Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Traduc Es en
Traduc Es en
Uploaded by
JoseOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Traduc Es en
Traduc Es en
Uploaded by
JoseCopyright:
Available Formats
WORDS support.
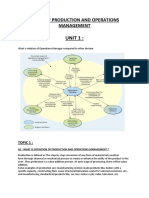
1. Goods and services: are goods, objects and activities that seek to meet the
needs of people. These are the result of a production process by economic
agents.
2. Production costs: costs that involves holding a project, team or company
running. They may come from different areas, whether the purchase of
inputs or raw materials, payment of energy consumption, wages of workers
or equipment maintenance.
3. Production times: Time needed to perform one or more operations. It
consists times: waiting, preparation, operation and transfer.
4. Quality: property or set of properties inherent in something, you can judge
their value.
5. Kaizen powerful tool for change and improvement. Its main use is actively
integrating all workers of an organization in continuous improvement
processes, processes of gradual and orderly implementation.
WORDS support.
1. Quantity: A number of units.
2. Efficiency: Ability You have someone or something to achieve a certain
effect.
3. Effectiveness: CapacityfromachievetheeffectwhatI knowyou wantorI
knowwait.
4. Productivity: Relation between what is produced and the means employed,
such as labor, materials, energy.
5. Process capacity: Degree of fitness has a process to comply with the
technical specifications desired.
6. Lean Manufacturing: It is a continuous and systematic process of identifying
and eliminating non-value added activities in a process, but if they involve
cost and effort.
7. Line balancing: The main objective of a balancing line corresponds to
equalize working times in all seasons of the process. Establish a balanced
production line requires a judicious achievement data, theoretical
application, movement of resources and even economic investments.
8. Poka-Yoke: Conceptually in quality assurance, inspection ideal is not to
delegate control of the operation to someone outside the operator thereof
9. Aggregate planning: process to determine in advance a strategy that would
meet the requirements (demand) of the system, while optimizing the
resources therein; whose development it is carried out in the short and
medium term.
10. Production indicators: The existence of performance indicators in a
production system is vital for the implementation of production processes,
as they allow the execution cycle of continuous improvement, in addition to
functioning as feasibility process parameters.
11. Results: Effect name formed from the participle of the verb be and this in
turn comes from the Latin proves (jump back, bounce, be returned, etc.). In
short when we speak of result it is not merely an effect or consequence of
fact.
12. PHVA: Acronyms of the cycle or formula PHVA form an acronym composed
of the initial words plan, do Check and Act.
13. Innovation: A process that allows you to modify or develop new products
and services that are perceived and accepted by its users, who pay for the
value it represents for them. Innovation often more than a new product,
opens a new category in the market.
14. Customers: The word customer has its roots in the Latin term cliens
expressing the quality of the person who relies on another to seek their help.
The client is the one who directly or indirectly uses the product or service
enjoys.
15. Teamwork: Work tool in order to optimize the performance of tasks.
Basically teamwork is to perform an action among a group of people.
You might also like
- Defining and Measuring CapacityDocument4 pagesDefining and Measuring CapacityJustin Luke Ang50% (2)
- Practical Definitions for the Working Professional: A Pocket DictionaryFrom EverandPractical Definitions for the Working Professional: A Pocket DictionaryNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Expressions of EngineeringDocument9 pagesKeywords: Expressions of EngineeringJoseNo ratings yet
- Workshop: Getting Started As A TranslatorDocument3 pagesWorkshop: Getting Started As A TranslatorJohi Bacca MorenoNo ratings yet
- Notes of POM Module 1 PDFDocument22 pagesNotes of POM Module 1 PDFRiyaNo ratings yet
- Good and Services in Operation Management: 3. Objectives of Operations ManagementDocument44 pagesGood and Services in Operation Management: 3. Objectives of Operations ManagementPrince AhmirNo ratings yet
- Value Chain OperationDocument27 pagesValue Chain OperationHARVY DAVIS CHUANo ratings yet
- Assessment 3 Part BDocument6 pagesAssessment 3 Part BShaily GargNo ratings yet
- Operations Management-Compre-ReviewerDocument8 pagesOperations Management-Compre-ReviewerDaily TaxPHNo ratings yet
- Productivity & Quality ManagementDocument15 pagesProductivity & Quality ManagementAkshay PanditNo ratings yet
- Reviewer TQMDocument8 pagesReviewer TQMMillicent AlmueteNo ratings yet
- First Chapter: IntroductionDocument16 pagesFirst Chapter: IntroductionMominul MominNo ratings yet
- DSC2006 Tutorial 1Document3 pagesDSC2006 Tutorial 1slimsprint100% (1)
- Operations ManagementDocument6 pagesOperations ManagementAllen DimaculanganNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship 12 Q2 Week 1 - 2Document10 pagesEntrepreneurship 12 Q2 Week 1 - 2Jackierain AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Lean Manufacturing, Lean Enterprise, or Lean Production, Often Simply, "Lean," Is A Production PracticeDocument4 pagesLean Manufacturing, Lean Enterprise, or Lean Production, Often Simply, "Lean," Is A Production PracticeDip PatelNo ratings yet
- Gurus of TQM Group 6 1Document90 pagesGurus of TQM Group 6 1Coleen Anne PinedaNo ratings yet
- Operations and Supply StrategyDocument2 pagesOperations and Supply StrategyAneJ OrtizNo ratings yet
- Pom 1Document39 pagesPom 1rushtoruchikaNo ratings yet
- Production and Operations Management Chapter: 04. Process ManagementDocument3 pagesProduction and Operations Management Chapter: 04. Process ManagementSN AdnanNo ratings yet
- Productivity & CompetitivenessDocument7 pagesProductivity & CompetitivenessHadeer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Glosario de Expresion Oral y Escrita II en Ingles.Document15 pagesGlosario de Expresion Oral y Escrita II en Ingles.jesus moralesNo ratings yet
- Production and Operation Management ProjectDocument51 pagesProduction and Operation Management ProjectsachitNo ratings yet
- MGTN11BDocument6 pagesMGTN11BJohn Lennard CostunaNo ratings yet
- VE Unit 3Document5 pagesVE Unit 3gauravpatel5436No ratings yet
- Production and Operation ManagementDocument8 pagesProduction and Operation ManagementBavya RajNo ratings yet
- Keyterms OPERATIONS MANAGEMENTDocument15 pagesKeyterms OPERATIONS MANAGEMENTArturo QuiñonesNo ratings yet
- Operational Management Assignment PDFDocument7 pagesOperational Management Assignment PDFYonas D. Ebren100% (1)
- Managing For Quality and ProductivityDocument12 pagesManaging For Quality and ProductivityJamil Kamara100% (1)
- BA7201 - 2 MarksDocument12 pagesBA7201 - 2 Markskumarakannan.reNo ratings yet
- Rupesh Patel: Productions and Operations Management ProfDocument51 pagesRupesh Patel: Productions and Operations Management ProfJayendra Patel100% (1)
- MB 0044 - Production and Operation Management: Q1. State The Important Considerations For Locating An Automobile PlantDocument9 pagesMB 0044 - Production and Operation Management: Q1. State The Important Considerations For Locating An Automobile PlantSaju AugustineNo ratings yet
- Pom NotesDocument126 pagesPom NotesManjunath ReddyNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Lean Management PrinciplesDocument2 pagesModule 5 - Lean Management PrinciplesNeena R KrishnaNo ratings yet
- PMI-ACP Exam Prep: Glossary of Agile TermsDocument17 pagesPMI-ACP Exam Prep: Glossary of Agile Termspromethuschow100% (1)
- Operations and ProductivityDocument3 pagesOperations and ProductivityaasthaNo ratings yet
- TQM Assignment-6Document5 pagesTQM Assignment-6api-282599777No ratings yet
- Answer Question 5: (6marks)Document13 pagesAnswer Question 5: (6marks)Amin YasminNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes q4 Week 1 EntrepDocument5 pagesLecture Notes q4 Week 1 EntrepMarishka Aviona AnchingesNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management ReviewerDocument7 pagesTotal Quality Management ReviewerTrisha Mae Mendoza MacalinoNo ratings yet
- PMP DefinitionDocument28 pagesPMP DefinitionPunitharan SivanathanNo ratings yet
- Evidencia 6GRUPOn74nGUIAnTECNICA - 846323695d2f9eeDocument9 pagesEvidencia 6GRUPOn74nGUIAnTECNICA - 846323695d2f9eeDaniel Ramirez RodriguezNo ratings yet
- BPR NotesDocument14 pagesBPR Notes12tahirniazi12No ratings yet
- POM AssignmentDocument8 pagesPOM AssignmentShubham VermaNo ratings yet
- TQM ReviewerDocument8 pagesTQM ReviewerAngel Mae SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Principal of Management 2023Document11 pagesPrincipal of Management 2023rdipali162No ratings yet
- Glossary - PMP2023Document81 pagesGlossary - PMP2023ginNo ratings yet
- Agile Software Development @VDocument12 pagesAgile Software Development @VKumar VikashNo ratings yet
- Quality Principles and ConceptsDocument32 pagesQuality Principles and ConceptsAnthony Charles ANo ratings yet
- Qualityprinciplesandconcepts 141214012537 Conversion Gate01 PDFDocument32 pagesQualityprinciplesandconcepts 141214012537 Conversion Gate01 PDFSuhendi SSNo ratings yet
- 4-Service Value SystemDocument30 pages4-Service Value Systemziad i alshowaiterNo ratings yet
- Sum POMDocument8 pagesSum POMTidene BaynoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ObjectivesDocument9 pagesChapter 1 ObjectivesMuhammad NadeemNo ratings yet
- Innovation Man. Recitation No. 2Document5 pagesInnovation Man. Recitation No. 2Jullie Kaye Frias DiamanteNo ratings yet
- Operation MNGMNT Group1Document6 pagesOperation MNGMNT Group1Lilian FredelucesNo ratings yet
- Basics of Scheduling, Value Engineering: Subject: Operations ManagementDocument16 pagesBasics of Scheduling, Value Engineering: Subject: Operations ManagementpradssssNo ratings yet
- Test 2 - Carolina Gomes SiqueiraDocument4 pagesTest 2 - Carolina Gomes SiqueiraCarolina S.No ratings yet
- Om 2022Document61 pagesOm 2022Rana SabryNo ratings yet
- PMIACP GlossaryDocument21 pagesPMIACP GlossaryzulnorainaliNo ratings yet
- Module 3-TQMDocument17 pagesModule 3-TQMRevenlie GalapinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology - 2013annualDocument6 pagesAnatomy & Physiology - 2013annualdileepkumar.duhs4817No ratings yet
- 17-20513 - HJK Status Report Oct 2016 PDFDocument70 pages17-20513 - HJK Status Report Oct 2016 PDFRecordTrac - City of OaklandNo ratings yet
- Material TestingDocument54 pagesMaterial TestingJochelle Mae Pecson100% (1)
- Crim 1 BDocument1 pageCrim 1 BJose Antonio Peralta Achaval Jr.No ratings yet
- CIVIL ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE 2nd SemDocument28 pagesCIVIL ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE 2nd SemJinu MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Levelleon1973No ratings yet
- What Is Military Psychology? Symposium Proceedings: Calhoun: The Nps Institutional Archive Dspace RepositoryDocument69 pagesWhat Is Military Psychology? Symposium Proceedings: Calhoun: The Nps Institutional Archive Dspace RepositoryMihaela Alina TiticaNo ratings yet
- Domain Theory and ReviewDocument2 pagesDomain Theory and ReviewJohnson RubasinghNo ratings yet
- Foreign Debt, Balance of Payments, and The Economic Crisis of The Philippines in 1983-84Document26 pagesForeign Debt, Balance of Payments, and The Economic Crisis of The Philippines in 1983-84Cielo GriñoNo ratings yet
- Damping Modification for Spectrum: Lap-Loi Chung (鍾立來)Document39 pagesDamping Modification for Spectrum: Lap-Loi Chung (鍾立來)陳俊鴻No ratings yet
- Introduction To Nearshore HydrodynamicsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Nearshore Hydrodynamicsjuand_121No ratings yet
- 2018amc J EngDocument7 pages2018amc J EngHero ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Theory of Equations - Objective QuestionsDocument19 pagesTheory of Equations - Objective Questionsdhathrireddy7No ratings yet
- Body Paragraph 2Document3 pagesBody Paragraph 2Helen SabuquelNo ratings yet
- NMM Gold TutorialDocument7 pagesNMM Gold TutorialTane67No ratings yet
- 14m3 Prefix E9s00342 - NewDocument1,039 pages14m3 Prefix E9s00342 - Newiwan nawiNo ratings yet
- Traffic Management and Accident Investigation With DrivingDocument18 pagesTraffic Management and Accident Investigation With DrivingPatrick LeysonNo ratings yet
- Zuckerberg Responses To Commerce Committee QFRs1Document229 pagesZuckerberg Responses To Commerce Committee QFRs1TechCrunch100% (2)
- DAQ SystemDocument10 pagesDAQ Systemgimmyhead_69No ratings yet
- 9 9 21 367 PDFDocument7 pages9 9 21 367 PDFaihuutran51No ratings yet
- Leica Absolute Interferometer White Paper enDocument4 pagesLeica Absolute Interferometer White Paper entheflamebearerNo ratings yet
- Harshita SinghDocument7 pagesHarshita Singhharshitaa.singh.2308No ratings yet
- ICAEW - Bus - Fin - Chapter 5 - StudentDocument123 pagesICAEW - Bus - Fin - Chapter 5 - StudentMai HuyenNo ratings yet
- 2020 SSC Guidelines For Septic Shock in Children PDFDocument58 pages2020 SSC Guidelines For Septic Shock in Children PDFAtmaSearch Atma JayaNo ratings yet
- Attitudes Towards Artificial IntelligenceDocument3 pagesAttitudes Towards Artificial IntelligencePhạm Quang DuyNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5: Chapter 6, Section 6.1, Page 396Document2 pagesExercise 5: Chapter 6, Section 6.1, Page 396allauddinbaloch84No ratings yet
- 1SDA066561R1 A3n 400 TMF 400 4000 3p F FDocument3 pages1SDA066561R1 A3n 400 TMF 400 4000 3p F FJessika duperly rueda vasquezNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal CastingDocument12 pagesCentrifugal Castingsamurai7_77100% (1)
- Nair Rodriguez-Hornedo PDFDocument34 pagesNair Rodriguez-Hornedo PDFAenhiequrra AlthafunnisaNo ratings yet
- PercentagesDocument10 pagesPercentagesLisa DiasNo ratings yet