Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Civilengenhandbook 52 PDF
Civilengenhandbook 52 PDF
Uploaded by
Elmo Charles0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageOriginal Title
civilengenhandbook 52.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageCivilengenhandbook 52 PDF
Civilengenhandbook 52 PDF
Uploaded by
Elmo CharlesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
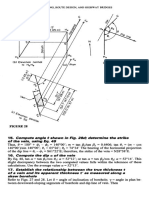
( a ) Assumed position of loaded cable
( c ) Force diagram
(b) True position of loaded cable
FIGURE 8
Calculation Procedure:
1. Sketch the loaded cable
Assume a position of the cable, such as PRSQ (Fig. So). In Fig. 8Z>, locate points P' and
Q', corresponding to P and Q, respectively, in Fig. 8a.
2. Take moments with respect to an assumed point
Assume that the maximum tension of 1800 Ib (8006 N) occurs in segment PR (Fig. 8).
The reaction at P, which is collinear with PR, is therefore 1800 Ib (8006 N). Compote the
true perpendicular distance m from Q to PR by taking moments with respect to Q. Or
^M6 = 180Om - 500(35) - 750(17) = O; m = 16.8 ft (5.1 m). This dimension establishes
the true position of PR.
3. Start the graphical solution of the problem
In Fig. 86, draw a circular arc having Q' as center and a radius of 16.8 ft (5.1 m). Draw a
line through P' tangent to this arc. Locate R' on this tangent at a horizontal distance of
15 ft (4.6 m) from P'.
4. Draw the force vectors
In Fig. Sc, draw vectors ab, be, and cd to represent the 750-lb (3336-N) load, the 500-lb
(2224-N) load, and the 1800-lb (8006-N) reaction at P, respectively. Complete the trian-
gle by drawing vector da, which represents the reaction at Q.
5. Check the tension assumption
Scale da to ascertain whether it is less than 1800 Ib (8006 N) This is found to be so, and
the assumption that the maximum tension exists in PR is validated.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- JMFDocument1 pageJMFElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Example 2.5: Figure 2.3: Concatenation of StringsDocument1 pageExample 2.5: Figure 2.3: Concatenation of StringsElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Using Message Box and Input Box: 3.1 The Msgbox FunctionDocument1 pageUsing Message Box and Input Box: 3.1 The Msgbox FunctionElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- General Definitions: I I R L V I L IDocument1 pageGeneral Definitions: I I R L V I L IElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- In Terms of The Known Angles) S P and BDocument1 pageIn Terms of The Known Angles) S P and BElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Table 3.2: Returned Values and Command ButtonsDocument1 pageTable 3.2: Returned Values and Command ButtonsElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Table 2.3: Arithmetic Operators Operator Mathematical Function ExampleDocument1 pageTable 2.3: Arithmetic Operators Operator Mathematical Function ExampleElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Table 3.1: Style Values and Command Buttons Style Value Named Constant Button DisplayedDocument1 pageTable 3.1: Style Values and Command Buttons Style Value Named Constant Button DisplayedElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Civilengenhandbook 440Document1 pageCivilengenhandbook 440Elmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Global Claims: SCL Delay and Disruption Protocol 2 Edition: February 2017 8Document1 pageGlobal Claims: SCL Delay and Disruption Protocol 2 Edition: February 2017 8Elmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- (D) Plan Plan (B) Elevation Normal Toh H: 15. Compute Angle O Shown in Fig. 2Bd Determine The StrikeDocument1 page(D) Plan Plan (B) Elevation Normal Toh H: 15. Compute Angle O Shown in Fig. 2Bd Determine The StrikeElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- A Preliminaries/Genera Conditions: Information Provided Measurement Rules Rules CoverageDocument1 pageA Preliminaries/Genera Conditions: Information Provided Measurement Rules Rules CoverageElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Of The Intersection Points and Point G: H H F FDocument1 pageOf The Intersection Points and Point G: H H F FElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Granting EOT: SCL Delay and Disruption Protocol 2 Edition: February 2017 6Document1 pageProcedure For Granting EOT: SCL Delay and Disruption Protocol 2 Edition: February 2017 6Elmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Guidance Part A: Delay, Disruption and Acceleration ConceptsDocument1 pageGuidance Part A: Delay, Disruption and Acceleration ConceptsElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Core Principles: 1. Programme and RecordsDocument1 pageCore Principles: 1. Programme and RecordsElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- SMM7 23Document1 pageSMM7 23Elmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Preliminaries/General Conditions: A ContinuedDocument1 pagePreliminaries/General Conditions: A ContinuedElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- SCL Delay and Disruption Protocol 2 Edition: February 2017 7Document1 pageSCL Delay and Disruption Protocol 2 Edition: February 2017 7Elmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- SMM7 21Document1 pageSMM7 21Elmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Recommended Criteria For Single Samples: Table 1 Table 1Document1 pageRecommended Criteria For Single Samples: Table 1 Table 1Elmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Pre I Aries/ Ene Al Itions Co N Ed: 3 Lo e S Q I Eme TS: Pec L Itations T Od/se Uence/t I G/ SeDocument1 pagePre I Aries/ Ene Al Itions Co N Ed: 3 Lo e S Q I Eme TS: Pec L Itations T Od/se Uence/t I G/ SeElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- 2020-04-Lockdown-Rollback-Checklist-Research-Note 3Document1 page2020-04-Lockdown-Rollback-Checklist-Research-Note 3Elmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- 2020-04-Lockdown-Rollback-Checklist-Research-Note 4Document1 page2020-04-Lockdown-Rollback-Checklist-Research-Note 4Elmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- 2020-04-Lockdown-Rollback-Checklist-Research-Note 2Document1 page2020-04-Lockdown-Rollback-Checklist-Research-Note 2Elmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- 2020-04-Lockdown-Rollback-Checklist-Research-Note 1Document1 page2020-04-Lockdown-Rollback-Checklist-Research-Note 1Elmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1 General AASHTO LRFD Design EquationDocument1 page1.3.1 General AASHTO LRFD Design EquationElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Nice Classification - 11 Edition, Version 2017Document1 pageNice Classification - 11 Edition, Version 2017Elmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- VMA in HMADocument1 pageVMA in HMAElmo CharlesNo ratings yet
- Truck LoadingDocument1 pageTruck LoadingElmo CharlesNo ratings yet