Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP: Acute Gastroenteritis
NCP: Acute Gastroenteritis
Uploaded by
hauteanicole0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
907 views3 pagesThe patient was experiencing hyperthermia related to dehydration, with an increased body temperature, hot flushed skin, increased heart rate, and increased respiratory rate. The nursing interventions were to monitor vital signs, determine the patient's age and weight, monitor fluid intake and output, eliminate excess clothing, encourage fluid intake, raise side rails for safety, start IV fluids as needed, and provide a high caloric diet. After 8 hours of nursing care, the goal was for the patient to stabilize and have their hyperthermia resolved.
Original Description:
nursing care plan: acute gastroenteritis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe patient was experiencing hyperthermia related to dehydration, with an increased body temperature, hot flushed skin, increased heart rate, and increased respiratory rate. The nursing interventions were to monitor vital signs, determine the patient's age and weight, monitor fluid intake and output, eliminate excess clothing, encourage fluid intake, raise side rails for safety, start IV fluids as needed, and provide a high caloric diet. After 8 hours of nursing care, the goal was for the patient to stabilize and have their hyperthermia resolved.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
907 views3 pagesNCP: Acute Gastroenteritis
NCP: Acute Gastroenteritis
Uploaded by
hauteanicoleThe patient was experiencing hyperthermia related to dehydration, with an increased body temperature, hot flushed skin, increased heart rate, and increased respiratory rate. The nursing interventions were to monitor vital signs, determine the patient's age and weight, monitor fluid intake and output, eliminate excess clothing, encourage fluid intake, raise side rails for safety, start IV fluids as needed, and provide a high caloric diet. After 8 hours of nursing care, the goal was for the patient to stabilize and have their hyperthermia resolved.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
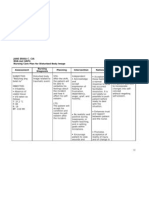
DATE CUES NEED NURSING PATIENT INTERVENTION IMPLEMEN EVALUATION
/ DIAGNOSIS OUTCOME TATION
TIME
Objective: N Hyperthermia After 8 hours of Monitor the patient’s HR,
- Body U related to nursing RR, and especially the
temperature T dehydration as intervention, the tympanic or rectal
above normal R evidenced by client will be able temperature.
- Hot, flushed I increase in body to: R: HR and RR increase as
skin T temperature higher hyperthermia progresses.
- Increase I than normal range Tympanic or rectal
heart rate O temperature gives a more
- Increase N accurate indication of core
respiratory A temperature.
rate L Determine the patient’s
- Loss of - age and weight.
M R: Extremes of age or weight
appetite
E increase the risk for the
- Malaise or
T inability to control body
weakness
A temperature.
- Seizures
B Monitor fluid intake
O and urine output. If the
L patient is unconscious,
I central venous pressure
C or pulmonary artery
pressure should be
P measured to monitor fluid
A status.
T R: Fluid resuscitation may be
T required to
E correct dehydration. The
R patient who is significantly
N dehydrated is no longer able
to sweat, which is necessary
for evaporative cooling.
Eliminate excess clothing
and covers.
R: Exposing skin to room air
decreases warmth and
increases evaporative
cooling.
Encourage ample fluid
intake by mouth.
R: If the patient is dehydrated
or diaphoretic, fluid loss
contributes to fever.
Raise the side rails at all
times.
R: This is to ensure patient’s
safety even without the
presence of seizure activity.
Start intravenous normal
saline solutions or as
indicated.
R: Intravenous normal saline
solution replenishes fluid
losses during shivering chills.
Provide high caloric diet
or as indicated by the
physician.
R: Appropriate diet is
necessary to meet the
metabolic demand of the
patient.
You might also like
- Human Reproduction Unit Review Worksheet KEY 2015-2016Document4 pagesHuman Reproduction Unit Review Worksheet KEY 2015-2016Lalaine Angela Denuna86% (7)
- Fever NCPDocument5 pagesFever NCPNikael Patun-ogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Isabel Barredo Del MundoNo ratings yet
- S in Reverse Order. SDocument2 pagesS in Reverse Order. ScreativeshuvoNo ratings yet
- Visceral Manip Lation Visceral Manipulation: Kenneth Lossing D.ODocument63 pagesVisceral Manip Lation Visceral Manipulation: Kenneth Lossing D.OIshita75% (4)
- NCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Document3 pagesNCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Jum ChumNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Student Nurse: Diestro, Angela Mae BSN 2BDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Student Nurse: Diestro, Angela Mae BSN 2BAngela Mae DiestroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaNo ratings yet
- NCP RiskDocument3 pagesNCP RiskMaricar Azolae MascualNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFswapnilazarusNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For RabiesDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For RabiesAngel VillamorNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPYesha Mae MartinNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAngela Neri0% (1)
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPRose AnnNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plans: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationRheeanne Mae Amilasan100% (1)
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument3 pagesImpaired Urinary EliminationAgcopra MtchNo ratings yet
- "Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientDocument2 pages"Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientMussaib Mushtaq100% (1)
- NCP - Altered ComfortDocument2 pagesNCP - Altered ComfortJhudiel Gabriel Go0% (1)
- Uti NCPDocument1 pageUti NCPAngelique Vinoya100% (2)
- NCP For CTTDocument2 pagesNCP For CTTKay D. BeredoNo ratings yet
- NCP DizzinessDocument2 pagesNCP Dizzinesschristine mercadoNo ratings yet
- Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1Document8 pagesRisk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1kint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionMitsika AnadiaNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document1 pageNCP 1hsiriaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care Planruggero07100% (2)
- Assessment Diagnosis Objectives of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Difficulty of Breathing (Rapid and Shallow)Document1 pageAssessment Diagnosis Objectives of Care Intervention Rationale Evaluation Difficulty of Breathing (Rapid and Shallow)Jamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- BFC NCPDocument2 pagesBFC NCPMonica Melo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanAldrein GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Imbalance Body TemperatureDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Risk For Imbalance Body TemperatureCarl J.No ratings yet
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesAcute GastroenteritisErika CadawanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresNo ratings yet
- DeficientDocument2 pagesDeficientVANNEZA TRIXZY TAMPARONGNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Problem Scientific Reason Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Problem Scientific Reason Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationeihjay-bravo-8041No ratings yet
- Patty NCP HyperthermiaDocument4 pagesPatty NCP HyperthermiaPatricia Jean FaeldoneaNo ratings yet
- SNU49Document2 pagesSNU49Nora BacolNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan ADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNo ratings yet
- Deficit)Document2 pagesDeficit)Lee DeeNo ratings yet
- NCP PSHDocument17 pagesNCP PSHMargareth OrtizNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPWendy Escalante100% (1)
- Risk For Aspiration Related To Esophageal Compromise Affecting The Lower Esophageal Sphincter As Evidenced by Heart Burn.Document2 pagesRisk For Aspiration Related To Esophageal Compromise Affecting The Lower Esophageal Sphincter As Evidenced by Heart Burn.eleinsamNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAnn AquinoNo ratings yet
- NCP DobDocument1 pageNCP DobsarahAcristobalNo ratings yet
- NCP HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP HypertensionCharisse VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Oraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardDocument1 pageOraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardJamie LeeNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPeun kyung shinNo ratings yet
- NCP For HemorrhoidsDocument3 pagesNCP For HemorrhoidsTADURAN RENE MAE ANGELLI F.No ratings yet
- NCP SEIZURE DISORDERDocument2 pagesNCP SEIZURE DISORDERPatricia FaraonNo ratings yet
- NCP FoodDocument1 pageNCP FoodAdrian ArdamilNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanAlvin DagumbalNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCP ActualDocument3 pagesCase Study NCP Actualdhamy florNo ratings yet
- PDF Albumin Drug StudyDocument1 pagePDF Albumin Drug StudyJamie John EsplanadaNo ratings yet
- BSN 3e Duropan Ncp-Knowledge DeficitDocument12 pagesBSN 3e Duropan Ncp-Knowledge DeficitJane DuropanNo ratings yet
- NCP DobDocument2 pagesNCP DobTata Wendz100% (1)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPDidith AbanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan BalnkDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan BalnkKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine CPDocument2 pagesAmlodipine CPRose EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Planning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byDocument10 pagesPlanning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byNicole Anne TungolNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- BSNURSE: NCP - HypertensionDocument3 pagesBSNURSE: NCP - Hypertensionmickey_beeNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance ChildDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance ChildMarion Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Need Objective Interventions Evaluation Subjective Data: C O G N I T I V E - P E R C E P T U A L Goal MetDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Need Objective Interventions Evaluation Subjective Data: C O G N I T I V E - P E R C E P T U A L Goal MetAngel Mikaela CilladoNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument4 pagesNCP HyperthermiaPrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- NCP-hepatitis-MATA (Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume)Document7 pagesNCP-hepatitis-MATA (Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume)Nicole Keesha MataNo ratings yet
- CEN 01/2018 (Assistant Loco Pilot (ALP) & Technicians) RRB: AjmerDocument3 pagesCEN 01/2018 (Assistant Loco Pilot (ALP) & Technicians) RRB: Ajmersaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia Country Energy Fact SheetDocument3 pagesEthiopia Country Energy Fact SheetMengistu MamuyieNo ratings yet
- RBS 85Document1 pageRBS 85SergiSerranoNo ratings yet
- Renesas M51995AFP#CF0J DatasheetDocument41 pagesRenesas M51995AFP#CF0J DatasheetheribertosfaNo ratings yet
- Rule of Procedure For Environmental CasesDocument84 pagesRule of Procedure For Environmental CasesjelyneptNo ratings yet
- Santosh Yadav: Education SkillsDocument1 pageSantosh Yadav: Education SkillsSantosh YadavNo ratings yet
- How To Pass The MRCS PresentationDocument27 pagesHow To Pass The MRCS PresentationKartik sridhar50% (2)
- Stretch Your ImaginationDocument3 pagesStretch Your ImaginationJilliene IsaacsNo ratings yet
- Exam Instructions 30062020 PDFDocument27 pagesExam Instructions 30062020 PDFAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Squizeer Machine: Presented by-Ar-Rafi HridayDocument11 pagesSquizeer Machine: Presented by-Ar-Rafi HridayAr Rafi HridayNo ratings yet
- Save Our Theater!: Spilled Milk: Great Read Detailing Hi Line InfrastructureDocument8 pagesSave Our Theater!: Spilled Milk: Great Read Detailing Hi Line InfrastructureBS Central, Inc. "The Buzz"No ratings yet
- DB en Macx MCR Ex SL Nam 2t SP 103752 en 02Document20 pagesDB en Macx MCR Ex SL Nam 2t SP 103752 en 02Seka Vilar SorucoNo ratings yet
- Topic SpecDocument2 pagesTopic SpecAira AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Roboshot 30 Tech Spec Rev ADocument2 pagesRoboshot 30 Tech Spec Rev Apinke01No ratings yet
- Orcus Game Master's GuideDocument210 pagesOrcus Game Master's GuideDaniel DeMarcNo ratings yet
- Geocongress 2020 ScourDocument11 pagesGeocongress 2020 ScourjalopezcNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Lake Isle of InnisfreeDocument28 pagesGrade 9 Lake Isle of InnisfreeSHALINI GUPTANo ratings yet
- Facts Worth Knowing About Frequency ConvertersDocument167 pagesFacts Worth Knowing About Frequency ConvertersEduardo SuarezNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Alternating Application of Cold and Hot Compresses On Reduction of Breast Engorgement Among Lactating Mothers: Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesEffectiveness of Alternating Application of Cold and Hot Compresses On Reduction of Breast Engorgement Among Lactating Mothers: Literature ReviewNovelty JournalsNo ratings yet
- Theravada Quiz-Grade 11Document3 pagesTheravada Quiz-Grade 11Joan BayanganNo ratings yet
- The Letter To The EditorDocument3 pagesThe Letter To The EditorDishu SinghNo ratings yet
- Alyssa Kim - Profile Final DraftDocument7 pagesAlyssa Kim - Profile Final Draftapi-609291897No ratings yet
- March Workout Yoga Schedule: Day 1 Day 5 Day 4 Day 3 Day 2 Day 6 Day 7Document1 pageMarch Workout Yoga Schedule: Day 1 Day 5 Day 4 Day 3 Day 2 Day 6 Day 7aidaiNo ratings yet
- SS FG230 enDocument2 pagesSS FG230 entolisNo ratings yet
- Ium Logik Oruday Out Romania 07 18 GB PDFDocument98 pagesIum Logik Oruday Out Romania 07 18 GB PDFBaciu Nicolae100% (1)
- Kathrein Iot Portfolio Catalog 2021 enDocument33 pagesKathrein Iot Portfolio Catalog 2021 enUrdaNo ratings yet
- Standard Schedule of Rates 2012 13 Government of Andhra PradeshDocument455 pagesStandard Schedule of Rates 2012 13 Government of Andhra Pradeshveera_swamy2No ratings yet