Professional Documents
Culture Documents
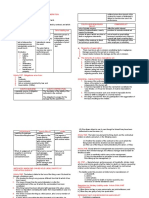
There Is No Pre-Existing Contractual Relation Between The Parties
There Is No Pre-Existing Contractual Relation Between The Parties
Uploaded by
JesterOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
There Is No Pre-Existing Contractual Relation Between The Parties
There Is No Pre-Existing Contractual Relation Between The Parties
Uploaded by
JesterCopyright:
Available Formats
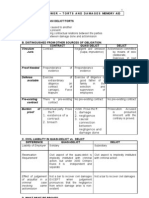
CHAPTER 2 Crime
NEGLIGENCE
Art. 365. Imprudence and Negligence.
Actionable negligence may either be A. Elements of the Crime
culpa contractual, culpa aquilana, and criminal 1. The offender does or fail to do
negligence. an act;
2. The doing or the failure to do
1. QUASI DELIT that act is voluntary;
Culpa Aquilana 3. It is without malice;
4. The material damage results
Art. 2176. Whoever by act or omission causes from the reckless imprudence;
damage to another, there being fault or and
negligence, is obligated to pay for the damage 5. There is inexcusable lack of
done. Such fault or negligence, if there is no precaution on the part of the
pre-existing contractual relation between the offender, taking into
parties, is called quasi-delict and is governed consideration his employment,
by the provision of this Chapter. degree of intelligence, physical
condition, and other
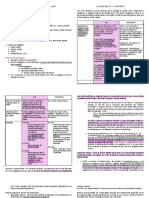
REQUISITES: circumstances regarding
1. There must be an act or omission persons, time, and place.
constituting fault or negligence;
2. Damage caused by the said act or 3. CONTRACT
omission; and Culpa Contractual
3. Causal relation between the damage
and the act or omission. Art. 1170. Those who in the performance of
4. There is no pre-existing contractual their obligations are guilty of fraud,
relation between the parties. negligence, or delay, and those who in any
manner contravene the tenor thereof, are
An action based on quasi delict can be liable for damages.
maintained even if there is an existing ART 1234 THE JOINNER
contractual relation between the parties.
ART. 1171. Responsibility arising from fraud is
The test (whether a quasi-delict can be deened demandable in all obligations. Any waiver of
to underlie the breach of a contract) was stated an action for future fraud is void.
thus:
Where, without a pre-existing contract ART. 1172. Responsibility arising from
between two parties, an act or omission can negligence in the performance of every kind of
nonetheless amount to an actionable tort by obligations is also demandable, but such
itself, the fact that the parties are liability may be regulated by the courts,
contractually bound is no bar to the according to the circumstances.
application of quasi delict provisions to the
case. ART. 1173. The fault or negligence of the
obligor consists in the omission of that
“DUTY” need not be alleged and proved in
order to recover.
GENERAL DUTY OF CARE- it is not for the
plaintiff to prove the existence of duty as an
element of cause of action.
“there is no requirement that the negligent act
or omission is directed at a specific person but it
suffices that a person suffers damages as a
consequence of a wrongful act of another in
order that indemnity could be demanded from
the wrongdoer”
The obligation based on quasi-delict must also
have the essential requisites of a obligation:
1. Active subject
2. Passive subject
3. Prestation
4. Vinculum juris
2. DELICT
You might also like
- 2017-0119 Torts and Damages - Book of de Leon 2016 - Atty. BundacDocument3 pages2017-0119 Torts and Damages - Book of de Leon 2016 - Atty. BundacJesterNo ratings yet
- Torts and Damages EnumerationDocument6 pagesTorts and Damages EnumerationShasharu Fei-fei LimNo ratings yet
- Civil Law QuasiDocument3 pagesCivil Law QuasisaitiNo ratings yet
- Quasi-Delict (January 6, 20180Document156 pagesQuasi-Delict (January 6, 20180Kim Boyles FuentesNo ratings yet
- Torts Midterms ReviewerDocument5 pagesTorts Midterms ReviewerFlorence RoseteNo ratings yet
- Negligence: Article 2176. Whoever by Act or OmissionDocument19 pagesNegligence: Article 2176. Whoever by Act or OmissionEmman FernandezNo ratings yet
- Eh401 Torts Midterms Topics I VDocument62 pagesEh401 Torts Midterms Topics I VGillian Alexis ColegadoNo ratings yet
- GDocument28 pagesGGeds DNo ratings yet
- OBLIGATIONS and CONTRACTSDocument213 pagesOBLIGATIONS and CONTRACTSPilacan KarylNo ratings yet
- Obl Icon Reviewer EditedDocument35 pagesObl Icon Reviewer EditedSage LingatongNo ratings yet
- Law 2Document33 pagesLaw 2boa13No ratings yet
- Quantum of Evidence: Was A Contract and Carried Out. It IsDocument14 pagesQuantum of Evidence: Was A Contract and Carried Out. It IsSharel LontocNo ratings yet
- FOR TOMORROW's TodeiDocument5 pagesFOR TOMORROW's TodeiRoasa Caryl Joshua SubaNo ratings yet
- Torts and Damages Notes FinalllyDocument192 pagesTorts and Damages Notes FinalllyVanessa VelascoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Obligations: CIVIL LAW REVIEW 2 - Pros. Felipe Macaldo JRDocument10 pagesChapter 1: Obligations: CIVIL LAW REVIEW 2 - Pros. Felipe Macaldo JRrHea sindoLNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Chapter 2Document5 pagesOblicon Chapter 2Donnnaan OreaNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Notes Obligations FinalsDocument51 pagesOblicon Notes Obligations FinalsMarco Ramon0% (1)
- 7-TORTS AND DAMAGES (San Beda) EditedDocument24 pages7-TORTS AND DAMAGES (San Beda) EditedLeayza Sta Maria CarreonNo ratings yet
- San Beda Red Book 2018, Personal Notes,,, by Lee Anne Yabut 1Document32 pagesSan Beda Red Book 2018, Personal Notes,,, by Lee Anne Yabut 1jon jonNo ratings yet
- Torts and Damages 2011Document42 pagesTorts and Damages 2011emmaniago0829No ratings yet
- Torts - Notes For MidtermsDocument5 pagesTorts - Notes For MidtermsJulia Cassandra CajaropNo ratings yet
- Sison Notes-Oblicon (Bar 2018)Document13 pagesSison Notes-Oblicon (Bar 2018)Yuri SisonNo ratings yet
- OBLIGATIONS and CONTRACTSDocument34 pagesOBLIGATIONS and CONTRACTSKristine Ritchel TorresNo ratings yet
- Torts Memory Aid AteneoDocument11 pagesTorts Memory Aid AteneoStGabrielleNo ratings yet
- Obligations and Contracts LectureDocument28 pagesObligations and Contracts LectureMila Casandra CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Torts Midterm Exam ReviewerDocument16 pagesTorts Midterm Exam ReviewerMary Ann LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Mora Solvendi (Delay of The Debtor)Document11 pagesMora Solvendi (Delay of The Debtor)John Paul100% (1)
- An Action or Omission That Constitutes An Offense That May Be Prosecuted by The State and Is Punishable by LawDocument5 pagesAn Action or Omission That Constitutes An Offense That May Be Prosecuted by The State and Is Punishable by LawAmer Lucman IIINo ratings yet
- Memo Aid ObliconDocument28 pagesMemo Aid ObliconJurish Ann JimenezNo ratings yet
- FINAL-Torts and DamagesDocument17 pagesFINAL-Torts and Damagesjon jonNo ratings yet
- Nature & Effects of ObligationsDocument62 pagesNature & Effects of ObligationsAVelino PagandiyanNo ratings yet
- Torts Quasi DelictsDocument10 pagesTorts Quasi DelictsSonnyNo ratings yet
- Torts and DamagesDocument32 pagesTorts and DamagesTess Legaspi100% (3)
- 2019 UP Civil Law - TortsDocument55 pages2019 UP Civil Law - TortshellohowareuNo ratings yet
- Torts Quasi DelictsDocument10 pagesTorts Quasi DelictsAlex GraciaNo ratings yet
- Nature and Effect of Obligations - 0Document6 pagesNature and Effect of Obligations - 0pam pamNo ratings yet
- TORTS Midterm Reviewer - JMRDocument15 pagesTORTS Midterm Reviewer - JMRjillian margaux royNo ratings yet
- TortsDocument12 pagesTortsKharrel GraceNo ratings yet
- Torts ReviewerDocument2 pagesTorts ReviewerMel CarununganNo ratings yet
- Q&a in Torts and DamagesDocument7 pagesQ&a in Torts and DamagesAxel FontanillaNo ratings yet
- ObligationsDocument13 pagesObligationsZydalgLadyz NeadNo ratings yet
- Torts and Damages: San Beda College of LawDocument29 pagesTorts and Damages: San Beda College of LawRégine NaldoNo ratings yet
- Torts Midterms Reviewer Final PDFDocument9 pagesTorts Midterms Reviewer Final PDFDarla GreyNo ratings yet
- Outline Lecture ObliconDocument21 pagesOutline Lecture ObliconPilacan KarylNo ratings yet
- Obligation and Contrcacts SummaryDocument10 pagesObligation and Contrcacts SummaryGwen CaldonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6elleNo ratings yet
- 1167-1178 Notes On LAWDocument4 pages1167-1178 Notes On LAWstyleshineeeeNo ratings yet
- Torts Codal and AnnotationsDocument16 pagesTorts Codal and AnnotationsFrancisCarloL.FlameñoNo ratings yet
- Nature and Effect of ObligationsDocument5 pagesNature and Effect of ObligationshoxhiiNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Fraud, Negligence or DelayDocument5 pagesModule 3 - Fraud, Negligence or Delaygiezel francoNo ratings yet
- Civillaw (Torts) Memoryaid A B O 2002Document14 pagesCivillaw (Torts) Memoryaid A B O 2002Maricar Corina CanayaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reviewer PDFDocument59 pagesMidterm Reviewer PDFAngelo Ibañez GargaritanoNo ratings yet
- Tort Defined: Culpa Contractual Is Governed by The CivilDocument2 pagesTort Defined: Culpa Contractual Is Governed by The CivilHuzzain PangcogaNo ratings yet
- Law of the People's Republic of China on Penalties for Administration of Public SecurityFrom EverandLaw of the People's Republic of China on Penalties for Administration of Public SecurityNo ratings yet
- LTD Jones vs. Insular GovDocument3 pagesLTD Jones vs. Insular GovJesterNo ratings yet
- DigestsDocument18 pagesDigestsJesterNo ratings yet
- 1 Rem 2 SyllabusDocument21 pages1 Rem 2 SyllabusJesterNo ratings yet
- Admin NgayonDocument14 pagesAdmin NgayonJesterNo ratings yet
- Reviewers HRDocument2 pagesReviewers HRJesterNo ratings yet
- Cta JurisdictionDocument21 pagesCta JurisdictionJesterNo ratings yet
- Local TaxationDocument57 pagesLocal TaxationJesterNo ratings yet
- Phil Pharmawealth, Inc., vs. Pfizer, Inc. and Pfizer (Phil.) Inc., G.R. No. 167715: November 17, 2010Document26 pagesPhil Pharmawealth, Inc., vs. Pfizer, Inc. and Pfizer (Phil.) Inc., G.R. No. 167715: November 17, 2010JesterNo ratings yet
- ATLAS PrescriptionDocument4 pagesATLAS PrescriptionJesterNo ratings yet
- Dangerous - Includes ThingsDocument4 pagesDangerous - Includes ThingsJesterNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. L-7154 February 21, 1912 ELEANOR ERICA STRONG, ET AL., Plaintiffs-Appellees, FRANCISCO GUTIERREZ REPIDE, Defendant-AppellantDocument4 pagesG.R. No. L-7154 February 21, 1912 ELEANOR ERICA STRONG, ET AL., Plaintiffs-Appellees, FRANCISCO GUTIERREZ REPIDE, Defendant-AppellantJesterNo ratings yet
- Transpo DIGESTDocument5 pagesTranspo DIGESTJesterNo ratings yet
- 2017-0119 Torts and Damages - Book of de Leon 2016 - Atty. BundacDocument3 pages2017-0119 Torts and Damages - Book of de Leon 2016 - Atty. BundacJesterNo ratings yet
- Case Digests I IVDocument25 pagesCase Digests I IVJesterNo ratings yet
- Dangerous - Includes ThingsDocument4 pagesDangerous - Includes ThingsJesterNo ratings yet
- Facts:: Third Person Who Contracted With The Agent Himself Acted in Good Faith. Good Faith Here Means That TheDocument5 pagesFacts:: Third Person Who Contracted With The Agent Himself Acted in Good Faith. Good Faith Here Means That TheJesterNo ratings yet
- False. Because According To Art. 52.1. Except For The Cases Specified in Clause 4Document4 pagesFalse. Because According To Art. 52.1. Except For The Cases Specified in Clause 4Cu Thi Hong NhungNo ratings yet
- Moot Respondent 1Document33 pagesMoot Respondent 1sonaambiyilNo ratings yet
- JLL India Office Update Q1 2021Document18 pagesJLL India Office Update Q1 2021jatin girotraNo ratings yet
- ICC Moot Court Competition IN THE English LanguageDocument48 pagesICC Moot Court Competition IN THE English LanguageSagar MajumdarNo ratings yet
- 2-3-20-Cynthia Aybar - Certificados-TC-TRADocument7 pages2-3-20-Cynthia Aybar - Certificados-TC-TRAEeulalia livano pumaNo ratings yet
- RULE 48 and 49Document10 pagesRULE 48 and 49Jade GanzanNo ratings yet
- Jessie Dotson PetitionDocument249 pagesJessie Dotson PetitionLydian CoombsNo ratings yet
- Admiralty Law - WikipediaDocument59 pagesAdmiralty Law - WikipediaHarel Santos RosaciaNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Article 1186-1190Document12 pagesOblicon Article 1186-1190Hasanah AmerilNo ratings yet
- International Cell, SLSH: 3-Day National Webinar Series OnDocument7 pagesInternational Cell, SLSH: 3-Day National Webinar Series OnSULAGNA DUTTANo ratings yet
- Child On The 20th November, 1989Document5 pagesChild On The 20th November, 1989Anum AkramNo ratings yet
- CT Secretary - Commissioner - Additional Commissioners - Joint CommissionersDocument5 pagesCT Secretary - Commissioner - Additional Commissioners - Joint CommissionersAdvocate KKNo ratings yet
- Lift Mode Minutes of Meeting-DraftDocument2 pagesLift Mode Minutes of Meeting-DraftManagement Danau ImpianNo ratings yet
- UAD Application Form (Non-Faculty Positions)Document3 pagesUAD Application Form (Non-Faculty Positions)nasirhussain19982016No ratings yet
- KG2-Registration FormDocument3 pagesKG2-Registration FormJohn Patrick IquinNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT MEC294-Boyle's LawDocument3 pagesLAB REPORT MEC294-Boyle's LawHamzah أسَدُ أللَّهNo ratings yet
- For and On Behalf of The Oriental Insurance Company LimitedDocument2 pagesFor and On Behalf of The Oriental Insurance Company LimitedASAVARI HUMANENo ratings yet
- Residential StatusDocument102 pagesResidential StatusRahul Piyush MehtaNo ratings yet
- Taxation: Tata Consultancy Services vs. State of Andhra PradeshDocument11 pagesTaxation: Tata Consultancy Services vs. State of Andhra PradeshkartikNo ratings yet
- Inocentes Et Al Vs RSCIDocument2 pagesInocentes Et Al Vs RSCIRex Regio100% (1)
- On The CaseDocument3 pagesOn The Casesamsuldahlan00No ratings yet
- Authorization Letter 2Document3 pagesAuthorization Letter 2Mercilita De Paz LeopardasNo ratings yet
- CMFRDocument89 pagesCMFRannadominiquereyesNo ratings yet
- Professionalism Ethics & Malpractice 12-6-2019Document205 pagesProfessionalism Ethics & Malpractice 12-6-2019Hugh WoodNo ratings yet
- Contract To SellDocument3 pagesContract To SellJefferson SilarioNo ratings yet
- Rights of Legal RepresentationDocument13 pagesRights of Legal RepresentationisayaNo ratings yet
- Maloney Young Stars Netball Academy ConstitutionDocument3 pagesMaloney Young Stars Netball Academy ConstitutionNjemile MontesNo ratings yet
- The French RevolutionDocument14 pagesThe French RevolutionMayank Sikarwal100% (3)
- AT2 Prelim Quizzes CompileDocument16 pagesAT2 Prelim Quizzes CompileHelen Faith EstanteNo ratings yet
- 4 Care - Best - International - Inc. - v. - Securities20210510-11-1yk6356Document2 pages4 Care - Best - International - Inc. - v. - Securities20210510-11-1yk6356MarieNo ratings yet