Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diagnostic Mycology I PDF
Diagnostic Mycology I PDF
Uploaded by
Wpj JanuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diagnostic Mycology I PDF
Diagnostic Mycology I PDF
Uploaded by
Wpj JanuCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Dermotophytes
“Commonest infectious agent of man”
Invades the keratinized portions of the hair, skin and nails. Use keratin as nitrogen source.
Dermatophytosis – a mycotic infection of the hair, skin and the nails caused by
dermatophytes.
Dermatomycosis – invasion of the cutaneous tissue by other fungi
Classification of dermatophytes according to the origin
Anthrophilic ( human loving)
Geophilic (soil loving)
Zoophilic (animal loving)
On the basis of clinical, morphologic, and microscopic characteristics 3 genera in
dermatophytes
Epidermophyton
Microsporum
Trichophyton
Epidermophyton Microsporum Trichophyton
Tissue affected Skin, nails Hair, skin Hair, skin nails
Microconidia none few many
Thick, rough walls, Smooth thin walls,
Macroconidia Smooth thin walls
many present relatively few
Fluorescence in
No Some species No
tissue
Specimens: Skin, Nails, Hair (when transporting specimens that believed to contain
dermatophytes – keep the specimen dry: this prevents overgrowth of the tissue and fungus by
bacteria and preserves the fungus for culture)
1. Wood lamp - detect dermatophyte infections – tissue affected with microsporum fluoresce
bright yellow green (other dermatophytes do not cause fluorescence).
False positive reactions – some hair oils, medications
2. Direct microscopic examination – not a sensitive method for dermatophytes.
Skin, hair – 10% KOH
Nails – 20% KOH
(Dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO] – increase the penetration of the stain into the tissue
3. Culture – media containing antibiotics (because specimens fro cutaneous sites almost
always contain the normal bacterial flora)
Emmon’s modification of sabouraud dextrose agar (modified SDA) with 4% glucose better
for the dermatophytes
SDA without antibiotics should always be included in any regimen for culture –
because pathogens sensitive to the microbial agents be missed.
PDA or PFA (potato flake agar)
4. Dermatophytes test medium (DTM) contain phenol red indicator – dermatophytes produce
alkaline metabolic products – colour changes from yellow to reddish orange or red.
(screening test)
5. Colony morphology – one feature that is helpful for distinguishing the dermatophytes from
other pathogenic fungi
“ colonies have one pigment in surface of the colony and another pigment (other
than the black) on the reverse.(not all dermatophytes have these pattern)
6. Microscopic features – Microconidia, macroconidia, - size, shape, septation, attachment
to the hyphae of the conidia, vegetative hyphal stuctures
Dermotophytes culture contain structures – pectinate hyphae, racquet hyphae, nodular
bodies, spiral hyphae
Epidermophyton Microsporum Trichophyton
Macroconidia thin smooth walls fusiform / spindle shapped cylindrical / pencil shaped /
contain 1-5 cells (taper from the center to both fusiform
ends) thin, smooth walls
wall –thick, echinulate with 2-12 cells per conidium
upto 15 septa.
(beavers tails/
snowshoes shape)
Microconidia Never produce Less common globose/pyriform, clavate.
Pyriform, clavate Borne in two patterens.
Born directly on the hyphae or
on short conidiophores
Trichophyton –
En thryses form a sleevelike arrangement around the hyphae
En grape form a clusters arrangement around the hyphae
You might also like
- Sample CPJE: Finasteride 1 MG Tablets #30 1 Tab P.O. Daily For Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument12 pagesSample CPJE: Finasteride 1 MG Tablets #30 1 Tab P.O. Daily For Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaHerne Balberde78% (9)
- DRRM-H Advocacy KitDocument32 pagesDRRM-H Advocacy KitERMED OFC R2TMC100% (2)
- Sermorelin Main InformationDocument4 pagesSermorelin Main InformationPedro MolinaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Surveys Catalog PDFDocument316 pages2016 Surveys Catalog PDFLuis TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Fungi Characteristics of Fungi Key Points Ascus. Reproduction Key PointsDocument4 pagesFungi Characteristics of Fungi Key Points Ascus. Reproduction Key PointsPrincess Z. DaelNo ratings yet
- Pistachio PresentationDocument18 pagesPistachio Presentationaudreebelle100% (2)
- NaturalHyperthyroidRecoveryGuide PDFDocument62 pagesNaturalHyperthyroidRecoveryGuide PDFAndreea IrinaNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Orthoptera and Allied Insects:, IncludingDocument9 pagesA Guide To Orthoptera and Allied Insects:, IncludingMaria Angela Caisapanta PachecoNo ratings yet
- Key Psocoptera PDFDocument83 pagesKey Psocoptera PDFkhawla zedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document28 pagesLecture 1Mamun_Abdullah_1612100% (1)
- Phthiraptera - Johari JalinasDocument24 pagesPhthiraptera - Johari JalinasJohari Jalinas100% (1)
- Blight: Symptom Plants Pathogenic Organism Chlorosis TissuesDocument10 pagesBlight: Symptom Plants Pathogenic Organism Chlorosis TissuesIlyas Khan AurakzaiNo ratings yet
- Mini Risk Assessment Grape Berry Moth, Lobesia Botrana (Denis & Schiffermuller) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae)Document29 pagesMini Risk Assessment Grape Berry Moth, Lobesia Botrana (Denis & Schiffermuller) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae)brkica2011No ratings yet
- Morphology and Life Cycle of Puccinia and The Symptoms of SmutsDocument21 pagesMorphology and Life Cycle of Puccinia and The Symptoms of SmutsRuchika PokhriyalNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Eumycota - The True Fungi2Document33 pagesKingdom Eumycota - The True Fungi2Mauricio LarrainNo ratings yet
- Presentation Draft: Course No.: 501 Course Title: MycologyDocument48 pagesPresentation Draft: Course No.: 501 Course Title: Mycologysidhu_agricoNo ratings yet
- Botany ReviewerDocument23 pagesBotany ReviewerIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- Agr 154 C1Document28 pagesAgr 154 C1Fatin Aisyah SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Full TextDocument295 pagesFull TextkanNo ratings yet
- Plant Resistance To Parasitic NematodesDocument261 pagesPlant Resistance To Parasitic Nematodesdouglasman100% (1)
- Fungi Complete NotesDocument22 pagesFungi Complete NotesAli Akber FerokeNo ratings yet
- Microbial EcologyDocument6 pagesMicrobial Ecologyakifuji913No ratings yet
- Nematology NotesDocument5 pagesNematology NotesBabar AliNo ratings yet
- Preview of The Prokaryotes Other Major Lineages of Bacteria and The ArchaeaDocument20 pagesPreview of The Prokaryotes Other Major Lineages of Bacteria and The ArchaeaLuis Javier Mendoza Estrada100% (1)
- BacterialPlantPathogens 001 PDFDocument7 pagesBacterialPlantPathogens 001 PDFMahnoor Khan QueenNo ratings yet
- PLPA 301 Lecture NotesDocument21 pagesPLPA 301 Lecture NotesLauren BoylesNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument3 pagesFungiKasturi RizNo ratings yet
- CP 121 Module 1Document82 pagesCP 121 Module 1JEYLAISA MANABATNo ratings yet
- Nematode Parasites of RiceDocument2 pagesNematode Parasites of RiceCPS_IRRINo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 NotesDocument60 pagesChapter 4 NotesLogan KerringtonNo ratings yet
- Indian Journal of Acarology Vol2Document46 pagesIndian Journal of Acarology Vol2jitenmechNo ratings yet
- Whitefly Biology PDFDocument27 pagesWhitefly Biology PDFJulian LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Types of LarvaDocument12 pagesTypes of LarvaFarrin Khanzlaluu Menunggunya100% (1)
- Book LiceDocument2 pagesBook LiceAuliya100% (2)
- Biological Control of NematodesDocument17 pagesBiological Control of NematodesYara Othman Abdel RaoufNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy and Classification....Document8 pagesTaxonomy and Classification....Andrew MarariaNo ratings yet
- MyxomycotaDocument4 pagesMyxomycotaMuneeb UllahNo ratings yet
- External Feature of The Insect: Prepared By: Ghada Abou EleineinDocument32 pagesExternal Feature of The Insect: Prepared By: Ghada Abou EleineinAlham MohammadNo ratings yet
- 03-Fungi Handbook PDFDocument205 pages03-Fungi Handbook PDFJuventino García Alvarado100% (1)
- Nematode Biology, Physiology & Ecology - Conversion GateDocument42 pagesNematode Biology, Physiology & Ecology - Conversion GatePra Youdha100% (1)
- Kingdom Fungi: - Characteristics of Fungi - Oomycota - Zygomycota - Ascomycota - Basidiomycota - DeuteromycotaDocument15 pagesKingdom Fungi: - Characteristics of Fungi - Oomycota - Zygomycota - Ascomycota - Basidiomycota - DeuteromycotaLeah Rice100% (1)
- Lect. 2 History Plant Virology PDFDocument16 pagesLect. 2 History Plant Virology PDFAbid NooriNo ratings yet
- Plant Disease ControlDocument12 pagesPlant Disease ControlAbhiyan Anala ArvindNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Entomology 10Document9 pagesStudy Guide For Entomology 10Alex TunqueNo ratings yet
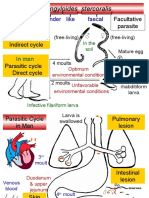
- Strongyloides Stercoralis: Faecal Like CylinderDocument18 pagesStrongyloides Stercoralis: Faecal Like CylinderAyop KhNo ratings yet
- TomatoDocument12 pagesTomatoAileen MontuyaNo ratings yet
- Entomology: Naming of TaxaDocument19 pagesEntomology: Naming of TaxaAliah Alleyne Canals - BSA - 1ANo ratings yet
- Diseases of SorghumDocument16 pagesDiseases of SorghumJagtap RamNo ratings yet
- Cat A PillarDocument26 pagesCat A PillartgeerawoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document19 pagesLecture 6ASHUTOSH MOHANTYNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in EntomologyDocument9 pagesBasic Concepts in Entomologyjyc roseNo ratings yet
- Phylum NematodaDocument24 pagesPhylum NematodaKaten KyoukotsuNo ratings yet
- TMP 79 CFDocument256 pagesTMP 79 CFFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Intro Botany PDFDocument184 pagesIntro Botany PDFharshNo ratings yet
- Economic EntomologyDocument36 pagesEconomic EntomologyMubeen KhanNo ratings yet
- EntomologyDocument37 pagesEntomologytariNo ratings yet
- GN 310 EntomologyDocument49 pagesGN 310 EntomologyKaira Mae CamiletNo ratings yet
- Plant Bacterial DiseaseDocument34 pagesPlant Bacterial DiseaseIsabella Cardona VelezNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam General Ecology Ws 2013-14-13900557Document2 pagesMidterm Exam General Ecology Ws 2013-14-13900557premoh0% (1)
- Ch-1 Nematology IntroductionDocument6 pagesCh-1 Nematology IntroductionHumaNazNo ratings yet
- Sugarcane DiseasesDocument6 pagesSugarcane DiseasesNkanyisoNo ratings yet
- 5.1. Diseases of Black Pepper: Indian Institute of Spices Research, Kozhikode-673 012, Kerala, IndiaDocument29 pages5.1. Diseases of Black Pepper: Indian Institute of Spices Research, Kozhikode-673 012, Kerala, IndiaAleksandra MilenkovićNo ratings yet
- EntomologyDocument52 pagesEntomologyHiroshi RyouNo ratings yet
- Ento Lab Midterms HandoutsDocument8 pagesEnto Lab Midterms Handoutshumanupgrade100% (1)
- Fungi: Biology and ApplicationsFrom EverandFungi: Biology and ApplicationsKevin KavanaghNo ratings yet
- A Still-Face Paradigm For Young Children 212 YearDocument78 pagesA Still-Face Paradigm For Young Children 212 YearFannyNo ratings yet
- Abrams Clinical Drug Therapy 10th Edition Frandsen Test BankDocument25 pagesAbrams Clinical Drug Therapy 10th Edition Frandsen Test BankMissKatherineGardnerfjcp100% (49)
- Clerking PatientsDocument7 pagesClerking PatientsJx ChamNo ratings yet
- Vitamins MCQs PDFDocument5 pagesVitamins MCQs PDFBijay Kumar MahatoNo ratings yet
- Total T3: For Use On The IMMULITE and Immulite 1000 SystemsDocument31 pagesTotal T3: For Use On The IMMULITE and Immulite 1000 SystemsEdgar Galván0% (1)
- Unit One Vocabulary: 'prɔvidәntDocument53 pagesUnit One Vocabulary: 'prɔvidәntKhanh Chi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Bosniak 2F Cysts - GuidelinesDocument9 pagesBosniak 2F Cysts - Guidelinesfelixsafar3243No ratings yet
- JHP 9 112Document9 pagesJHP 9 112drugdrugNo ratings yet
- Some Important Leave Rules For WB TeachersDocument27 pagesSome Important Leave Rules For WB TeachersNupur MandalNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Dentistry: The Use of Nitrous Oxide Inhalation Sedation For Dental Treatment in Agitated ChildrenDocument15 pagesPediatric Dentistry: The Use of Nitrous Oxide Inhalation Sedation For Dental Treatment in Agitated ChildrenmahmoodNo ratings yet
- Misconceptions, Myths, and Beliefs About Common Communicable DiseasesDocument24 pagesMisconceptions, Myths, and Beliefs About Common Communicable DiseasesDanah Verniz Baldoz100% (1)
- MarketLineIC - Johnson Johnson - Profile - 120323Document59 pagesMarketLineIC - Johnson Johnson - Profile - 120323JULIAN MAURICIO MARTINEZ ORTEGONNo ratings yet
- Why Computer ErgonomicsDocument6 pagesWhy Computer ErgonomicsediealiNo ratings yet
- Advancedtechniquesin Nonsurgicalrhinoplasty: Umang Mehta,, Zachary FridiriciDocument11 pagesAdvancedtechniquesin Nonsurgicalrhinoplasty: Umang Mehta,, Zachary FridiriciRaphaela TravassosNo ratings yet
- Patient Counselling Technique For TuberculosisDocument1 pagePatient Counselling Technique For TuberculosisShreyas PatilNo ratings yet
- R. Gundo Medical/Surgical Nursing Department: History TakingDocument39 pagesR. Gundo Medical/Surgical Nursing Department: History Takingchifunndo charlesNo ratings yet
- 2021 Term 1 Grade 8 Integrated Science Test 1Document4 pages2021 Term 1 Grade 8 Integrated Science Test 1Davies Masumba50% (2)
- Practical Approach To Determining Protein Requirements of The Critically Ill 2023 - 0107 JBO NHS DefDocument50 pagesPractical Approach To Determining Protein Requirements of The Critically Ill 2023 - 0107 JBO NHS DefMateo LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Normative Data For Ten Spanish-Language Neuropsychological Tests in Eleven Latin American Countries PDFDocument239 pagesNormative Data For Ten Spanish-Language Neuropsychological Tests in Eleven Latin American Countries PDFNicol Mariana V. FernándezNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 mRNA Pfizer-BioNTech Vaccine Analysis PrintDocument66 pagesCOVID-19 mRNA Pfizer-BioNTech Vaccine Analysis PrintWilfred BakkerNo ratings yet
- Hydrotherapy Referral Form and Risk Assessment Template For SystmOneDocument3 pagesHydrotherapy Referral Form and Risk Assessment Template For SystmOnetajwer amjadNo ratings yet
- Health and WellnessDocument59 pagesHealth and Wellnessvenkata karthikNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2Document12 pagesPMLS 2Mary Nicole ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Biotelemetry System For Primary Healthcare Center in Rural IndiaDocument8 pagesAdvanced Biotelemetry System For Primary Healthcare Center in Rural IndiaRudra KNo ratings yet