Professional Documents
Culture Documents
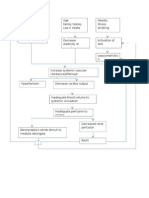
Concept Map Covid
Concept Map Covid
Uploaded by
Maieca DemecilloCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concept Map Covid
Concept Map Covid
Uploaded by
Maieca DemecilloCopyright:
Available Formats
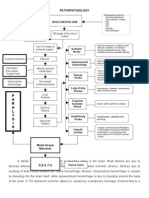
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CONCEPT MAP
Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, High Risk, Severe acute Respiratory Infection.
Viral Pneumonia Related To Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection
Predisposing Factor Precipitating Factors
Travellers that travels
Age: >60 years old, (WHO) to places with COVID
<14 years old (pediatric CC)
Infected person cough, sneeze or 19
Patient with the following
talk without social distancing Direct or Indirect
disease condition: (DM, HIV,
Cardiovascular diseases,
contact with the
cancer ) infected person
Extreme obesity Immunocompromised
Taking Immunosuppresant Smoking
drugs
Undergoing chemotherapy Droplets with virus will spread to
another person
Inhalation of virus from the People touches contaminated
infected person objects
LEGEND
Virus will enters to URT and LRT Direct contact with the virus
Prediposing Factors
Precipitating Factors
Nursing Diagnosis
Signs and symptoms
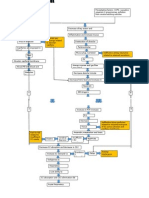
Medical/nursing management
Accidentally touches the mouth,
Disease process eyes, and nose
Virus will enter to mucous
membranes
From mucous membranes to
Respiratory tract
Virus rapidly replicate to the lungs
Invasion of virus in the lungs Sensory detects Foreign substance
in the lungs (Virus)
High fever-38.8C
Hot flushed skin Immune response triggered Stimulation of cough in attempts
RR-56cpm suddenly, instead of gradually to remove the foreign substance
PR-120bpm
Irritable
Hyperactive Immune Response No-productive cough Ineefective airway
Altered body Excessive coughing clearance related to
temperature related o ineffective cough
viral infection
Oxygen supplementation
Unexpected Excessive release of
MDI-Albuterol 2 puff
Loosen clothing inflammatory Cytokines
Elavate HOB
Analgesics
Tepid sponge bath
Monitor I and O
Influx of inflammatory cells
(Neutrophils, Macrophages, platelets)
Neutrophil aggregation and
release of mediators
(ROS, Proteolysic Enzyme, PAF,
Compliment activation
Damage to lung tissues
Progressive Fibrosis Increase Capillary Injury to bronchial Mucuosa
and Scarring permeability
Progressive Fibrosis
and Scarring
Causing fluid to
leak in and out of
the lungs Damage to goblet Cells Destruction of the cells Irritation of Vagus Nerve
Progressive Fibrosis
and Scarring
Decrease mucous Accumulation of cell debris Cough Reflex/Stimulation
Production in the lungs
Accumulation of cell debris
in the lungs
Allowing virus to enter in Accumulation of fluid in the
different parts of the body alveoli and alveolar space
Elevated WBC-
20,000mEq/dL Alveolar inflammation
High grade fever
Pain and discomfort
Cold clammy skin
Systemic Viral replication Alveolar Edema Impaired gas exchange
related to ineffective
lung function secondary
Analgesic to alveolar edema
Tepid sponge bath
Extreme shortness of
Crystalloids fluid
breath that worsens
Vassopresor
Septic Shock when lying down Oxygen supplementation
steroids
Feeling of drowning MDI-Albuterol 2 puff
Cold clammy skin Elavate HOB
Restless
Risk for deficient fluid volume related O2sat- 88%
increase capillary permeability
Consolidation Impaired Oxygen Circulation
Impaired gas exchange
related to ineffective
z lung function secondary ABG result: Impaired Oxygen Circulation
Pneumonia pH-7.0mmHg
to alveolar edema
PCO2-50mmHg
Oxygen supplementation O2sat- 88%
MDI-Albuterol 2 puff
Elavate HOB
Decrease oxygen in the
body
And increase Carbon Dioxide
Ineffective tissue
perfusion related to
decrease oxygen in the Decrease in tissue Perfusion PCO2 retention
body secondary to
decrease lung expansion
Oxygen supplementation Cyanosis
MDI-Albuterol 2 puff Pallor
Body response to abnormal
Elavate HOB Delayed capillary refill
activity
4 seconds
Generalized weakness
Body malaise
Stimulation of SNS to alter
functions of the lungs and
heart in attempts to
compensate abnormalities
Shortness of breath
Shallow breathing
Irritable Increase in RR as the body An increase HR as the body
Palpatation
RR-56cpm attempts to get rid-off attempts to deliver enough
PR- 120 bpm
Use of retained carbon dioxide oxygen all throughout the
Restless
sternocledomastiod And get more oxygen for body
muscle when inhaling the body needs
Increase cardiac output
related to Compensatory Increase cardiac workload
Ineffective breathing mechanism
pattern related to
compensatory mech. Tachypnea
Oxygen supplementation
ECG
Oxygen supplementation
Anti-arrythmic agent Tachycardia
MDI-Albuterol 2 puff
Elavate HOB
Recovery Acute Respiratory Distress Death
syndrome
You might also like
- CBT Sample MCQs - Source Royal Marsden ANSWERSDocument16 pagesCBT Sample MCQs - Source Royal Marsden ANSWERSarchana100% (9)
- ARDS Concept MapDocument1 pageARDS Concept Mapadro100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaAnn Wincel Nobleza82% (17)
- COPD PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DiagramDocument2 pagesCOPD PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Diagramcris_198893% (15)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeAqeel Al-Mahdaly0% (1)
- A&P 1 2016 Course OutlineDocument22 pagesA&P 1 2016 Course OutlinewizzieeNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Sa CobidDocument7 pagesPathophysiology Sa Cobidkuro hanabusa100% (2)
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsDocument6 pagesNon-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsNeil Andro Marcelo100% (1)
- Coronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology PDFMohd Amir Bin Bashir0% (1)
- Congestive Heart Failure Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageCongestive Heart Failure Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionKen100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaShermane Criszen F. Sallan100% (4)
- Case Study - EmphysemaDocument6 pagesCase Study - Emphysemamackie_041992No ratings yet
- Final Lung Cancer Concept MapDocument3 pagesFinal Lung Cancer Concept MapKaycee TolingNo ratings yet
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHypertension PathophysiologyZaida Eunice EstabayaNo ratings yet
- NCP: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and AsthmaDocument15 pagesNCP: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and AsthmaJavie100% (5)
- Pathophysilogy of Primary HypertensionDocument1 pagePathophysilogy of Primary Hypertensionromeo rivera75% (4)
- Qtsoi Concept MapDocument5 pagesQtsoi Concept MapGenella BabantoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AsthmaDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of AsthmaEden Mae100% (4)
- Pathophysiology: Patient B's Age: 28 Years OldDocument7 pagesPathophysiology: Patient B's Age: 28 Years Oldkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - PathophysiologyJoann67% (3)
- Patho Pleural EffusionDocument2 pagesPatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- Hypovolemic ShockDocument2 pagesHypovolemic Shockatilano_patrickNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesPathophysiologyCee SanchezNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAcute Respiratory Failure Pa Tho Physiologyroseanne18100% (4)
- Stoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Document7 pagesStoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Mark Anthony Taña GabiosaNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument3 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress SyndromeJorie Roco100% (1)
- Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePneumonia PathophysiologyDee Sarajan100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of COPDDocument42 pagesPathophysiology of COPDRegineCuasSulib100% (3)
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument2 pagesAcute Respiratory FailurePaolo Luis MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of COPD - The BasicsDocument11 pagesPathophysiology of COPD - The BasicstiaranindyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Acute Respiratory FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Respiratory FailureKimberly Regacho88% (8)
- PneumoniaDocument20 pagesPneumoniaKartika RezkyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Angina PectorisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Angina PectorisCheryl100% (1)
- Covid NCPDocument6 pagesCovid NCPNathalia Cabalse100% (2)
- Left Sided & Right Sided Heart FailureDocument29 pagesLeft Sided & Right Sided Heart FailureRachelle Ayn100% (3)
- Ards Cmap FinalDocument4 pagesArds Cmap FinalPam Araune67% (3)
- Pancreatitis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Document7 pagesPancreatitis: (Alterations in Metabolic and Endocrine Functions)Jorie Roco0% (1)
- Munity Acquired Pneumonia PathoDocument1 pageMunity Acquired Pneumonia PathoJohanna Elaine Tandoc100% (1)
- Renal Diseases PathophysiologyDocument6 pagesRenal Diseases PathophysiologyBilly Gayados100% (1)
- Case Study of Pneumonia With Underlying Covid 19Document41 pagesCase Study of Pneumonia With Underlying Covid 19Angel CauilanNo ratings yet
- AnginaDocument12 pagesAnginaHermiie Joii Galang Maglaquii0% (1)
- Hiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageHiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramTrixie Arabit100% (1)
- Pathophysiology PTBDocument1 pagePathophysiology PTBNikki Galvez Braganza100% (2)
- Nursing InterventionsDocument10 pagesNursing Interventionspaulinian_nurseNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CVD InfarctDocument1 pagePathophysiology CVD InfarctElisa KerrNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBronchitis PathophysiologyMichael Urrutia100% (1)
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHypertension PathophysiologyLuis LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Top 3 Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesTop 3 Nursing Care PlanAC TamayoNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure COncept MapDocument2 pagesHeart Failure COncept MapJrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument54 pagesPulmonary Embolismعزيزي أحمد نوردين0% (1)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5Document21 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Stage 5Kristine Anne Soriano100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of MI, COPD and BPHDocument10 pagesPathophysiology of MI, COPD and BPHSarah Lim100% (1)
- Pleural Effusion Case StudyDocument5 pagesPleural Effusion Case Studyjanice ianNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAppendicitis PathophysiologyAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument3 pagesPathophysiology CHFKim Franzel M. Rabe100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of CHFDocument1 pagePathophysiology of CHFLance MarquezNo ratings yet
- ChickenpoxDocument2 pagesChickenpoxyai19100% (2)
- Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable Factors: Cellular Destruction of Infected Cells Attracts Nearby Immune Cells (NK Cells)Document2 pagesNon-Modifiable Factors Modifiable Factors: Cellular Destruction of Infected Cells Attracts Nearby Immune Cells (NK Cells)Venice Joy CelociaNo ratings yet
- Selincio Activity05Document2 pagesSelincio Activity05Ella Jane SelincioNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaMaria Cristina100% (1)
- Corona Virus Report by Ayush MittalDocument9 pagesCorona Virus Report by Ayush MittalAyush MittalNo ratings yet
- IGCSE - CIE - Combined 2017 2018 SyllabusDocument57 pagesIGCSE - CIE - Combined 2017 2018 SyllabusYu SunNo ratings yet
- Nclex Test 04Document47 pagesNclex Test 04Humberto RussoNo ratings yet
- The Critically Ill Child Pediatrics 2018 - PDFDocument17 pagesThe Critically Ill Child Pediatrics 2018 - PDFgtsantosNo ratings yet
- E REVIEW ASSIGNMENT 2013 Website AnnouncementDocument3 pagesE REVIEW ASSIGNMENT 2013 Website AnnouncementwiltechworksNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Imaging ChestDocument1,485 pagesDiagnostic Imaging ChestMạnh Đình Nguyễn100% (1)
- Foreign Body in Pharynx, Larynx, Trachea & Tracheobronchial TreeDocument26 pagesForeign Body in Pharynx, Larynx, Trachea & Tracheobronchial TreehashyNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesDisorders of The Respiratory SystemAjay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 - Just Go With The FlowDocument24 pagesActivity 3 - Just Go With The FlowJessica Manawes NavorNo ratings yet
- Papp 2015 PFTDocument30 pagesPapp 2015 PFTWivina Bancoro100% (1)
- Understanding Embryonic Breathing, Part 1 - Abdominal Breathing - The Four Corners of Breath - Meditation For BeginnersDocument16 pagesUnderstanding Embryonic Breathing, Part 1 - Abdominal Breathing - The Four Corners of Breath - Meditation For BeginnersDard Tong100% (3)
- 2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE - GULF) Biology Practical Booklet-Ch1-6Document32 pages2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE - GULF) Biology Practical Booklet-Ch1-6Van halenNo ratings yet
- Computer-Controlled Mechanical Simulation of The Artificially Ventilated Human Respiratory SystemDocument13 pagesComputer-Controlled Mechanical Simulation of The Artificially Ventilated Human Respiratory SystemOancea AdrianNo ratings yet
- DNB Respiratory Medicine Paper2Document4 pagesDNB Respiratory Medicine Paper2lakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System - Grade 7Document39 pagesThe Circulatory System - Grade 7VANSHIKA AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Ma. Leah Bas RHD Case 1Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan Ma. Leah Bas RHD Case 1Jezzy VeeNo ratings yet
- Organs and Organ Systems P1Document8 pagesOrgans and Organ Systems P1Arniel CatubigNo ratings yet
- Gas Exhange Grade 11 Life SciencesDocument22 pagesGas Exhange Grade 11 Life Sciencesgg5834256No ratings yet
- Phylum Chordata-BirdsDocument49 pagesPhylum Chordata-BirdsJerome JeremiasNo ratings yet
- A Study of Efficiency of Breathing Exercises To Improve Pulmonary FX in SCi PtsDocument6 pagesA Study of Efficiency of Breathing Exercises To Improve Pulmonary FX in SCi PtsMarion AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Bubble CPAPDocument36 pagesBubble CPAPSamsul MujakarNo ratings yet
- 11 Mechanical Ventilation & Endotracheal Intubation Nursing Care Plans and Management - NurseslabsDocument55 pages11 Mechanical Ventilation & Endotracheal Intubation Nursing Care Plans and Management - NurseslabsCarissa EstradaNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Breathing: The Functional Screening Frequently ForgottenDocument24 pagesDysfunctional Breathing: The Functional Screening Frequently ForgottenHONGJYNo ratings yet
- MCNDocument12 pagesMCNIan CarodanNo ratings yet
- Episode 10Document18 pagesEpisode 10Pang Chixx90% (31)
- Thorax and Lungs: Chapter EighteenDocument12 pagesThorax and Lungs: Chapter Eighteengrool29r67% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology of LarynxDocument13 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of LarynxAmin MasromNo ratings yet
- Dapus VAPDocument2 pagesDapus VAPsaniaNo ratings yet