Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medical Surgical
Medical Surgical
Uploaded by
pink_rp16205260 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views1 pageThe document provides an overview of the structures and functions of the nervous system. It describes the central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, and autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system includes the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system is involved in the fight or flight response and increases heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, and blood flow to muscles. It causes pupil dilation, dry mouth, and constipation. The parasympathetic nervous system has opposite effects and decreases body activities except in the gastrointestinal tract, where it causes increased activity and diarrhea.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides an overview of the structures and functions of the nervous system. It describes the central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, and autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system includes the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system is involved in the fight or flight response and increases heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, and blood flow to muscles. It causes pupil dilation, dry mouth, and constipation. The parasympathetic nervous system has opposite effects and decreases body activities except in the gastrointestinal tract, where it causes increased activity and diarrhea.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views1 pageMedical Surgical
Medical Surgical
Uploaded by
pink_rp1620526The document provides an overview of the structures and functions of the nervous system. It describes the central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, and autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system includes the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system is involved in the fight or flight response and increases heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, and blood flow to muscles. It causes pupil dilation, dry mouth, and constipation. The parasympathetic nervous system has opposite effects and decreases body activities except in the gastrointestinal tract, where it causes increased activity and diarrhea.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
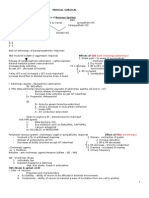
MEDICAL SURGICAL
Overview of the Structures & Functions of Nervous System
Central NS PNS ANS
Brain & spinal cord 31 spinal & cranial sympathetic NS
Parasypathatic NS
Somatic NS
C- 8
T- 12
L- 5
S- 5
C- 1
ANS (or adrenergic of parasympatholitic response)
SNS involved in fight or aggression response Effects of SNS (anti-cholinergic/adrenergic)
1. Dilate pupil – to aware of surroundings
Release of norepinephrine (adrenaline – cathecolamine) - medriasis
Adrenal medulla (potent vasoconstrictor) 2. Dry mouth
Increases body activities VS = Increase 3. BP & HR= increased
Except GIT – decrease GITmotility bronchioles dilated to take more oxygen
4. RR increased
* Why GIT is not increased = GIT is not important! 5. Constipation & urinary retention
Increase blood flow to skeletal muscles, brain & heart.
I. Adrenergic Agents – Epinephrine (adrenaline)
SE: SNS effect
II. PNS: Beta adrenergic blocking agents (opposite of adrenergic agents) (all end in –‘lol’)
- Blocks release of norepinephrine.
- Decrease body activities except GIT (diarrhea)
Ex. Propanolol, Metopanolol
SE:
B – broncho spasm (bronchoconstriction)
You might also like
- Medical-Surgical Nursing ReviewDocument90 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing Reviewɹǝʍdןnos99% (316)
- The Bone Sparrow, by Zara Fraillon: Question BookletDocument20 pagesThe Bone Sparrow, by Zara Fraillon: Question BookletGaurav Jobanputra100% (2)
- Simple Exercises to Stimulate the Vagus Nerve: An Illustrated Guide to Alleviate Stress, Depression, Anxiety, Pain, and Digestive ConditionsFrom EverandSimple Exercises to Stimulate the Vagus Nerve: An Illustrated Guide to Alleviate Stress, Depression, Anxiety, Pain, and Digestive ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Polyvagal Theory: A Self-Help Polyvagal Theory Guide to Reduce with Self Help Exercises Anxiety, Depression, Autism, Trauma and Improve Your Life.From EverandPolyvagal Theory: A Self-Help Polyvagal Theory Guide to Reduce with Self Help Exercises Anxiety, Depression, Autism, Trauma and Improve Your Life.Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Comparative Government and Politics: An IntroductionDocument3 pagesComparative Government and Politics: An IntroductionIlhamEffendiYahyaNo ratings yet
- MS Notes-LexsimbulanfileDocument90 pagesMS Notes-LexsimbulanfileStephanie Villanueva AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical NotesDocument18 pagesMedical Surgical NotesshalomNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Effects ofDocument18 pagesNervous System: Effects ofClark LlameraNo ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical Nursing Lecture NotesDocument90 pagesMedical-Surgical Nursing Lecture NotesJessica AnisNo ratings yet
- Ms Penta NotesDocument84 pagesMs Penta Notesstuffednurse100% (2)
- Medical Surgical Nursing ReviewDocument97 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing ReviewBernadeth Josefa BorelaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical: Nervous SystemDocument94 pagesMedical Surgical: Nervous SystemAngelika DomondonNo ratings yet
- Medical and Surgical Nursing Notes For NLEDocument63 pagesMedical and Surgical Nursing Notes For NLEBel Zeta DonaireNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical: Nervous SystemDocument90 pagesMedical Surgical: Nervous SystemCatherine G. Borras100% (1)
- MedicalSurgical Nursing ReviewDocument89 pagesMedicalSurgical Nursing ReviewPopa D. SilviuNo ratings yet
- MS Notes 1Document75 pagesMS Notes 1Marygrace Gan SabanalNo ratings yet
- MedicalSurgical Nursing ReviewDocument86 pagesMedicalSurgical Nursing ReviewPopa D. SilviuNo ratings yet
- Medsurg PrintDocument82 pagesMedsurg PrintjennywatsurproblemNo ratings yet
- MEdical Surgical REVEWERDocument86 pagesMEdical Surgical REVEWERennaedNo ratings yet
- MS ReviewDocument82 pagesMS ReviewRey P. Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Ms Penta NotesDocument84 pagesMs Penta Notesshenric16No ratings yet
- Memorizing Pharmacology for NCLEX: How to Memorize Pharmacological Terms with EaseFrom EverandMemorizing Pharmacology for NCLEX: How to Memorize Pharmacological Terms with EaseNo ratings yet
- Clinical Autonomic and Mitochondrial Disorders: Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment for Mind-Body WellnessFrom EverandClinical Autonomic and Mitochondrial Disorders: Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment for Mind-Body WellnessNo ratings yet
- The Brain-Body Connection: Understanding the Impact of Physical Health on Mental HealthFrom EverandThe Brain-Body Connection: Understanding the Impact of Physical Health on Mental HealthNo ratings yet
- Adrenal Fatigue: Understanding the Symptoms: How Malfunctioning Adrenal Glands Negatively Affect the BodyFrom EverandAdrenal Fatigue: Understanding the Symptoms: How Malfunctioning Adrenal Glands Negatively Affect the BodyNo ratings yet
- Vagus Nerve Exercises To Rewire Your Brain: Stimulate Your Vagus Nerve With Natural Self-Healing Daily Exercises For Anxiety, Depression, Trauma & OverthinkingFrom EverandVagus Nerve Exercises To Rewire Your Brain: Stimulate Your Vagus Nerve With Natural Self-Healing Daily Exercises For Anxiety, Depression, Trauma & OverthinkingNo ratings yet
- Daily Vagus Nerve Exercises For Self-Healing (2 in 1): Natural Techniques & Habits To Help With Anxiety, Overthinking, Depression, Stress-Relief, Brain Fog, Inflammation & MoreFrom EverandDaily Vagus Nerve Exercises For Self-Healing (2 in 1): Natural Techniques & Habits To Help With Anxiety, Overthinking, Depression, Stress-Relief, Brain Fog, Inflammation & MoreNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandNervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Search for Antidepressants - An Integrative View of Drug DiscoveryFrom EverandThe Search for Antidepressants - An Integrative View of Drug DiscoveryNo ratings yet
- The Neuroscience of Meditation: Rewiring Your Brain for Health and HappinessFrom EverandThe Neuroscience of Meditation: Rewiring Your Brain for Health and HappinessNo ratings yet
- Summary of John J. Ratey with Eric Hagerman's SparkFrom EverandSummary of John J. Ratey with Eric Hagerman's SparkRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Evaluation and Management of Autonomic Disorders: A Case-Based Practical GuideFrom EverandEvaluation and Management of Autonomic Disorders: A Case-Based Practical GuideJuan IdiaquezNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals and Clinics of Deep Brain Stimulation: An Interdisciplinary ApproachFrom EverandFundamentals and Clinics of Deep Brain Stimulation: An Interdisciplinary ApproachYasin TemelNo ratings yet
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Physical and Chemical Bases of Stress and CopingFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Physical and Chemical Bases of Stress and CopingNo ratings yet
- Cranial Relaxation Technique: A Simple Technique to Calm the Mind, Nourish the Eyes and Balance the Nervous SystemFrom EverandCranial Relaxation Technique: A Simple Technique to Calm the Mind, Nourish the Eyes and Balance the Nervous SystemNo ratings yet
- Vagus Nerve: Stimulate and Activate your Vagus Nerve by Effectively Reducing Inflammation, Anxiety, Migraine, Stress and other Chronic Diseases with Natural Exercises and TechniquesFrom EverandVagus Nerve: Stimulate and Activate your Vagus Nerve by Effectively Reducing Inflammation, Anxiety, Migraine, Stress and other Chronic Diseases with Natural Exercises and TechniquesNo ratings yet
- The Dislocated Brain: Innovation in Traumatic Brain Injury and IrrigationFrom EverandThe Dislocated Brain: Innovation in Traumatic Brain Injury and IrrigationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Last Quarter Exam - TrendsDocument6 pagesLast Quarter Exam - TrendsRamwen Jamero100% (1)
- Global Democracy PPT 20012021 012844amDocument14 pagesGlobal Democracy PPT 20012021 012844amalpha five100% (1)
- Compare Contrast American Ancient Greece Democracy J SerafinDocument11 pagesCompare Contrast American Ancient Greece Democracy J Serafinapi-213888247No ratings yet
- 110 PDFDocument16 pages110 PDFZûé ZûéNo ratings yet
- Full List of Approved Sending Organization of MyanmarDocument16 pagesFull List of Approved Sending Organization of Myanmarzayyar htooNo ratings yet
- Truckcom BT Te 2 12 6 Rev4 01 2018Document22 pagesTruckcom BT Te 2 12 6 Rev4 01 2018jennifermaldonado041189drs100% (126)
- H. Hale - Regime Cycles. Democracy, Autocracy, and Revolution in Post-Soviet EurasiaDocument34 pagesH. Hale - Regime Cycles. Democracy, Autocracy, and Revolution in Post-Soviet EurasiaYakuAtokNo ratings yet
- Class Notes: Class: IX Topic: What Is Democracy? Why Democracy? Subject: Democratic PoliticsDocument10 pagesClass Notes: Class: IX Topic: What Is Democracy? Why Democracy? Subject: Democratic PoliticsDeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- Members of Parliament Since 1944Document14 pagesMembers of Parliament Since 1944daddyroy21No ratings yet
- Form of Government: DemocracyDocument6 pagesForm of Government: DemocracyAzhar MehmoodNo ratings yet
- No, People Really Aren't Turning Away From Democracy - The Washington PostDocument5 pagesNo, People Really Aren't Turning Away From Democracy - The Washington PostRobertAlxNo ratings yet
- HIST 300 - Module 2 - Section 1 - Essay Question 1Document2 pagesHIST 300 - Module 2 - Section 1 - Essay Question 1Berrak GüloğluNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument218 pagesUntitledMaría Florencia BóNo ratings yet
- Democratic Anchorage of Infrastructural Governance Networks: The Case of The Femern Belt ForumDocument27 pagesDemocratic Anchorage of Infrastructural Governance Networks: The Case of The Femern Belt ForumHilwan GivariNo ratings yet
- NEW SYLLABUS Political - Science 2nd SemesterDocument5 pagesNEW SYLLABUS Political - Science 2nd SemesterAditi PradhanNo ratings yet
- Trends Module 8Document4 pagesTrends Module 8Joy Ann PaunonNo ratings yet
- Euronymous As Kafka - ValterDocument11 pagesEuronymous As Kafka - ValterDepressive Rebellion Against the World D-RAWNo ratings yet
- BotswanaDocument5 pagesBotswanaadrian lozanoNo ratings yet
- PENGEMBANGAN PASCA AMANDEME KONTITUSI Hisbun NashorDocument11 pagesPENGEMBANGAN PASCA AMANDEME KONTITUSI Hisbun Nashorإلهام البدوNo ratings yet
- "Democracy As Civilisation": Christopher HobsonDocument22 pages"Democracy As Civilisation": Christopher HobsonAlvaro FriasNo ratings yet
- Tsehai Publishers International Journal of Ethiopian StudiesDocument33 pagesTsehai Publishers International Journal of Ethiopian StudiesAbenezer SamuelNo ratings yet
- Outcomes of Democracy One Shot PDFDocument9 pagesOutcomes of Democracy One Shot PDFKshitiz sharmaNo ratings yet
- Munich Security Report 2020Document69 pagesMunich Security Report 2020Talha AsifNo ratings yet
- V-Dem Democracyreport2023 LowresDocument56 pagesV-Dem Democracyreport2023 LowresCharly CardenasNo ratings yet
- Book Review - Has The West Lost It? (Kishore Mahbubani) - by J. MohanasakthivelDocument4 pagesBook Review - Has The West Lost It? (Kishore Mahbubani) - by J. MohanasakthivelRaNo ratings yet
- Architects in Bahrain NewDocument6 pagesArchitects in Bahrain NewGulf RubberNo ratings yet
- Srps Co. List A 5 1.4.19Document13 pagesSrps Co. List A 5 1.4.19Mg PhyoNo ratings yet
- ANC History TakingDocument8 pagesANC History TakingShowbhik RoyNo ratings yet