Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electronic Component Function and Symbols ...
Electronic Component Function and Symbols ...
Uploaded by
Janneal Ann Endaya AlanoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Electronic Components: Symbols & FunctionsDocument6 pagesElectronic Components: Symbols & FunctionsAlexander San Juan91% (114)
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument21 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsHassaan ShahNo ratings yet
- Electrical SymbolsDocument10 pagesElectrical SymbolsJulia Veatrice PerezNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsFrom EverandA Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Automatic Fire Alarm and Fire Controlling SystemDocument22 pagesAutomatic Fire Alarm and Fire Controlling SystemHaymanot LegesseNo ratings yet
- Components SymbolsDocument15 pagesComponents SymbolsDay Nonz GetinoNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocument3 pagesElectrical & Electronic Circuit Symbolspc100xohmNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument17 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsMuhammad SajedNo ratings yet
- 100+ Electrical & Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocument35 pages100+ Electrical & Electronic Circuit SymbolsRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- 100+ Electrical & Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocument22 pages100+ Electrical & Electronic Circuit SymbolsDavid Atkinson100% (1)
- Electrical ComponentsDocument29 pagesElectrical ComponentshariprasadNo ratings yet
- Circuits 1Document110 pagesCircuits 1Mark Ian Tanangonan Maravilloso100% (1)
- Electrical and Electronics SymbolsDocument52 pagesElectrical and Electronics SymbolssorcererpcNo ratings yet
- Symbols of Electronic ComponenetsDocument21 pagesSymbols of Electronic ComponenetsMehmet KARAHANLINo ratings yet
- House WiringDocument8 pagesHouse WiringUncle DrewNo ratings yet
- Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje Centro de Electricidad Electronica Y Telecomnunicaciones Circuit SymbolsDocument4 pagesServicio Nacional de Aprendizaje Centro de Electricidad Electronica Y Telecomnunicaciones Circuit Symbols伊文伊文No ratings yet
- ELECTRIC WORKSHOP Student VersionDocument25 pagesELECTRIC WORKSHOP Student Versionnaqirustambajwa90No ratings yet
- Eelctrical Components and Symbols Wire Name SymbolDocument3 pagesEelctrical Components and Symbols Wire Name SymbolMarianne NorombabaNo ratings yet
- Wire To Pass Current Very Easily From One Part of A Circuit To AnotherDocument8 pagesWire To Pass Current Very Easily From One Part of A Circuit To AnotherPRincess ScarLetNo ratings yet
- Pesit: AE LAB - Supporting NotesDocument40 pagesPesit: AE LAB - Supporting NotesRohit Patil100% (2)
- Engineering Utilities 2: Electrical SymbolsDocument22 pagesEngineering Utilities 2: Electrical SymbolsMona fabrigarNo ratings yet
- Tle 9-10 M6w6lessonDocument13 pagesTle 9-10 M6w6lessonKathlyn AlbercaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols: Ar. Richard DonguezDocument11 pagesElectrical Symbols: Ar. Richard DonguezMary Jessica UyNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke 2a - Pengenalan Komponen Dasar ElektronikaDocument16 pagesPertemuan Ke 2a - Pengenalan Komponen Dasar ElektronikaAffan NaufalNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Technical Education and Skills Development Authority Regional Manpower Development Center (RMDC)Document6 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Technical Education and Skills Development Authority Regional Manpower Development Center (RMDC)Latif Santiago KhalidNo ratings yet
- ComponentDocument5 pagesComponentapi-26570979100% (1)
- Electrical and Electronic Schematic SymbolsDocument16 pagesElectrical and Electronic Schematic SymbolsSanjana Singh100% (1)
- ECE Workshop Exp No. 1Document6 pagesECE Workshop Exp No. 1Jai JohnNo ratings yet
- Applied Phy Lab ManualDocument109 pagesApplied Phy Lab Manualamirmehmood88No ratings yet
- Electronic Parts Symbols Labeling and ApplicationDocument23 pagesElectronic Parts Symbols Labeling and ApplicationRonald ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Electronics SymbolsDocument5 pagesElectronics SymbolsJemuel NavarraNo ratings yet
- Wires and ConnectionsDocument22 pagesWires and ConnectionsDanilo AlbayNo ratings yet
- Simple Diagrams For Electrical / Electronic: Symbol Component Name Meaning Wire SymbolsDocument15 pagesSimple Diagrams For Electrical / Electronic: Symbol Component Name Meaning Wire SymbolsCiprian MihailaNo ratings yet
- Table of Electrical/ Electronic SymbolsDocument7 pagesTable of Electrical/ Electronic Symbolscarmelle de lunaNo ratings yet
- 10 Types of Electrical Tool1Document5 pages10 Types of Electrical Tool1Noreen Dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Jao - SR-Block Diagrams and Flowcharts ResearchDocument4 pagesJao - SR-Block Diagrams and Flowcharts Researchfostedapepo251No ratings yet
- Electrical SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectrical SymbolsMegu MeguNo ratings yet
- Electronics Ckts SymbolsDocument16 pagesElectronics Ckts SymbolsRobert ColomaNo ratings yet
- Electric Shop Lab ManualDocument13 pagesElectric Shop Lab ManualHuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Familiarization of Electronic Symbol: Experiment No.1Document12 pagesFamiliarization of Electronic Symbol: Experiment No.1ManuelitoBorjaNo ratings yet
- Table of Electrical SymbolsDocument5 pagesTable of Electrical SymbolsMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- MSP Automatic-Street-Light-Using-LdrDocument16 pagesMSP Automatic-Street-Light-Using-Ldrjigyasa BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Automatic Street Light Using LDRDocument16 pagesAutomatic Street Light Using LDRRohan KandekarNo ratings yet
- Resistors: PotentiometerDocument48 pagesResistors: PotentiometerjojoNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in TleDocument16 pagesPortfolio in TleAileen Javines50% (2)
- 2 Basic Electronics - Electronic Components and Equipments.Document36 pages2 Basic Electronics - Electronic Components and Equipments.anon_475597919No ratings yet
- Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectronic Circuit SymbolsCarlos Andres Jaimes HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cebu Institute of Technology University: ECE 162 W1Document8 pagesCebu Institute of Technology University: ECE 162 W1meshin yuNo ratings yet
- Workshop Practice (Electric Shop)Document13 pagesWorkshop Practice (Electric Shop)muhammad omer100% (1)
- Safety Rules in An Electrical Worksho1Document29 pagesSafety Rules in An Electrical Worksho1Arfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Notes: 3.1 Laser ClassesDocument9 pagesNotes: 3.1 Laser ClassesAaron Pesch TerrornoizeIndustryNo ratings yet
- KSK 203 - Electronic I) Electronic Components Symbol: Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument12 pagesKSK 203 - Electronic I) Electronic Components Symbol: Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsAmendaNo ratings yet
- Electronics For Mechanical EngineersDocument35 pagesElectronics For Mechanical EngineersRamanujam O SNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 1 Familiarization of Electronic Components AimDocument49 pagesExperiment No: 1 Familiarization of Electronic Components Aimarun joseNo ratings yet
- Meralco Safety TipsDocument8 pagesMeralco Safety TipsKim SantosNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols and FunctionsDocument6 pagesElectrical Symbols and Functionsara jelitaNo ratings yet
- Different Electrical SymbolsDocument11 pagesDifferent Electrical SymbolsMich DoligosaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Symbol T1Document8 pagesCircuit Symbol T1Ahmed Khaled100% (1)
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument13 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorsKRISHAN MEENANo ratings yet
- BJT Fabrication 2018Document13 pagesBJT Fabrication 2018عہۣۗثہۣۗمہۣۗان الہۣۗضہۣۗاحہۣۗيNo ratings yet
- P-N Junction Practical Class 12Document3 pagesP-N Junction Practical Class 12Swapnil Sahu67% (6)
- Physice 2013 Unsolved Paper Outside Delhi PDFDocument7 pagesPhysice 2013 Unsolved Paper Outside Delhi PDFAbhilashaNo ratings yet
- Vaap Project 123Document5 pagesVaap Project 123soundharyaNo ratings yet
- Unit1 PHY125Document108 pagesUnit1 PHY125Kishan DixitNo ratings yet
- Newnes - Electrical and Electronic Principles and Technology, 2nd Ed - 2003 - (By Laxxuss)Document366 pagesNewnes - Electrical and Electronic Principles and Technology, 2nd Ed - 2003 - (By Laxxuss)tdn200320002087100% (1)
- Bypass Diodes in Solar Panels and ArraysDocument11 pagesBypass Diodes in Solar Panels and ArraysAyanda MhlangaNo ratings yet
- The Junction Diode: Junction Diode Symbol and Static I-V CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesThe Junction Diode: Junction Diode Symbol and Static I-V CharacteristicsNithya MohanNo ratings yet
- Elecs RefresherDocument46 pagesElecs Refreshermario sanchezNo ratings yet
- Electronics AssignmentsDocument7 pagesElectronics AssignmentsSoumyaranjan PandaNo ratings yet
- Equation of The Static CharacteristicDocument5 pagesEquation of The Static CharacteristicYohannes Bekuma BekereNo ratings yet
- DAGA Lab8Document23 pagesDAGA Lab8Kristan Oneal DagaNo ratings yet
- 20 Talking ElectronicsDocument23 pages20 Talking ElectronicsBalaki SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) BasicsDocument8 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) BasicsApurva NagdeoteNo ratings yet
- Gupta 1991Document3 pagesGupta 1991Estudiante2346No ratings yet
- PHD Entrance Model Test Paper 2023Document43 pagesPHD Entrance Model Test Paper 2023Walelign Wudu100% (1)
- Diodo Regulador de CorrienteDocument6 pagesDiodo Regulador de CorrienteHector Jose Murillo CordobaNo ratings yet
- 新版中興電機所100 111年歷試簡答Document31 pages新版中興電機所100 111年歷試簡答game davidNo ratings yet
- Compressor Less Refrigerator Using Peltier Effect: Major Project Report 2018-19Document41 pagesCompressor Less Refrigerator Using Peltier Effect: Major Project Report 2018-19Anshul GourNo ratings yet
- Module-2: Power TransistorsDocument25 pagesModule-2: Power TransistorsLokesh LokeshNo ratings yet
- K.G.R.L. College (Autonomous), Bhimavaram: UNIT - II: (12hrs)Document2 pagesK.G.R.L. College (Autonomous), Bhimavaram: UNIT - II: (12hrs)srinidhi2allNo ratings yet
- Mahadevaswamy U B Analog Electronic Circuits A Simplified APDocument720 pagesMahadevaswamy U B Analog Electronic Circuits A Simplified APkuttubuddinbaig100% (2)
- MSE-21-Optical Properties (61) - 2007-05-31Document61 pagesMSE-21-Optical Properties (61) - 2007-05-31Surendra PandaNo ratings yet
- Transistor CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesTransistor Characteristicssumantamurmu945No ratings yet
- Quick Start GuideDocument128 pagesQuick Start GuidePavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document38 pagesLecture 3muhammad saeedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - SemiconductorDocument49 pagesChapter 3 - SemiconductorBalqis yasin100% (1)
- 7 Segment DisplayDocument9 pages7 Segment DisplayindranildasNo ratings yet
Electronic Component Function and Symbols ...
Electronic Component Function and Symbols ...
Uploaded by
Janneal Ann Endaya AlanoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electronic Component Function and Symbols ...
Electronic Component Function and Symbols ...
Uploaded by
Janneal Ann Endaya AlanoCopyright:
Available Formats
Technological University of the Philippines
Lopez Extension Campus
Brgy. Villahermosa Lopez, Quezon
AY, 2018-2019
(EST 1) Electronics 1
Name: _________________________ Instructor: _____________________
Course: ________________________ Date: _________________________
Electronics Components
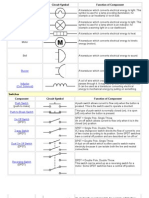
NAME FUNCTION SYMBOLS
Wire Represents a conductor that
conducts electrical current. Also
called a power line or electric
line or wire.
Shielded wire A wire which is protected or
shielded with a coupled of
shielded wire or any plastic
which is used insulating
materials in wire.
Wire cross not In complex diagrams it is often
connected necessary to draw wires crossing
even though they are not
connected. I prefer the bridge
symbol show on the right
because the simple crossing on te
left may be misread as a join
where you have forgotten to add
a ‘blob’!
Wire cross connected A ‘blob’ should be drawn where
wires are connected(joined), but
it is sometimes omitted. Wires
connected at crossroads should
be staggered slightly to form
T-junction, as shown in the right.
SWITCHES
Push Button (Normally This switch is initially in ON
Open) state. This goes to OFF state
when it is released.
Push Button (Normally This switch is initially in ON
Closed) state. This goes to OFF state
when it is released.
Single pole single throw This acts as ON/OFF switch.
Switch Poles define the number of
circuits it can be connected to
and throws defines the number of
positions that a pole connects.
SPDT Switch Single pole double throw is
abbreviated as SPDT. This
switch allows the current to flow
in any one of the two directions
by adjusting its position.
DPST Switch Double pole single throw is
abbreviated as DPST. This
switch can drive two circuits at a
time.
DPDT Switch Double pole double throw is the
full form of DPDT. This can
connect the four circuits by
changing the position.
Rotary Switch It is a switch operated by
allowing rotation to control
different circuit functions.
Reed Switch A reed switch is an
electromagnetic switch used to
control the flow of electricity in a
circuit.
Relay Switch This represents the relay switch.
This can control the AC Loads
using the DC voltage applied to
the coil.
Silicon Unilateral A four-layer or Shockley diode
Switch with a gate
Silicon Bilateral switch A bidirectional break over device
Unijunction Transistor A semiconductor device
consisting of thin silicon bar on
which a single pn junction acting
as an emitter is formed near one
end.
SOURCES
AC Supply This represents AC supply in the
circuit.
DC Supply This represents the DC power
supply. It applies DC supply to
the circuit.
Constant Current The symbol represents an
Source independent current source which
delivers constant current.
WAVE GENERATORS
Sinusoidal Generator Represents sine wave generator.
Pulse Generator Represents pulse or square wave
generator.
Triangular Wave Represents triangular wave
generator.
GROUND SYMBOLS
Ground It is equivalent to theoretical 0V
and is used as zero potential
reference. It is the potential of
perfectly conducting earth.
Signal Ground It is a reference point from which
the signal is measured. There
may be several signal grounds in
a circuit due to the voltage drops
in a circuit.
Chassis Ground It acts as a barrier between user
and the circuit and prevents
electric shock.
ANTENNA
Antenna General A device that radiate or receive
radio waves. British term is
AERIAL
Antenna Dipole An antenna approximately one
half wave length long, split at its
electrical center for connection to
a transmission line.
Antenna loop An antenna consists of one or
more complete turns of a
conductor usually turned to
resonance by a variable of a
capacitor
Antenna Ferrite A magnetic antenna that has high
resistivity consisting of ferric
oxide combined with one or more
metal .
RESISTOR
Fixed Resistor It is a device that opposes the
flow of current in a circuit.
Tapped Resistor A wire wound fixed resistor that
has one more additional terminal
along its length generally for
voltage divider application
VARIABLE RESISTOR
Rheostat It is a two terminal variable
resistor. They are generally used
to control the current in the
circuit. Generally used in tuning
circuits and power control
applications like heaters, ovens
etc
Thermistor It is a temperature sensitive
resistor. They are used in
temperature sensing, current
limiting circuits, over-current
protection circuits etc.
Varistor It is a Voltage Dependent
Resistor. It has non-linear
current-voltage characteristics.
Generally used in circuit
protection from voltage surges
and excessive transient voltages.
Magneto Resistor They are also called as Magnetic
Dependent Resistors (MDR). The
resistance of magneto resistor
varies according to the external
magnetic field strength. They are
used in electronic compass,
ferrous material detection,
position sensors etc.
Humidity Sensor A resistor that changes its
resistance in accordance of
humidity in the environment
LDR They are also called as Photo
Resistors. The resistance of LDR
varies with the intensity of the
light incident on it. They are
generally used in light sensing
applications.
Tapped resistor A wire-wound type fixed resistor
with one or more terminals along
its length. Generally used in
voltage divider applications.
Attenuator It is a device used to lower the
power of a signal. They are made
from simple voltage dividers and
hence can be classified in the
family of the resistors.
CAPACITOR SYMBOL
Non-Polarized Capacitor stores the charge in the
Capacitor form of electrical energy. Non-
polarized capacitors are big in
size with small capacitance. They
can be used in both AC and DC
circuits.
Polarized Capacitor Polarized capacitors are small in
size but have high capacitance.
They are used in DC circuits.
They can be used as filters, for
bypassing or passing low
frequency signals.
Electrolytic Capacitor Almost all electrolytic capacitors
are polarized and hence used in
DC circuits
Variable Capacitor The capacitance of the variable
capacitor can be adjusted by
turning the knob. They are
widely used to adjust the
frequency, that is for tuning.
Three Ganged Variable A three gang capacitor whose
Capacitor capacitance can be varied by
moving three sets of metal plates
with respect to another.
INDUCTORS
Iron Core Inductor These are used as substitutes to
ferrite core inductors. Ferrite core
or Ferromagnetic inductors have
high permeability and require air
gap to reduce it. Iron powdered
core inductors have this air gap
integrated.
Ferrite Core Inductors Core material, in this type of
inductors is made of ferrite
material. These are mostly used
to suppress the interference of
electromagnetic waves.
Center Tapped These are used in coupling of
Inductors signals,
Variable Inductors Movable ferrite magnetic core
variable inductors are most
common. The inductance is
varied by sliding the core in or
out of the coil.
Variometer A variable inductance that has
two coils in series, one mounted
inside the other, with provision
for rotating the inner coil to vary
the total inductance of the unit
over a wide range.
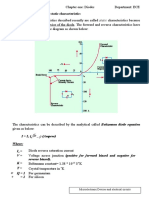
DIODES
Rectifier Diode A PN junction diode allows the
current to flow only in forward
bias condition. These diodes can
be used in clipping and clamping
circuits, as rectifiers in dc circuits
etc.
Zener Diode In forward bias condition, it acts
as normal diode and allows
current. It also allows current to
flow in reverse bias condition
when the voltage reaches a
certain break-down point.
Generally used in voltage
regulator and over voltage
protection circuits.
Photodiode Photodiode detects the light
energy and converts it into
current or voltage by a
mechanism called photoelectric
effect. These are used in CD
players, Cameras etc.
Led Light emitting diode is similar to
PN junction diode but they emit
energy in the form of light
instead of heat. These are mostly
used in indication, lightening
applications.
Varactor Diode Varactor diode is called varicap
or variable capacitance diode.
The capacitance of this diode
varies according to the applied
input voltage. This is used in
frequency controlled oscillators,
frequency multipliers etc.
Shockley Diode This is a four-layer diode. This
had fast switching operation and
hence is used in switching
applications.
Schottky Diode It represents Schottky diode. It
has low forward voltage drop and
it can switch rapidly. Used in
voltage clamping, rectifiers,
reverse current and discharge
protection
Tunnel Diode This is also known as Esaki
diode.It can switch very fastly
and can perform well in micro
wave frequency range. This is
used in oscillator circuits and
micro wave circuits.
Photo diode A semiconductor device of which
the reverse saturation current
increase as lights strikes into its
opening.
Thyristor It consists of four layers of
alternating P and N materials.
They act as bistable switches and
are used in circuits where high
voltages and currents are
involved.
Laser Diode The laser diode is similar to light
emitting diode. The active region
is formed in intrinsic region in
PIN structure. Laser diodes find
its applications in laser printing,
laser scanning etc.
Seven Segment Diode A light emitting diode that has
negative resistance in the forward
direction over a portion of its
operating range, due to quantum
mechanical tunneling.
TRANSISTOR SYMBOLS
NPN It is made of combination of P-
type semiconductor between two
N-type semiconductors. It is
switched ON when the base-
emitter junction is forward
biased. They are commonly used
for amplifying and switching
applications.
PNP It is made of combination of N-
type semiconductor between two
P-type semiconductors. It is
switched ON when the base-
emitter junction is reverse biased.
These are used for amplifying
and switching applications.
JFET
N- Channel JFET N-channel JFET is made by n-
type silicon bars which form two
PN junctions at the side. Majority
charge carriers here are electrons.
P-Channel JFET P-Channel JFET is made by p-
type silicon bar which forms two
PN junctions at the side. Majority
charge carriers here are holes.
MOSFET
Enhancement MOSFET The enhancement mode
MOSFET has positive gate
operation. It induces negative
charges into the n-channel and
thus number of negative charges
increases, enhancing the channel
conductivity.
Depletion MOSFET The depletion mode has negative
gate operation. This decreases the
width of the depletion layer.
Phototransistor The photo transistor converts the
light energy falling on it to its
corresponding electrical energy.
This can be used in light sensing
applications. Base is left
disconnected as light is used to
enable the flow of current.
Photo Darlington Photo Darlington Transistor is
similar to phototransistor with
very high gain and sensitivity
Darlington Transistor This configuration produces high
current gain. They are used in
power regulators, output stages
of audio amplifiers, display
drivers etc.
LOGIC GATES
And Gate This is the basic gate and it
implements logical conjunction.
The output of the AND gate is
high, only if both the inputs are
high otherwise both are low.
Or Gate The OR gate implements logical
disjunction. The output is high if
any one of the inputs is high.
Nand Gate It is complement of AND gate.
The output is low only when both
the inputs are high, otherwise it is
high.
Nor Gate NOR gate is a not OR gate.
Output of this gate is high, if both
the inputs are Low, otherwise it
is High.
Not Gate Inverter or NOT gate implements
logical negation. This gate
inverts the input.
Exor This gate implements exclusive
OR logic. The output of this gate
is high, if both the inputs are
different.
Exnor This gate implements negation of
EXOR logic. The output of this
gate is high, only if the two
inputs are identical.
Buffer It is an audio signaling device.
Generally used in alarms, timers
and for confirmation messages.
Tri-State Buffer Similar to a normal buffer but
with a control signal. In case of
active high buffer, it operates
normally only when control
signal is 1. In case of active low
buffer, it operates normally only
when control signal is 0.
Flip Flop Flip flop is the also
a memory element but this is a
synchronous device. The figure
below shows the basic D-flip-
flop.
AMPLIFIERS
Basic Amplifier An amplifier is a device that
amplifies a relatively small input
signal i.e. it increases the power
of the signal. They are used in
communication systems, audio
devices etc
Operational Amplifier Operational Amplifier (Op Amp)
is a voltage amplifier with very
high gain. The input is
differential. They are used in
instrumentation devices, signal
processing, control systems etc
ANTENNA
Aerial Antenna This symbol belongs to Aerial or
Antenna. It converts electrical
power into radio waves. It is used
in wireless communication to
transmit or receive the signals.
Loop Antenna Loop antenna is named after its
loop like shape of wire or other
electrical conductor. They are
used as receiving antennas in low
frequency range.
Dipole Antenna It is most widely used antenna.
Generally used in set-top TV,
shortwave transmission and FM
receivers.
TRANSFORMER
Transformer Transformer is the basic element
that transfers energy in one
circuit to the other circuit through
electromagnetic induction. They
are generally used in electric
power applications to increase or
decrease the voltage of AC
current.
Iron Core Uses a piece of magnetic material
as core. Generally Ferro magnetic
metals like iron are used. The
core has high permeability and is
used to confine the magnetic
field.
Center Tapped The center tapped transformer
has its secondary winding
divided into two parts with same
number of turns in each part.
This results in two individual
output voltages across two line
ends. Used in rectifier circuits.
Push, Pull Transformer An AF transformer that has a
center tapped winding, for use in
a push-pull amplifier.
Step Up Transformer The no. of turns in secondary
winding is more than that of
primary winding. The output
voltage is higher than input
voltage. Significantly used in
inverters.
Step Down Transformer The no. of turns in secondary
winding is less than that of
primary winding. The output
voltage is lesser than input
voltage. It is widely used in low
power applications.
Other components
Buzzer This is sound producing device.
This produces buzz sound when
the voltage is applied.
Loud Speaker This is also an audio device. The
electrical signal is converted into
sound signal here.
Light Bulb The symbol represents the light
bulb. The bulb glows when
required voltage is applied.
Motor This converts the electric energy
to mechanical energy.
Fuse Symbol represents the fuse that
protects the circuit from over
current.
Crystal Oscillator Used to generate clock signal of
very precise frequency.
ADC Analog to Digital converter is
used convert analog signals
(usually voltage) to digital
values.
DAC Digital to Analog converter is
used to convert digital code to
analog signals.
Thermocouple It is used to measure temperature.
6 Volts Battery 6 DC voltages source made up of
one or more cells that converts
chemical into electric energy.
Neon Light A glow lamp that contains neon
gas.
Pilot Lamp A small lamp used to indicate
that the circuit is energized.
You might also like
- Electronic Components: Symbols & FunctionsDocument6 pagesElectronic Components: Symbols & FunctionsAlexander San Juan91% (114)
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument21 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsHassaan ShahNo ratings yet
- Electrical SymbolsDocument10 pagesElectrical SymbolsJulia Veatrice PerezNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsFrom EverandA Guide to Electronic Maintenance and RepairsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Automatic Fire Alarm and Fire Controlling SystemDocument22 pagesAutomatic Fire Alarm and Fire Controlling SystemHaymanot LegesseNo ratings yet
- Components SymbolsDocument15 pagesComponents SymbolsDay Nonz GetinoNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocument3 pagesElectrical & Electronic Circuit Symbolspc100xohmNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument17 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsMuhammad SajedNo ratings yet
- 100+ Electrical & Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocument35 pages100+ Electrical & Electronic Circuit SymbolsRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- 100+ Electrical & Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocument22 pages100+ Electrical & Electronic Circuit SymbolsDavid Atkinson100% (1)
- Electrical ComponentsDocument29 pagesElectrical ComponentshariprasadNo ratings yet
- Circuits 1Document110 pagesCircuits 1Mark Ian Tanangonan Maravilloso100% (1)
- Electrical and Electronics SymbolsDocument52 pagesElectrical and Electronics SymbolssorcererpcNo ratings yet
- Symbols of Electronic ComponenetsDocument21 pagesSymbols of Electronic ComponenetsMehmet KARAHANLINo ratings yet
- House WiringDocument8 pagesHouse WiringUncle DrewNo ratings yet
- Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje Centro de Electricidad Electronica Y Telecomnunicaciones Circuit SymbolsDocument4 pagesServicio Nacional de Aprendizaje Centro de Electricidad Electronica Y Telecomnunicaciones Circuit Symbols伊文伊文No ratings yet
- ELECTRIC WORKSHOP Student VersionDocument25 pagesELECTRIC WORKSHOP Student Versionnaqirustambajwa90No ratings yet
- Eelctrical Components and Symbols Wire Name SymbolDocument3 pagesEelctrical Components and Symbols Wire Name SymbolMarianne NorombabaNo ratings yet
- Wire To Pass Current Very Easily From One Part of A Circuit To AnotherDocument8 pagesWire To Pass Current Very Easily From One Part of A Circuit To AnotherPRincess ScarLetNo ratings yet
- Pesit: AE LAB - Supporting NotesDocument40 pagesPesit: AE LAB - Supporting NotesRohit Patil100% (2)
- Engineering Utilities 2: Electrical SymbolsDocument22 pagesEngineering Utilities 2: Electrical SymbolsMona fabrigarNo ratings yet
- Tle 9-10 M6w6lessonDocument13 pagesTle 9-10 M6w6lessonKathlyn AlbercaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols: Ar. Richard DonguezDocument11 pagesElectrical Symbols: Ar. Richard DonguezMary Jessica UyNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke 2a - Pengenalan Komponen Dasar ElektronikaDocument16 pagesPertemuan Ke 2a - Pengenalan Komponen Dasar ElektronikaAffan NaufalNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Technical Education and Skills Development Authority Regional Manpower Development Center (RMDC)Document6 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Technical Education and Skills Development Authority Regional Manpower Development Center (RMDC)Latif Santiago KhalidNo ratings yet
- ComponentDocument5 pagesComponentapi-26570979100% (1)
- Electrical and Electronic Schematic SymbolsDocument16 pagesElectrical and Electronic Schematic SymbolsSanjana Singh100% (1)
- ECE Workshop Exp No. 1Document6 pagesECE Workshop Exp No. 1Jai JohnNo ratings yet
- Applied Phy Lab ManualDocument109 pagesApplied Phy Lab Manualamirmehmood88No ratings yet
- Electronic Parts Symbols Labeling and ApplicationDocument23 pagesElectronic Parts Symbols Labeling and ApplicationRonald ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Electronics SymbolsDocument5 pagesElectronics SymbolsJemuel NavarraNo ratings yet
- Wires and ConnectionsDocument22 pagesWires and ConnectionsDanilo AlbayNo ratings yet
- Simple Diagrams For Electrical / Electronic: Symbol Component Name Meaning Wire SymbolsDocument15 pagesSimple Diagrams For Electrical / Electronic: Symbol Component Name Meaning Wire SymbolsCiprian MihailaNo ratings yet
- Table of Electrical/ Electronic SymbolsDocument7 pagesTable of Electrical/ Electronic Symbolscarmelle de lunaNo ratings yet
- 10 Types of Electrical Tool1Document5 pages10 Types of Electrical Tool1Noreen Dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Jao - SR-Block Diagrams and Flowcharts ResearchDocument4 pagesJao - SR-Block Diagrams and Flowcharts Researchfostedapepo251No ratings yet
- Electrical SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectrical SymbolsMegu MeguNo ratings yet
- Electronics Ckts SymbolsDocument16 pagesElectronics Ckts SymbolsRobert ColomaNo ratings yet
- Electric Shop Lab ManualDocument13 pagesElectric Shop Lab ManualHuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Familiarization of Electronic Symbol: Experiment No.1Document12 pagesFamiliarization of Electronic Symbol: Experiment No.1ManuelitoBorjaNo ratings yet
- Table of Electrical SymbolsDocument5 pagesTable of Electrical SymbolsMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- MSP Automatic-Street-Light-Using-LdrDocument16 pagesMSP Automatic-Street-Light-Using-Ldrjigyasa BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Automatic Street Light Using LDRDocument16 pagesAutomatic Street Light Using LDRRohan KandekarNo ratings yet
- Resistors: PotentiometerDocument48 pagesResistors: PotentiometerjojoNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in TleDocument16 pagesPortfolio in TleAileen Javines50% (2)
- 2 Basic Electronics - Electronic Components and Equipments.Document36 pages2 Basic Electronics - Electronic Components and Equipments.anon_475597919No ratings yet
- Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectronic Circuit SymbolsCarlos Andres Jaimes HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cebu Institute of Technology University: ECE 162 W1Document8 pagesCebu Institute of Technology University: ECE 162 W1meshin yuNo ratings yet
- Workshop Practice (Electric Shop)Document13 pagesWorkshop Practice (Electric Shop)muhammad omer100% (1)
- Safety Rules in An Electrical Worksho1Document29 pagesSafety Rules in An Electrical Worksho1Arfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Notes: 3.1 Laser ClassesDocument9 pagesNotes: 3.1 Laser ClassesAaron Pesch TerrornoizeIndustryNo ratings yet
- KSK 203 - Electronic I) Electronic Components Symbol: Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument12 pagesKSK 203 - Electronic I) Electronic Components Symbol: Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsAmendaNo ratings yet
- Electronics For Mechanical EngineersDocument35 pagesElectronics For Mechanical EngineersRamanujam O SNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 1 Familiarization of Electronic Components AimDocument49 pagesExperiment No: 1 Familiarization of Electronic Components Aimarun joseNo ratings yet
- Meralco Safety TipsDocument8 pagesMeralco Safety TipsKim SantosNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols and FunctionsDocument6 pagesElectrical Symbols and Functionsara jelitaNo ratings yet
- Different Electrical SymbolsDocument11 pagesDifferent Electrical SymbolsMich DoligosaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Symbol T1Document8 pagesCircuit Symbol T1Ahmed Khaled100% (1)
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument13 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorsKRISHAN MEENANo ratings yet
- BJT Fabrication 2018Document13 pagesBJT Fabrication 2018عہۣۗثہۣۗمہۣۗان الہۣۗضہۣۗاحہۣۗيNo ratings yet
- P-N Junction Practical Class 12Document3 pagesP-N Junction Practical Class 12Swapnil Sahu67% (6)
- Physice 2013 Unsolved Paper Outside Delhi PDFDocument7 pagesPhysice 2013 Unsolved Paper Outside Delhi PDFAbhilashaNo ratings yet
- Vaap Project 123Document5 pagesVaap Project 123soundharyaNo ratings yet
- Unit1 PHY125Document108 pagesUnit1 PHY125Kishan DixitNo ratings yet
- Newnes - Electrical and Electronic Principles and Technology, 2nd Ed - 2003 - (By Laxxuss)Document366 pagesNewnes - Electrical and Electronic Principles and Technology, 2nd Ed - 2003 - (By Laxxuss)tdn200320002087100% (1)
- Bypass Diodes in Solar Panels and ArraysDocument11 pagesBypass Diodes in Solar Panels and ArraysAyanda MhlangaNo ratings yet
- The Junction Diode: Junction Diode Symbol and Static I-V CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesThe Junction Diode: Junction Diode Symbol and Static I-V CharacteristicsNithya MohanNo ratings yet
- Elecs RefresherDocument46 pagesElecs Refreshermario sanchezNo ratings yet
- Electronics AssignmentsDocument7 pagesElectronics AssignmentsSoumyaranjan PandaNo ratings yet
- Equation of The Static CharacteristicDocument5 pagesEquation of The Static CharacteristicYohannes Bekuma BekereNo ratings yet
- DAGA Lab8Document23 pagesDAGA Lab8Kristan Oneal DagaNo ratings yet
- 20 Talking ElectronicsDocument23 pages20 Talking ElectronicsBalaki SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) BasicsDocument8 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) BasicsApurva NagdeoteNo ratings yet
- Gupta 1991Document3 pagesGupta 1991Estudiante2346No ratings yet
- PHD Entrance Model Test Paper 2023Document43 pagesPHD Entrance Model Test Paper 2023Walelign Wudu100% (1)
- Diodo Regulador de CorrienteDocument6 pagesDiodo Regulador de CorrienteHector Jose Murillo CordobaNo ratings yet
- 新版中興電機所100 111年歷試簡答Document31 pages新版中興電機所100 111年歷試簡答game davidNo ratings yet
- Compressor Less Refrigerator Using Peltier Effect: Major Project Report 2018-19Document41 pagesCompressor Less Refrigerator Using Peltier Effect: Major Project Report 2018-19Anshul GourNo ratings yet
- Module-2: Power TransistorsDocument25 pagesModule-2: Power TransistorsLokesh LokeshNo ratings yet
- K.G.R.L. College (Autonomous), Bhimavaram: UNIT - II: (12hrs)Document2 pagesK.G.R.L. College (Autonomous), Bhimavaram: UNIT - II: (12hrs)srinidhi2allNo ratings yet
- Mahadevaswamy U B Analog Electronic Circuits A Simplified APDocument720 pagesMahadevaswamy U B Analog Electronic Circuits A Simplified APkuttubuddinbaig100% (2)
- MSE-21-Optical Properties (61) - 2007-05-31Document61 pagesMSE-21-Optical Properties (61) - 2007-05-31Surendra PandaNo ratings yet
- Transistor CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesTransistor Characteristicssumantamurmu945No ratings yet
- Quick Start GuideDocument128 pagesQuick Start GuidePavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document38 pagesLecture 3muhammad saeedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - SemiconductorDocument49 pagesChapter 3 - SemiconductorBalqis yasin100% (1)
- 7 Segment DisplayDocument9 pages7 Segment DisplayindranildasNo ratings yet