Professional Documents
Culture Documents
QTCM
QTCM
Uploaded by
Alvin Jis0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views15 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views15 pagesQTCM
QTCM
Uploaded by
Alvin JisCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 15
E9250 Gayle
Dual carriageway
Fig. 25 — Sign Separation Fig. 26 — Signs Not Requiring Full Vertical Clearance
‘The vertical clearance to the underside ofthe bottom sign must conform to the requirements of Section
232 except where
(0) A regulatory sign is mounted on a trafic signal pole
(i) Sign 909 is used with Sign 414, 415 oF 416 in advance of a roundabout.
(i) Signs 208, 209, 211 or 212 are used at the leading edge of a trafic island
In these cases the vertical clearance may be reduced to 0.9 metres, even though the signs may be
sited where pedestrians are present.
2.4 DESIGN OF SIGN SUPPORTS
“Tree different cross-sections of sign suppor are available, these being hollow circular posts, hollow
rectangular posts and |-beam sections. Sign plates which are less than 3m in area may oniy be
supported by hollow section posts. Signs larger than this may be supported by any of the permitted
sections
24,1 THE SIGN SUPPORT NOMOGRAMS
‘The nomograms provided in this section are suitable for use in nearly all cases. However, where a sign
would be subject to constant exposure to wind speeds exceeding 100kph a separate structural
analysis should be carried out
‘The nomograms are used thus:—
(i) The sign face area and the height of the centre of the sign above ground level are plotted
Cn their respective scales.
(i) These two points are joined by a straight line which is continued until itintersects the pivot
line.
(il) From this point a horizontal ine is drawn to intersect the post reference lines.
2.05
(v) The required number of supports for each size of support is alven at the foot of the
columns) at which the intersections) occur.
(¥) The preferred combination of support section and number of supports is then selected,
subject to the folowing constraints:
() The span betwoen adjacent supports may not exceed 3.6 metres.
(0) The overhang from the outer support to the edge of the sign plate may not exceed
12 metres.
(vi) Where two intersection points occur in the same column, the first point to be reached
Indicates the correct combination,
(vil) Sign supports should be positioned as shown in Fig. 27.
Fig. 27 — Spacing of Sign Supports
206
‘Area of Sign in square metres
0s
19
Pivot Line
lExamote 2431
Height to centre of sign in metres
Numberof posts
Post ‘rar Fecingdar Section
Fteronco Post Post Best
a sxs sox SDxS =
e yeix32 Be ax32
° 8ox4, 00x 60x92
D Mss xedn36
e wo7xS 6D XEDXS aT TOR
F Weesxs 150% 1006S 152 BF
8 1807 %54 — 200% 100x5 178 x 100"
4 21963 200 100x69 209% 130
1 2H5 x63 280K 50x63 245 x 140
4 2TV0x63 —_280x 150x638 245 x 146
‘Note A = ASU (oled seal
UE U5 (uiverea beam)
Fig. 2.8a — Sign Support Nomogram
207
‘rea of Sign in square metres
Pivot Line
y
Is
A
28
304
35:
40.
454
80]
5.
80.
65:
79
15
89. “
854 st
8
ee] 8
106.
105, “
n104
118]
x20] .
128
199.
135 °
140. \ €
50
pe
2
\ -
2° €
st
" |e
LJ —
___—_+——.}
=
z 3
Height to contre of sign in metros Number of posts
Fos raver Fecengular Peston
Peleence Post Post Poet
a 3x8 Wxtoxs =
8 weixa2 = @xaxo2
lc sexe woxsos2 =
D maxs xoxo —
& 1987x510 80xS 127 7H
F 1eBxS 15x 10069 152x560"
6 se7x54 © 20x 100%5 178x102"
21989 Ox 1COSS 708. 1950
' 2ubx69 250% 160x69 245 x 1460
4 2130x632 16OxES AS x 148
‘Noi’ A = FSU (oled ste! ow)
= U8 drvereal beam!
Fig. 2.88 — Sign Support Nomogram
2.08
‘Area of Sign in square metres
Phvot Line
A
140. o
150.
1 8
17
eo} °
x90
200 “
aol
2204
23 °
240
250. a
280. a8
210.
230.
x
at
as 6
2
20
, | —]
4 | 1
fT —___ + |
Se
z 3 7
Height to centre of signin metes Number of posts
Pos Gram ——~ecepan ‘Seaton
Furence Post Pom Pom
a woxs soxsoxs
8 Tins? Oxa0x92
c gaoxe 00x sx32
D y4ge5 1206x586 =
e ores MOxBDxS 127 TE
16535 50x 1006S TEKH
6 or xs4 Ox 00S 170x100"
W 29x68 Dx 1OOxOs AB 18
' PUSHES — BDI XES BE 18
J 0x63 —_-2Ox150x63 248 x HY
Tow f= AS oed gests
OF UB (imeea bea!
Fig. 2.8¢ — Sign Support Nomogram
2.08
‘Area of Sign in square metres
Pivot Line
C—
Et
‘ 2 3
Height to conte of sign in metres Number of posts
Pos Crevar Fecangulay ——-Secton
Pelernce Post Post Post
a waxes xeKS
8 qeixa2 © @xaxoz
c eeaxe © 100x80x92
° msxs — 120x60x36
E wo7xs — 160x@dxS 127 7H
e W659%S 15010069152
6 W87x54 2001005 1TB 02%
H 29x63 200 10069 209 x 1900
i 25x69 250 150%63 245% 1460
4 20x63 50x 15DXES Sx 146?
Note: f= ASU (led seal joisd
= Us trmarea boa).
- 2.8d — Sign Support Nomogram
210
2431
WORKED EXAMPLES
‘A Direction Sign, 0.55 m high by 1.85 m wide, isto be installed in an urban area, Determine the number
‘and size of the sign supports.
Solution:
(i) Determine the sign face area:
055 x 185m
A= 102 me
(i) Determine the height to the centre of the sign:
Mounting height = 2.1m (Assuming that the sign is to be located in an area where
pedestrians are present)
Hal sign height = 0.275
‘Therefore height lo the centre ofthe sign = 2375 m
(i) Use Fig. 2880 determine the number and size of he sign supports
From Fig. 28a, no. of supports = 2 (minimum requirement for direction signs)
Therefore size of supports = Type B.
Dye to the small width of the sign, no check need be made for compliance with support spaces:
requirement. Therefore this solution should be adopted,
2432 An advance direction sign, 430 m high by 9.00 m wide, is to be installed on @ mejor rural route,
Determine the number and size of the sign supports.
Soiution:
{) Determine the sign face area:
Am 430 x 9.00 = 98:70 m?
(i) Determine the height to the centre of the sign:
‘Mounting height = 1.5 m (maximum permitted in rural areas)
Half sign height = 2.15 m
‘Therefore height lo the Centre of the sign = 3.65 m
(ii) Use Fig. 2.84 to determine the number and size of the sign supports:
From Fig. 2.84, 2 no. type J supports would be adequate
‘Check against section 2.4.1 (v) for compliance with support spacing requirement.
Span = 60% x 900m = 54m) 36m maximum
Overhang = 20% x 900m = 1.8m) 1.2m maximum
Therefore this solution is not acceptable.
From Fig. 2.8, 9 no. type | supports are an alternative
Check against Section 2.4.1 (v) for compliance with support spacing requirement,
Span = 35% x 9.00 m = 3.15 m 43.6 m maximum,
Ovethang = 18% x 9.00 m = 1.35 m> 12m maximum
‘Therefore this solution is not acceptable.
From Fig. 284, 4 no. type H posts are an alternative.
‘Check against Section 2.4.1 (¥) for compliance with support spacing requirement.
Span = 25% x 9.00 = 225 (36m maximum
Overhang = 125% x 900m = 1.13m¢ 12m maximum
‘Therefore this solution should be adopted,
212
28 DESIGN OF SIGN SUPPORT FOUNDATIONS
‘Two types of foundation are avaliable, as shown in Fig. 29. Type 1 is used: mainly with small sized
< mn l
aN
a iwerer)
‘Type 2 Foundation
. Fig. 2.9 — Sign Support Foundations
213
25.44
‘The graphs provided in this section are suitable for determining the required length (L) ef foundation in
‘most cases. However, where poor ground conditions exist, or where the full depth of foundation cannot
be, achieved due to obstructions such as service cables or pipes, individual calculations must be
carried out.
‘THE FOUNDATION DESIGN GRAPHS:
TYPE 1 FOUNDATION
(i) Select the appropriate graph trom Fig. 2.10.
(i) Plot the height ofthe sign plate (h,) and project this point horizontally
(ii) Plot the breadth of sign plate (b) and project it vertically unt it intersects the projection of
hy
(iv) Read the required length of foundation (L) from the band in which the intersection fas
(¥) Compare the value obtained with the minimum permitted value of L, given in Table 22, for
the chosen si
permitted minimum
(vi) ithe calculated value of L exceeds 1.5m, a Type 2 foundation must be used,
SUPPORT TYPE | MINIMUM L VALUE (m)
AaB 06
cao ‘0
. Eto 13
Table 22 — Minimum Permitted Lengths of Foundation
Loe?
of sign support. f the calculated value is less, it must be increased to the
eer?
24
hha (matres)
36:
20:
05 70
» (metres)
MOUNTING HEIGHT = 21m
08 19 15 20 26 08 10 15 20 25
(metres) (motres)
MOUNTING HEIGHT = 15m MOUNTING HEIGHT = 08m
Fig. 2:10a — Type 1 Foundations Single Support
Keyl of “in,
NOTE Erampie 263.1 Sign
See wn 9 ae,
‘mama ‘eng
sitem epee
MOUNTING HEIGHT = 21m
7046
bimetes) of Sign
20 25 90 95 40 45 60
MOUNTING HEIGHT = 1m
oe MOUNTING HEIGHT = 09m
rr a er)
Fig. 2.10b — Type 1 Foundations (cont) Twit Supports
216
vO Due,
pyre
25.12 TYPE 2 FOUNDATION
() Using Fg. 21, select he column appropriate tothe mounting height (h,) being used.
(Gj) Plot the height of sign face (hs) on the vertical axis and project it horizontally to intersect
with the chosen column,
(i) Read the required value of L from the band in which the intersection fails,
(¥) Compare the value obtained with the minimum permitted value of L in Table 22 for the
chosen size of sign support. I the calculated value is less, it must be increased to the
i permitied minimum,
(\) Ifthe intersection falls outside the range of the graph, a separate analysis must be carried
out
he es|
(metres)
ho(metres)
Fig. 2.11 — Type 2 Foundations
S
2n7
2531
2532
WORKED EXAMPLES
‘A Direction Sign, 0.55 m high by 1.85 m wide, is to be installed in an urban area. Determine the type
and size of foundation.
Solution:
() Determine the mounting height and the number and size of the sign supports.
‘See Section 243.1 — Mounting height = 2,1 m
No.of supports = 2
Size of supports = Type B
i) Use Fig. 2.10b or Fig. 211 to determine the type and size of the foundation:
From Fig. 2:10b, select the graph for twin supports and 2.1 m mounting hi
Foundation is Type 1.0.6 m tong
Check against Table 22 for compliance with minimum length of foundation requirement.
For support Type B, minimum length = 0.6 m
‘Thetefore this solution should be adopted.
‘An Advance Direction Sign, 430 m high by 9.00 m wide, is to be installed on @ major rural route.
Determine the type and size of foundation.
Solution:
() Determine the mounting height and the number and size of the sign supports:
See Section 24.32 - Mounting height = 1.5m
No. of supports = 4
Size of supports = Type H
(ii) Use Fig. 2.10 oF Fig. 2:11 to determine the type and sizo of the foundation:
From Section 25, where more than 2 No. supports are required, a Type 2 foundation must
be used, so use Fig. 2.11
From Fig. 2.14, forh, = 430 and h, = 1.5, length of foundation = 1.7m
Check against Teble 22 for compliance with minimum length of foundation requirement.
For support Type H, minimum length = 1.3 m
‘Therefore this solution should be adopted.
218
26
SIGN REFLECTORISATION
All road traffic signs must be relectorised by the application of reflective material to all paris of the sign
face (except those letters or symbols coloured black). This material must, when illuminated by @
vehicle's headlights, reflect light back along as near as possible the seme path go that the driver sees
the sign brightly iluninated,
Reflective material Is graded in ‘classes of reflectivity’, namely Class 1 (or High Intensity Grade) and
Class 2 (or Engineering Grade). The required coeficients of retro-rellection for each grade are
specified in Table 23.
(MINIMUM COEFFICIENT OF RETRO-REFLECTION
(Candelas/ux/m?)
ENTRANCE OBSERVATION iu
ret oeRvAT ied_| Yellow | Green | Blue | white
Class of Material
Degrees? Minutes’ vfetite}rfe|sfe}rfe
~8° o> 12" 35 | 12 |170] 50 | 90 | 5 | 20 | 4 |250] 70
0° * 20 25 | 10 |120| 35 | 20} 5 | 14} 3 |180] 50
1° 9 2|15} 2] 3] 1] 1] 1 {oe} | 5
18° oO 12 30 | 10 ]120} 35 | 20 | 3 | 15} 3 |200] 55
0° 20 20] 8| e] 20/15] 3] 10} 2|150] 3
1 0 15| 1] 8] 2] 1] 1Jo7Jos|is| 3
40° oo 12 16} 3| a) 8} 9] 1] 9] 1/120] 15
0 20 13 }25| | 5] 7] 1] 7 Joa] 95] 10
19 oo 1 }o3| sos }os}oz}os}or| s}1s
‘Table 2:3 — Minimum Coefficients of Retro-Reflection
Cass 1 reflective material must be used on all signs located in areas where street lighting is present or
‘where there is a high level of background lighting from some other source. Elsewhere, Class 2 material
may be used,
‘The colour of the material must comply with Table 24 which, for ease of relerence has been plotted
to show the chromaticity dlagram (Fig. 2.12). The luminance factors of the material must comply with
Table 25.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- General: Roads Approved Material ListDocument5 pagesGeneral: Roads Approved Material ListAlvin JisNo ratings yet
- Artwork PDFDocument1 pageArtwork PDFAlvin JisNo ratings yet
- QS049 P03 AEC CON REP A10016 - Part06 - Compressed - 035 035Document1 pageQS049 P03 AEC CON REP A10016 - Part06 - Compressed - 035 035Alvin JisNo ratings yet
- Arwork PDFDocument1 pageArwork PDFAlvin JisNo ratings yet
- Arwork PDFDocument1 pageArwork PDFAlvin JisNo ratings yet
- For Information Only: Outgoing TransmittalDocument5 pagesFor Information Only: Outgoing TransmittalAlvin JisNo ratings yet
- Mill Test CertificateDocument1 pageMill Test CertificateAlvin JisNo ratings yet
- For Information Only: Outgoing TransmittalDocument3 pagesFor Information Only: Outgoing TransmittalAlvin JisNo ratings yet
- Temporary Directional Signboard PDFDocument2 pagesTemporary Directional Signboard PDFAlvin JisNo ratings yet
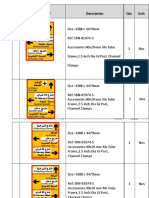
- Description QTY U/ Rate Amount (QR) Sign NO.: Signs & SignagesDocument1 pageDescription QTY U/ Rate Amount (QR) Sign NO.: Signs & SignagesAlvin JisNo ratings yet
- Description QTY U/ Rate Amount (QR) Sign NO.: Signs & SignagesDocument1 pageDescription QTY U/ Rate Amount (QR) Sign NO.: Signs & SignagesAlvin JisNo ratings yet
- Description QTY U/ Rate Amount (QR) Sign NO.: Signs & SignagesDocument1 pageDescription QTY U/ Rate Amount (QR) Sign NO.: Signs & SignagesAlvin JisNo ratings yet
- Description QTY U/ Rate Amount (QR) Sign NO.: Signs & SignagesDocument1 pageDescription QTY U/ Rate Amount (QR) Sign NO.: Signs & SignagesAlvin JisNo ratings yet