Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Triangular Interval Syndrome
Triangular Interval Syndrome
Uploaded by
EidertxuOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Triangular Interval Syndrome
Triangular Interval Syndrome
Uploaded by
EidertxuCopyright:
Available Formats
TRIANGULAR INTERVAL SYNDROME (TIS)
Stefan Duell
2020/01/07
SHOULDER OR ARM PAIN?
The Triangular Interval (also known as the lateral triangular space, lower
triangular space and triceps hiatus) is a space connecting the axilla to
the posterior compartment of the arm. It is one of the three intermuscular
spaces found in the axillary space. The other two spaces are
Quadrangular Space and Triangular Space.
Triangular Interval (4)
Borders
▪️superior: teres major
▪️lateral: lateral head of the triceps or the humerus
▪️medial: long head of the triceps
Contents
▪️profunda brachii artery
▪️radial nerve
⠀
Quadrangular Space (5)
Borders
▪️medial: long head of triceps
▪️lateral: humeral shaft
▪️superior: teres minor
▪️inferior: teres major
Contents
▪️axillary nerve
▪️posterior humeral circumflex artery
⠀
Triangular Space (3)
Borders
▪️inferior: teres major
▪️lateral: long head of triceps
▪️superior: lower border of teres minor
Contents
▪️scapular circumflex artery
⠀
Triangular Interval Syndrome (TIS) was described as a differential
diagnosis for radicular pain in the upper extremity.
It is a condition where the radial nerve is entrapped in the triangular
interval resulting in upper extremity radicular pain.
The radial nerve and profunda brachii pass through the triangular interval
and are hence vulnerable. The triangular interval has a potential for
compromise secondary alterations in thickness of the teres major and
triceps. It is described based on cadaveric studies that fibrous bands
were commonly present between the teres major and triceps. When
these bands were present, rotation of the shoulder caused a reduction in
cross sectional area of the space.
Hypertrophy of the teres major can occur secondary to weight training
and potentially compromise the triangular interval with resultant
entrapment of the radial nerve.
Shoulder dysfunctions have a potential for shortening and hypertrophy of
the teres major.
The triceps brachii has a potential to entrap the radial nerve in the
triangular interval secondary to hypertrophy. The presence of a fibrous
arch in the long head and lateral head further complicates the situation.
#Anatomy #Physiotherapy #Osteopathy #Doctor
You might also like
- 2009 - Mil HDBK 1823a PDFDocument171 pages2009 - Mil HDBK 1823a PDFEidertxuNo ratings yet
- Shoulder GirdleDocument29 pagesShoulder GirdleogbokobolaNo ratings yet
- Upper Part: Genu Valgum (Knock Knee) Genu Varum (Bow-Leggedness)Document2 pagesUpper Part: Genu Valgum (Knock Knee) Genu Varum (Bow-Leggedness)1223moNo ratings yet
- Neck TrianglesDocument5 pagesNeck TrianglesMaxi RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Torso - Thorax Overview - Cherchi - 1999Document17 pagesTorso - Thorax Overview - Cherchi - 1999clubstarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Femur: Syarifah Nazira 1610211050Document13 pagesAnatomy of Femur: Syarifah Nazira 1610211050syarifah naziraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of NeckDocument100 pagesAnatomy of NeckdiptidigheNo ratings yet
- TrapeziusDocument4 pagesTrapeziusAntony David LauraNo ratings yet
- Thorax ScriptDocument3 pagesThorax ScriptEspiritu, ChriscelNo ratings yet
- Thoracic and Coracoid Arteries In Two Families of Birds, Columbidae and HirundinidaeFrom EverandThoracic and Coracoid Arteries In Two Families of Birds, Columbidae and HirundinidaeNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument59 pagesSpinal Cordveegeer100% (1)
- Thoracic WallDocument54 pagesThoracic WallSimran KumariNo ratings yet
- The Humerus - Proximal - Shaft - Distal - TeachMeAnatomyDocument5 pagesThe Humerus - Proximal - Shaft - Distal - TeachMeAnatomymuhammad HaseebNo ratings yet
- 2022 Thorax ExamDocument57 pages2022 Thorax ExamratuNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy of Chest WallDocument31 pagesSurgical Anatomy of Chest WallArockia DharshanaNo ratings yet
- L5 Surface Anatomy & DiaphragmDocument45 pagesL5 Surface Anatomy & DiaphragmatefmoussaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of ThoraxDocument43 pagesAnatomy of ThoraxNunmoy HnialumNo ratings yet
- Nerves and Arterial Supply of The Upper Limb: Circumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus DorsiDocument4 pagesNerves and Arterial Supply of The Upper Limb: Circumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus DorsiMichelleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Upper Limb ScapulohumeraDocument48 pagesAnatomy Upper Limb ScapulohumeraGhaidaa SadeqNo ratings yet
- Axillary NerveDocument17 pagesAxillary Nerveshrishti shadangiNo ratings yet
- Acb 49 213Document4 pagesAcb 49 213Haru SahaNo ratings yet
- Upper LimbDocument17 pagesUpper LimbPapadoveNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ChecklistDocument16 pagesLaboratory ChecklistkatNo ratings yet
- 2.08 Brachial Region (Arm) - Compartments, Muscles, Nerves, and VesselsDocument3 pages2.08 Brachial Region (Arm) - Compartments, Muscles, Nerves, and VesselsDi CanNo ratings yet
- SternumDocument6 pagesSternumrkumar1313No ratings yet
- Orientation of Thoracic Wall.Document54 pagesOrientation of Thoracic Wall.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- II Sem Pysioyherapy, BS, SSDocument23 pagesII Sem Pysioyherapy, BS, SSAlexander VonPatrickNo ratings yet
- An Unusual Supernuemerary Third Head of Biceps Brachii Muscle in Malayasian Male Cadaver-A Case ReportDocument4 pagesAn Unusual Supernuemerary Third Head of Biceps Brachii Muscle in Malayasian Male Cadaver-A Case ReportIOSR Journal of PharmacyNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall Lecrure 7 DiaphragmDocument38 pagesThoracic Wall Lecrure 7 DiaphragmHumrazNo ratings yet
- Notes Jun 30, 2014 Anatomy Part 1Document37 pagesNotes Jun 30, 2014 Anatomy Part 1Diwakesh C BNo ratings yet
- Clavicle - WikipediaDocument8 pagesClavicle - WikipediaVaishnavi TradersNo ratings yet
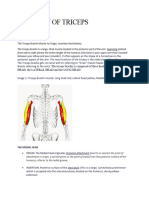
- Anatomy of TricepsDocument5 pagesAnatomy of TricepsspacefitnesscurepipeNo ratings yet
- Posterior Compartment of Arm 9 Mar 2024Document25 pagesPosterior Compartment of Arm 9 Mar 2024aamna.nadeem101No ratings yet
- As UpperlimbDocument3 pagesAs UpperlimbUma MounaNo ratings yet
- Median NerveDocument27 pagesMedian Nerve7pk548hdqtNo ratings yet
- Anatomia y Fisiologia Del DiafragmaDocument11 pagesAnatomia y Fisiologia Del Diafragmaflechudo1235408No ratings yet
- The Humerus - Proximal - Shaft - Distal - TeachMeAnatomyDocument4 pagesThe Humerus - Proximal - Shaft - Distal - TeachMeAnatomyDelta MuNo ratings yet
- Circumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus DorsiDocument4 pagesCircumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus Dorsispeedy.catNo ratings yet
- DMS (PBL3) Mohamad Arbian Karim FMUI20Document24 pagesDMS (PBL3) Mohamad Arbian Karim FMUI20Mohamad Arbian KarimNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument14 pagesPresentationshubhankarboudhNo ratings yet
- Membrul Superior MGDocument118 pagesMembrul Superior MGMihai OpreaNo ratings yet
- The Shoulder JointDocument17 pagesThe Shoulder JointBhargavNo ratings yet
- The Shoulder JointDocument17 pagesThe Shoulder JointBhargavNo ratings yet
- Ana211 HUMERUSDocument4 pagesAna211 HUMERUSKalu ComforterNo ratings yet
- Elraiah Mohamed MakieDocument65 pagesElraiah Mohamed MakieAhmed YousifNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Surface Anatomy and Surface Landmarks For Thoracic SurgeryDocument13 pages1.1 Surface Anatomy and Surface Landmarks For Thoracic SurgeryResidentes CirugíaNo ratings yet
- ANAT:Lecture Note Forearm1Document7 pagesANAT:Lecture Note Forearm1Nur Liyana MohamadNo ratings yet
- BRACHIAL PLEXUS (Autosaved)Document51 pagesBRACHIAL PLEXUS (Autosaved)Coy EnNo ratings yet
- N420 N421 TG2-03A TG2-03B Practical1 Practical2: OsteologyDocument7 pagesN420 N421 TG2-03A TG2-03B Practical1 Practical2: OsteologyNaina Karamina SakinaNo ratings yet
- Dissection 11 - Extensor Compartment of The Forearm, Deep Hand, Wrist and Hand JointsDocument29 pagesDissection 11 - Extensor Compartment of The Forearm, Deep Hand, Wrist and Hand JointsLeonard EllerbeNo ratings yet
- Variation in The Branching Pattern of Right Axillary Artery in A Malaysian Adult Male Cadaver - A Case ReportDocument4 pagesVariation in The Branching Pattern of Right Axillary Artery in A Malaysian Adult Male Cadaver - A Case ReportIOSR Journal of PharmacyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3Document33 pagesAnatomy 3bikedet268No ratings yet
- Lecture 12 Skeletal System Lower Limb (Surface Anatomy)Document29 pagesLecture 12 Skeletal System Lower Limb (Surface Anatomy)hafiz patahNo ratings yet
- Radial and Median NervesDocument33 pagesRadial and Median NervesveegeerNo ratings yet
- 02 Appendicular SkeletonDocument40 pages02 Appendicular SkeletonkalyanNo ratings yet
- Posterior TriangleDocument13 pagesPosterior TrianglenoorulaashimasNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument9 pagesSpinal Cordpromisearinzechi4No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Thoracic Outlet SyndromeDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Thoracic Outlet SyndromeDony Astika WigunaNo ratings yet
- Femur and PatellaDocument15 pagesFemur and PatellaaroojNo ratings yet
- North American Recent Soft-Shelled Turtles (Family Trionychidae)From EverandNorth American Recent Soft-Shelled Turtles (Family Trionychidae)No ratings yet
- Recent Advances in MAPOD - June 2009Document61 pagesRecent Advances in MAPOD - June 2009EidertxuNo ratings yet
- 2005 Usamentiaga PDFDocument16 pages2005 Usamentiaga PDFEidertxuNo ratings yet
- Crack Propagation in EBW JointsDocument8 pagesCrack Propagation in EBW JointsEidertxuNo ratings yet