Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 8 Conditional Clauses PDF
Unit 8 Conditional Clauses PDF
Uploaded by
Jorge LunaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Mixed Tenses PDFDocument4 pagesMixed Tenses PDFJoe Benegas50% (2)
- English Grammar Practice: Explanations and Exercises with KeyFrom EverandEnglish Grammar Practice: Explanations and Exercises with KeyNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Passive Voice PDFDocument4 pagesUnit 7 Passive Voice PDFJorge LunaNo ratings yet
- Latinitas Perennis New Exercises in Lati PDFDocument117 pagesLatinitas Perennis New Exercises in Lati PDFGiuseppe Emanuele Caruso50% (2)
- ConditionalsDocument11 pagesConditionalsКоля МогильниковNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences 1Document1 pageConditional Sentences 1Bozhidara KaragyozovaNo ratings yet
- Meeting 3 - ConditionalDocument7 pagesMeeting 3 - ConditionalIkram Wahyu PratamaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesGrace Gesto RubillosNo ratings yet
- Class 3: Practice Revision Conditionals or If Clauses 1 June 2020Document18 pagesClass 3: Practice Revision Conditionals or If Clauses 1 June 2020Jose C. Chaca100% (1)
- English Portfolio Fernando Fernàndez #8: Zero ConditionalDocument9 pagesEnglish Portfolio Fernando Fernàndez #8: Zero Conditional123 cesarNo ratings yet
- Conditional-Easy ExplanationDocument1 pageConditional-Easy ExplanationFernanda Shine SantosNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument3 pagesConditionalsVera AtanasovaNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 9, Q1 - LAS, WK 4 Day 1-5Document5 pagesENGLISH 9, Q1 - LAS, WK 4 Day 1-5kenNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 ConditionalsDocument11 pagesUnit 8 ConditionalsSharo rooNo ratings yet
- Summary 1 Topic: Review Conditional Zero, First and Second: General ExplanationDocument6 pagesSummary 1 Topic: Review Conditional Zero, First and Second: General ExplanationJaime G. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Conditional TensesDocument3 pagesConditional TensesMuhammad yousafNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument8 pagesConditionalsIrene BertoloNo ratings yet
- 02-English-UH2 - Second Conditional - ExerciseDocument29 pages02-English-UH2 - Second Conditional - ExerciseAnanta PradhanaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument3 pagesConditional Sentencesabdellah dandoumNo ratings yet
- Zero Conditional (Autosaved)Document17 pagesZero Conditional (Autosaved)MARIA PAMELA VICERANo ratings yet
- English I - CONDITIONALSDocument22 pagesEnglish I - CONDITIONALSJulissa Graciela Salas VegaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument8 pagesConditionalsAntoni TF SianturiNo ratings yet
- University of ColimaDocument4 pagesUniversity of ColimaCHAVEZ VALADEZ JUAN DIEGONo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences in Englis Fix 112027Document3 pagesConditional Sentences in Englis Fix 112027adittyapratamaNo ratings yet
- Zero and First Conditionals GrammarDocument4 pagesZero and First Conditionals GrammarPablo Morales VargasNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Conditional Sentences: ClauseDocument8 pages2.1 Conditional Sentences: ClauseArmeliaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals: Verb Tense in "If" Clauses: What This Handout Is AboutDocument13 pagesConditionals: Verb Tense in "If" Clauses: What This Handout Is AboutGulden Fergan EmminikNo ratings yet
- Trabalho de Ingles 5 GrupoDocument16 pagesTrabalho de Ingles 5 GrupoEdson ChaleNo ratings yet
- First ConditionalDocument7 pagesFirst ConditionalInessaAshmarinaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals Part 1: If I Cook More, I'll Get Better at CookingDocument6 pagesConditionals Part 1: If I Cook More, I'll Get Better at CookingLidia Mateos RomeroNo ratings yet
- Conditional (If Clause)Document8 pagesConditional (If Clause)Meiri NadiaNo ratings yet
- GrammaR LessonDocument24 pagesGrammaR LessonLettie MilesNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence and Conditional ConjunctionsDocument4 pagesConditional Sentence and Conditional ConjunctionsNCD NAWADANo ratings yet
- 1.a.IF-CLAUSES (0,1,2,3.types) - 2-2Document2 pages1.a.IF-CLAUSES (0,1,2,3.types) - 2-2joanaNo ratings yet
- Actividades Avanzadas de RepasoDocument3 pagesActividades Avanzadas de RepasoPriscilaGuadalupe BogadoNo ratings yet
- Let's Play The Game, "What If"Document29 pagesLet's Play The Game, "What If"Justine ZablanNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument3 pagesConditionalsSara HagemannNo ratings yet
- Conjunction and Conditional SentencesDocument11 pagesConjunction and Conditional SentencesRahmatia Candra DewiNo ratings yet
- Conditionals English For UniDocument4 pagesConditionals English For UniKandhro KandhroNo ratings yet
- Conditionals LessonDocument8 pagesConditionals LessonGrace ManuelNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences Zero FirstDocument21 pagesConditional Sentences Zero FirstJosé Henrique Tobias PereiraNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument12 pagesConditional Sentencesniko_blue55No ratings yet
- Conditional-Sentences - Wish Time Clauses ADVANCEDDocument32 pagesConditional-Sentences - Wish Time Clauses ADVANCEDMiriam ChiovettaNo ratings yet
- FILE - Zero and First ConditionalsDocument4 pagesFILE - Zero and First ConditionalsIsha Claire AliliranNo ratings yet
- I. Identificación de La Presentación N°001/2020: Idioma Extranjero. Inglés Verónica Díaz Morales Tercero Medio PrimeroDocument13 pagesI. Identificación de La Presentación N°001/2020: Idioma Extranjero. Inglés Verónica Díaz Morales Tercero Medio PrimeroCesarSilvestreRendónVázquezNo ratings yet
- Unit 5B Zero and First Conditionals MPFDocument1 pageUnit 5B Zero and First Conditionals MPFAndy PazmiñoNo ratings yet
- Conditional ClausesDocument18 pagesConditional ClausesAitor 206No ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument32 pagesConditional Sentenceslara ElkassemNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence - Group 11Document22 pagesConditional Sentence - Group 11apriyanisagitae dwiNo ratings yet
- IF ConditionalsDocument7 pagesIF ConditionalskeenanjmNo ratings yet
- Conditionals 0-1-2Document12 pagesConditionals 0-1-2solodeilseNo ratings yet
- ZERO CONDITIONAL Verbs PPT222222222Document22 pagesZERO CONDITIONAL Verbs PPT222222222Clara ArejaNo ratings yet
- 1st and Zero - ConditionalsDocument3 pages1st and Zero - ConditionalsDarkCreeper13No ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument11 pagesConditional SentencesAdelia SafitriNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument2 pagesConditionalselyd1509No ratings yet
- ConditionalsentenseDocument9 pagesConditionalsentenseyahaha.hayyun1No ratings yet
- CONDITIONALDocument95 pagesCONDITIONALmmmmmNo ratings yet
- Conditional If Type 0, 1 & 2Document3 pagesConditional If Type 0, 1 & 2obengNo ratings yet
- Conditionals GrammarDocument24 pagesConditionals GrammarJúlia LopesNo ratings yet
- Lesson On Conditional SentencesDocument2 pagesLesson On Conditional SentencesMarina PeshovskaNo ratings yet
- If ClausesDocument13 pagesIf ClausesYunanda Alya MustikaNo ratings yet
- Fizzyx for Fun, Exploring Physics through Experiment & Creative PlayFrom EverandFizzyx for Fun, Exploring Physics through Experiment & Creative PlayNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Relative ClausesDocument5 pagesUnit 6 Relative ClausesJorge LunaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 The Perfect TenseDocument6 pagesUnit 5 The Perfect TenseJorge LunaNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Conditional Clauses PDFDocument3 pagesUnit 8 Conditional Clauses PDFJorge LunaNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Unit 7 The Lab PDFDocument5 pagesVocabulary Unit 7 The Lab PDFJorge LunaNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary CellsDocument6 pagesVocabulary CellsJorge LunaNo ratings yet
- Eenadu Spoken EnglishDocument1 pageEenadu Spoken Englishpvrsrpvarma899No ratings yet
- Handout 2 - Unit 1 L PDFDocument2 pagesHandout 2 - Unit 1 L PDFJavier Andres Vega NeiraNo ratings yet
- Concessive Clauses: Subordinators in Contrast ClausesDocument2 pagesConcessive Clauses: Subordinators in Contrast ClausesPatricia CopelloNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect TenseDocument4 pagesPast Perfect TenseLee Kok LianNo ratings yet
- Cultural DifferencesDocument3 pagesCultural DifferencesEmese Ebert TóthNo ratings yet
- Jawablah Pertanyaan Dibawah Ini Dengan Bahasa Anda Sendiri!Document2 pagesJawablah Pertanyaan Dibawah Ini Dengan Bahasa Anda Sendiri!wandi wardiana rahayuNo ratings yet
- GCSE French Teacher Guide Free Sample Chapter 1 HigherDocument26 pagesGCSE French Teacher Guide Free Sample Chapter 1 Higherthedummy07No ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document3 pagesQuiz 1fitrinadia922No ratings yet
- Verbs Which Cannot Be Used in The Passive VoiceDocument3 pagesVerbs Which Cannot Be Used in The Passive VoiceDamaris Neny KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Contrastive Conjunction: After in Order (That) UnlessDocument3 pagesContrastive Conjunction: After in Order (That) UnlessFatiha Nur HasanaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Grammar For IELTS - ArticlesDocument21 pagesAdvanced Grammar For IELTS - ArticlesDrSushma PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- British English Vs American EnglishDocument20 pagesBritish English Vs American EnglishReda RakiNo ratings yet
- Proyecto Peter and The WolfDocument36 pagesProyecto Peter and The WolfsburgoslorenzoNo ratings yet
- InversionDocument5 pagesInversionalinaNo ratings yet
- Seeing ClearlyDocument7 pagesSeeing ClearlyFaysal JemaiNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Practice 1Document1 pagePresent Perfect Practice 1CarlosNo ratings yet
- 3° Simulado de InglêsDocument7 pages3° Simulado de InglêsMike NunesNo ratings yet
- Modulo Ingles Ciclo V Grado Decimo PDFDocument46 pagesModulo Ingles Ciclo V Grado Decimo PDFWilson Nava100% (2)
- Class-4-Annual Syllabus 2024-25Document5 pagesClass-4-Annual Syllabus 2024-25Girish TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Coldest Place On EarthDocument5 pagesThe Coldest Place On EarthAnonymous khRYSEPkNo ratings yet
- Amliz Danilow: Student S BookDocument108 pagesAmliz Danilow: Student S BookAngel Garcia FloresNo ratings yet
- Sentence Combining. Emphasis and VarietyDocument8 pagesSentence Combining. Emphasis and VarietyYamila ReynosoNo ratings yet
- ProductivityDocument10 pagesProductivityAdeNov ChannelNo ratings yet
- KLU - Eng - IP-UNIT 1 - SESSION 3Document42 pagesKLU - Eng - IP-UNIT 1 - SESSION 3venu sree guduriNo ratings yet
- Preterito IndefinidoDocument16 pagesPreterito IndefinidolittlefbitchNo ratings yet
- 1relative pronouns2ED&ING3PASSIVEVsACTIVEDocument8 pages1relative pronouns2ED&ING3PASSIVEVsACTIVEMiguelRodriguezCalderonNo ratings yet
- Sanskrit Vol1Document203 pagesSanskrit Vol1ngc1729100% (7)
- English Test 10°Document5 pagesEnglish Test 10°Liliana fernandezNo ratings yet
Unit 8 Conditional Clauses PDF
Unit 8 Conditional Clauses PDF
Uploaded by
Jorge LunaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 8 Conditional Clauses PDF
Unit 8 Conditional Clauses PDF
Uploaded by
Jorge LunaCopyright:
Available Formats
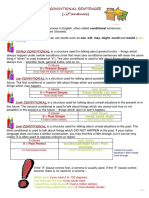
UNIT 8
CONDITIONAL CLAUSES
What are conditionals in English grammar?
Sometimes we call them 'if clauses'. They describe the result of something that might happen (in the
present or future) or might have happened but didn't (in the past). They are made using different English
verb tenses.
There are 4 main types of if sentences in English:
1.1 ZERO CONDITIONAL (THE LOGICAL CONDITIONAL)
The zero conditional is used to talk about things which are always true -- scientific facts, general truths,
things which always happen under certain conditions.
if clause main clause
If + Present Simple Present Simple
If you heat the water to 100 degrees, it boils.
If you press this button, The computer turns on.
* We can put the 'if' at the beginning, or in the middle. It doesn't matter at all.
Example: The computer turns on, if you press the button.
1.2 FIRST CONDITIONAL (THE PROBABLE FUTURE CONDITIONAL)
The first conditional is used to talk about possibilities or situations which are possible in the present or
the future; things which may happen.
if clause main clause
If + Present Simple Future Simple (Will) + Infinitive
Página 1
Unit 8 Inglés Técnico II
If you study hard, you will pass the test.
If the weather is fine, We will go to the beach.
* First vs. Zero Conditional
The first conditional describes a particular situation, whereas the zero conditional describes what
happens in general.
For example (zero conditional): if you sit in the sun, you get burned (here I'm talking about every time
a person sits in the sun - the burning is a natural consequence of the sitting)
But (first conditional): if you sit in the sun, you'll get burned (here I'm talking about what will happen
today, another day might be different)
1.3 SECOND CONDITIONAL (THE HYPOTHETICAL CONDITIONAL)
The second conditional is used to talk about things or situations which are unreal (not true or not
possible) in the present or the future -- things which don't or won't happen.
if clause main clause
If + Past Simple Would + Infinitive
If I had a million dollars, I would buy a big house.
If my parents were alive, They would be very proud of me.
* How is this different from the first conditional?
This kind of conditional sentence is different from the first conditional because this is a lot more unlikely.
For example (second conditional): If I had enough money I would buy a house. (I'm probably not going
to have this much money, it's just a dream, not very real)
But (first conditional): If I have enough money, I'll buy a house (It's much more likely that I will have
enough money to buy a house)
1.4 THIRD CONDITIONAL (THE PAST CONDITIONAL)
The third conditional is used to talk about things which DID NOT HAPPEN in the past. It is often used to
express criticism or regret.
if clause main clause
If + Past Perfect Would + have + Past Participle
If I had studied harder, I would have passed the exam.
Página 2
If she had married him She would have been very happy.
Unit 8 Inglés Técnico II
Example 1: I failed the exam, because I didn’t study hard enough.
Example 2: She is not happy now because she didn’t married him in the past.
IMPORTANT: If the "if" clause comes first, a comma is usually used. If the "if" clause comes second,
there is no need for a comma:
Water boils if you heat it to 100 degrees.
You will pass the test if you study hard.
I would buy a big house if I had a million dollars.
I would have passed the exam if I had studied harder
Página 3
Unit 8 Inglés Técnico II
You might also like
- Mixed Tenses PDFDocument4 pagesMixed Tenses PDFJoe Benegas50% (2)
- English Grammar Practice: Explanations and Exercises with KeyFrom EverandEnglish Grammar Practice: Explanations and Exercises with KeyNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Passive Voice PDFDocument4 pagesUnit 7 Passive Voice PDFJorge LunaNo ratings yet
- Latinitas Perennis New Exercises in Lati PDFDocument117 pagesLatinitas Perennis New Exercises in Lati PDFGiuseppe Emanuele Caruso50% (2)
- ConditionalsDocument11 pagesConditionalsКоля МогильниковNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences 1Document1 pageConditional Sentences 1Bozhidara KaragyozovaNo ratings yet
- Meeting 3 - ConditionalDocument7 pagesMeeting 3 - ConditionalIkram Wahyu PratamaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesGrace Gesto RubillosNo ratings yet
- Class 3: Practice Revision Conditionals or If Clauses 1 June 2020Document18 pagesClass 3: Practice Revision Conditionals or If Clauses 1 June 2020Jose C. Chaca100% (1)
- English Portfolio Fernando Fernàndez #8: Zero ConditionalDocument9 pagesEnglish Portfolio Fernando Fernàndez #8: Zero Conditional123 cesarNo ratings yet
- Conditional-Easy ExplanationDocument1 pageConditional-Easy ExplanationFernanda Shine SantosNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument3 pagesConditionalsVera AtanasovaNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 9, Q1 - LAS, WK 4 Day 1-5Document5 pagesENGLISH 9, Q1 - LAS, WK 4 Day 1-5kenNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 ConditionalsDocument11 pagesUnit 8 ConditionalsSharo rooNo ratings yet
- Summary 1 Topic: Review Conditional Zero, First and Second: General ExplanationDocument6 pagesSummary 1 Topic: Review Conditional Zero, First and Second: General ExplanationJaime G. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Conditional TensesDocument3 pagesConditional TensesMuhammad yousafNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument8 pagesConditionalsIrene BertoloNo ratings yet
- 02-English-UH2 - Second Conditional - ExerciseDocument29 pages02-English-UH2 - Second Conditional - ExerciseAnanta PradhanaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument3 pagesConditional Sentencesabdellah dandoumNo ratings yet
- Zero Conditional (Autosaved)Document17 pagesZero Conditional (Autosaved)MARIA PAMELA VICERANo ratings yet
- English I - CONDITIONALSDocument22 pagesEnglish I - CONDITIONALSJulissa Graciela Salas VegaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument8 pagesConditionalsAntoni TF SianturiNo ratings yet
- University of ColimaDocument4 pagesUniversity of ColimaCHAVEZ VALADEZ JUAN DIEGONo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences in Englis Fix 112027Document3 pagesConditional Sentences in Englis Fix 112027adittyapratamaNo ratings yet
- Zero and First Conditionals GrammarDocument4 pagesZero and First Conditionals GrammarPablo Morales VargasNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Conditional Sentences: ClauseDocument8 pages2.1 Conditional Sentences: ClauseArmeliaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals: Verb Tense in "If" Clauses: What This Handout Is AboutDocument13 pagesConditionals: Verb Tense in "If" Clauses: What This Handout Is AboutGulden Fergan EmminikNo ratings yet
- Trabalho de Ingles 5 GrupoDocument16 pagesTrabalho de Ingles 5 GrupoEdson ChaleNo ratings yet
- First ConditionalDocument7 pagesFirst ConditionalInessaAshmarinaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals Part 1: If I Cook More, I'll Get Better at CookingDocument6 pagesConditionals Part 1: If I Cook More, I'll Get Better at CookingLidia Mateos RomeroNo ratings yet
- Conditional (If Clause)Document8 pagesConditional (If Clause)Meiri NadiaNo ratings yet
- GrammaR LessonDocument24 pagesGrammaR LessonLettie MilesNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence and Conditional ConjunctionsDocument4 pagesConditional Sentence and Conditional ConjunctionsNCD NAWADANo ratings yet
- 1.a.IF-CLAUSES (0,1,2,3.types) - 2-2Document2 pages1.a.IF-CLAUSES (0,1,2,3.types) - 2-2joanaNo ratings yet
- Actividades Avanzadas de RepasoDocument3 pagesActividades Avanzadas de RepasoPriscilaGuadalupe BogadoNo ratings yet
- Let's Play The Game, "What If"Document29 pagesLet's Play The Game, "What If"Justine ZablanNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument3 pagesConditionalsSara HagemannNo ratings yet
- Conjunction and Conditional SentencesDocument11 pagesConjunction and Conditional SentencesRahmatia Candra DewiNo ratings yet
- Conditionals English For UniDocument4 pagesConditionals English For UniKandhro KandhroNo ratings yet
- Conditionals LessonDocument8 pagesConditionals LessonGrace ManuelNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences Zero FirstDocument21 pagesConditional Sentences Zero FirstJosé Henrique Tobias PereiraNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument12 pagesConditional Sentencesniko_blue55No ratings yet
- Conditional-Sentences - Wish Time Clauses ADVANCEDDocument32 pagesConditional-Sentences - Wish Time Clauses ADVANCEDMiriam ChiovettaNo ratings yet
- FILE - Zero and First ConditionalsDocument4 pagesFILE - Zero and First ConditionalsIsha Claire AliliranNo ratings yet
- I. Identificación de La Presentación N°001/2020: Idioma Extranjero. Inglés Verónica Díaz Morales Tercero Medio PrimeroDocument13 pagesI. Identificación de La Presentación N°001/2020: Idioma Extranjero. Inglés Verónica Díaz Morales Tercero Medio PrimeroCesarSilvestreRendónVázquezNo ratings yet
- Unit 5B Zero and First Conditionals MPFDocument1 pageUnit 5B Zero and First Conditionals MPFAndy PazmiñoNo ratings yet
- Conditional ClausesDocument18 pagesConditional ClausesAitor 206No ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument32 pagesConditional Sentenceslara ElkassemNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence - Group 11Document22 pagesConditional Sentence - Group 11apriyanisagitae dwiNo ratings yet
- IF ConditionalsDocument7 pagesIF ConditionalskeenanjmNo ratings yet
- Conditionals 0-1-2Document12 pagesConditionals 0-1-2solodeilseNo ratings yet
- ZERO CONDITIONAL Verbs PPT222222222Document22 pagesZERO CONDITIONAL Verbs PPT222222222Clara ArejaNo ratings yet
- 1st and Zero - ConditionalsDocument3 pages1st and Zero - ConditionalsDarkCreeper13No ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument11 pagesConditional SentencesAdelia SafitriNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument2 pagesConditionalselyd1509No ratings yet
- ConditionalsentenseDocument9 pagesConditionalsentenseyahaha.hayyun1No ratings yet
- CONDITIONALDocument95 pagesCONDITIONALmmmmmNo ratings yet
- Conditional If Type 0, 1 & 2Document3 pagesConditional If Type 0, 1 & 2obengNo ratings yet
- Conditionals GrammarDocument24 pagesConditionals GrammarJúlia LopesNo ratings yet
- Lesson On Conditional SentencesDocument2 pagesLesson On Conditional SentencesMarina PeshovskaNo ratings yet
- If ClausesDocument13 pagesIf ClausesYunanda Alya MustikaNo ratings yet
- Fizzyx for Fun, Exploring Physics through Experiment & Creative PlayFrom EverandFizzyx for Fun, Exploring Physics through Experiment & Creative PlayNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Relative ClausesDocument5 pagesUnit 6 Relative ClausesJorge LunaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 The Perfect TenseDocument6 pagesUnit 5 The Perfect TenseJorge LunaNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Conditional Clauses PDFDocument3 pagesUnit 8 Conditional Clauses PDFJorge LunaNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Unit 7 The Lab PDFDocument5 pagesVocabulary Unit 7 The Lab PDFJorge LunaNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary CellsDocument6 pagesVocabulary CellsJorge LunaNo ratings yet
- Eenadu Spoken EnglishDocument1 pageEenadu Spoken Englishpvrsrpvarma899No ratings yet
- Handout 2 - Unit 1 L PDFDocument2 pagesHandout 2 - Unit 1 L PDFJavier Andres Vega NeiraNo ratings yet
- Concessive Clauses: Subordinators in Contrast ClausesDocument2 pagesConcessive Clauses: Subordinators in Contrast ClausesPatricia CopelloNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect TenseDocument4 pagesPast Perfect TenseLee Kok LianNo ratings yet
- Cultural DifferencesDocument3 pagesCultural DifferencesEmese Ebert TóthNo ratings yet
- Jawablah Pertanyaan Dibawah Ini Dengan Bahasa Anda Sendiri!Document2 pagesJawablah Pertanyaan Dibawah Ini Dengan Bahasa Anda Sendiri!wandi wardiana rahayuNo ratings yet
- GCSE French Teacher Guide Free Sample Chapter 1 HigherDocument26 pagesGCSE French Teacher Guide Free Sample Chapter 1 Higherthedummy07No ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document3 pagesQuiz 1fitrinadia922No ratings yet
- Verbs Which Cannot Be Used in The Passive VoiceDocument3 pagesVerbs Which Cannot Be Used in The Passive VoiceDamaris Neny KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- Contrastive Conjunction: After in Order (That) UnlessDocument3 pagesContrastive Conjunction: After in Order (That) UnlessFatiha Nur HasanaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Grammar For IELTS - ArticlesDocument21 pagesAdvanced Grammar For IELTS - ArticlesDrSushma PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- British English Vs American EnglishDocument20 pagesBritish English Vs American EnglishReda RakiNo ratings yet
- Proyecto Peter and The WolfDocument36 pagesProyecto Peter and The WolfsburgoslorenzoNo ratings yet
- InversionDocument5 pagesInversionalinaNo ratings yet
- Seeing ClearlyDocument7 pagesSeeing ClearlyFaysal JemaiNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Practice 1Document1 pagePresent Perfect Practice 1CarlosNo ratings yet
- 3° Simulado de InglêsDocument7 pages3° Simulado de InglêsMike NunesNo ratings yet
- Modulo Ingles Ciclo V Grado Decimo PDFDocument46 pagesModulo Ingles Ciclo V Grado Decimo PDFWilson Nava100% (2)
- Class-4-Annual Syllabus 2024-25Document5 pagesClass-4-Annual Syllabus 2024-25Girish TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Coldest Place On EarthDocument5 pagesThe Coldest Place On EarthAnonymous khRYSEPkNo ratings yet
- Amliz Danilow: Student S BookDocument108 pagesAmliz Danilow: Student S BookAngel Garcia FloresNo ratings yet
- Sentence Combining. Emphasis and VarietyDocument8 pagesSentence Combining. Emphasis and VarietyYamila ReynosoNo ratings yet
- ProductivityDocument10 pagesProductivityAdeNov ChannelNo ratings yet
- KLU - Eng - IP-UNIT 1 - SESSION 3Document42 pagesKLU - Eng - IP-UNIT 1 - SESSION 3venu sree guduriNo ratings yet
- Preterito IndefinidoDocument16 pagesPreterito IndefinidolittlefbitchNo ratings yet
- 1relative pronouns2ED&ING3PASSIVEVsACTIVEDocument8 pages1relative pronouns2ED&ING3PASSIVEVsACTIVEMiguelRodriguezCalderonNo ratings yet
- Sanskrit Vol1Document203 pagesSanskrit Vol1ngc1729100% (7)
- English Test 10°Document5 pagesEnglish Test 10°Liliana fernandezNo ratings yet