Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gcic - Laws Governing Nurses
Gcic - Laws Governing Nurses
Uploaded by
hanyaklein0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views1 pageThe document discusses the relationship between law and ethics, using the landmark Karen Ann Quinlan case as an example. It outlines that ethics tell people what they should do, while law provides boundaries and consequences. In the Quinlan case, the court agreed patients have a legal right to refuse treatment, and allowed Quinlan's parents to remove her ventilator against doctor objections. The ventilator was removed but Quinlan continued breathing on her own for nearly 10 more years until dying of pneumonia.
Original Description:
Original Title
Gcic_laws Governing Nurses
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the relationship between law and ethics, using the landmark Karen Ann Quinlan case as an example. It outlines that ethics tell people what they should do, while law provides boundaries and consequences. In the Quinlan case, the court agreed patients have a legal right to refuse treatment, and allowed Quinlan's parents to remove her ventilator against doctor objections. The ventilator was removed but Quinlan continued breathing on her own for nearly 10 more years until dying of pneumonia.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views1 pageGcic - Laws Governing Nurses
Gcic - Laws Governing Nurses
Uploaded by
hanyakleinThe document discusses the relationship between law and ethics, using the landmark Karen Ann Quinlan case as an example. It outlines that ethics tell people what they should do, while law provides boundaries and consequences. In the Quinlan case, the court agreed patients have a legal right to refuse treatment, and allowed Quinlan's parents to remove her ventilator against doctor objections. The ventilator was removed but Quinlan continued breathing on her own for nearly 10 more years until dying of pneumonia.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
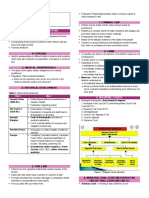
LAWS GOVERNING NURSING
on medical ethics, which they believed prohibited taking an action
A. FUNCTIONS OF LAW that might lead to the death of the patient. The lawyers of Quinlan
1) Nature of Law family argued that what was at stake was not medical ethics but
(a) Normative: obligatory on human conduct the legal rights of the individual patient to refuse medical treatment
that was highly invasive and offered no chance for a cure.
(b) Institutionalized The court agreed that patients have the legal right to
(c) Coercive refuse medical treatment, determined that honouring such a refusal
(d) General application was consistent with medical ethics, and decided that the parents of
(2) Functions of Law Karen Ann Quinlan could exercise her right to refuse treatment on
(a) Law as preservation of order her behalf. In order to reassure the physicians involved, however,
-public order law, criminal law the court also decreed that if a hospital’s ethics committee agreed
(b) Law as platform for human co-operation with the prognosis of permanent coma, the removal of the ventilator
-law of contract could take place and all parties involved would have legal immunity
(c) Law as medium of dispute resolution from civil or criminal prosecution.
Karen Ann Quinlan’s ventilator was removed, although
-law of tort she continued to breathe on her own. She survived in a coma until
(d) Law as tool of domination she died ofpneumonia almost 10 years later.
-counter-revolutionary offences
(e) Law as mechanism for social engineering C. SOURCES OF LAW
-land registration
(f) Law as bulwark of morality 1. Constitution- is fundamental laws or
-decriminalizing homosexual acts between
principles that govern a nation, society,
consenting adults
(g) Law as regulation of governmental powers and corporation.
-constitutional law, administrative law •
The purpose is to establish basic governing
(h) Law as protection of individual freedom system.
-bill of rights, anti-discrimination legislation 2. Statutes- laws that govern.
(i) Law as attainment of justice • Enacted by the legislative body and compile
-rules of natural justice, bill of rights, social security into codes, collections of statutes and
law ordinances.
(3) Limits of Law 3. Administrative agencies- third source of law.
(a) What law could not achieve • Bodies to manage crises, redress serious
-e.g. love social problems, or oversee complex
(b) What law should not interfere with: matters of governmental concern beyond
-private life the expertise of legislators.
• Example: National Youth Commission (NYC),
B. RELATIONSHIPS OF ETHICS AND LAW Professional Regulation Commission, Bangko
Sentral ng Pilipinas, Department of Health,
According to Lon Fuller an American Legal Philosopher: Department of Interior and Local Government,
Department of Justice, Department of Labor and
Employment
Ethics tells people what they should do and embodies the ideals
they should strive to attain.
4. Court Decision- interprets legal issues that are in
dispute.
Unethical behaviour leads to punishments that are related to how
an individual is perceived, both by himself or herself and others.
Types of Law and Court
Law, on the other hand, provides boundaries of actions, set by http://law.hku.hk/lawgovtsociety/nature.htm
society, beyond which a person may go only by risking external http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/372
sanctions, such as incarceration or loss of a medical license. 261/health-law/35626/Relationship-of-law-and-
ethics
This may explain why ethical codes usually involve generalities,
while laws tend to be more specific. http://legal-
dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Administrative
EXAMPLE:
The landmark case of Karen Ann Quinlan. Her parents requested +Agency
that physicians remove the mechanical ventilator in order to let their
daughter die a natural death. The doctors refused, relying primarily http://www.lawphil.net/administ/administ.html
LAWS GOVERNING NURSING | Error! No text of specified style in document. 1
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Criminal Law 13th Edition Thomas J Gardner Terry M Anderson Isbn 10 1305966368 Isbn 13 9781305966369Document14 pagesSolution Manual For Criminal Law 13th Edition Thomas J Gardner Terry M Anderson Isbn 10 1305966368 Isbn 13 9781305966369Dan Holland100% (43)
- Philosophy of Law ReviewerDocument7 pagesPhilosophy of Law ReviewerClayde Von Jape Pogado94% (16)
- Ilw1501 Exam Pack 2015 Edition 1 3Document32 pagesIlw1501 Exam Pack 2015 Edition 1 3Luvashen Gounden67% (3)
- A Position Paper On The Illegalization of Abortion in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesA Position Paper On The Illegalization of Abortion in The PhilippinesCristine Joy Remerata Villarosa80% (150)
- Civil Code Paras Reviewer. 1docxDocument39 pagesCivil Code Paras Reviewer. 1docxPrincess Venice Cuizon Villegas87% (15)
- Ethical, Legal and Organisational Aspects of MedicineDocument22 pagesEthical, Legal and Organisational Aspects of Medicinecanndy202No ratings yet
- OSCE Master List - Ethic Communication SkillsDocument4 pagesOSCE Master List - Ethic Communication SkillsjellyjohnNo ratings yet
- JURISDocument15 pagesJURISSharmaine Juco100% (1)
- Seven Blunders Committed by Human Society: Lapitan v. Philippine Charity Sweepstakes Office, 60 O.G. 6841 4Document4 pagesSeven Blunders Committed by Human Society: Lapitan v. Philippine Charity Sweepstakes Office, 60 O.G. 6841 4Charlyn Jane AcostaNo ratings yet
- Topic A-C (ObliCon)Document5 pagesTopic A-C (ObliCon)kingmonterea.lNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Criminal Law, 13th Edition, Thomas J. Gardner, Terry M. Anderson, ISBN-10: 1305966368, ISBN-13: 9781305966369Document37 pagesSolution Manual For Criminal Law, 13th Edition, Thomas J. Gardner, Terry M. Anderson, ISBN-10: 1305966368, ISBN-13: 9781305966369hixsonkocar100% (5)
- ILW1501 MemorandumsDocument29 pagesILW1501 MemorandumsDonald ThabangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Legal Issues and TheoriesDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Legal Issues and TheoriesmmaNo ratings yet
- Obligations PDFDocument49 pagesObligations PDFGio ReyesNo ratings yet
- OBLICON01 Introduction To Law Obligations and ContractsDocument7 pagesOBLICON01 Introduction To Law Obligations and ContractsJennalyn S. GanalonNo ratings yet
- Laws and Bioethics TransesDocument17 pagesLaws and Bioethics TransesPrincess Ezra U. GregorioNo ratings yet
- Natural Justice2Document105 pagesNatural Justice2Twinkl MehtaNo ratings yet
- Admin Class Lecture NotesDocument47 pagesAdmin Class Lecture NotesFadhil Mnoche100% (1)
- 2nd Periodical Examintion Science 10Document12 pages2nd Periodical Examintion Science 10DENNIS N. MUÑOZNo ratings yet
- Philo ReviewerDocument13 pagesPhilo ReviewerJeul AzueloNo ratings yet
- Nature of Man. These Moral Laws Govern His FreeDocument10 pagesNature of Man. These Moral Laws Govern His FreeJoshua MaulaNo ratings yet
- Notes Justice Puno SODocument8 pagesNotes Justice Puno SOAbigail Beloy CaliboNo ratings yet
- Law, Its Concept and Classification Intro To Law: Law Is The Ten Commandments and of Divine Human Positive LawDocument2 pagesLaw, Its Concept and Classification Intro To Law: Law Is The Ten Commandments and of Divine Human Positive LawJrac100% (1)
- AS Law Paper DownloadDocument83 pagesAS Law Paper DownloadStudy resourcesNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Philosophy of Law Reviewer PRDocument7 pagesToaz - Info Philosophy of Law Reviewer PRglitchNo ratings yet
- PFR Notes 2017Document37 pagesPFR Notes 2017Niko Mangaoil AguilarNo ratings yet
- Insignis Legal Med IntroductionDocument2 pagesInsignis Legal Med IntroductionAla'a Emerald AguamNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 What Is Meant by LawwDocument31 pagesUnit 1 What Is Meant by LawwsunuuNo ratings yet
- Itl NotesDocument9 pagesItl NotesJames PabonitaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Legal MedicineDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Legal MedicineDianne GalangNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To LawDocument3 pages1 - Introduction To LawIvy Gelyn C. OlaNo ratings yet
- Philawsophia Lecture Notes 1Document5 pagesPhilawsophia Lecture Notes 1Jeul AzueloNo ratings yet
- Prelim Reviewer ObliconDocument37 pagesPrelim Reviewer ObliconFerl ElardoNo ratings yet
- Essay JurisDocument8 pagesEssay Juris75q6xvjcgpNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Reviewer MidtermDocument18 pagesOblicon Reviewer MidtermAndrew Gino CruzNo ratings yet
- Pollaw NotesDocument19 pagesPollaw NotesEyanna CabicoNo ratings yet
- OBLICON - Compilation of ReviewersDocument54 pagesOBLICON - Compilation of ReviewersChelsea SabadoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LawDocument18 pagesIntroduction To LawNica Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Reviewer - FinalsDocument47 pagesOblicon Reviewer - FinalsNica Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Jurisprudence Lecture NotesDocument13 pagesJurisprudence Lecture NotesVittu7kNo ratings yet
- Mtlbe Lecture IntroductionDocument11 pagesMtlbe Lecture IntroductionAndrea Galang CruzNo ratings yet
- Theories of Law: Prepared By: MDM Namirah Mohd AkahsahDocument39 pagesTheories of Law: Prepared By: MDM Namirah Mohd AkahsahUmar MahfuzNo ratings yet
- 1.1a Introduction To Legal Med PDFDocument2 pages1.1a Introduction To Legal Med PDFBea SamonteNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Law 2017/2018Document21 pagesFaculty of Law 2017/2018Juin KerkNo ratings yet
- Law On Obligations and Contracts PrelimsDocument56 pagesLaw On Obligations and Contracts PrelimsSheila Grace BajaNo ratings yet
- Philosophy ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhilosophy ReviewerAirelle AvilaNo ratings yet
- Common Law Academy Lesson 1Document4 pagesCommon Law Academy Lesson 1kandycxane87No ratings yet
- Legal Medicine, Forensic Medicine and Medical Jurisprudence Are SynonymousDocument3 pagesLegal Medicine, Forensic Medicine and Medical Jurisprudence Are SynonymousRA BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lect. 2 Natural and Positive LawDocument5 pagesLect. 2 Natural and Positive LawSasha Frankson0% (1)
- Philosophia: Philosophy and Theory of Law by Bernardo 2017 Summary NotesDocument39 pagesPhilosophia: Philosophy and Theory of Law by Bernardo 2017 Summary NotesTeri Castano100% (6)
- Due ProcessDocument6 pagesDue ProcessDiane VirtucioNo ratings yet
- Philo Reviewer PDFDocument7 pagesPhilo Reviewer PDFAirelle AvilaNo ratings yet
- Imbong Vs Ochoa Case DigestDocument4 pagesImbong Vs Ochoa Case DigestJazztine ArtizuelaNo ratings yet
- Ho1 Oblicon 1Document3 pagesHo1 Oblicon 1bherona bayaniNo ratings yet
- Jil 521 - Jurisprudence-2Document63 pagesJil 521 - Jurisprudence-2gratoerunsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Conflict of Laws ReviewerDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - Conflict of Laws ReviewerJojemar EncisoNo ratings yet
- Bill of Rights ReviewerDocument14 pagesBill of Rights ReviewerLizzie GleeNo ratings yet
- Imbong ChoaDocument5 pagesImbong ChoaMonaVargasNo ratings yet
- Juris Prudence Pharmacy IntroductionDocument5 pagesJuris Prudence Pharmacy IntroductionjellfffNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Challenges to the Drug Law: A Case StudyFrom EverandConstitutional Challenges to the Drug Law: A Case StudyNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Study of LawFrom EverandIntroduction to the Study of LawRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- AlcoholismDocument11 pagesAlcoholismSuraj PawarNo ratings yet
- AYUSH CCIM - Telemedicine - GuidelinesDocument33 pagesAYUSH CCIM - Telemedicine - GuidelinesNishantNo ratings yet
- Performance Task in TheologyDocument1 pagePerformance Task in TheologyGuile DeoNo ratings yet
- MLC Protocols and Its Awareness Among Dental Professionals - A ReviewDocument4 pagesMLC Protocols and Its Awareness Among Dental Professionals - A ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mohamed Mosaad Hasan MD, MPH, CPHQ, CPPS, GbssDocument48 pagesDr. Mohamed Mosaad Hasan MD, MPH, CPHQ, CPPS, GbssKristine Marie PateñoNo ratings yet
- Ies RDocument3 pagesIes RNikoleta HirleaNo ratings yet
- Leskovac Nur 460 PGC Reflection PaperDocument9 pagesLeskovac Nur 460 PGC Reflection Paperapi-527774673No ratings yet
- Drunkorexia Stalks Young Women Around The WorldDocument3 pagesDrunkorexia Stalks Young Women Around The WorldThe Stacie Mathewson FoundationNo ratings yet
- A Position Paper On The Illegalization of Abortion in The Philippines by Chester Jake DuqueDocument2 pagesA Position Paper On The Illegalization of Abortion in The Philippines by Chester Jake DuqueAlexis Sevilla DuqueNo ratings yet
- MLC Protocols and Its Awareness Among Dental Professionals - A ReviewDocument4 pagesMLC Protocols and Its Awareness Among Dental Professionals - A ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Abortion Position PaperDocument4 pagesAbortion Position Paperapi-306698224No ratings yet
- Medical Ethics: Introduction To Basic PrinciplesDocument19 pagesMedical Ethics: Introduction To Basic PrinciplessatyachakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Joel ParisDocument4 pagesJoel ParisJazeel JameelNo ratings yet
- Classification of Mental Disorder, Antisocial Personalities, Drug and Alcohol DependenceDocument15 pagesClassification of Mental Disorder, Antisocial Personalities, Drug and Alcohol DependenceAdrian SingsonNo ratings yet
- Aff - Human Germline Genetic Engineering - MSDI 2022Document97 pagesAff - Human Germline Genetic Engineering - MSDI 2022HyperrealHNo ratings yet
- My Lala My Life - An AutoethnographyDocument13 pagesMy Lala My Life - An Autoethnographyapi-403955181No ratings yet
- Bioethics NOTES 108 - Week 2Document6 pagesBioethics NOTES 108 - Week 2ArmySapphireNo ratings yet
- Tests in Psychiatry-1Document72 pagesTests in Psychiatry-1Javier Saad100% (3)
- 68 Sudds-IvDocument4 pages68 Sudds-IvtriNo ratings yet
- 10 Romania Code of Medical Ethics 2012Document23 pages10 Romania Code of Medical Ethics 2012jmdominguezNo ratings yet
- A Thin Steel Plate Having 8 MM Through The Thickness Single Edge Crack Size Is Design To Hold A 60KN Static Tension LoadDocument37 pagesA Thin Steel Plate Having 8 MM Through The Thickness Single Edge Crack Size Is Design To Hold A 60KN Static Tension LoadBerihu GirmayNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Disorders in Children...Document3 pagesBehavioral Disorders in Children...Abhishek1789No ratings yet
- Our Lady of Fatima UniversityDocument2 pagesOur Lady of Fatima UniversityMICHAEL M. ISIDRONo ratings yet
- Ensayo de Inglés Aborto.Document3 pagesEnsayo de Inglés Aborto.Daniela VillalpandoNo ratings yet
- Factitious DisorderDocument22 pagesFactitious DisorderDenz Marc Alea100% (1)
- Psychriatric Nursing Learning Exp.Document82 pagesPsychriatric Nursing Learning Exp.Benedict James BermasNo ratings yet
- Code of Conduct For Health Professionals FinalDocument28 pagesCode of Conduct For Health Professionals FinalAtifBhore100% (1)
- Ethics in Anaesthesia (June 2004) Write Briefly On Research Ethics (Dec 2008)Document6 pagesEthics in Anaesthesia (June 2004) Write Briefly On Research Ethics (Dec 2008)Sirisha Ckv100% (1)