Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Seven Traditions of Communication Theory
Seven Traditions of Communication Theory
Uploaded by
Таня Мовчан0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views3 pagesThe document outlines 7 traditions of communication theory - rhetorical, semiotic, phenomenological, cybernetic, socio-psychological, socio-cultural, and critical. Each tradition theorizes communication and problems of communication differently and appeals to different audiences. The traditions also take differing approaches in their arguments against each other based on their key terms, explanations of communication, and views on challenges.
Original Description:
Original Title
TOC-Seminar 1-tables
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines 7 traditions of communication theory - rhetorical, semiotic, phenomenological, cybernetic, socio-psychological, socio-cultural, and critical. Each tradition theorizes communication and problems of communication differently and appeals to different audiences. The traditions also take differing approaches in their arguments against each other based on their key terms, explanations of communication, and views on challenges.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views3 pagesSeven Traditions of Communication Theory
Seven Traditions of Communication Theory
Uploaded by
Таня МовчанThe document outlines 7 traditions of communication theory - rhetorical, semiotic, phenomenological, cybernetic, socio-psychological, socio-cultural, and critical. Each tradition theorizes communication and problems of communication differently and appeals to different audiences. The traditions also take differing approaches in their arguments against each other based on their key terms, explanations of communication, and views on challenges.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
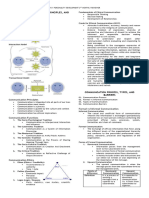
Seven Traditions of Communication Theory
Rhetorical Semiotic Phenomenological Cybernetic Socio- Socio-Cultural Critical
Psychological
Communication The practical art Intersubjective Experience of Information Expression, inter- (Re)production Discursive
theorized as: of discourse mediation by otherness; processing action & influence of social order reflection
signs dialogue
Problems of Social exigency Misunderstanding Absence of, or Noise; overload; Situation requiring Conflict; Hegemonic
communication requiring or gap between failure to sustain, underload; a manipulation of alienation; ideology;
theorized as: collective subjective authentic human malfunction or causes of behavior misalignment; systematically
deliberation and viewpoints relationship "bug" in a system to achieve specified failure of distorted speech
judgment outcomes coordination situation
Key terms with Art, method, Sign, symbol, icon, Experience, self Source, receiver, Behavior, variable, Society, Ideology,
specific communicator, index, meaning, &other, dialogue, signal, informa- effect, personality, structure, dialectic,
meaning audience, referent, code, genuineness, tion, noise, feed- emotion, practice, ritual, oppression,
strategy, language, medium, supportiveness, back, redundancy, perception, rule, consciousness-
commonplace, (mis)understanding openness network, function cognition, attitude, socialization, raising,
logic, emotion interaction culture, identity, resistance,
co-construction emancipation
Plausible when Power of words; Understanding All need human Identity of mind Communication beliefs & people in groups
appeals to: value of requires common contact, should and brain; value of reflects personality feelings bias affect one
informed language; treat others as information and judgments another.
judgment; omnipresent persons, respect logic; complex
improvability of danger of differences, seek systems can be
practice miscommunication common ground unpredictable
Useful results Mere words are Words have Communication is Humans and Humans are Individual Naturalness &
for challenges not actions; correct meanings skill; the word is machines differ; rational beings; we agency & rationality of
in: appearance is & stand for not the thing; facts emotion is not know our own responsibility; tradi-tional
not reality; style thoughts; codes & are objective and logical; linear minds; we know absolute social order;
is not substance; media are neutral values subjective order of cause and what we see. identity of self; objectivity of
opinion is not channels effect naturalness of sci-ence &
truth the social order technology
Argumentation across Traditions
Rhetorical Semiotic Phenomenological Cybernetic Socio-psychological Socio-cultural Critical
Against The art of rhetoric We do not use Strategic communi- Intervention in Rhetoric lacks good Rhetorical theory is Rhetoric reflects
rhetoric can be learned signs; rather cation is inherently complex systems empirical evidence culture bound & traditionalist,
only by practice; they use us. inauthentic & often involves technical that its persuasive overemphasizes instrumentalist,
theory merely counterproductive. problems rhetoric techniques actually individual agency vs. & individualist
distracts. fails to grasp. work as intended. social structure. ideologies.
Against All use of signs is Langue is a fic- Langue-parole and Meaning consists Semiotics fails to Sign systems are not Meaning is not
semiotics rhetorical. tion; meaning & signifier-signified of functional re- explain factors that autonomous; they fixed by a code;
intersubjecti- are false distinc- lationships within influence the pro- exist only in the it is a site of
vity are tions. Languaging dynamic in- duction & inter- shared practices of social conflict.
indeterminate constitutes world. formation systems. pretation of messages. actual communities.
Against Authenticity is a Self & other are Other’s experience Phenomenologica Phenomenological Intersubjectivity is Individual
pheno- dangerous myth; semiotically de- is not experienced l "experience" introspection falsely produced by social consciousness is
menolo- good communica- termined subject directly but only as must occur in the assumes self-aware- processes that socially consti-
gy tion must be positions & exist constituted in ego’s brain as ness of cognitive phenomenology fails tuted, thus
artful, hence only in/as signs. consciousness. information processes. to explain. ideolo-gically
strategic. processing. distorted.
Against Practical reason Functionalist Functionalism fails The observer Cybernetics is too Cybernetic models Cybernetics re-
cyberne- cannot (or should explanations to explain meaning must be included rationalistic; e.g. it fail to explain how flects the domi-
tics not) be reduced to ignore subtleties as embodied, con- in the system, underestimates the meaning emerges in nance of instru-
formal calculation. of sign systems. scious experience. rendering it role of emotion. social interaction. mental reason.
indeterminate.
Against Effects are Socio-psycholo- The subject-object Communication Socio-psychological Socio-psychological Socio-psycho-
socio- situational and gical "effects" dichotomy of involves circular theories have limited "laws" are culture logy reflects
psycho- cannot be are internal socio-psychology causation, not predictive power, bound & biased by ideologies of
logy precisely properties of must be linear causation. even in laboratory. individualism. individualism,
predicted. sign systems. transcended. instrumentalism.
Against Socio-cultural Socio-cultural The social life- The functional Socio-cultural theory Socio-cultural order Socio-cultural
socio- rules etc. are rules etc. are all world has a organization of is vague, untestable, is particular & theory privileges
cultural contexts & systems of phenomenological any social system ignores psychological locally negotiated consensus over
theory resources for rhe- signs. foundation. can be modeled processes that under- but theory must be conflict &
torical discourse. formally. lie all social order. abstract and general. change
Against Practical reason is There is nothing Critique is Self-organizing Critical theory Critical theory im- Critical theory is
critical based in particular outside the text. immanent in every systems models confuses facts & poses an interpretive elitist & without
theory situations not uni- authentic encounter account for social values, imposes a frame, fails to appre- real influence on
versal principles. with tradition. conflict & change dogmatic ideology. ciate local meanings. social change.
You might also like
- Deleuze and Geophilosophy. A Guide and GlossaryDocument224 pagesDeleuze and Geophilosophy. A Guide and GlossaryAlex Paulsen Espinoza100% (1)
- Framing, Agenda Setting and PrimingDocument13 pagesFraming, Agenda Setting and PrimingNely ChambiNo ratings yet
- Ca-103 MAPPING THE TERRITORYDocument4 pagesCa-103 MAPPING THE TERRITORYJerica BonusNo ratings yet
- Rupert Yal P ayala-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesRupert Yal P ayala-WPS OfficeViricoNo ratings yet
- Communication TheoriesDocument39 pagesCommunication TheoriesbungdudiNo ratings yet
- Framework Model For Intercultural CompetencesDocument4 pagesFramework Model For Intercultural CompetencesLylia MezNo ratings yet
- Paradigms For Framing The Conduct of EthnographicDocument1 pageParadigms For Framing The Conduct of EthnographicLAZET618294No ratings yet
- Participatory SensemakingDocument23 pagesParticipatory SensemakingGabana17No ratings yet
- Research ParadigmsDocument7 pagesResearch ParadigmsMitchell Lazarro100% (3)
- Two Social Psychologies - An Integrative Approach - Ch.2 (1985) (Stephan & Stephan)Document27 pagesTwo Social Psychologies - An Integrative Approach - Ch.2 (1985) (Stephan & Stephan)StefNo ratings yet
- 246 - Organizational Behaviour-Pearson Education Limited (2020)Document5 pages246 - Organizational Behaviour-Pearson Education Limited (2020)mozam haqNo ratings yet
- WI2017 EmotionalAffordances PDFDocument7 pagesWI2017 EmotionalAffordances PDFmilanialfredoNo ratings yet
- Top 5 Features of Social Action TheoriesDocument1 pageTop 5 Features of Social Action TheoriesahmeduuonfireNo ratings yet
- Diss WSDocument9 pagesDiss WSJoeyboy MateoNo ratings yet
- A Model of IccDocument13 pagesA Model of Iccnthung13No ratings yet
- Johnson - Image-Schematic Bases of MeaningDocument6 pagesJohnson - Image-Schematic Bases of MeaningRicardo Cunha LimaNo ratings yet
- Approach AnalysisDocument8 pagesApproach AnalysisniceyNo ratings yet
- Survey: Paradigma PenelitianDocument18 pagesSurvey: Paradigma PenelitianHazizah Luvy MahenggarNo ratings yet
- Social Work As Symbolic Interaction: Ben H. KnottDocument8 pagesSocial Work As Symbolic Interaction: Ben H. KnottAnissa AbdiNo ratings yet
- K. J. Holsti - Mixed Emotion 3Document1 pageK. J. Holsti - Mixed Emotion 3Dario KršićNo ratings yet
- Importance of Quali, Etc.Document5 pagesImportance of Quali, Etc.John Ace Revelo-JubayNo ratings yet
- Communication TraditionDocument1 pageCommunication TraditionJustin De VeraNo ratings yet
- Recall, Rethink, Rewrite:: Name: Year and Section: ActivityDocument2 pagesRecall, Rethink, Rewrite:: Name: Year and Section: ActivityJennie KimNo ratings yet
- PComm Lesson 1 Ethics and PrinciplesDocument10 pagesPComm Lesson 1 Ethics and PrinciplesShanley ConcordiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Group 2Document34 pagesChapter 2-Group 2Stelito JumaranNo ratings yet
- Communication, Process, Principles, and EthicsDocument21 pagesCommunication, Process, Principles, and EthicsJohnloyd TamondongNo ratings yet
- Purcom ReviewerDocument6 pagesPurcom ReviewerSambajon, King Ezra BSP 1-3No ratings yet
- Undertanding Social Interaction in Everyday LifeDocument2 pagesUndertanding Social Interaction in Everyday Life24kxrooNo ratings yet
- Teorias de La ComunicacionDocument1 pageTeorias de La ComunicacionLele Joha RozoNo ratings yet
- A Computational Model of Empathy For Interactive AgentsDocument6 pagesA Computational Model of Empathy For Interactive AgentsQysrNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology ReviewerDocument3 pagesSocial Psychology ReviewerAngelou CincoNo ratings yet
- Meneses 2015Document30 pagesMeneses 2015Jeremy BastantaNo ratings yet
- Klapp, O (1958) - Social Types - Process and StructureDocument6 pagesKlapp, O (1958) - Social Types - Process and StructureTesfaye TafereNo ratings yet
- Symbolic From LittlejohnDocument3 pagesSymbolic From LittlejohnDee DeeNo ratings yet
- Carmen-Caldas-Coulthard-Critical Discourse Analysis, Multimodality, and Intercultural CommunicationDocument38 pagesCarmen-Caldas-Coulthard-Critical Discourse Analysis, Multimodality, and Intercultural CommunicationMohammed Al-SharawiNo ratings yet
- Interactive Time TravelDocument27 pagesInteractive Time TravelMaría MarchianoNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document7 pagesDocument 1Winston WolfNo ratings yet
- BrierDocument44 pagesBrierlicgermancruzNo ratings yet
- UCSPDocument3 pagesUCSPCaselyn Magat BuzonNo ratings yet
- Meet 2 - Leadership in Relationship PerspectiveDocument16 pagesMeet 2 - Leadership in Relationship PerspectiveRia FiNo ratings yet
- S1A1 EscalonaL LorenaDocument5 pagesS1A1 EscalonaL LorenaLore EscaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Introduction To CommunicationDocument40 pagesWeek 1 - Introduction To CommunicationShayan AlimohammadiNo ratings yet
- Personality Development 2 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPersonality Development 2 Reviewerralphsimons32No ratings yet
- 10 Principles in Communication TheoryDocument11 pages10 Principles in Communication TheoryJansheer ShahNo ratings yet
- Basic Beliefs Associated With The Major ParadigmsDocument2 pagesBasic Beliefs Associated With The Major ParadigmsMozadded HassanNo ratings yet
- PE10 Lesson 4 5Document33 pagesPE10 Lesson 4 5Evelyn Mae FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Little John and Face CommunicationDocument2 pagesLittle John and Face CommunicationFarel HakimNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Intricacies of Intersubjectivity in Philosophy A Formal AnalysisDocument11 pagesExploring The Intricacies of Intersubjectivity in Philosophy A Formal AnalysisGeron BigayNo ratings yet
- Name: Mario Fabian Ek EstradaDocument4 pagesName: Mario Fabian Ek EstradaTygaNo ratings yet
- Sybolic Interaction Theory/ Symbolic InterctionismDocument2 pagesSybolic Interaction Theory/ Symbolic Interctionismdenmar balbonaNo ratings yet
- Evidence 3 HBSDocument3 pagesEvidence 3 HBSDaniela DuranNo ratings yet
- SOCIETY and CULTURE - Sociological and ANthropological PersDocument29 pagesSOCIETY and CULTURE - Sociological and ANthropological PersEmmanuel Lupo TemplaNo ratings yet
- Phenomenology Vs EthnomethodologyDocument2 pagesPhenomenology Vs EthnomethodologyMargarito EscalanteNo ratings yet
- 4 - Symbolic Interaction TheoryDocument6 pages4 - Symbolic Interaction TheoryBonbon BonitaNo ratings yet
- Communication-The Human Connection-Is The Key To Personal and Career Success.' (Paul J. Meyer)Document6 pagesCommunication-The Human Connection-Is The Key To Personal and Career Success.' (Paul J. Meyer)johnmaximo100% (1)
- MGT 330 Chapter 3 4Document24 pagesMGT 330 Chapter 3 4ahmedeNo ratings yet
- Notes Structural Human EnvironmentDocument5 pagesNotes Structural Human EnvironmentJairo NalugonNo ratings yet
- The Art and Science of Mind-Reading: Guide to Theories, Techniques, and Applications of Mind-ReadingFrom EverandThe Art and Science of Mind-Reading: Guide to Theories, Techniques, and Applications of Mind-ReadingNo ratings yet
- Dark Manipulation Techniques: Persuasion, NLP, Dark Psychology, Emotional Intelligence, Mind-Control, and How to Manage your Emotions (2022 Guide for Beginners)From EverandDark Manipulation Techniques: Persuasion, NLP, Dark Psychology, Emotional Intelligence, Mind-Control, and How to Manage your Emotions (2022 Guide for Beginners)No ratings yet
- The Art of Conscious Communication: Transforming Difficult ConversationsFrom EverandThe Art of Conscious Communication: Transforming Difficult ConversationsNo ratings yet
- Building trust: How to establish empathic relations when designing with peopleFrom EverandBuilding trust: How to establish empathic relations when designing with peopleNo ratings yet
- 88-Article Text-167-1-10-20150920Document22 pages88-Article Text-167-1-10-20150920Ansori DanuzNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument35 pagesLeadershipShubhekchha Neupane PandayNo ratings yet
- Ngec 8Document11 pagesNgec 8Mary Joma InfanteNo ratings yet
- Greenroads Manual v1 5Document471 pagesGreenroads Manual v1 5PIERO JEANPOOL CUYUTUPA MANTARI100% (1)
- Illouz - Cold Intimacies - The Rise of The Homo Sentimentalis PDFDocument22 pagesIllouz - Cold Intimacies - The Rise of The Homo Sentimentalis PDFNéstor Felipe Espitia CabrejoNo ratings yet
- Functions of Culture: A Essay by Mr. G.L.S Anuradha Sab/Bsc/2020A14/007Document5 pagesFunctions of Culture: A Essay by Mr. G.L.S Anuradha Sab/Bsc/2020A14/007Shehan AnuradaNo ratings yet
- Social Media Addiction, RelationshipDocument11 pagesSocial Media Addiction, Relationshipimrulkayes168No ratings yet
- Social Research Notes (2023)Document46 pagesSocial Research Notes (2023)COA DSWD7No ratings yet
- The Lost of San AntonioDocument3 pagesThe Lost of San AntonioJustin Joe GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Collocation & Corpus LinguisticsDocument14 pagesCollocation & Corpus LinguisticsrioNo ratings yet
- Reckitt Benckiser BrochureDocument5 pagesReckitt Benckiser BrochureAbdullah NisarNo ratings yet
- Al-Afkar,: Reformulation of The Islamic Education Philosophy A Study of The Epistemological Thought of Al-FarabiDocument16 pagesAl-Afkar,: Reformulation of The Islamic Education Philosophy A Study of The Epistemological Thought of Al-FarabiHome Tuition Cikgu FarahNo ratings yet
- Mighty Muscles Activity Sheet - Pictures IncludedDocument6 pagesMighty Muscles Activity Sheet - Pictures IncludedamayalibelulaNo ratings yet
- Recognition, Redistribution, RepresentationDocument11 pagesRecognition, Redistribution, RepresentationArun SharmaNo ratings yet
- Questions For Reading Text Meeting 3 English For ArchitectureDocument3 pagesQuestions For Reading Text Meeting 3 English For ArchitectureAnonymous CbIIJLUJNo ratings yet
- The Role and Value of Public Libraries in The Age of Digital TechnologiesDocument9 pagesThe Role and Value of Public Libraries in The Age of Digital TechnologiesDarcy stylesNo ratings yet
- 3 The Value of Doing PhilosophyDocument31 pages3 The Value of Doing PhilosophyJonoel TaborNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Social Studies 8Document9 pagesLesson Plan in Social Studies 8Marie Faith DumpaNo ratings yet
- Anthro N HistoryDocument5 pagesAnthro N HistoryXiaofeng DaiNo ratings yet
- Green Economy and Sustainbledevelopment: Oppose or IntegrateDocument21 pagesGreen Economy and Sustainbledevelopment: Oppose or IntegrateZeghba TalalNo ratings yet
- 2020 Book GreenBuildingsAndRenewableEner PDFDocument641 pages2020 Book GreenBuildingsAndRenewableEner PDFdavid kassisNo ratings yet
- The Ethics of Management Research: An Exploratory Content AnalysisDocument15 pagesThe Ethics of Management Research: An Exploratory Content AnalysisSaravanakkumar KRNo ratings yet
- Sistem Kearsipan Di Sekolah Studi KasusDocument12 pagesSistem Kearsipan Di Sekolah Studi KasusJae TeaNo ratings yet
- A Greek PhilosopherDocument5 pagesA Greek PhilosopherKatowa JimmyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Basic Cognitive Process - Week 1Document6 pagesIntroduction To Basic Cognitive Process - Week 1varshaaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 The Nature of The Human PersonDocument8 pagesMODULE 2 The Nature of The Human PersonMary Grace Lobina ColamboNo ratings yet
- Full Test Bank For Essential Environment The Science Behind The Stories 4Th Edition Withgott PDF Docx Full Chapter ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Test Bank For Essential Environment The Science Behind The Stories 4Th Edition Withgott PDF Docx Full Chapter Chapteroverspinmeetklac40100% (14)
- METHODOLOGY PR2 AllDocument11 pagesMETHODOLOGY PR2 AllSMTOWN SM ENTERTAINMENTNo ratings yet