Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsJummave Sillapi Abs
Jummave Sillapi Abs
Uploaded by
gautialekaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Intropao PDFDocument1 pageIntropao PDFgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Leggaemochiting PDFDocument1 pageLeggaemochiting PDFgautialekaNo ratings yet
- PcoigningeeDocument8 pagesPcoigningeegautialekaNo ratings yet
- S.No File Name Criteria: List of Files and DocumentsDocument1 pageS.No File Name Criteria: List of Files and DocumentsgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Fliesavinling PDFDocument1 pageFliesavinling PDFgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Publish Your Own Recipe: Vegetarian ChiliDocument1 pagePublish Your Own Recipe: Vegetarian ChiligautialekaNo ratings yet
- On The WEB: Dictionaries and EncyclopediasDocument1 pageOn The WEB: Dictionaries and EncyclopediasgautialekaNo ratings yet
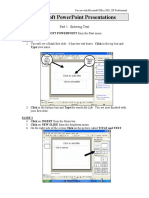
- Microsoft Powerpoint Presentations: Part 1: Entering TextDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Powerpoint Presentations: Part 1: Entering TextgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Internet Explorer: Exercise 1: How Can I Access The Internet?Document4 pagesInternet Explorer: Exercise 1: How Can I Access The Internet?gautialekaNo ratings yet
- List of Files To Be Maintained in The Department For NAAC 2016-17Document3 pagesList of Files To Be Maintained in The Department For NAAC 2016-17gautialekaNo ratings yet
- Go To A Website On The InternetDocument1 pageGo To A Website On The InternetgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Thiruvalluvar Government Arts College, RasipuramDocument2 pagesThiruvalluvar Government Arts College, RasipuramgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Open Internet Explorer. 2. Go To 3. Click On DIRECTIONSDocument2 pagesOpen Internet Explorer. 2. Go To 3. Click On DIRECTIONSgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Profile: S. No. Degree / Diploma Subject Name of The College / University Year of PassingDocument4 pagesProfile: S. No. Degree / Diploma Subject Name of The College / University Year of PassinggautialekaNo ratings yet
- VemmalakaDocument1 pageVemmalakagautialekaNo ratings yet
- Vasun Dhas Ki CitizDocument7 pagesVasun Dhas Ki CitizgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Kpgal JakirathaiDocument4 pagesKpgal JakirathaigautialekaNo ratings yet
- Vivekanandha College of Engineering For Women: Elayampalayam - 637 205, Tiruchengode, Namakkal DT., Tamil NaduDocument12 pagesVivekanandha College of Engineering For Women: Elayampalayam - 637 205, Tiruchengode, Namakkal DT., Tamil NadugautialekaNo ratings yet
- Vivekanandha College of Engineering For WomenDocument5 pagesVivekanandha College of Engineering For WomengautialekaNo ratings yet
- Daily Report Staff Name: S.Sreemanjari Ap/EeeDocument1 pageDaily Report Staff Name: S.Sreemanjari Ap/EeegautialekaNo ratings yet
- Total Number of Students From 2012 - 2017: Female 114 3 262 0 379Document1 pageTotal Number of Students From 2012 - 2017: Female 114 3 262 0 379gautialekaNo ratings yet
- Vivekanandha College of Engineering For Women: Elayampalayam - 637 205, Tiruchengode, Namakkal DT., Tamil NaduDocument12 pagesVivekanandha College of Engineering For Women: Elayampalayam - 637 205, Tiruchengode, Namakkal DT., Tamil NadugautialekaNo ratings yet
- Vivekanandha College of Engineering For WomenDocument11 pagesVivekanandha College of Engineering For WomengautialekaNo ratings yet
- Dilbarjane and The HerculeDocument21 pagesDilbarjane and The HerculegautialekaNo ratings yet
- Average Shortcut Methods: (Standard Types in Problem Execution and Solving)Document8 pagesAverage Shortcut Methods: (Standard Types in Problem Execution and Solving)gautialekaNo ratings yet
- Maram Vecha Thannio ThuDocument20 pagesMaram Vecha Thannio ThugautialekaNo ratings yet
Jummave Sillapi Abs
Jummave Sillapi Abs
Uploaded by
gautialeka0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageOriginal Title
jummave sillapi abs.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageJummave Sillapi Abs
Jummave Sillapi Abs
Uploaded by
gautialekaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
SEMANTIC SIGNATURES USING ON WEB IMAGE
RE-RANKING
ABSTRACT
Image re-ranking, as an effective way to improve the results of web-based
image search, has been adopted by current commercial search engines such as Bing
and Google. Given a query keyword, a pool of images is first retrieved based on
textual information. By asking the user to select a query image from the pool, the
remaining images are re-ranked based on their visual similarities with the query
image. A major challenge is that the similarities of visual features do not well
correlate with images’ semantic meanings which interpret users’ search intention.
Recently people proposed to match images in a semantic space which used
attributes or reference classes closely related to the semantic meanings of images
as basis. However, learning a universal visual semantic space to characterize
highly diverse images from the web is difficult and inefficient. In this thesis, we
propose a novel image re-ranking framework, which automatically offline learns
different semantic spaces for different query keywords. The visual features of
images are projected into their related semantic spaces to get semantic signatures.
At the online stage, images are re-ranked by comparing their semantic signatures
obtained from the semantic space specified by the query keyword.
The proposed query-specific semantic signatures significantly improve both
the accuracy and efficiency of image re-ranking. The original visual features of
thousands of dimensions can be projected to the semantic signatures as short as 25
dimensions. Experimental results show that 25-40 percent relative improvement
has been achieved on re-ranking precisions compared with the state-of-the-art
methods.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Intropao PDFDocument1 pageIntropao PDFgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Leggaemochiting PDFDocument1 pageLeggaemochiting PDFgautialekaNo ratings yet
- PcoigningeeDocument8 pagesPcoigningeegautialekaNo ratings yet
- S.No File Name Criteria: List of Files and DocumentsDocument1 pageS.No File Name Criteria: List of Files and DocumentsgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Fliesavinling PDFDocument1 pageFliesavinling PDFgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Publish Your Own Recipe: Vegetarian ChiliDocument1 pagePublish Your Own Recipe: Vegetarian ChiligautialekaNo ratings yet
- On The WEB: Dictionaries and EncyclopediasDocument1 pageOn The WEB: Dictionaries and EncyclopediasgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Powerpoint Presentations: Part 1: Entering TextDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Powerpoint Presentations: Part 1: Entering TextgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Internet Explorer: Exercise 1: How Can I Access The Internet?Document4 pagesInternet Explorer: Exercise 1: How Can I Access The Internet?gautialekaNo ratings yet
- List of Files To Be Maintained in The Department For NAAC 2016-17Document3 pagesList of Files To Be Maintained in The Department For NAAC 2016-17gautialekaNo ratings yet
- Go To A Website On The InternetDocument1 pageGo To A Website On The InternetgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Thiruvalluvar Government Arts College, RasipuramDocument2 pagesThiruvalluvar Government Arts College, RasipuramgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Open Internet Explorer. 2. Go To 3. Click On DIRECTIONSDocument2 pagesOpen Internet Explorer. 2. Go To 3. Click On DIRECTIONSgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Profile: S. No. Degree / Diploma Subject Name of The College / University Year of PassingDocument4 pagesProfile: S. No. Degree / Diploma Subject Name of The College / University Year of PassinggautialekaNo ratings yet
- VemmalakaDocument1 pageVemmalakagautialekaNo ratings yet
- Vasun Dhas Ki CitizDocument7 pagesVasun Dhas Ki CitizgautialekaNo ratings yet
- Kpgal JakirathaiDocument4 pagesKpgal JakirathaigautialekaNo ratings yet
- Vivekanandha College of Engineering For Women: Elayampalayam - 637 205, Tiruchengode, Namakkal DT., Tamil NaduDocument12 pagesVivekanandha College of Engineering For Women: Elayampalayam - 637 205, Tiruchengode, Namakkal DT., Tamil NadugautialekaNo ratings yet
- Vivekanandha College of Engineering For WomenDocument5 pagesVivekanandha College of Engineering For WomengautialekaNo ratings yet
- Daily Report Staff Name: S.Sreemanjari Ap/EeeDocument1 pageDaily Report Staff Name: S.Sreemanjari Ap/EeegautialekaNo ratings yet
- Total Number of Students From 2012 - 2017: Female 114 3 262 0 379Document1 pageTotal Number of Students From 2012 - 2017: Female 114 3 262 0 379gautialekaNo ratings yet
- Vivekanandha College of Engineering For Women: Elayampalayam - 637 205, Tiruchengode, Namakkal DT., Tamil NaduDocument12 pagesVivekanandha College of Engineering For Women: Elayampalayam - 637 205, Tiruchengode, Namakkal DT., Tamil NadugautialekaNo ratings yet
- Vivekanandha College of Engineering For WomenDocument11 pagesVivekanandha College of Engineering For WomengautialekaNo ratings yet
- Dilbarjane and The HerculeDocument21 pagesDilbarjane and The HerculegautialekaNo ratings yet
- Average Shortcut Methods: (Standard Types in Problem Execution and Solving)Document8 pagesAverage Shortcut Methods: (Standard Types in Problem Execution and Solving)gautialekaNo ratings yet
- Maram Vecha Thannio ThuDocument20 pagesMaram Vecha Thannio ThugautialekaNo ratings yet