Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Young Ji College: Bridging The Gap Between Traditional and Whole Language Perspective in Teaching Reading
Young Ji College: Bridging The Gap Between Traditional and Whole Language Perspective in Teaching Reading
Uploaded by
KathMae BoaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Young Ji College: Bridging The Gap Between Traditional and Whole Language Perspective in Teaching Reading
Young Ji College: Bridging The Gap Between Traditional and Whole Language Perspective in Teaching Reading
Uploaded by
KathMae BoaCopyright:
Available Formats
YOUNG JI COLLEGE
S1 B1 L2 SUNNY BROOKE II, BRGY. SAN FRANCISCO, GENERAL TRIAS CITY,
CAVITE
COURSE SYLLABUS
nd
2 Semester AY 2020-2021
COURSE CODE : HUMANITIES 2
COURSE TITLE : Art, Man and Society
COURSE CREDIT : 3 units
TIME DURATION : 3 hours/week (Room 201)
A. COURSE DESCRIPTION
The purpose of this course is to improve your reading skills through the practice of
vocabulary enrichment, reading comprehension exercises, speed reading strategies, written
responses, discussions, and reflections. Exploring and examining the entire reading process, you
will become a more confident, independent, effective, and efficient reader.
B. COURSE OBJECTIVES
At the end of the course, the students are expected to be able to:
By the completion of this course you should be able to:
1. Describe the historical situations of the prophets Daniel and John
2. Summarize the developing sequence of Gentile world powers as described by Daniel
3. Demonstrate how Daniel’s vision of the 70 “weeks” relates to Christ’s first and second
comings
4. Discuss the seven churches of Revelation showing how they might relate to church
history
5. Summarize the possible sequencings of the seal, trumpet, and bowl judgments in
Revelation
6. Relate the various visions of Revelation to the anticipated tribulation, kingdom, and
eternal state
A. COURSE OUTLINE
Week Topics
1 Introduction to course
A Reading System for Effective Readers
2 Bridging the Gap Between Traditional and Whole Language
Perspective in Teaching Reading
Phonics vs. Whole Language Approach
The Reading Teacher
3 Making Transitions Toward Holistic Teaching
Instructional Beliefs
Reading Materials
Curriculum Designs
Classroom Environment
Community Involvement
4 Preliminary Examinations
5 Understanding Reading: Defining and Redefining Beliefs
Understanding the Reading Process
Linear
cyclical
learning alphabet
recognizing
decoding
mouthing of words
fluency
6 Aspects that influence reading development
Cognitive Aspects
Affective Aspects
Social Aspects
Linguistic Aspects
7 Theories of Reading Process
Bottom-Up Theory
Top-Down Theory
Interactive Theory
Transactional Theory
8 Developing Word Recognition Skills (Word Attack or Decoding
Skills)
Phonics or Whole Language
What is phonics instruction
Goal of phonics instruction
Content of Phonics Instruction word families
9 Word Recognition Instruction
Alphabetic Principle
Alphabetic Knowledge
Phonemic Awareness – letter-sound relationship
phonological Awareness – ability to produce sounds
Print Awareness
Decodable Text
10 Midterm Examinations
11 Acquiring a Reading Vocabulary
Strategies of Building Vocabulary
Structural Analysis
Word Associations
Context Clues
Homonyms, Homographs,
Heteronyms
Figures of Speech
Idioms
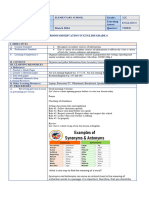
Synonyms and Antonyms
Word Map
12 Comprehending Text
A. Issues in Teaching Reading Comprehension (Other
Online Resources)
1. Less Time in Reading
2. Teachers Manual in Reading
3. Curriculum in Reading
4. School Management and Priorities in Reading
5. Teacher's Role in Reading
13 Word Recognition Strategies
. Sight Words – Dolche List, Phil-IRI, Frye List
Context Clues
Structural Analysis
Dictionary
Alphabet Book and Chart
Songs, Chants, Rhymes and Jingles
14 Two Theories in Comprehending Text
1. Scheme Theory – Schema? Schemata?
2. Generative Learning Theory
Reading Difficulties and Disability
A. ADHD
B. Myopia
C. Hyperopia
15 Some Teaching Strategies in Developing Reading
Comprehension
A. Story Grammar
B. Story Maps
C. Story Frames
D. Story Sequence/ Clothesline
E. Cloze Procedure
F. Predicting Outcomes
G. Generalizing
H. Noting Details
I. Open-Ended Questions
E. Types of Comprehension Skills
1. Literal
2. Inference
3. Prediction
4. Evaluation
5. Application
16 Bloom's Taxonomy of Cognitive Domain
1. Knowledge
2. Comprehension
3. Application
4. Analysis
5. Synthesis
17 Developing Independent and Fluent Readers
A. Sustained Silent Reading (SSR)
B. Fluency in Reading
C. Question – Answer Relationship (QAR by Raphael)
D. Reciprocal Questioning (ReQuest by Dresher et. al.)
18 Final Examinations
A. COURSE REQUIREMENTS
Class Standing/ Participation (attendance, recitation, quizzes, activities and portfolios)
Major Examinations (Prelims, Midterms and Finals)
Project (research materials on assigned topics, narrative reports and well-written
compositions)
B. GRADING SYSTEM
Class Standing (50%)
Attendance 5%
Class Recitation/ Participation 10%
Quizzes 10%
Assignments/Homework 10%
Portfolio 15%
Periodical Examinations (30%)
Projects (20%)
Total (100%)
C. REFERENCES
Ocvirk, et.al. Art Fundamentals, Theory and Practice (Tenth Edition). Mc
Graw Hill Companies, Inc., 2006.
Martin, F. David, Jacobus, Lee A. The Humanities through the Arts (Sixth
Edition). Mc Graw Hill Companies, Inc., 2004.
Ortiz, M.A., Art Perception and Appreciation.
Sanchez, et.al. Introduction to the Humanities
Francisco, Zulueta M. The Humanities
You might also like
- Developmental ReadingDocument35 pagesDevelopmental ReadingCamille Punongbayan AlicawayNo ratings yet
- Developmental Reading Syllabus OBEDocument9 pagesDevelopmental Reading Syllabus OBEPearl Ogayon83% (6)
- Module 8 - Reading DevelopmentDocument51 pagesModule 8 - Reading DevelopmentRachelle malnawaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Reading 2Document24 pagesDevelopmental Reading 2Maricel Rudela100% (6)
- EL 3 Theories of LanguageDocument6 pagesEL 3 Theories of LanguageMarcelino TayamenNo ratings yet
- tsl515 Scheme of Work LatestDocument17 pagestsl515 Scheme of Work LatestMohamed RizalNo ratings yet
- Comprehension and Communication Skills in English PDFDocument130 pagesComprehension and Communication Skills in English PDFshivakumarNo ratings yet
- RPS 202320180114Document11 pagesRPS 202320180114meribrt8No ratings yet
- Listen To A Lecture and Define The Following Statements.: Activity 1. Listening Comprehension What Is A Language?Document6 pagesListen To A Lecture and Define The Following Statements.: Activity 1. Listening Comprehension What Is A Language?Жанат СарсеноваNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Psycholinguistics, BA BOS-1Document6 pagesIntroduction To Psycholinguistics, BA BOS-1Katyayni ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Science of ReadingDocument41 pagesIntro To Science of Readingapi-223530755No ratings yet
- RPS ReadingDocument11 pagesRPS ReadingNursalinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Lesson 1Document20 pagesChapter 1 Lesson 1Daniel Toralba LptNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives: Phrases EN7G-II-b-1: PhrasesDocument12 pagesI. Objectives: Phrases EN7G-II-b-1: PhrasesJosenia Constantino100% (1)
- ENG 8 Course Syllabus 2018 FullDocument17 pagesENG 8 Course Syllabus 2018 FullRalph Benedict CruzNo ratings yet
- Second Language Acquisition and Foreign Language TeachingDocument5 pagesSecond Language Acquisition and Foreign Language TeachingOllian300No ratings yet
- ENG 467 - Course OutlineDocument7 pagesENG 467 - Course OutlineAbdullah Khalid Turki AlmutairiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Teaching Reading and ListeningDocument4 pagesSyllabus Teaching Reading and ListeningRonel Gautane Fresado100% (1)
- Philo 1 Course Guide FT 2013Document13 pagesPhilo 1 Course Guide FT 2013Andrea Jasmien P. ArreolaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Reading 2 OutlineDocument4 pagesDevelopmental Reading 2 OutlineJuville Anne CarletNo ratings yet
- ENGL101Document133 pagesENGL101Kashif Noor MirzaNo ratings yet
- Weeek 3-Q1Document3 pagesWeeek 3-Q1Lyn VallesNo ratings yet
- Eng01: Study and Thinking Skills SyllabusDocument5 pagesEng01: Study and Thinking Skills Syllabusbibliosensei93% (14)
- Oral Comm DLL q1 Wk8Document5 pagesOral Comm DLL q1 Wk8galangmj95No ratings yet
- Report PreparationDocument4 pagesReport PreparationLovely ann BantiloNo ratings yet
- EL 10 SemanticsDocument7 pagesEL 10 SemanticsMarcelino TayamenNo ratings yet
- RPS PSYCHOLINGUISTICS (English)Document9 pagesRPS PSYCHOLINGUISTICS (English)Samsung MedanNo ratings yet
- 5th DLP - Eng 9Document5 pages5th DLP - Eng 9Kaye EscobarNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1: Inquiry-Based Learning and Research-Based LearningDocument7 pagesLESSON 1: Inquiry-Based Learning and Research-Based Learningromil monisNo ratings yet
- Discourse Analysis Weeks Topics Sub TopicsDocument2 pagesDiscourse Analysis Weeks Topics Sub TopicsDifia OctafaniNo ratings yet
- Didactic Unit TemplateDocument3 pagesDidactic Unit TemplateRosa Pancorbo100% (1)
- Scheme of Studies Department Course Title Eligibility Credit Hours DurationDocument4 pagesScheme of Studies Department Course Title Eligibility Credit Hours DurationMariaNo ratings yet
- ENG-018 ModuleDocument150 pagesENG-018 ModuleAmery Colin Pagayunan LagartaNo ratings yet
- Language, Learning, and TeachingDocument36 pagesLanguage, Learning, and TeachingAngela DiazNo ratings yet
- LalamovesDocument4 pagesLalamovesAbby CastroNo ratings yet
- Psycholinguistics Syllabus I Period 2022Document6 pagesPsycholinguistics Syllabus I Period 2022Keyrin Meholy Euceda PazNo ratings yet
- Grade 6-3rd Quarter Week 7Document4 pagesGrade 6-3rd Quarter Week 7Kim Lester CatarojaNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan For English 8: Western Mindanao Adventist Academy "The School For Better Future"Document3 pagesLearning Plan For English 8: Western Mindanao Adventist Academy "The School For Better Future"SirJo Rios NillosNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Teching Listening and ReadingDocument10 pagesSyllabus in Teching Listening and ReadingEmelita Abe CoronelNo ratings yet
- Performance Standard Learning Competency & Its Code Key ConceptDocument5 pagesPerformance Standard Learning Competency & Its Code Key Conceptmariannemaegalay778No ratings yet
- Speech Purposes, Speech Delivery and Physical Features of A Speaker DLLDocument3 pagesSpeech Purposes, Speech Delivery and Physical Features of A Speaker DLLRJ FernandezNo ratings yet
- Compiled Module in Eed 17Document27 pagesCompiled Module in Eed 17Ruby Jane DuradoNo ratings yet
- FLE 2 KoreanDocument5 pagesFLE 2 KoreanMarcelino TayamenNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris LV IIIDocument154 pagesBahasa Inggris LV IIIAndini PermataNo ratings yet
- Speech and Oral Communication Module (Front Page)Document4 pagesSpeech and Oral Communication Module (Front Page)Deah Dee100% (1)
- An Overview of Literacy Development ShareDocument58 pagesAn Overview of Literacy Development ShareEndiNo ratings yet
- G9 English DLL - Q1 - Week 1Document5 pagesG9 English DLL - Q1 - Week 1Roylyn Joy CarlosNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Universidad Nacional de San Cristobal de HuamangaDocument4 pagesSyllabus: Universidad Nacional de San Cristobal de HuamangaCarlos RamosNo ratings yet
- Proud AsiansDocument1 pageProud AsiansKristelle Joy TapiaNo ratings yet
- 11 Pca 9TH GradeDocument35 pages11 Pca 9TH GradeGeraldine AlcivarNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LOG: GRADE 1 To 12Document3 pagesDaily Lesson LOG: GRADE 1 To 12RJ FernandezNo ratings yet
- 8b Bics Calp ChecklistchartDocument6 pages8b Bics Calp ChecklistchartJuan BautistaNo ratings yet
- Performance Standard Learning Competency & Its Code Key ConceptDocument5 pagesPerformance Standard Learning Competency & Its Code Key Conceptmariannemaegalay778No ratings yet
- Comprehension and Communication Skills in English Engl101Document133 pagesComprehension and Communication Skills in English Engl101Aryan rajNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ELE 501 Descriptive and Applied LinguisticsDocument3 pagesSyllabus ELE 501 Descriptive and Applied LinguisticsEL FuentesNo ratings yet
- Eng 10 Teaching of Listening and ReadingDocument2 pagesEng 10 Teaching of Listening and ReadingRamil GofredoNo ratings yet
- Teaching ListeningDocument17 pagesTeaching ListeningMontasser El Joudi100% (1)
- DLP English 6 DEARDocument3 pagesDLP English 6 DEARHek AdelNo ratings yet
- Mod 1.1 Language Learning ConceptsDocument43 pagesMod 1.1 Language Learning Conceptsivan.el.rey1340No ratings yet
- Developing Language and Literacy: Effective Intervention in the Early YearsFrom EverandDeveloping Language and Literacy: Effective Intervention in the Early YearsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Know Where Your Are in The CyberspaceDocument3 pagesKnow Where Your Are in The CyberspaceKathMae BoaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument10 pagesBIOLOGYKathMae BoaNo ratings yet
- ActivityDocument2 pagesActivityKathMae BoaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System and Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesDigestive System and Respiratory SystemKathMae BoaNo ratings yet
- The Causes of The Reformation: Long-Term Cause Short-Term Cause Event Short-Term Consequence Long-Term ConsequenceDocument2 pagesThe Causes of The Reformation: Long-Term Cause Short-Term Cause Event Short-Term Consequence Long-Term ConsequenceKathMae BoaNo ratings yet
- 9 PDFDocument11 pages9 PDFKathMae BoaNo ratings yet
- Complete The Given Sentences. Write The Letter of Your Answer On Your Answer SheetDocument5 pagesComplete The Given Sentences. Write The Letter of Your Answer On Your Answer SheetReminily Ranque DahanNo ratings yet
- Edward William Lane's Lexicon - Volume 7 - Page 186 To 277Document92 pagesEdward William Lane's Lexicon - Volume 7 - Page 186 To 277Serge BièvreNo ratings yet
- Afm Early Childhood ApplicationDocument17 pagesAfm Early Childhood ApplicationShan Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- List of Irregular VerbsDocument4 pagesList of Irregular Verbsuniversal_symph1225No ratings yet
- Unit 10: Communication A. PhoneticsDocument14 pagesUnit 10: Communication A. PhoneticsVinh Lê HoàngNo ratings yet
- Andrei Platonov - The Foundation Pit (1975)Document164 pagesAndrei Platonov - The Foundation Pit (1975)blackonstage100% (1)
- Better Spoken English Prof. Shreesh Chaudhary Department of Humanities & Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasDocument30 pagesBetter Spoken English Prof. Shreesh Chaudhary Department of Humanities & Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasmuralitlcNo ratings yet
- Test Shakespeare 11Document2 pagesTest Shakespeare 11camiloNo ratings yet
- HW Elem TRD Unit Test 12bDocument3 pagesHW Elem TRD Unit Test 12bKiggundu Aslan BadruNo ratings yet
- Rubric DetailDocument1 pageRubric Detailapi-250002450No ratings yet
- Phonics Scope & Sequence - The Measured MomDocument4 pagesPhonics Scope & Sequence - The Measured MomSathya Bharathi100% (1)
- Vis DK 25 Programming GuideDocument210 pagesVis DK 25 Programming GuideshrihnNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology Introductory LectureDocument21 pagesPhonetics and Phonology Introductory LectureDr.Eman LinguisticsNo ratings yet
- L1 6Document32 pagesL1 6anshikamittal2626No ratings yet
- Guidelines For Preparation of Project Proposal: (BBA Students)Document4 pagesGuidelines For Preparation of Project Proposal: (BBA Students)Abdul GhaniNo ratings yet
- Conditionals & Mixed ConditionalsDocument8 pagesConditionals & Mixed ConditionalsMarcela CoroleaNo ratings yet
- Pecha KuchaDocument20 pagesPecha KuchaAlexis SolimanNo ratings yet
- Focus4 2E Vocabulary Quiz Unit5 GroupA 1kolDocument2 pagesFocus4 2E Vocabulary Quiz Unit5 GroupA 1kolAleksandra GonetNo ratings yet
- History Unit 1 G-12Document7 pagesHistory Unit 1 G-12Ebsa Ademe100% (1)
- Grammar: Present Tense Verb Be, Subject PronounsDocument2 pagesGrammar: Present Tense Verb Be, Subject PronounsLuna LuneraNo ratings yet
- Readme PDFDocument10 pagesReadme PDFHudson BenevidesNo ratings yet
- Ingles Tema 4 5º Santillana .2Document4 pagesIngles Tema 4 5º Santillana .2Miriam Carcelén LópezNo ratings yet
- Writing PHD Thesis Using LATEXDocument57 pagesWriting PHD Thesis Using LATEXvimalhetNo ratings yet
- Olympic 2018 - Tien Giang 11Document17 pagesOlympic 2018 - Tien Giang 11Trần Quốc ToảnNo ratings yet
- Remedial Quiz For Infinitive PhraseDocument18 pagesRemedial Quiz For Infinitive PhraseSyrile MangudangNo ratings yet
- The Natural Approach: Alexis Martínez-RamírezDocument33 pagesThe Natural Approach: Alexis Martínez-RamírezAlePsics MrtínzNo ratings yet
- IInd Year SyllabusDocument238 pagesIInd Year SyllabusKamal KishoreNo ratings yet
- Who Is Noah ChomskyDocument4 pagesWho Is Noah ChomskyAna100% (1)
- Complete Exam and Solution Aptis PDFDocument70 pagesComplete Exam and Solution Aptis PDFGracemmrNo ratings yet
- Grammar Book 1Document121 pagesGrammar Book 1auma100% (1)