Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsChapter 5 Motion Part 1
Chapter 5 Motion Part 1
Uploaded by
shirlynKBSM Form 5 Science
Four stroke petrol engine, Four stroke diesel engine and two stroke petrol engine
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- DG SetDocument103 pagesDG Setlvsaru67% (3)
- Thunderbird Service ManualDocument480 pagesThunderbird Service ManualJames100% (1)
- Engines NotesDocument11 pagesEngines NotesAgbulkaraNo ratings yet
- MAT Lite 610 LectureDocument42 pagesMAT Lite 610 LectureJkevin John Capada DardoNo ratings yet
- Eme 170510150242Document18 pagesEme 170510150242nilminaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Automotive Components and Vehicle SystemDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Automotive Components and Vehicle SystemnahomNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Automotive Components and Vehicle SystemDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Automotive Components and Vehicle SystemnahomNo ratings yet
- DG SetDocument103 pagesDG SetRajkumar SNo ratings yet
- Engine FundamentalsDocument36 pagesEngine FundamentalsRahul RaiNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke Engine Presentation 7-6-2022Document15 pagesFour Stroke Engine Presentation 7-6-2022saisae KwanhlaineNo ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To EngineDocument30 pages2 Introduction To EngineNoemie DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Lab Mannual Cloud ComputingDocument7 pagesLab Mannual Cloud ComputingThiruppathi KuttalingamNo ratings yet
- Basic Automobile EngineeringDocument47 pagesBasic Automobile EngineeringGautam PrajapatNo ratings yet
- Diesel 4S Engine ModelDocument12 pagesDiesel 4S Engine Modelmeenu_04julyNo ratings yet
- Two Stroke EngineDocument5 pagesTwo Stroke EngineBombo Alarcon Juan AndresNo ratings yet
- Two-Stroke EngineDocument5 pagesTwo-Stroke EngineArun PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Ic EngineDocument22 pagesIc EngineShafiul AlamNo ratings yet
- Petrol Engine1virkDocument3 pagesPetrol Engine1virkapi-3703711No ratings yet
- Operating Principle of Diesel and Petrol EnginesDocument8 pagesOperating Principle of Diesel and Petrol EnginesJonathan MalamulaNo ratings yet
- Internal-Combustion Engines: Prepared By: Angelie A. Cabande BSED-ScienceDocument9 pagesInternal-Combustion Engines: Prepared By: Angelie A. Cabande BSED-ScienceAnne Gie LeeNo ratings yet
- 2-Ic EngineDocument49 pages2-Ic EngineTOBIN THOMAS MENo ratings yet
- 1.5 Terminology & CombustionDocument29 pages1.5 Terminology & CombustionSachin GautamNo ratings yet
- 2 Stroke Cycle EnginesDocument16 pages2 Stroke Cycle EnginesUsman Ali Usman AliNo ratings yet
- 03 Four Stroke Diesel CycleDocument34 pages03 Four Stroke Diesel CyclenareshNo ratings yet
- Engines: Sancho MccannDocument27 pagesEngines: Sancho MccannDeliaChiaNo ratings yet
- IC EnginesDocument17 pagesIC EnginesS V Garata ReddyNo ratings yet
- 451 Slides 1Document16 pages451 Slides 1Caleb RaphaelNo ratings yet
- Ic Engine: Kim.J.SeelanDocument41 pagesIc Engine: Kim.J.SeelanDrKim J SeelanNo ratings yet
- Auto Material EngineDocument36 pagesAuto Material EngineHardik ShahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Internal CombussionDocument80 pagesLecture 2 - Internal Combussionchoongwenkang100% (1)
- Diesel Fuel SystemDocument56 pagesDiesel Fuel Systemmtnronoh98No ratings yet
- Automotive Lecture 2Document33 pagesAutomotive Lecture 2kaliboisaac149No ratings yet
- Four Stroke Engine - by SaisaekwanhlaineDocument14 pagesFour Stroke Engine - by Saisaekwanhlainesaisae KwanhlaineNo ratings yet
- Unit III Part XIDocument11 pagesUnit III Part XIPrakash KatdareNo ratings yet
- DieselDocument23 pagesDieselVijay GaneshNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine: Aguinaldo, Cellan, Gregorio, MedranoDocument33 pagesDiesel Engine: Aguinaldo, Cellan, Gregorio, MedranoHannah AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- 4 Stroke Ignition SystemDocument33 pages4 Stroke Ignition Systemspruhatech0% (1)
- Ic EngineDocument12 pagesIc EngineAbdi samad MohamedNo ratings yet
- IC Engines AutomobilesDocument91 pagesIC Engines Automobileskapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- IC Engines Assignment 1: by - Prateek Gauba B12108 ME, 3 YearDocument16 pagesIC Engines Assignment 1: by - Prateek Gauba B12108 ME, 3 YearPrtkkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 The Four-Stroke Cycle and Cylinder ArrangementsDocument16 pagesChapter 10 The Four-Stroke Cycle and Cylinder ArrangementsROSAN YUMANGNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument51 pagesUntitledhalil yıldırımNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke Engine 4TH WorksheetDocument2 pagesFour Stroke Engine 4TH WorksheetlorenitasuarNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument35 pagesInternal Combustion EngineMuhammad FaizNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke Petrol EngineDocument12 pagesFour Stroke Petrol EngineSyed Zaheer SajjadNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke Cycle Theory: Intake Stroke Piston Moving Down Intake Valve Open Exhaust Valve ClosedDocument57 pagesFour Stroke Cycle Theory: Intake Stroke Piston Moving Down Intake Valve Open Exhaust Valve ClosedIndirajithNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke Diesel EngineDocument4 pagesFour Stroke Diesel EngineSwati SutarNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines - The DieselDocument25 pagesInternal Combustion Engines - The DieselTarun PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument12 pagesUnit IIotakoothanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 To 10Document54 pagesLecture 8 To 10Memo KhalidNo ratings yet
- Engines and Steam Turbine Generator: by Muhammad Hassan Siddique Internship Batch: 2021Document23 pagesEngines and Steam Turbine Generator: by Muhammad Hassan Siddique Internship Batch: 2021hassaanNo ratings yet
- Team Nozzle Present .: Four Stroke Petrol EngineDocument33 pagesTeam Nozzle Present .: Four Stroke Petrol EngineChamfreit AxereasNo ratings yet
- Engines Classification and Its ComponentsDocument43 pagesEngines Classification and Its ComponentsKLUniveristyNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine / Diesel Engine CyclesDocument55 pagesInternal Combustion Engine / Diesel Engine CyclesAthul P PNo ratings yet
- Final Project Mechanical PowerDocument163 pagesFinal Project Mechanical PowerVikrant KumarNo ratings yet
- 4-Valve Engines: Guided by Mr. P. D. Sudersanan Asst Prof, Mech Dept, Dr. TtitDocument37 pages4-Valve Engines: Guided by Mr. P. D. Sudersanan Asst Prof, Mech Dept, Dr. TtittarunskumarNo ratings yet
- Ariel Portugal and Vince RiveraDocument81 pagesAriel Portugal and Vince RiveraAriel PortugalNo ratings yet
- The Four Stroke 5-Event Cycle of An AircraftDocument8 pagesThe Four Stroke 5-Event Cycle of An AircraftCarlo PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Engine BlockDocument23 pagesEngine Blockno oneNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 07052020Document2 pagesWorksheet 07052020shirlynNo ratings yet
- 230420essay Section BDocument2 pages230420essay Section BshirlynNo ratings yet
- 160420essay Section CDocument3 pages160420essay Section CshirlynNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Carbon Compounds Part 2Document52 pagesChapter 4 Carbon Compounds Part 2shirlynNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: A Conductor by Changing Magnetic FieldDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: A Conductor by Changing Magnetic FieldshirlynNo ratings yet
- A Technical Seminar Report: Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering CollegeDocument27 pagesA Technical Seminar Report: Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering CollegeK. Vamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Lean Angle Training - Hitch - Moto Gymkhana NederlandDocument4 pagesLean Angle Training - Hitch - Moto Gymkhana Nederlandswisskomputer3865No ratings yet
- Trail/Beaver Valley/Rossland Pennywise May 14, 2013Document64 pagesTrail/Beaver Valley/Rossland Pennywise May 14, 2013Pennywise PublishingNo ratings yet
- Soal To Gundar 2018 Atw Sekitarnya LahDocument13 pagesSoal To Gundar 2018 Atw Sekitarnya LahayaNo ratings yet
- Achievers B1 Units 1 and 2Document24 pagesAchievers B1 Units 1 and 2Leticia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Two-Stroke Engine - WikipediaDocument59 pagesTwo-Stroke Engine - WikipediaDIPU KUMARNo ratings yet
- Classifiers MASTERDocument16 pagesClassifiers MASTERleonardehmiNo ratings yet
- Army Public School For Girls CKL GarsDocument5 pagesArmy Public School For Girls CKL GarsKamila AhsanNo ratings yet
- Multistrada 1200 Enduro 2016 SERVICE MANUALDocument1,163 pagesMultistrada 1200 Enduro 2016 SERVICE MANUALFelipe SafadiNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Attachment of SidecarDocument1 pageAffidavit of Attachment of SidecarKathleenJoyEnSagun100% (2)
- Urban Transportation Planning Department of Civil EngineeringDocument23 pagesUrban Transportation Planning Department of Civil EngineeringShovon HalderNo ratings yet
- List Game (08976560120)Document2,832 pagesList Game (08976560120)Daffa Al israNo ratings yet
- Full Thesis On MRTDocument213 pagesFull Thesis On MRTNazim UddinNo ratings yet
- New Mechanical ProjectDocument10 pagesNew Mechanical Projectवैज्ञानिक बाबाNo ratings yet
- Format Import Data Identitas Balita 040520053537Document184 pagesFormat Import Data Identitas Balita 040520053537puskesmas jetis 1No ratings yet
- Reliance General Insurance Company Limited: Long Term Two Wheeler Package Policy-ScheduleDocument6 pagesReliance General Insurance Company Limited: Long Term Two Wheeler Package Policy-ScheduleJitendra KambleNo ratings yet
- Kuwait Parking Design Criteria Manual - August 2007 - MunicipalityDocument100 pagesKuwait Parking Design Criteria Manual - August 2007 - Municipalityvijaya guniputiNo ratings yet
- IELTS Reading Practice Test ADocument7 pagesIELTS Reading Practice Test AMenon HariNo ratings yet
- 70-Triumph T120 Repair-Manual-63-70 PDFDocument236 pages70-Triumph T120 Repair-Manual-63-70 PDFSimon TudorNo ratings yet
- Ventura Rack C003BDocument2 pagesVentura Rack C003Bgenedem67No ratings yet
- 1memo - IVMS For Contractors - FINAL - SignedDocument3 pages1memo - IVMS For Contractors - FINAL - SignedCharles Rommel TadoNo ratings yet
- Cables k7 PDFDocument6 pagesCables k7 PDFlombardiacmNo ratings yet
- Geography X With ImagesDocument43 pagesGeography X With ImagesLEARN WITH AGALYANo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Ex2Document3 pagesVocabulary Ex2tayaNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Holdings & Investment Ltd. - Research Center: Balance SheetDocument6 pagesBajaj Holdings & Investment Ltd. - Research Center: Balance Sheetsarathkumarreddy855081No ratings yet
- Ladakh Budget Motorcycle Expeditions - 2023Document21 pagesLadakh Budget Motorcycle Expeditions - 2023preethu shenoyNo ratings yet
- Uz 125Document117 pagesUz 125c4zch62kphNo ratings yet
- J220BIKEPACKDocument2 pagesJ220BIKEPACKAhmad BatranNo ratings yet
- Dibels 8 Benchmark Maze 3 Scoring Key 2020-1Document19 pagesDibels 8 Benchmark Maze 3 Scoring Key 2020-1Amanda HookeNo ratings yet
Chapter 5 Motion Part 1
Chapter 5 Motion Part 1
Uploaded by
shirlyn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views37 pagesKBSM Form 5 Science
Four stroke petrol engine, Four stroke diesel engine and two stroke petrol engine
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentKBSM Form 5 Science
Four stroke petrol engine, Four stroke diesel engine and two stroke petrol engine
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views37 pagesChapter 5 Motion Part 1
Chapter 5 Motion Part 1
Uploaded by
shirlynKBSM Form 5 Science
Four stroke petrol engine, Four stroke diesel engine and two stroke petrol engine
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 37
Chapter 5 Motion
5.1 The motion of vehicles on land
Vehicles without engine
• Many vehicles do not use engines to
move about example bicycles, bullock
carts and wheelbarrows.
• The bicycle uses human energy to paddle
and move it.
• The rear cog of the bicycle is joined to the front
cog by the metal chain.
• Therefore, when we pedal to make the front
cog turn, the rear cog will also turn.
• This will turn the rear wheel and make the
bicycle move.
• The faster a person pedals, the faster the
bicycle moves.
• The gear system allows cyclist to pedal
comfortable and efficient rate, especially when
travelling uphill and downhill.
Vehicles with engines
• The four-cylinder engine is
commonly used in motor vehicles.
• A fuel is burnt in the engine to move
the pistons.
• The up and down motion of the
pistons causes the shafts in the
vehicle to rotate and the wheels to
turn.
• This makes the vehicle to move.
Four stroke petrol engine
Induction stroke
• The piston moves down the
cylinder.
• The inlet valve opens and
exhaust valve is closed.
• The mixture of air and petrol
vapour enters the cylinder
through the inlet valve.
Compression stroke
• Both the valves are
closed.
• The piston moves up the
cylinder.
• The mixture of air and
petrol vapour is
compressed and heated.
Power stroke
• Both the valves are
closed.
• The spark plug produces
a spark, ignites the fuel
and causes an explosion
• The force of the
expanding gases drives
the piston down.
Exhaust stroke
• The exhaust valve opens
and inlet valve remains
closed.
• The piston moves up and
drives out the exhaust
gases through the exhaust
valve.
• A new cycle starts when
the piston moves down.
Summary ( four stroke petrol engine)
Stroke Inlet Exhaust Piston Notes
valve valve
Induction Open Close Move Petrol and air
downward enter
Compression Close Close Move Petrol and air
upward became hot
Power Close Close Move Spark plug
downward produce
sparks
Exhaust Close Open Move Exhaust gas
upward out
Four stroke diesel engine
Induction stroke
• The inlet valve opens
and the exhaust valve
is closed.
• The piston moves
down the cylinder.
• Air enters the cylinder
due to air pressure.
Compression stroke
• Both the valves are
closed.
• The piston moves up and
compresses the air,
which becomes very hot.
• Just before the piston
reaches the top, the fuel
injector injects diesel
into the hot compressed
air.
Power stroke
• Both the valves are still
closed.
• The mixture of air and
diesel burns due to the
high temperature.
• The force of the expanding
gases pushes the piston
down.
Exhaust stroke
• The inlet valve remains
closed, and the exhaust
valve opens.
• The piston moves up and
pushed the exhaust gas
out through exhaust
valve.
• A new induction stroke
starts when the piston
moves down.
Summary ( four stroke diesel engine)
Stroke Inlet Exhaust Piston Notes
valve valve
Induction Open Close Move Air enter
downward
Compression Close Close Move Air became
upward hot
Power Close Close Move Fuel injector
downward inject diesel
Exhaust Close Open Move Exhaust gas
upward out
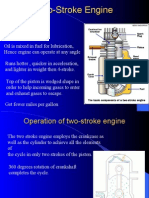
Two stroke petrol engine
• It is used for small machines example
motor boats, motorcycles and lawn
mowers.
• It is an inlet tube for the petrol-air
mixture to go in and an outlet tube
for exhaust gases to up escape.
• The inlet tube and the outlet tube
are open or closed by the piston
moving up and down.
Upward stroke
• The piston moves up the
cylinder.
• The inlet tube opens and the
petrol-air mixture enters the
cylinder due to lower pressure
in cylinder.
• Piston closes the outlet tube.
• Petrol-air mixture above the
piston is compressed by the
rising piston.
Downward stroke
• When the piston reaches the top of
the cylinder, a spark fired by the
spark plug ignites the petrol-air
mixture in the upper part of the
cylinder.
• The force of the expanding gases
pushes the piston down, opening the
outlet tube and allowing the exhaust
gases to escape.
• The piston closes the inlet tube as it
is moving down and forces petrol-air
mixture into the upper part of the
cylinder through a transfer passage.
Transfer of motion in a car
• When the engine of car is started, the pistons
move up and down and rotate a crankshaft.
• When the gear is engaged, the crankshaft is
connected to the transmission system (clutch
and gearbox) and a drive shaft.
• The rotating crankshaft rotates the drive shaft,
the differential gear, and the wheel axle,
causing the wheel to turn.
1
You might also like
- DG SetDocument103 pagesDG Setlvsaru67% (3)
- Thunderbird Service ManualDocument480 pagesThunderbird Service ManualJames100% (1)
- Engines NotesDocument11 pagesEngines NotesAgbulkaraNo ratings yet
- MAT Lite 610 LectureDocument42 pagesMAT Lite 610 LectureJkevin John Capada DardoNo ratings yet
- Eme 170510150242Document18 pagesEme 170510150242nilminaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Automotive Components and Vehicle SystemDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Automotive Components and Vehicle SystemnahomNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Automotive Components and Vehicle SystemDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Automotive Components and Vehicle SystemnahomNo ratings yet
- DG SetDocument103 pagesDG SetRajkumar SNo ratings yet
- Engine FundamentalsDocument36 pagesEngine FundamentalsRahul RaiNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke Engine Presentation 7-6-2022Document15 pagesFour Stroke Engine Presentation 7-6-2022saisae KwanhlaineNo ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To EngineDocument30 pages2 Introduction To EngineNoemie DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Lab Mannual Cloud ComputingDocument7 pagesLab Mannual Cloud ComputingThiruppathi KuttalingamNo ratings yet
- Basic Automobile EngineeringDocument47 pagesBasic Automobile EngineeringGautam PrajapatNo ratings yet
- Diesel 4S Engine ModelDocument12 pagesDiesel 4S Engine Modelmeenu_04julyNo ratings yet
- Two Stroke EngineDocument5 pagesTwo Stroke EngineBombo Alarcon Juan AndresNo ratings yet
- Two-Stroke EngineDocument5 pagesTwo-Stroke EngineArun PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Ic EngineDocument22 pagesIc EngineShafiul AlamNo ratings yet
- Petrol Engine1virkDocument3 pagesPetrol Engine1virkapi-3703711No ratings yet
- Operating Principle of Diesel and Petrol EnginesDocument8 pagesOperating Principle of Diesel and Petrol EnginesJonathan MalamulaNo ratings yet
- Internal-Combustion Engines: Prepared By: Angelie A. Cabande BSED-ScienceDocument9 pagesInternal-Combustion Engines: Prepared By: Angelie A. Cabande BSED-ScienceAnne Gie LeeNo ratings yet
- 2-Ic EngineDocument49 pages2-Ic EngineTOBIN THOMAS MENo ratings yet
- 1.5 Terminology & CombustionDocument29 pages1.5 Terminology & CombustionSachin GautamNo ratings yet
- 2 Stroke Cycle EnginesDocument16 pages2 Stroke Cycle EnginesUsman Ali Usman AliNo ratings yet
- 03 Four Stroke Diesel CycleDocument34 pages03 Four Stroke Diesel CyclenareshNo ratings yet
- Engines: Sancho MccannDocument27 pagesEngines: Sancho MccannDeliaChiaNo ratings yet
- IC EnginesDocument17 pagesIC EnginesS V Garata ReddyNo ratings yet
- 451 Slides 1Document16 pages451 Slides 1Caleb RaphaelNo ratings yet
- Ic Engine: Kim.J.SeelanDocument41 pagesIc Engine: Kim.J.SeelanDrKim J SeelanNo ratings yet
- Auto Material EngineDocument36 pagesAuto Material EngineHardik ShahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Internal CombussionDocument80 pagesLecture 2 - Internal Combussionchoongwenkang100% (1)
- Diesel Fuel SystemDocument56 pagesDiesel Fuel Systemmtnronoh98No ratings yet
- Automotive Lecture 2Document33 pagesAutomotive Lecture 2kaliboisaac149No ratings yet
- Four Stroke Engine - by SaisaekwanhlaineDocument14 pagesFour Stroke Engine - by Saisaekwanhlainesaisae KwanhlaineNo ratings yet
- Unit III Part XIDocument11 pagesUnit III Part XIPrakash KatdareNo ratings yet
- DieselDocument23 pagesDieselVijay GaneshNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine: Aguinaldo, Cellan, Gregorio, MedranoDocument33 pagesDiesel Engine: Aguinaldo, Cellan, Gregorio, MedranoHannah AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- 4 Stroke Ignition SystemDocument33 pages4 Stroke Ignition Systemspruhatech0% (1)
- Ic EngineDocument12 pagesIc EngineAbdi samad MohamedNo ratings yet
- IC Engines AutomobilesDocument91 pagesIC Engines Automobileskapun kumar nayakNo ratings yet
- IC Engines Assignment 1: by - Prateek Gauba B12108 ME, 3 YearDocument16 pagesIC Engines Assignment 1: by - Prateek Gauba B12108 ME, 3 YearPrtkkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 The Four-Stroke Cycle and Cylinder ArrangementsDocument16 pagesChapter 10 The Four-Stroke Cycle and Cylinder ArrangementsROSAN YUMANGNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument51 pagesUntitledhalil yıldırımNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke Engine 4TH WorksheetDocument2 pagesFour Stroke Engine 4TH WorksheetlorenitasuarNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument35 pagesInternal Combustion EngineMuhammad FaizNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke Petrol EngineDocument12 pagesFour Stroke Petrol EngineSyed Zaheer SajjadNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke Cycle Theory: Intake Stroke Piston Moving Down Intake Valve Open Exhaust Valve ClosedDocument57 pagesFour Stroke Cycle Theory: Intake Stroke Piston Moving Down Intake Valve Open Exhaust Valve ClosedIndirajithNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke Diesel EngineDocument4 pagesFour Stroke Diesel EngineSwati SutarNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines - The DieselDocument25 pagesInternal Combustion Engines - The DieselTarun PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument12 pagesUnit IIotakoothanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 To 10Document54 pagesLecture 8 To 10Memo KhalidNo ratings yet
- Engines and Steam Turbine Generator: by Muhammad Hassan Siddique Internship Batch: 2021Document23 pagesEngines and Steam Turbine Generator: by Muhammad Hassan Siddique Internship Batch: 2021hassaanNo ratings yet
- Team Nozzle Present .: Four Stroke Petrol EngineDocument33 pagesTeam Nozzle Present .: Four Stroke Petrol EngineChamfreit AxereasNo ratings yet
- Engines Classification and Its ComponentsDocument43 pagesEngines Classification and Its ComponentsKLUniveristyNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine / Diesel Engine CyclesDocument55 pagesInternal Combustion Engine / Diesel Engine CyclesAthul P PNo ratings yet
- Final Project Mechanical PowerDocument163 pagesFinal Project Mechanical PowerVikrant KumarNo ratings yet
- 4-Valve Engines: Guided by Mr. P. D. Sudersanan Asst Prof, Mech Dept, Dr. TtitDocument37 pages4-Valve Engines: Guided by Mr. P. D. Sudersanan Asst Prof, Mech Dept, Dr. TtittarunskumarNo ratings yet
- Ariel Portugal and Vince RiveraDocument81 pagesAriel Portugal and Vince RiveraAriel PortugalNo ratings yet
- The Four Stroke 5-Event Cycle of An AircraftDocument8 pagesThe Four Stroke 5-Event Cycle of An AircraftCarlo PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Engine BlockDocument23 pagesEngine Blockno oneNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 07052020Document2 pagesWorksheet 07052020shirlynNo ratings yet
- 230420essay Section BDocument2 pages230420essay Section BshirlynNo ratings yet
- 160420essay Section CDocument3 pages160420essay Section CshirlynNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Carbon Compounds Part 2Document52 pagesChapter 4 Carbon Compounds Part 2shirlynNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: A Conductor by Changing Magnetic FieldDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: A Conductor by Changing Magnetic FieldshirlynNo ratings yet
- A Technical Seminar Report: Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering CollegeDocument27 pagesA Technical Seminar Report: Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering CollegeK. Vamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Lean Angle Training - Hitch - Moto Gymkhana NederlandDocument4 pagesLean Angle Training - Hitch - Moto Gymkhana Nederlandswisskomputer3865No ratings yet
- Trail/Beaver Valley/Rossland Pennywise May 14, 2013Document64 pagesTrail/Beaver Valley/Rossland Pennywise May 14, 2013Pennywise PublishingNo ratings yet
- Soal To Gundar 2018 Atw Sekitarnya LahDocument13 pagesSoal To Gundar 2018 Atw Sekitarnya LahayaNo ratings yet
- Achievers B1 Units 1 and 2Document24 pagesAchievers B1 Units 1 and 2Leticia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Two-Stroke Engine - WikipediaDocument59 pagesTwo-Stroke Engine - WikipediaDIPU KUMARNo ratings yet
- Classifiers MASTERDocument16 pagesClassifiers MASTERleonardehmiNo ratings yet
- Army Public School For Girls CKL GarsDocument5 pagesArmy Public School For Girls CKL GarsKamila AhsanNo ratings yet
- Multistrada 1200 Enduro 2016 SERVICE MANUALDocument1,163 pagesMultistrada 1200 Enduro 2016 SERVICE MANUALFelipe SafadiNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of Attachment of SidecarDocument1 pageAffidavit of Attachment of SidecarKathleenJoyEnSagun100% (2)
- Urban Transportation Planning Department of Civil EngineeringDocument23 pagesUrban Transportation Planning Department of Civil EngineeringShovon HalderNo ratings yet
- List Game (08976560120)Document2,832 pagesList Game (08976560120)Daffa Al israNo ratings yet
- Full Thesis On MRTDocument213 pagesFull Thesis On MRTNazim UddinNo ratings yet
- New Mechanical ProjectDocument10 pagesNew Mechanical Projectवैज्ञानिक बाबाNo ratings yet
- Format Import Data Identitas Balita 040520053537Document184 pagesFormat Import Data Identitas Balita 040520053537puskesmas jetis 1No ratings yet
- Reliance General Insurance Company Limited: Long Term Two Wheeler Package Policy-ScheduleDocument6 pagesReliance General Insurance Company Limited: Long Term Two Wheeler Package Policy-ScheduleJitendra KambleNo ratings yet
- Kuwait Parking Design Criteria Manual - August 2007 - MunicipalityDocument100 pagesKuwait Parking Design Criteria Manual - August 2007 - Municipalityvijaya guniputiNo ratings yet
- IELTS Reading Practice Test ADocument7 pagesIELTS Reading Practice Test AMenon HariNo ratings yet
- 70-Triumph T120 Repair-Manual-63-70 PDFDocument236 pages70-Triumph T120 Repair-Manual-63-70 PDFSimon TudorNo ratings yet
- Ventura Rack C003BDocument2 pagesVentura Rack C003Bgenedem67No ratings yet
- 1memo - IVMS For Contractors - FINAL - SignedDocument3 pages1memo - IVMS For Contractors - FINAL - SignedCharles Rommel TadoNo ratings yet
- Cables k7 PDFDocument6 pagesCables k7 PDFlombardiacmNo ratings yet
- Geography X With ImagesDocument43 pagesGeography X With ImagesLEARN WITH AGALYANo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Ex2Document3 pagesVocabulary Ex2tayaNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Holdings & Investment Ltd. - Research Center: Balance SheetDocument6 pagesBajaj Holdings & Investment Ltd. - Research Center: Balance Sheetsarathkumarreddy855081No ratings yet
- Ladakh Budget Motorcycle Expeditions - 2023Document21 pagesLadakh Budget Motorcycle Expeditions - 2023preethu shenoyNo ratings yet
- Uz 125Document117 pagesUz 125c4zch62kphNo ratings yet
- J220BIKEPACKDocument2 pagesJ220BIKEPACKAhmad BatranNo ratings yet
- Dibels 8 Benchmark Maze 3 Scoring Key 2020-1Document19 pagesDibels 8 Benchmark Maze 3 Scoring Key 2020-1Amanda HookeNo ratings yet