo ratings yet
- Condrete Testing Solutions LTD Rev 1: 1. PurposeDocument6 pagesCondrete Testing Solutions LTD Rev 1: 1. PurposeAnonymous TvM4DyNo ratings yet
- Nabl 124 PDFDocument39 pagesNabl 124 PDFavmr100% (1)
- 06 - KAN - RLK - 01 Requirements For Calibration Laboratory (En)Document22 pages06 - KAN - RLK - 01 Requirements For Calibration Laboratory (En)Ali ZafarNo ratings yet
- Calibration Interval: How To Increase The Calibration Frequency of InstrumentsDocument10 pagesCalibration Interval: How To Increase The Calibration Frequency of InstrumentsINSTRUCAL CALIBRATION SERVICESNo ratings yet
- Why Laboratory Accreditation?Document2 pagesWhy Laboratory Accreditation?Samiksha SarafNo ratings yet
- 4 Egac SystemDocument55 pages4 Egac SystemWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- KAN - RLK-01-requirements-for-calibration-laboratoryDocument22 pagesKAN - RLK-01-requirements-for-calibration-laboratoryNurul RochmawatiNo ratings yet
- Sac-Singlas 001, Oct 10Document15 pagesSac-Singlas 001, Oct 10Yash PennaNo ratings yet
- Proficiency Testing RequirementsDocument5 pagesProficiency Testing RequirementssanjaydgNo ratings yet
- Laboraoty Accreditation & Implementation of Qms As Per Is/Iso/Iec 17025Document30 pagesLaboraoty Accreditation & Implementation of Qms As Per Is/Iso/Iec 17025nirmal_gcetNo ratings yet
- A2LA General Requirements For Proficiency TestingDocument7 pagesA2LA General Requirements For Proficiency Testingcinvehbi711No ratings yet
- Laboratory Scope: Heyco Metals, Inc. Quality Assurance Test Facility Manual and Laboratory ScopeDocument9 pagesLaboratory Scope: Heyco Metals, Inc. Quality Assurance Test Facility Manual and Laboratory ScopeAbhishek ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visser2006 Article InterpretationOfInterlaboratorDocument6 pagesVisser2006 Article InterpretationOfInterlaboratorRiki Effendi AlKhawarizmiNo ratings yet
- Nabl 122 09 PDFDocument19 pagesNabl 122 09 PDFmaheshNo ratings yet
- EA 4 16 EA Guidelines On The Expression of Uncertainty in Quantitative TestingDocument27 pagesEA 4 16 EA Guidelines On The Expression of Uncertainty in Quantitative TestingBercamUSCNo ratings yet
- Nabl 100Document39 pagesNabl 100Vishal Sharma67% (3)
- NABL CronologyDocument3 pagesNABL CronologyvermadevanjNo ratings yet
- Proficiency Testing CheatsheetDocument1 pageProficiency Testing CheatsheetRafael GarzónNo ratings yet
- NABL 163 - Policy For Participation in Proficiency Testing Activities PDFDocument8 pagesNABL 163 - Policy For Participation in Proficiency Testing Activities PDFzilangamba_s4535No ratings yet
- BCB 110 (IB) - NABCB Accreditation Criteria For IBs - Mar 2017 PDFDocument8 pagesBCB 110 (IB) - NABCB Accreditation Criteria For IBs - Mar 2017 PDFMani Rathinam RajamaniNo ratings yet
- Application Form For For Testing Labs ISO17025Document14 pagesApplication Form For For Testing Labs ISO17025PK Jha100% (2)
- 61a0264109a87c7fd5dfd0f09b14ddbb (1).pptDocument183 pages61a0264109a87c7fd5dfd0f09b14ddbb (1).pptANISH KHAITANNo ratings yet
- SP2 PDFDocument8 pagesSP2 PDFaridaconceptNo ratings yet
- Faq - OngcDocument7 pagesFaq - Ongcamitgh91No ratings yet
- Accreditation of Laboratories: A General ApproachDocument65 pagesAccreditation of Laboratories: A General ApproachkuttiNo ratings yet
- The Concise Calibration & Test Equipment Management Guide: The Concise Collection, #1From EverandThe Concise Calibration & Test Equipment Management Guide: The Concise Collection, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- BioethicsDocument32 pagesBioethicsJireh RiveraNo ratings yet
- AR1810.00-PRO-REP-004 Rev 00 - HAZID TERMS OF REFERENCE PDFDocument10 pagesAR1810.00-PRO-REP-004 Rev 00 - HAZID TERMS OF REFERENCE PDFYaakoubi FethiNo ratings yet
- DLL Health 2 Q3 W5 8Document7 pagesDLL Health 2 Q3 W5 8Brenda GenelazoNo ratings yet
- Safety Officer1Document5 pagesSafety Officer1Noryati AbdullahNo ratings yet
- PESTEL AnalysisDocument14 pagesPESTEL Analysisp943272882% (11)
- Childcare Application FormDocument2 pagesChildcare Application Formapi-655739915No ratings yet
- Paracetamol CalpolDocument1 pageParacetamol Calpolunkown userNo ratings yet
- Approved SystemsDocument25 pagesApproved SystemsadrianrrccNo ratings yet
- Applied Pharmacology For The Dental Hygienist 7th Edition Haveles Solutions ManualDocument34 pagesApplied Pharmacology For The Dental Hygienist 7th Edition Haveles Solutions Manualatop.remiped25zad100% (16)
- B Meg Integra - Multi Max - Multi Vitamins + Minerals + Amino Acids - Gamecock Apparel and SuppliesDocument3 pagesB Meg Integra - Multi Max - Multi Vitamins + Minerals + Amino Acids - Gamecock Apparel and SuppliesCu AgNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Toxic Positivity To The Purpose in Life and Environmental Mastery of Laid-Off Young Adult Workers During PandemicDocument189 pagesThe Influence of Toxic Positivity To The Purpose in Life and Environmental Mastery of Laid-Off Young Adult Workers During PandemicRolando Balgos IIINo ratings yet
- OEKO-TEX Quality Assurance SystemDocument3 pagesOEKO-TEX Quality Assurance Systemzman99No ratings yet
- Stock GDL-CDMX 26-09-22Document3 pagesStock GDL-CDMX 26-09-22Ivan Domínguez LopezNo ratings yet
- Freud's Structural and Topographical Models of PersonalityDocument3 pagesFreud's Structural and Topographical Models of PersonalityWajiha Asad KiyaniNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 9 Respiratory System PhysiologyDocument5 pagesLab Exercise 9 Respiratory System PhysiologySophia Nicole RosalesNo ratings yet
- PT1A - Salvadora, N. Assignment 1Document2 pagesPT1A - Salvadora, N. Assignment 1N.No ratings yet
- 06 Offline Module CourseDocument15 pages06 Offline Module CourseDylan Angelo AndresNo ratings yet
- Products Medicine WarehouseDocument54 pagesProducts Medicine WarehouseksdmksdmNo ratings yet
- MSDS Blasocut: Blaser Swisslube IncDocument4 pagesMSDS Blasocut: Blaser Swisslube InczaqNo ratings yet
- Transes Tra - PediaDocument9 pagesTranses Tra - PediaJoshua DelantarNo ratings yet
- Inclusiveness - Chapter OneDocument22 pagesInclusiveness - Chapter OneFena Ad100% (1)
- Emergence Delirium in Pediatric PatientsDocument6 pagesEmergence Delirium in Pediatric PatientsJZ100% (1)
- Alteraciones Cromosomicas Molecular GeneticsDocument14 pagesAlteraciones Cromosomicas Molecular GeneticsChristian AguirreNo ratings yet
- Rko Obat Agustus 2023Document40 pagesRko Obat Agustus 2023Adi IsnawanNo ratings yet
- Snowflakes FactsDocument13 pagesSnowflakes FactsAbigail LorenzanaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On The Benefits of ExerciseDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On The Benefits of Exercisegxuqjkhkf100% (1)
- Prothrombin Time (Protime) : Activity #9Document20 pagesProthrombin Time (Protime) : Activity #9Kei Ef SiNo ratings yet
- Nejmoa 2304146Document13 pagesNejmoa 2304146Njeodo VignyNo ratings yet