Professional Documents
Culture Documents
004 08 DrugInteractions Probenecid PDF
004 08 DrugInteractions Probenecid PDF
Uploaded by
RumahBontang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageOriginal Title
004-08-DrugInteractions-probenecid.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 page004 08 DrugInteractions Probenecid PDF
004 08 DrugInteractions Probenecid PDF
Uploaded by
RumahBontangCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Clinical Pharmacology Bulletin
Department of Clinical Pharmacology,Christchurch Hospital, Private Bag 4710, Christchurch
Drug Information Service Phone: 80900 Fax: 80902
Drug Utilisation Review Phone: 89971 Fax: 81003
March 2008 No. 004/08
Drug Interactions with probenecid
Probenecid was introduced in the 1950’s to reduce the renal Probenecid also reduces the renal clearance of several β-lactam
elimination and extend the plasma half-life of penicillins. This use antibiotics. This effect is exploited therapeutically in the treatment
continues to the present day. It was subsequently found that of cellulitis and other infections. Co-administration of probenecid
probenecid lowers serum uric acid concentrations and it has been allows for longer dosing intervals for some cephalosporins and
used extensively as a uricosuric agent for the prevention of gout. penicillins.
This bulletin will discuss drug interactions with probenecid that
may be therapeutically useful or undesirable. Reduced renal toxicity: Probenecid reduces the accumulation of
nephrotoxic drugs in the proximal tubule cells. Co-administration
Drug transporters of probenecid is now recommended to reduce renal damage from
the antiviral drug cidofovir.
The action of probenecid results from the inhibition of membrane
transporters. Transporters control the cellular influx of nutrients Altered diuretic effect: Co-administration of loop diuretics and
and the efflux of cellular waste. Several are also known to probenecid has been shown to result in altered diuresis. The
transport drugs and are found in the kidney, liver, gut wall and mechanism is unclear, but may involve the inhibition of loop
other sites. They are important for drug absorption, distribution diuretic tubular secretion by probenecid.
and excretion and usually have a protective or detoxifying role.
Other possible mechanisms: Probenecid may inhibit the
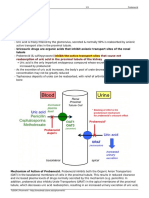
Renal transporters and probenecid (Figure 1) glucuronidation of some drugs, though data are limited. This may
In the kidney, probenecid reduces the active tubular secretion of explain the reduced clearance of NSAIDs and some
drugs by inhibiting organic anion transporters (OATs) in the benzodiazepines by probenecid.
basolateral membrane of the proximal tubular cells. This results in
reduced drug clearance and elevated plasma drug concentrations The effect of other drugs on probenecid: Aspirin (>325mg)
of substrate drugs. By contrast, the uricosuric action of and pyrazinamide diminish the uricosuric activity of probenecid,
probenecid results from the inhibition of urate transporters most likely by reducing the active tubular secretion of uric acid
(URATs) in the apical membrane of the proximal tubule, from the blood into the tubules. This results in elevated serum
decreasing uric acid reabsorption. uric acid concentrations but reduced uric acid in the renal tubule,
where probenecid exerts its uricosuric effect.
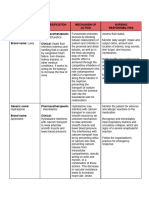
Table 1. The effect of probenecid on other drugs
blood proximal urine
tubule cell ↓ renal clearance, ↑ plasma concentration or ↑ half-life
aciclovir fexofenadine
OAT captopril ganciclovir
Ï plasma carbapenems (eg meropenem) loop diuretics (altered diuresis)
concentration
cephalosporins (not ceftazidime & methotrexate
Ï elimination ceftriaxone)
half-life ciprofloxacin oseltamivir
URAT Ï urinary dapsone penicillins (many)
excretion enalapril zidovudine
Other documented effects
cidofovir – È nephrotoxicity
Figure 1. The actions of probenecid: cisplatin – may È nephrotoxicity (conflicting data)
1 - Ð tubular secretion (eg pencillin)
some benzodiazepines (eg lorazepam) - È clearance (mechanism
2 - Ð tubular reabsorption (eg uric acid) unclear)
some NSAIDs (eg naproxen) - È clearance (mechanism unclear)
Drug interactions The effect of other drugs on probenecid
Reduced renal clearance: The renal clearance of drugs that aspirin (>325mg) –È probenecid effectiveness
undergo tubular secretion via OAT transporters may be reduced allopurinol – Ç probenecid plasma concentrations
by probenecid (Table 1). The significance of the interaction will
pyrazinamide - È probenecid effectiveness
depend on the therapeutic index of the drug, the patient’s renal
function and whether other elimination pathways exist. For
example, the plasma concentrations of methotrexate may be Summary
elevated 3-4 fold by the co-administration of probenecid and Probenecid has the propensity to interact with a large number of
severe toxicity has been reported. By contrast, the renal drugs. Many relatively small hydrophilic drugs (<500 daltons) may
clearance of captopril has been found to be reduced by 44% with be OAT substrates. However, the study of drug transporters is a
the co-administration of probenecid. However, as other relatively new field and OAT substrates are being continually
elimination pathways exist, the total clearance of captopril is only identified. Recent discoveries include, amongst others, losartan
reduced by 19% (unlikely to be clinically significant). and adefovir, which may be candidates for clinically important
interactions with probenecid.
The information contained within this bulletin is provided on the understanding that although it may be used to assist in your final clinical decision,
the Clinical Pharmacology Department at Christchurch Hospital does not accept any responsibility for such decisions.
You might also like
- OSCE Book 2010Document256 pagesOSCE Book 2010mansi_v199078% (18)
- Drug CardsDocument4 pagesDrug CardsBrittany Lynn MyersNo ratings yet
- Acute Heart Failure WORKBOOKDocument28 pagesAcute Heart Failure WORKBOOKFadhlan ABNo ratings yet
- PRC Board Questions in Pharma 2005Document43 pagesPRC Board Questions in Pharma 2005jose carlo araojoNo ratings yet
- ProbenecidDocument3 pagesProbenecidFlower100% (2)
- Drugs and The Kidney: Continuing Medical EducationDocument6 pagesDrugs and The Kidney: Continuing Medical EducationJANINE PASIONNo ratings yet
- Drug Name MagsnDocument3 pagesDrug Name MagsnBryant Von Andrew EstradaNo ratings yet
- Idei GeneraleDocument7 pagesIdei GeneraleGeorgiana FrăţilăNo ratings yet
- هام Vasoactive Peptides-PHL351Document4 pagesهام Vasoactive Peptides-PHL351ALNAKINo ratings yet
- Drugs Interaction Basic & Clinical Pharmacology (PDFDrive) - 1170-1187Document18 pagesDrugs Interaction Basic & Clinical Pharmacology (PDFDrive) - 1170-1187Ismail Ali إسماعيل عليNo ratings yet
- 6 Pharmacological Treatment of The ElderlyDocument11 pages6 Pharmacological Treatment of The ElderlyAbdulhamid KassabNo ratings yet
- GinjalDocument11 pagesGinjalOneng IfayaniNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument102 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryMichelleValeriaFredy100% (2)
- 1 - Renal Excretion of DrugsDocument18 pages1 - Renal Excretion of DrugsKashar SaeedNo ratings yet
- Rta PDFDocument4 pagesRta PDFtraceyNo ratings yet
- 6 Effects of Chronic Kidney Disease and Uremia On Hepatic Drug Metabolism and Transport 2014Document7 pages6 Effects of Chronic Kidney Disease and Uremia On Hepatic Drug Metabolism and Transport 2014AdipNo ratings yet
- Kam 1998Document7 pagesKam 1998Viraghg UniNo ratings yet
- 4 Drug ExcretionDocument20 pages4 Drug ExcretionAman GulNo ratings yet
- Routes of Excretion Routes of Excretion Renal Excretion Non Renal Excretion Biliary ExcretionDocument5 pagesRoutes of Excretion Routes of Excretion Renal Excretion Non Renal Excretion Biliary Excretiontanuja reddyNo ratings yet
- Brat Er 2000Document13 pagesBrat Er 2000Carla MantillaNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Ijprbs Chirag Modi, IJPRBS, 2012: Volume1 (3) : 120-132Document13 pagesReview Article: Ijprbs Chirag Modi, IJPRBS, 2012: Volume1 (3) : 120-132Uci Ramadhanty D3 2018No ratings yet
- Anti GoutDocument9 pagesAnti GoutYATIN GULSHANNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Treatment in Heart FailureDocument12 pagesDiuretic Treatment in Heart FailureRoberto López Mata100% (1)
- Tajdid Gerakan MuhammadiyahDocument17 pagesTajdid Gerakan MuhammadiyahSih AtiiNo ratings yet
- Overactive Bladder & IncontinenceDocument7 pagesOveractive Bladder & IncontinenceGaurav GargNo ratings yet
- Dose Adjustment in Renal and Hepatic FailureDocument27 pagesDose Adjustment in Renal and Hepatic Failurevanita100% (1)
- Prevention of Contrast Induced Renal FailureDocument13 pagesPrevention of Contrast Induced Renal Failurenaxo128No ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Kidney Disease: ArticleDocument11 pagesDrug-Induced Kidney Disease: Articledwi harisNo ratings yet
- K.23 Farmakologi (2) Pada Gagal GinjalDocument52 pagesK.23 Farmakologi (2) Pada Gagal GinjalHernita FerliyaniNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Drugs Acting On Renal SystemDocument20 pagesPharmacology of Drugs Acting On Renal SystemBestha Chakri100% (2)
- Kuliah Ginjal TerbaruDocument45 pagesKuliah Ginjal TerbaruityNo ratings yet
- Anestesi Intravenous AnestheticsDocument3 pagesAnestesi Intravenous AnestheticsJenniferNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument14 pagesGoutElisa KartikaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 22. Drugs Used in Renal and Urinary Tract DisordersDocument38 pagesLecture 22. Drugs Used in Renal and Urinary Tract DisorderskrisnadewirahadiNo ratings yet
- ASHP Chapter 29 - Medication Dosing in Patients With Renal DysfunctionDocument5 pagesASHP Chapter 29 - Medication Dosing in Patients With Renal DysfunctionTammyNo ratings yet
- Renal Excretion of Drugs 3Document36 pagesRenal Excretion of Drugs 3Noorulhuda AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Neuron BlockersDocument3 pagesAdrenergic Neuron BlockersSyeda Nishat Fathima TajNo ratings yet
- Allopurinol: Gouty Nephropathy and Renal DialysisDocument3 pagesAllopurinol: Gouty Nephropathy and Renal DialysisAnonymous G26HIUtzVNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyAysaaa DCNo ratings yet
- Modulation of Paraoxonase Activity (PON) - 1 by Xanthone in Sub Chronic Exposure of Orgnophosphate: Antioxidant in Dichorvos IntoxicityDocument7 pagesModulation of Paraoxonase Activity (PON) - 1 by Xanthone in Sub Chronic Exposure of Orgnophosphate: Antioxidant in Dichorvos IntoxicityFaris AdliNo ratings yet
- Renal Pharma 2Document13 pagesRenal Pharma 2Pranjali WeladiNo ratings yet
- PUT 822 Coursework 2Document4 pagesPUT 822 Coursework 2Stephen KokoNo ratings yet
- Drug Particle Size Reduction For Decreasing Gastric Irritancy and Enhancing Absorption of Naproxen in RatsDocument5 pagesDrug Particle Size Reduction For Decreasing Gastric Irritancy and Enhancing Absorption of Naproxen in RatsSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Diuretic TherapyDocument23 pagesDiuretic TherapyAgung Angga KesumaNo ratings yet
- Renal Pharma 3Document14 pagesRenal Pharma 3Pranjali WeladiNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes and Acid Base Common Fluid and Enlectrolyte DisordersDocument9 pagesElectrolytes and Acid Base Common Fluid and Enlectrolyte Disordersninta karinaNo ratings yet
- DinovoDocument1 pageDinovo17031 MD. IFTAKHAR HASSAN SAZALNo ratings yet
- Dapoxetine Hydrochloride Prescribing InformationDocument17 pagesDapoxetine Hydrochloride Prescribing InformationAdnan TowfiqueNo ratings yet
- Analgesic Agents: Maya Ganda Ratna Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy Faculty of Medicine - Lampung UniversityDocument46 pagesAnalgesic Agents: Maya Ganda Ratna Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy Faculty of Medicine - Lampung UniversityMuhammad GilangNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Regimen Selection (Quick AnswersL Pharmacy Book)Document16 pagesAntimicrobial Regimen Selection (Quick AnswersL Pharmacy Book)Yasmin ElsobkyNo ratings yet
- Vasoactive PeptidesDocument8 pagesVasoactive PeptidesSeff CausapinNo ratings yet
- Drug Induced Kidney DeseaseDocument12 pagesDrug Induced Kidney DeseaseNurul MasyithahNo ratings yet
- 8 Drug ExcretionDocument61 pages8 Drug ExcretionAhmed YTNo ratings yet
- Antiseizure DrugsDocument8 pagesAntiseizure DrugsCamile ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Caso ArtritisDocument4 pagesCaso ArtritisAnaly RocioNo ratings yet
- AntiemeticsDocument37 pagesAntiemeticsAriel OlshevskyNo ratings yet
- 10 - PHAR0004 - 9 - 7 Adrenergics - 2 - RB - 2018 - NotesDocument4 pages10 - PHAR0004 - 9 - 7 Adrenergics - 2 - RB - 2018 - NotesArthi ArumukasamyNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy TomDocument19 pagesDrugstudy TomGradefive MolaveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Drug ProfileDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Drug ProfileSandeepNo ratings yet
- Beta Blockers and Other Sympatholytic AgentsDocument43 pagesBeta Blockers and Other Sympatholytic AgentsAriel OlshevskyNo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions in PatientsDocument2 pagesDrug Interactions in PatientsckasapNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage/Route Mechanism of Action/ Classification Indication/Contraindication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesName of Drug Dosage/Route Mechanism of Action/ Classification Indication/Contraindication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMonica Gagarin CortezNo ratings yet
- Ungu PolosDocument2 pagesUngu PolosRumahBontangNo ratings yet
- Bunga BagusDocument2 pagesBunga BagusRumahBontangNo ratings yet
- Click To Edit Master Subtitle Style: Evaluasi Pelayanan Perbekalan Farmasi Pasien Rawat Inap DiDocument4 pagesClick To Edit Master Subtitle Style: Evaluasi Pelayanan Perbekalan Farmasi Pasien Rawat Inap DiRumahBontangNo ratings yet
- Presentation Title: Subheading Goes HereDocument2 pagesPresentation Title: Subheading Goes HereRumahBontangNo ratings yet
- Ungu BungaDocument2 pagesUngu BungaRumahBontangNo ratings yet
- Ungu PolosDocument2 pagesUngu PolosRumahBontangNo ratings yet
- Presentation Title: Subheading Goes HereDocument4 pagesPresentation Title: Subheading Goes HereRumahBontangNo ratings yet
- Click To Edit Master Subtitle Style: Evaluasi Pelayanan Perbekalan Farmasi Pasien Rawat Inap DiDocument4 pagesClick To Edit Master Subtitle Style: Evaluasi Pelayanan Perbekalan Farmasi Pasien Rawat Inap DiRumahBontangNo ratings yet
- Bunga PutihDocument4 pagesBunga PutihRumahBontangNo ratings yet
- Presentation Title: Subheading Goes HereDocument2 pagesPresentation Title: Subheading Goes HereRumahBontangNo ratings yet
- Presenta: Subtitle Goes HereDocument3 pagesPresenta: Subtitle Goes HereRumahBontangNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacy Answer Key-PINK PACOPDocument29 pagesClinical Pharmacy Answer Key-PINK PACOPKaguraNo ratings yet
- Diuretics:: Acetazolamide Carbonic Anhydrase InhibitorsDocument3 pagesDiuretics:: Acetazolamide Carbonic Anhydrase InhibitorsFatimah FaqihiNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury in HFDocument14 pagesAcute Kidney Injury in HFAnonymous NeRC5JYiSNo ratings yet
- 6 Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDocument11 pages6 Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsloshieloeNo ratings yet
- PHA 824 The Pharmacodynamics of Diuretic Drugs Dr. M.T. Piascik ObjectivesDocument12 pagesPHA 824 The Pharmacodynamics of Diuretic Drugs Dr. M.T. Piascik ObjectivespriapisNo ratings yet
- SGLT2 Inhibitors and Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Benefit: A State-Of-The-Art ReviewDocument10 pagesSGLT2 Inhibitors and Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Benefit: A State-Of-The-Art ReviewLucian SiriteanuNo ratings yet
- Drugs Mechanism Side Effect DiureticDocument3 pagesDrugs Mechanism Side Effect DiureticRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- Compression Fracture PathoDocument13 pagesCompression Fracture PathoMarrahCarrollNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Drugs: TEACH For Nurses ForDocument9 pagesDiuretic Drugs: TEACH For Nurses ForLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- Christine VanguardiaDocument7 pagesChristine VanguardiaJoshua PascasioNo ratings yet
- AldactoneDocument16 pagesAldactonesameidNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesPharmacology Practice QuestionsVipin JainNo ratings yet
- HFA Position Papers 2019Document264 pagesHFA Position Papers 2019Irina Cabac-PogoreviciNo ratings yet
- Slide 2 Drugs Used in Pregnancy Labour Post Partum and NewbornDocument21 pagesSlide 2 Drugs Used in Pregnancy Labour Post Partum and NewbornSanjay Kumar Sanju100% (2)
- Aipg11 AnswersDocument175 pagesAipg11 AnswersVivek ChoukseNo ratings yet
- Celery Seed ExtractDocument2 pagesCelery Seed Extract'Linda MasindaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology List of DrugsDocument66 pagesPharmacology List of DrugsSohail Adnan100% (2)
- Beige Brown Vintage Group Project Presentation - 20230922 - 184226 - 0000Document25 pagesBeige Brown Vintage Group Project Presentation - 20230922 - 184226 - 0000Mercurio AysonNo ratings yet
- Diuretics TableDocument5 pagesDiuretics TableLaylee ClareNo ratings yet
- TTTTDocument26 pagesTTTTMoataz TrabehNo ratings yet
- MBBS Made Easy, Second MBBS Examination, Manoj Vimal, Jaypee Bros., 2nd Edition 2009 PDFDocument329 pagesMBBS Made Easy, Second MBBS Examination, Manoj Vimal, Jaypee Bros., 2nd Edition 2009 PDFMonica KaranthNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Agent: Prof. Clement Belvis RN, RM, MPHDocument86 pagesCardiovascular Agent: Prof. Clement Belvis RN, RM, MPHEimhie Lee CasiNo ratings yet
- 05-Physical Examination of UrineDocument7 pages05-Physical Examination of Urinekalantan23No ratings yet
- Brand Name - Generic NameDocument6 pagesBrand Name - Generic Namejonette carataoNo ratings yet
- Ksa PH Exam Mcqs With AnswersDocument35 pagesKsa PH Exam Mcqs With AnswersMohamed Abdelhafiz100% (1)
- Urinary System Regulation of Fluid BalanceDocument8 pagesUrinary System Regulation of Fluid BalanceQuỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet