Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900047
JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900047
Uploaded by
Dang KhueCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Network Automation Cookbook Pdf00016Document5 pagesNetwork Automation Cookbook Pdf00016Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- Network Automation Cookbook Pdf00015Document5 pagesNetwork Automation Cookbook Pdf00015Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- Network Automation Cookbook Pdf00007Document5 pagesNetwork Automation Cookbook Pdf00007Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900020Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900020Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- Network Automation Cookbook Pdf00017Document5 pagesNetwork Automation Cookbook Pdf00017Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- Network Automation Cookbook Pdf00005Document5 pagesNetwork Automation Cookbook Pdf00005Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900017Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900017Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900012Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900012Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- Network Automation Cookbook Pdf00002Document5 pagesNetwork Automation Cookbook Pdf00002Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900033Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900033Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900001Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900001Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Initial Configuration: JNCIA-Junos Study Guide-Part 1Document1 pageChapter 3: Initial Configuration: JNCIA-Junos Study Guide-Part 1Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900016Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900016Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900045Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900045Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900035Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900035Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900032Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900032Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900041Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900041Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900037Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900037Dang KhueNo ratings yet
JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900047
JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900047
Uploaded by
Dang KhueOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900047
JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900047
Uploaded by
Dang KhueCopyright:
Available Formats
JNCIA-Junos Study Guide—Part 1
Identification Parameters
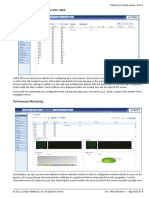
The graphic shows how to use the CLI to configure the hostname and a root password. As displayed on the graphic, a check is
made when the root password is entered to ensure that it has been entered correctly. In the event that both entered passwords
do not match, an error will be generated, the change is not made, and the password will need to be reentered.
The example on the graphic uses the plain-text authentication option. Unlike the software from some vendors, the Junos OS
never actually displays the password in its plain-text format but rather encrypts the password for you. You can see the encrypted
password by viewing the relevant configuration:
[edit system]
root# show root-authentication
encrypted-password "$1$ti58nUSg$8xnQtTJeA0dA/.eUjjZOq1"; ## SECRET-DATA
Because you cannot retrieve the passwords by looking at the configuration file, you should keep the configured passwords in a
secure location. If you do forget the password and cannot log in, you can always perform the password recovery process, which
we cover in a subsequent chapter.
Time Parameters
The graphic shows how to use the CLI to configure the
time settings. You can configure the current date and
time information along with the proper time zone for the
device. The default time zone on Junos devices is UTC
(Coordinated Universal Time, formerly known as
Greenwich Mean Time, or GMT). When you define the
local time on a Junos device, you must account for the
time difference between the defined time zone and the
default time zone. Once the time zone is changed and
committed, the local time is adjusted accordingly to
account for the difference. If you do not want to make the
necessary adjustments, you can simply set the system’s time after the defined time zone parameter has been committed.
Instead of setting the local time on each network device in your network, you might consider implementing the Network Time
Protocol (NTP). We cover NTP in detail in the “Secondary System Configuration” chapter.
© 2012 Juniper Networks, Inc. All rights reserved. Initial Configuration • Chapter 3–5
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Network Automation Cookbook Pdf00016Document5 pagesNetwork Automation Cookbook Pdf00016Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- Network Automation Cookbook Pdf00015Document5 pagesNetwork Automation Cookbook Pdf00015Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- Network Automation Cookbook Pdf00007Document5 pagesNetwork Automation Cookbook Pdf00007Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900020Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900020Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- Network Automation Cookbook Pdf00017Document5 pagesNetwork Automation Cookbook Pdf00017Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- Network Automation Cookbook Pdf00005Document5 pagesNetwork Automation Cookbook Pdf00005Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900017Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900017Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900012Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900012Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- Network Automation Cookbook Pdf00002Document5 pagesNetwork Automation Cookbook Pdf00002Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900033Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900033Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900001Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900001Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Initial Configuration: JNCIA-Junos Study Guide-Part 1Document1 pageChapter 3: Initial Configuration: JNCIA-Junos Study Guide-Part 1Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900016Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900016Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900045Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900045Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900035Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900035Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900032Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900032Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900041Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900041Dang KhueNo ratings yet
- JNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900037Document1 pageJNCIA Junos P1 - 2012 12 1900037Dang KhueNo ratings yet