Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WEEK 1 Notes PDF
WEEK 1 Notes PDF
Uploaded by
AparmaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WEEK 1 Notes PDF
WEEK 1 Notes PDF
Uploaded by
AparmaCopyright:
Available Formats
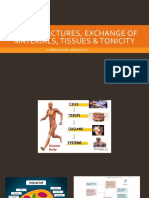
Describe, compare and contrast the divisions and
subdivision of both anatomy & physiology
Name and describe the components of the plasma
membrane, and state their function.
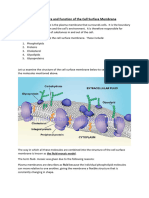
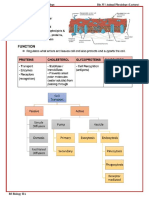
PLASMA MEMBRANE
- Fluid matrix
- Composed of an equal mixture (by weight) of lipids and proteins
- Regulates movement of substances into and out of the cell
Lipid components:
- Phospholipid
1. Hydrophilic polar heads stay pointing outwards.
2. Hydrophobic nonpolar tails point inwards.
3. Heads and tails readily form a phospholipid bilayer.
4. Main function to separate cytosol from the interstitial fluid
- Glycolipid
1. Lipids attached with a carbohydrate group.
2. Placed on a phospholipid in the outer layer.
3. The carbohydrate chain is exposed to interstitial fluids.
4. Produces glycocalyx.
- cholesterol
1. Found in hydrophobic region
2. Strengthens the membrane
3. Stabilises the membrane at temperature extremes
Describe and explain the processes that control the
movement of substances (including water) across the
cell membrane.
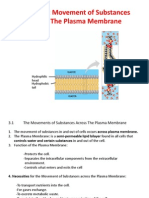
Membrane transport
- Substance being moved across the cellular membrane is collectively known as
membrane transport.
- Passive - no cellular energy required.
1. Diffusion
- movement of solutes down their concentration gradient through a
semipermeable layer.
- Unopposed until the substance reaches equilibrium.
- Rate of diffusion depends on the steepness of concentration
gradient and temperature.
- Higher the difference in steepness faster the diffusion.
- High temperature-> high kinetic energy->increase in random
movement of solutes.
- The plasma membrane cannot regulate simple diffusion—rather,
the movement of these molecules is dependent only upon the
concentration gradient.
- Movement of small and non-polar substances across- simple
diffusion.
- 2 types FD:Channel mediated diffusion and carrier mediated
diffusion.
2. Osmosis
- the movement of water down their concentration gradient through
a semipermeable layer.
- cells can alter the amount of water that crosses the plasma
membrane by changing the number of aquaporins.
- Osmotic pressure is the pressure exerted by the movement of water
across a semipermeable membrane due to a difference in solution
concentration. The steeper the gradient, the greater the amount of
water moved by osmosis and the higher the osmotic pressure.
Isotonic- concentration gradient same
Hypertonic solution - conc. Of solutes higher outside the cell.
Hypotonic solution - conc. Of solutes less outside the cell.
- Active- cellular energy required.
● Name and describe the components of the cell, and provide a description of their
function
You might also like
- Teachings in The Science of Osteopathy PDFDocument336 pagesTeachings in The Science of Osteopathy PDFAlex92% (12)
- Chapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument28 pagesChapter 3: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneMohd Asraf90% (10)
- David Dent - Insect Pest ManagementDocument425 pagesDavid Dent - Insect Pest Managementsaphito83% (6)
- Davidson, Donald - Knowing One's Own MindDocument19 pagesDavidson, Donald - Knowing One's Own Mindgalen_mitchell100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureDocument4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and Cell TransportDocument4 pagesCell Membrane and Cell TransportAtasha MojecaNo ratings yet
- X Membrane and TransportDocument35 pagesX Membrane and TransportHitesh MoreNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (Cells)Document6 pagesReviewer (Cells)Sophia Mae ClavecillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Membrane Structure and FunctionIrish Jem BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesCell MembraneQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- The Plasma MembraneDocument5 pagesThe Plasma MembraneFarhana AktharNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismsDocument1 pageTransport MechanismsJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Movement of MoleculesDocument17 pagesMovement of MoleculesMatthew ThomasNo ratings yet
- 7 Transport-Mechanism2Document62 pages7 Transport-Mechanism2aldrin braganzaNo ratings yet
- 1 Cellular Transport VidDocument57 pages1 Cellular Transport Vidchizy bananaNo ratings yet
- Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument11 pagesMembrane Structure and FunctionShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: Lipid Bilayer - 2 Layers of PhospholipidsDocument18 pagesHomeostasis: Lipid Bilayer - 2 Layers of PhospholipidsLoraine Anne Marie BaguioNo ratings yet
- Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument11 pagesTransport Across The Cell MembraneMae Balubar PolidoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Transport Across Cell MembranesDocument10 pagesChapter 4 Transport Across Cell Membranesnoreen dorani100% (1)
- Reminder B3Document9 pagesReminder B3Daniel thanh ducNo ratings yet
- Transport MembraneDocument35 pagesTransport MembranebellatanschoolNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument27 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsVince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Transport Across The Cell Membrane - OdpDocument67 pagesTransport Across The Cell Membrane - OdpSilver CypressNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Transport NotesDocument24 pagesCell Membrane Transport NotesJason RobinsonNo ratings yet
- AkdogDocument10 pagesAkdognorhain4.aNo ratings yet
- (W3) Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument4 pages(W3) Cellular Level of OrganizationFRANCES DEANNE ALABADONo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 3Document13 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3vtangarocan33932No ratings yet
- Movement of Subtances Across Plasma MembraneDocument414 pagesMovement of Subtances Across Plasma MembranezazaNo ratings yet
- Transport Mec Hanisms in Biological MembranesDocument51 pagesTransport Mec Hanisms in Biological Membranesjm earlytepNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Bio QuizDocument5 pagesCell Membrane Bio QuizMafalda SeabraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Movement of Subtances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument4 pagesChapter 3-Movement of Subtances Across The Plasma MembraneMuhammad AddinNo ratings yet
- Transport Membrane (Lengkap)Document53 pagesTransport Membrane (Lengkap)Isma Suss LolaloadingNo ratings yet
- Significance of Liquid in Biological Membranes and Transport MechanismDocument10 pagesSignificance of Liquid in Biological Membranes and Transport Mechanismroshan khanNo ratings yet
- Raven Biology of Plants: Eighth EditionDocument29 pagesRaven Biology of Plants: Eighth EditionMoath EnnabNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport Mechanism: General Biology 1Document12 pagesCellular Transport Mechanism: General Biology 1Kenn KennNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Document7 pagesBIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Student Alejandro Zhou WeiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ReveiwerDocument8 pagesChapter 3 ReveiwerrizzamaegomezoctavianoNo ratings yet
- PRINTED Cell HandoutsDocument8 pagesPRINTED Cell HandoutsKate GutierrezNo ratings yet
- BIO 35 Chapter 1C - Cell Membrane PhysiologyDocument6 pagesBIO 35 Chapter 1C - Cell Membrane PhysiologyJake EverettNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument75 pagesCell Membrane Transportvinay chaudhary100% (1)
- MODULE 1.3 Cell Membrane TransportDocument11 pagesMODULE 1.3 Cell Membrane TransportBrandon James SevillaNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument12 pagesGen BioJohn Paul ArandiaNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Cell MembraneDocument23 pagesWeek 6 Cell Membranesabeera.ahmadNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 Cell TransportDocument39 pagesLec 6 Cell TransportMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Lect 2 Membrane TransportDocument29 pagesLect 2 Membrane Transportramadan100% (1)
- Membran Sel DAN Sistem Transpor Pada MembranDocument51 pagesMembran Sel DAN Sistem Transpor Pada MembranPratidinaDeboraNo ratings yet
- Transport of Systems in Microbial CellsDocument25 pagesTransport of Systems in Microbial CellsDiptomoy Bhattacharya100% (1)
- The Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisDocument13 pagesThe Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisMaxellLanceClementNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Cell Exchange of Materials Tissues Tonicity 2021Document72 pagesTopic 2 - Cell Exchange of Materials Tissues Tonicity 2021Ralph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Reviewer 1Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Reviewer 1Shane Patricia CalmaNo ratings yet
- From The Soil by The Root CellsDocument13 pagesFrom The Soil by The Root CellsChristina RañaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Transport PhysioDocument37 pagesCell Membrane Transport PhysioWandera GodfreyNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument73 pagesCellsTon CopinesNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisDocument13 pagesThe Plasma Membrane and HomeostasismadhutkNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisDocument13 pagesThe Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisMal FujitakaNo ratings yet
- Physiology U-2 Transport Across The Plasma MembraneDocument48 pagesPhysiology U-2 Transport Across The Plasma Membranesinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Movements Across Cell MembraneDocument30 pagesMovements Across Cell Membraneعلیزہ نعیمNo ratings yet
- Significance of Lipids in Biological Membranes and Transport MechanismsDocument9 pagesSignificance of Lipids in Biological Membranes and Transport Mechanismsroshan khan100% (2)
- Significance of Lipids in Biological Membranes and Transport MechanismsDocument9 pagesSignificance of Lipids in Biological Membranes and Transport Mechanismsroshan khanNo ratings yet
- General Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)Document4 pagesGeneral Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)alfonsogwenmnqNo ratings yet
- GWAS NatureDocument18 pagesGWAS NatureIsaac Falcón ReveloNo ratings yet
- A Hybrid Open-Top Light-Sheet MicroscopeDocument51 pagesA Hybrid Open-Top Light-Sheet MicroscopePeterClementNo ratings yet
- Bruker Almanac 2011Document205 pagesBruker Almanac 2011Sandi WijayaNo ratings yet
- Histology ReviewerDocument7 pagesHistology ReviewerJulius FrondaNo ratings yet
- AEX 102-Fundamentals of Agricultural Extension Education (2+1)Document14 pagesAEX 102-Fundamentals of Agricultural Extension Education (2+1)Sneha ThillaigovindhanNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids Vol. 2 (1972) A Review of Chemical Literature Specialist Periodical ReportsDocument308 pagesAlkaloids Vol. 2 (1972) A Review of Chemical Literature Specialist Periodical ReportsLuděk SpurnýNo ratings yet
- Choose The Best Answer! The Text Is For Number 1 To 3Document7 pagesChoose The Best Answer! The Text Is For Number 1 To 3Kainan KnightNo ratings yet
- Showpdf PDFDocument35 pagesShowpdf PDFAnonymous EaTbndn1No ratings yet
- THEORYDocument32 pagesTHEORYKenneth PatronNo ratings yet
- 2022 - 2nd Term Test - Grd9Document5 pages2022 - 2nd Term Test - Grd9zkeonline g10.10% (1)
- ELISA E-BookDocument26 pagesELISA E-BookShahil AlamNo ratings yet
- Microbial Fuel Cells-Challenges and Applications: ArticleDocument10 pagesMicrobial Fuel Cells-Challenges and Applications: ArticleObande OrinyaNo ratings yet
- RPT Bahasa Inggeris KRDocument28 pagesRPT Bahasa Inggeris KRFaris AdlyNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Holiday Work First Term 2022Document29 pagesGrade 4 Holiday Work First Term 2022mandloescNo ratings yet
- Chapter10 PDFDocument20 pagesChapter10 PDFsgw67No ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument92 pagesCells and TissuesElizabeth SmithNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Province of RizalDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Province of RizalPearl Joy FrancoNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Everyday LifeDocument4 pagesThe Physiology of Everyday LifeElenananaNo ratings yet
- Journal Impact FactorDocument26 pagesJournal Impact Factorapi-3744715100% (15)
- An Investigation of Cranial Motion Through A Review of Biomechanically Based Skull Deformation LiteratureDocument8 pagesAn Investigation of Cranial Motion Through A Review of Biomechanically Based Skull Deformation LiteratureLadykaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: Points To RememberDocument9 pagesHuman Reproduction: Points To RememberPREM277272No ratings yet
- Eligio Stephen Gallegos INDIJANSKO ISCJELJENJE ČAKRI, PartDocument12 pagesEligio Stephen Gallegos INDIJANSKO ISCJELJENJE ČAKRI, Partnina_susaNo ratings yet
- Entrance Exam AssessmentDocument14 pagesEntrance Exam AssessmentMaxwell MalcomNo ratings yet
- Polymers: Production of Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) and Factors Impacting Its Chemical and Mechanical CharacteristicsDocument20 pagesPolymers: Production of Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) and Factors Impacting Its Chemical and Mechanical CharacteristicsJuan Jesús Cruz MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Eshoppy Lounching PlanDocument19 pagesEshoppy Lounching PlanSANUNo ratings yet
- Stochastic Conformational Pumping: A Mechanism For Free-Energy Transduction by MoleculesDocument44 pagesStochastic Conformational Pumping: A Mechanism For Free-Energy Transduction by MoleculesDean AstumianNo ratings yet
- Organelle Biochemical Process ImportanceDocument5 pagesOrganelle Biochemical Process Importanceaira roperezNo ratings yet