Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Drug Study On Prednisone
A Drug Study On Prednisone
Uploaded by
Princess Alane Moreno0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
266 views5 pagesThis document summarizes a study on the drug prednisone. It provides information on the generic and brand names, classification, mode of action, dosing, indications, contraindications, side effects, adverse effects, drug interactions, nursing responsibilities, and references for prednisone. The study was presented to the Faculty of Nursing Department to fulfill requirements for a pediatric nursing rotation.
Original Description:
Original Title
A Drug Study on Prednisone
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes a study on the drug prednisone. It provides information on the generic and brand names, classification, mode of action, dosing, indications, contraindications, side effects, adverse effects, drug interactions, nursing responsibilities, and references for prednisone. The study was presented to the Faculty of Nursing Department to fulfill requirements for a pediatric nursing rotation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
266 views5 pagesA Drug Study On Prednisone
A Drug Study On Prednisone
Uploaded by
Princess Alane MorenoThis document summarizes a study on the drug prednisone. It provides information on the generic and brand names, classification, mode of action, dosing, indications, contraindications, side effects, adverse effects, drug interactions, nursing responsibilities, and references for prednisone. The study was presented to the Faculty of Nursing Department to fulfill requirements for a pediatric nursing rotation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
A Drug Study on Prednisone
A Drug Study Presented to
The Faculty of Nursing Department
Mrs. Josephine B. Magno, RN, MN
In Partial Fulfillment on the
Requirements in NCM 209
Pediatric Nursing Rotation
By:
Princess Alane Marie T. Moreno, St.N
BSN 2H
March 28, 2020
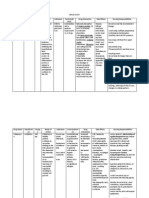
Generic Name: predniSONE
Brand Name: Apo-PredniSONE, PredniSONE Intensol
Classification: Pharmacotherapeutic: Adrenal corticosteroid
Clinical: Anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressant.
Mode of Action: Inhibits accumulation of inflammatory cells at inflammation
sites, phagocytosis, lysosomal enzyme release/synthesis, release of mediators of
inflammation.
Dose and Route: PO: ADULTS, ELDERLY: 5–60 mg/day in divided doses.
CHILDREN: 0.05–2 mg/kg/ day in 1–4 divided doses.
Indication: Dose dependent upon condition treated, patient response rather than rigid adherence to age,
weight, or body surface area.
Contraindication: Prednisone tablets are contraindicated in systemic fungal infections and known
hypersensitivity to components.
Side Effects: Frequent: Insomnia, heartburn, nervousness, abdominal distention, diaphoresis, acne, mood
swings, increased appetite, facial flushing, delayed wound healing, increased susceptibility to
infection, diarrhea, and constipation.
Occasional: Headache, edema, change in skin color, frequent urination.
Rare: Tachycardia, allergic reaction (rash, urticaria), psychological changes, hallucinations,
depression.
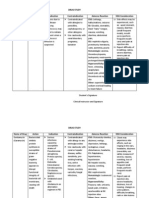
Adverse Effects: CNS: headache,nervousness,depression,euphoria,personality changes,
psychosis,vertigo,paresthesia,insomnia,restlessness,seizures,meningitis, increased
intracranial pressure
CV: hypotension, hypertension, vasculitis, heart failure, thrombophlebitis, thromboembolism,
fat embolism, arrhythmias, shock
EENT: posterior subcapsular cataracts (especially in children), glaucoma, nasal irritation and
congestion, rebound congestion, sneezing, epistaxis, nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal
fungal infections, perforated nasal septum, anosmia, dysphonia, hoarseness, throat irritation
(all with longterm use)
GI: nausea, vomiting, abdominal distention, rectal bleeding, esophageal candidiasis, dry
mouth, esophageal ulcer, pancreatitis, peptic ulcer
GU: amenorrhea, irregular menses
Hematologic: purpura
Metabolic: sodium and fluid retention, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, hyperglycemia, decreased
carbohydrate tolerance, diabetes mellitus, growth retardation (in children), cushingoid effects
(with long-term use), hypothalamicpituitary-adrenal suppression (with systemic use longer than
5 days), adrenal suppression (with high-dose, longterm use)
Musculoskeletal: muscle weakness or atrophy, myalgia, myopathy, osteoporosis, aseptic joint
necrosis, spontaneous fractures (with long-term use), osteonecrosis, tendon rupture
Respiratory: cough, wheezing, bronchospasm
Skin: rash, pruritus, contact dermatitis, acne, striae, poor wound healing, hirsutism, thin fragile
skin, petechiae, bruising, subcutaneous fat atrophy, urticaria, angioedema
Other: bad taste, increased or decreased appetite, weight gain (with long-term use), facial
edema, aggravation or masking of infections, hypersensitivity reaction
Drug Interaction: Drug-drug. Amphotericin B, mezlocillin, piperacillin, thiazide and loop diuretics, ticarcillin:
additive hypokalemia
Aspirin, other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: increased risk of GI discomfort and
bleeding Cardiac glycosides: increased risk of digitalis toxicity due to hypokalemia
Cyclosporine: therapeutic benefits in organ transplant recipients, but with increased risk of
toxicity Erythromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, ketoconazole,ritonavir,saquinavir: increased
prednisone blood level and effects
Hormonal contraceptives: impaired metabolism and increased effects of prednisone
Isoniazid: decreased isoniazid blood level
Live-virus vaccines: decreased antibody response to vaccine, increase risk of adverse effects
Oral anticoagulants: reduced anticoagulant requirements, opposition to anticoagulant action
Phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampin: decreased prednisone efficacy
Salicylates: reduced salicylate blood level Somatrem: inhibition of somatrem’s growth-
promoting effects
Theophylline: altered pharmacologic effects of either drug
Drug-diagnostic tests. Calcium, potassium, thyroid 131I uptake, thyroxine, triiodothyronine:
decreased levels
Cholesterol, glucose: increased levels
Nitroblue tetrazolium test for bacterial infection: false-negative result
Drug-herbs. Alfalfa: activation of quiescent systemic lupus erythematosus
Echinacea: increased immune-stimulating effects
Ephedra (ma huang): decreased drug blood level
Ginseng: potentiation of immunomodulating effect
Licorice: prolonged drug activity
Drug-behaviors. Alcohol use: increased risk of gastric irritation and GI ulcers
Nursing Responsibility:
Obtain baselines for height, weight, B/P, serum glucose, electrolytes.
Check results of initial tests (tuberculosis [TB] skin test, X-rays, EKG).
Monitor B/P,serum electrolytes, glucose, results of bone mineral density test, height, weight
in children.
Be alert to infection (sore throat, fever, vague symptoms); assess oral cavity daily for
signs of Candida infection.
Monitor for symptoms of adrenal insufficiency, or immunosuppression.
Report if there is fever, sore throat, muscle aches, sudden weight gain, swelling, loss of
appetite, or fatigue.
Avoidalcohol, minimize use of caffeine.
Maintain fastidious oral hygiene.
Do not abruptly discontinue without physician’s approval.
Avoidexposure to chickenpox, measles.
Long-term use may significantly increase risk of serious infections.
References:
Kizior, R.J., Hodgson, B.B., Hodgson, K.J, & Witmer, J.B. (2016). Saunders nursing drug
handbook 2019. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier
Kizior, R.J., & Hodgson, K.J. (2019). Saunders nursing drug handbook 2019. St. Louis,
MO: Elsevier
Prednisone (Prednisone Tablets, USP): Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, Interactions, Warning.
(2019, October 24). Retrieved from https://www.rxlist.com/prednisone-
drug.htm#clinpharm S
You might also like
- 1000 Drug CardsDocument33 pages1000 Drug Cardstfish106587% (91)
- Cramsheet (Exam Cram Nclex PN)Document2 pagesCramsheet (Exam Cram Nclex PN)Katrina Reyes94% (32)
- Medication Template PrednisoneDocument5 pagesMedication Template PrednisoneJudith MeranvilNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Drug CardsDocument33 pagesPharmacology Drug CardsAidenhunter05100% (1)
- MALNUTRITIONDocument23 pagesMALNUTRITIONPrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone DrugStudyDocument8 pagesDexamethasone DrugStudySophia IbuyanNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLDocument6 pagesA Drug Study On MISOPROSTOLAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On: Monaliza J. Lee, RN, MNDocument6 pagesA Drug Study On: Monaliza J. Lee, RN, MNJeah Bearl AbellarNo ratings yet
- Group-3-Ward-Class 20240213 182023 0000Document31 pagesGroup-3-Ward-Class 20240213 182023 0000Hanna CarsanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineDocument6 pagesDrug Cefaclor IsoxsuprineJelly Ong 王金玉No ratings yet
- Drug Study PrednisoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study PrednisoneAMIN BARINo ratings yet
- DactinomycinDocument4 pagesDactinomycinKeith MadarangNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyMaria Charlene Orpilla0% (1)
- Anti TB DrugsDocument22 pagesAnti TB DrugsIsmael JaaniNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Effects: Death of Rapidly Replicating Cells, ParticularlyDocument3 pagesTherapeutic Effects: Death of Rapidly Replicating Cells, ParticularlyMarc Louise DatoyNo ratings yet
- AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesAmoxicillindheng05No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyMc Joewell HudencialNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument8 pagesGeneric Namemel aquinoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJoel MadjosNo ratings yet
- Drug STUDY CefotaximeDocument5 pagesDrug STUDY CefotaximeJeffrey Calicdan Bucala75% (8)
- Drug Study 408Document13 pagesDrug Study 408Jheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Drug NameDocument8 pagesDrug Nameleslie_macasaetNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument6 pagesDexamethasoneapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Study ShenDocument12 pagesDrug Study ShenLass KazeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studysarah1217No ratings yet
- Drugstudy and SoapieDocument17 pagesDrugstudy and SoapieYasi EcheniqueNo ratings yet
- Covid19-Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCovid19-Drug StudynicoleNo ratings yet
- Piperacillin Tazobactam Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPiperacillin Tazobactam Drug StudyKathlene Boleche100% (2)
- CHN Drug StudyDocument10 pagesCHN Drug StudyJoshua Cyryll ComiaNo ratings yet
- MG Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMG Drug StudySandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- CiprofloxacinDocument1 pageCiprofloxacinMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Propylthiouracil Drug StudyDocument7 pagesPropylthiouracil Drug StudyAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Propylthiouracil DSDocument7 pagesPropylthiouracil DSAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument16 pagesDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- NLM MedicatingDocument11 pagesNLM MedicatingQuimberly ModequilloNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Toxic Effects, Drug CalculationDocument185 pagesToxic Effects, Drug CalculationAntonette Africa MercadoNo ratings yet
- Pharma Sheet1Document7 pagesPharma Sheet1Lyssa ShannenNo ratings yet
- The Principles of Drugs Prescribing & Drug InteractionDocument87 pagesThe Principles of Drugs Prescribing & Drug InteractionRastia AlimmattabrinaNo ratings yet
- Budesonide Drug CardDocument3 pagesBudesonide Drug CardJanet SheldonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyAbigail LonoganNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Uterine ProlapseDocument9 pagesDrug Study-Uterine ProlapseANNA V. LARITANo ratings yet
- Generic/ Trade Name Dosage/ Frequency Classification Indication Contraindication Side-Effects Nsg. Responsibilities Moderate To Severe InfectionsDocument5 pagesGeneric/ Trade Name Dosage/ Frequency Classification Indication Contraindication Side-Effects Nsg. Responsibilities Moderate To Severe InfectionsRose TumaruNo ratings yet
- C C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentDocument12 pagesC C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentEarl Tony TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Pharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarDocument33 pagesPharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarnamitaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKristine-Joy Legaspi FrancoNo ratings yet
- Additional Pharma CardsDocument21 pagesAdditional Pharma CardsBrilie Karl Viray100% (1)
- KetorolacDocument5 pagesKetorolacMichelle Ann P. NacuaNo ratings yet
- PrednisoneDocument22 pagesPrednisoneAlthea AlicandoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studyjeanylou chachi coronadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeDocument5 pagesNursing Considerations Assessment: History: Infections Kidney Disease Liver Disease, Hypothyroidism UlcerativeSophia limNo ratings yet
- History of Present Illness: Magno, Corisette Corsino Flores C C C C C C C CDocument4 pagesHistory of Present Illness: Magno, Corisette Corsino Flores C C C C C C C CDaniele Katrina PimentelNo ratings yet
- Ncp&drugstudDocument12 pagesNcp&drugstudSarah Mae Billano BermudezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On PtuDocument4 pagesDrug Study On PtuDizzy BualanNo ratings yet
- WarfarinDocument10 pagesWarfarinMar Ordanza100% (1)
- Drug Study NRMFDocument11 pagesDrug Study NRMFKristine ReyesNo ratings yet
- CortisoneDocument2 pagesCortisoneJulioNo ratings yet
- POC Drug StudyDocument9 pagesPOC Drug Studydanni LNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System & Homeopathy: Personalized Nutrition Concept Depicted in Homeopathy & AyurvedaFrom EverandAutonomic Nervous System & Homeopathy: Personalized Nutrition Concept Depicted in Homeopathy & AyurvedaNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainPrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP HyperthermiaPrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocument5 pagesNCP - Activity IntolerancePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument4 pagesNCP HyperthermiaPrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument6 pagesMagnesium SulfatePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Hyperten Sion: Princess Alane Marie T. Moreno, St. NDocument16 pagesHyperten Sion: Princess Alane Marie T. Moreno, St. NPrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Magnesium SulfateDocument6 pagesDrug Study - Magnesium SulfatePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- BioChem ReviewerDocument3 pagesBioChem ReviewerPrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Family Size Beyond What Family Resources Can Adequately ProvideDocument3 pagesFamily Size Beyond What Family Resources Can Adequately ProvidePrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Study GuideDocument40 pagesFinal Exam Study GuideLillabinNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of SleDocument7 pagesDrug Study of Slejoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Adrenocortical SteroidsDocument10 pagesAdrenocortical SteroidsAyu Laisitawati FirlafinzaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Asthma Pathway: ED Phase 1a: Initial Assessment - 1st HourDocument2 pagesClinical Asthma Pathway: ED Phase 1a: Initial Assessment - 1st Hourd'Agung NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Zalameda - Hypothalamic and Pituitary Agents Adrenocortical Agents Thyroid and Parathyroid Anti Diabetic AgentsDocument55 pagesZalameda - Hypothalamic and Pituitary Agents Adrenocortical Agents Thyroid and Parathyroid Anti Diabetic AgentsNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Pharm Quiz 1Document59 pagesPharm Quiz 1Anonymous vXOM1Wxt100% (1)
- Mepolizumab For Prednisone-Dependent Asthma With Sputum EosinophiliaDocument9 pagesMepolizumab For Prednisone-Dependent Asthma With Sputum EosinophiliaSurya Perdana SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Richard Legaspi Crohn's DiseaseDocument12 pagesRichard Legaspi Crohn's DiseaseRichard RLNo ratings yet
- IncompatibilityDocument8 pagesIncompatibilitypoonamNo ratings yet
- ADDISONS DSE - Etio Trends&Issues + DSDocument9 pagesADDISONS DSE - Etio Trends&Issues + DSgraceNo ratings yet
- Med Surg4Document27 pagesMed Surg4Hasan A AsFourNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome in ChildrenDocument36 pagesNephrotic Syndrome in ChildrenMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Form Pg-Sga PDFDocument2 pagesForm Pg-Sga PDFzain syalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Exam 3 Pharmacology Exam 3Document44 pagesPharmacology Exam 3 Pharmacology Exam 3LillabinNo ratings yet
- Abaya 2018Document6 pagesAbaya 2018Muhammad Imam NoorNo ratings yet
- Side Effects of Systemic Corticosteroids in ChildrenDocument6 pagesSide Effects of Systemic Corticosteroids in ChildrenChamara AtukoralaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Andrea Q. Carigma, R.PH., M.D. February 2015Document63 pagesPharmacology: Andrea Q. Carigma, R.PH., M.D. February 2015Leonibel GhloeNo ratings yet
- Scored Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment (PG-SGA)Document2 pagesScored Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment (PG-SGA)Misbah sabirNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Drug Formulary2014 English PDFDocument19 pagesVeterinary Drug Formulary2014 English PDFSamuel LamNo ratings yet
- Blue Book 2023Document193 pagesBlue Book 2023YS NateNo ratings yet
- Prednisone Taper Instead of A Shot - CompressedDocument1 pagePrednisone Taper Instead of A Shot - Compressedh.brovina231573No ratings yet
- Exam Cram Cheet SheetDocument2 pagesExam Cram Cheet SheetSheila Stenson-Roberts100% (1)
- Steroids PDFDocument35 pagesSteroids PDFPratyusha VallamNo ratings yet
- PcolDocument17 pagesPcolThea JulianaNo ratings yet
- Orbital Trauma NCP and Drug StudyDocument5 pagesOrbital Trauma NCP and Drug StudyDersly LaneNo ratings yet
- Nataraja2019 Hiperglikemia Induced SteroidDocument5 pagesNataraja2019 Hiperglikemia Induced SteroidLia WieNo ratings yet
- Steroid-CIDP (2017)Document34 pagesSteroid-CIDP (2017)Nattawat TeerawattanapongNo ratings yet
- 603v16n04 90399541mmc1Document83 pages603v16n04 90399541mmc1ShashiNo ratings yet
- MS Set 8Document8 pagesMS Set 8John Derama SagapsapanNo ratings yet