Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 viewsVs 4 2015
Vs 4 2015
Uploaded by
api-297727492The document summarizes life in colonial Virginia, focusing on agriculture, slavery, culture, economics, and everyday life. It explains that tobacco became the dominant cash crop and drove the use of slave labor. As tobacco plantations grew, Williamsburg replaced Jamestown as the capital due to health issues. Money was scarce so the economy relied on barter, credit, and tobacco as currency. Culture blended European, African, and Native American influences. Daily life differed between social classes and races, with most working as farmers or slaves in a basic agrarian society.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Slavery ContractDocument4 pagesSlavery ContractAlfee Azli Yajid100% (1)
- Middle Passage Questions PDFDocument5 pagesMiddle Passage Questions PDFJonathan Mlawski100% (3)
- 8th Grade Social Studies STAAR Review by ErasDocument12 pages8th Grade Social Studies STAAR Review by ErasElsa De Leon100% (2)
- Naima Van Tyn - Homegoing Close Reading AnalysisDocument3 pagesNaima Van Tyn - Homegoing Close Reading Analysisapi-439121896No ratings yet
- Mistress Ezada Sinns Male Chastity ContractDocument4 pagesMistress Ezada Sinns Male Chastity ContractPaul100% (2)
- 5th Grade HistoryDocument8 pages5th Grade HistoryBrett Sparrgrove100% (1)
- Reading Comprehension Worksheet Abraham LincolnDocument2 pagesReading Comprehension Worksheet Abraham Lincolnbayefall kandji88% (8)
- Lesson 3 PPDocument7 pagesLesson 3 PPapi-507996900No ratings yet
- Socials 11 Counterpoints - Notes Chapter 1: A Different CanadaDocument3 pagesSocials 11 Counterpoints - Notes Chapter 1: A Different CanadawallaceyuenNo ratings yet
- Failed Colonies and Early Successful English Settlements in North AmericaDocument49 pagesFailed Colonies and Early Successful English Settlements in North AmericaLucas AccastelloNo ratings yet
- 13 ColoniesDocument25 pages13 Colonieser9rughNo ratings yet
- Life of Indigenous People in AmericaDocument13 pagesLife of Indigenous People in AmericaAnshika GargNo ratings yet
- The Acadian ExpulsionsDocument20 pagesThe Acadian ExpulsionsLuke Marchand100% (1)
- Weebly Unit 1a Part 6 - Life in Colonial AmericaDocument26 pagesWeebly Unit 1a Part 6 - Life in Colonial Americaapi-327777794No ratings yet
- Slave Trade and ColonialismDocument21 pagesSlave Trade and ColonialismTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument2 pagesHistoryCharisma MasongsongNo ratings yet
- Life in The King CottonDocument13 pagesLife in The King Cottonapi-327653481100% (1)
- VS.2 - V G, N P: D G Irginia Eography Ative EoplesDocument2 pagesVS.2 - V G, N P: D G Irginia Eography Ative Eoplesapi-297727492No ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document16 pagesChapter 21Urshia Wren Basiyo HolgadoNo ratings yet
- Comparing and Contrasting The North and SouthDocument1 pageComparing and Contrasting The North and SouthGenesis Lissette Loyola OrtizNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography: The Big IdeaDocument16 pagesPhysical Geography: The Big IdeakanikaNo ratings yet
- 1 Colonization of AmericaDocument52 pages1 Colonization of Americamarinusm100% (1)
- THE WAY WEST (Chapter 13 Notes.)Document5 pagesTHE WAY WEST (Chapter 13 Notes.)swampfsNo ratings yet
- African Americans Help Create A New NationDocument51 pagesAfrican Americans Help Create A New NationAnanya Varahabhatla Student - PantherCreekHSNo ratings yet
- 13 Colonies Study GuideDocument3 pages13 Colonies Study Guideحمـزه HamzahNo ratings yet
- The Making of A Global World Part 2Document18 pagesThe Making of A Global World Part 2amulyajadhav119No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 EARLY FILIPINOS AND THEIR CULTURE AutosavedDocument31 pagesChapter 1 EARLY FILIPINOS AND THEIR CULTURE AutosavedbngynreaNo ratings yet
- CH 18Document3 pagesCH 18Dessi Anjelika CeballosNo ratings yet
- The Southern ColoniesDocument2 pagesThe Southern ColoniesRosalba DallamyNo ratings yet
- Plenary 4 2017Document14 pagesPlenary 4 2017Safiya JamesNo ratings yet
- SpanishDocument43 pagesSpanishJerry De Leon LptNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For ColonizationDocument2 pagesStudy Guide For ColonizationNathan RolfeNo ratings yet
- The Free Village Movement 125-133Document9 pagesThe Free Village Movement 125-133yanique mooreNo ratings yet
- 2021 Chapter 4 and 5Document46 pages2021 Chapter 4 and 5fo25804No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The World Before 1600: Section Notes Video MapsDocument55 pagesChapter 1 - The World Before 1600: Section Notes Video MapsVu YzNo ratings yet
- History Notes-February 10 2011Document3 pagesHistory Notes-February 10 2011infograydonNo ratings yet
- APUSH Period 1 - 1491-1607 Study GuideDocument8 pagesAPUSH Period 1 - 1491-1607 Study GuideElla KalinowskiNo ratings yet
- For Land OwnershipDocument12 pagesFor Land OwnershipFelimar CalaNo ratings yet
- APUSH Notes, Chapters 4-5Document7 pagesAPUSH Notes, Chapters 4-5HelieNo ratings yet
- Sugar Revolution The Mid-To-late 17th CenturyDocument24 pagesSugar Revolution The Mid-To-late 17th CenturypreyaNo ratings yet
- European Rule (1760AD - 1947AD)Document12 pagesEuropean Rule (1760AD - 1947AD)Oyon Nur newazNo ratings yet
- History SBA Auto Saved)Document3 pagesHistory SBA Auto Saved)Rochelle Ramkissoon100% (2)
- Economic and Social Development in E.africa S.3Document16 pagesEconomic and Social Development in E.africa S.3Shafic RuckyNo ratings yet
- Tainos & Caribs: Rediscovering HeritageDocument8 pagesTainos & Caribs: Rediscovering Heritagejoelito mNo ratings yet
- WhenThree Worlds CollideDocument31 pagesWhenThree Worlds Collideer9rughNo ratings yet
- Caribbean Economy and SlaveryDocument22 pagesCaribbean Economy and SlaveryNeiliah Jackson100% (2)
- Group 4 Farmers, Servants, Workers and CraftsmenDocument5 pagesGroup 4 Farmers, Servants, Workers and Craftsmenoneplus du hocNo ratings yet
- Conquistadores, and To Understand The Transformations of Their Communal Lives Through ChangingDocument11 pagesConquistadores, and To Understand The Transformations of Their Communal Lives Through ChangingRicky Faith SantosNo ratings yet
- Life and Works of Rizal 1.0Document16 pagesLife and Works of Rizal 1.0lorenadelejero14No ratings yet
- Firstamericans 2Document31 pagesFirstamericans 2Kizzie SmithNo ratings yet
- 04 Handout 3Document13 pages04 Handout 3Kylee PerezNo ratings yet
- Victorian EnglandDocument17 pagesVictorian Englandbzlara17No ratings yet
- Antebellum SouthDocument67 pagesAntebellum SouthAnna100% (2)
- Chapters 2 and 3Document90 pagesChapters 2 and 3hirahsyed00No ratings yet
- The South 1Document22 pagesThe South 1clarkcarmNo ratings yet
- Riph111 FinalDocument15 pagesRiph111 FinalIVY SUPNETNo ratings yet
- The Establishment of The Peasantry 1838 To 1900Document4 pagesThe Establishment of The Peasantry 1838 To 1900Aswani HarrisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The World Before 1600: Section Notes Video MapsDocument67 pagesChapter 1 - The World Before 1600: Section Notes Video MapsEmily HoardNo ratings yet
- Periods of Caribbean HistoryDocument57 pagesPeriods of Caribbean HistoryCall Mi BlacksNo ratings yet
- Indigenous PeopleDocument26 pagesIndigenous PeopleAbby GoodingsNo ratings yet
- 13 British ColoniesDocument46 pages13 British ColoniesSarah SunNo ratings yet
- Rizal AssignmentDocument1 pageRizal AssignmentmeriiNo ratings yet
- Probability Sol 4Document3 pagesProbability Sol 4api-297727492No ratings yet
- Probability Vocabulary CardsDocument12 pagesProbability Vocabulary Cardsapi-297727492No ratings yet
- VS.2 - V G, N P: D G Irginia Eography Ative EoplesDocument2 pagesVS.2 - V G, N P: D G Irginia Eography Ative Eoplesapi-297727492No ratings yet
- 4Document3 pages4api-504443760No ratings yet
- Sex Trafficking, Rape and ProstitutionDocument24 pagesSex Trafficking, Rape and ProstitutionAna MarkovićNo ratings yet
- Civil War Station Project Question Sheet Set 1: Lincoln DocumentsDocument10 pagesCivil War Station Project Question Sheet Set 1: Lincoln DocumentsNikki Nguyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- Art. 333 - 346 - Crimes Against ChastityDocument6 pagesArt. 333 - 346 - Crimes Against ChastityLeomar Despi LadongaNo ratings yet
- African American Humor EssayDocument4 pagesAfrican American Humor EssayKarla PerezNo ratings yet
- Ask The White GuyDocument192 pagesAsk The White GuywettsjulNo ratings yet
- History SbaDocument12 pagesHistory SbaTrapGNo ratings yet
- Some Thoughts On Haunting and FuturityDocument21 pagesSome Thoughts On Haunting and FuturityNina Hoechtl100% (1)
- Apush DBQ 1Document3 pagesApush DBQ 1Jeremy D AllenNo ratings yet
- 02.09 Just Courage - God's Great Expedition For The Restless Christian (Gary Haughen)Document14 pages02.09 Just Courage - God's Great Expedition For The Restless Christian (Gary Haughen)newbeginningNo ratings yet
- 08 - American Civil WarDocument9 pages08 - American Civil WarHeidy Teresa MoralesNo ratings yet
- According To French Poet Alfred de MussetDocument7 pagesAccording To French Poet Alfred de MussetChelsea JoyeauNo ratings yet
- Conversations Between Michael Albert and Noam ChomskyDocument47 pagesConversations Between Michael Albert and Noam ChomskyJustin SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Research Paper hd341Document7 pagesResearch Paper hd341api-379926458No ratings yet
- History of Black AmericansDocument1 pageHistory of Black AmericansJavier Campos LainezNo ratings yet
- 2016 NHD Theme BookDocument69 pages2016 NHD Theme Bookcorbinmoore1No ratings yet
- Gladiators - of LegendDocument98 pagesGladiators - of LegendBen100% (1)
- Chapte R: Evolution of Industrial Relations in IndiaDocument9 pagesChapte R: Evolution of Industrial Relations in IndianimeshvadhelNo ratings yet
- Santhal RebellionDocument25 pagesSanthal RebellionAnushka DattaNo ratings yet
- Phillis Wheatley - An Eighteenth-Century Genius in Bondage - The Public Domain ReviewDocument18 pagesPhillis Wheatley - An Eighteenth-Century Genius in Bondage - The Public Domain ReviewClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Ñ, Ñ, Ñ, Ñ, Ñ,,,,,,,LLLLLLLDocument3 pagesÑ, Ñ, Ñ, Ñ, Ñ,,,,,,,LLLLLLLVenezuela NocturnaNo ratings yet
- The English Language in British Guiana: Richard AllsoppDocument8 pagesThe English Language in British Guiana: Richard AllsoppPaulo PilarNo ratings yet
- CAPE History 2015 U1 P1Document6 pagesCAPE History 2015 U1 P1Savannah-Rae ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 21 Slavery in America, The "Peculiar Institution" StudentDocument25 pagesLesson 21 Slavery in America, The "Peculiar Institution" StudentGabriel Balderrama100% (1)
- Slavery, Religion, and The Philosophy of FreedomDocument3 pagesSlavery, Religion, and The Philosophy of FreedomMark AlznauerNo ratings yet
- Mindslaver DLCDocument6 pagesMindslaver DLCUday SraNo ratings yet
Vs 4 2015
Vs 4 2015
Uploaded by
api-2977274920 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views2 pagesThe document summarizes life in colonial Virginia, focusing on agriculture, slavery, culture, economics, and everyday life. It explains that tobacco became the dominant cash crop and drove the use of slave labor. As tobacco plantations grew, Williamsburg replaced Jamestown as the capital due to health issues. Money was scarce so the economy relied on barter, credit, and tobacco as currency. Culture blended European, African, and Native American influences. Daily life differed between social classes and races, with most working as farmers or slaves in a basic agrarian society.
Original Description:
Original Title
vs-4-2015
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes life in colonial Virginia, focusing on agriculture, slavery, culture, economics, and everyday life. It explains that tobacco became the dominant cash crop and drove the use of slave labor. As tobacco plantations grew, Williamsburg replaced Jamestown as the capital due to health issues. Money was scarce so the economy relied on barter, credit, and tobacco as currency. Culture blended European, African, and Native American influences. Daily life differed between social classes and races, with most working as farmers or slaves in a basic agrarian society.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views2 pagesVs 4 2015
Vs 4 2015
Uploaded by
api-297727492The document summarizes life in colonial Virginia, focusing on agriculture, slavery, culture, economics, and everyday life. It explains that tobacco became the dominant cash crop and drove the use of slave labor. As tobacco plantations grew, Williamsburg replaced Jamestown as the capital due to health issues. Money was scarce so the economy relied on barter, credit, and tobacco as currency. Culture blended European, African, and Native American influences. Daily life differed between social classes and races, with most working as farmers or slaves in a basic agrarian society.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
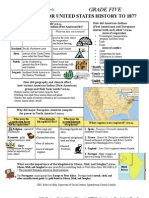
VIRGINIA STUDIES 2015 CURRICULUM FRAMEWORK (CONDENSED) – STUDY GUIDE
VS.4 LIFE IN THE VIRGINIA COLONY
STANDARD VS.4A
AGRICULTURE & SLAVERY
The success of tobacco as a cash crop transformed life
in the Virginia colony and encouraged slavery.
Terms to know
• Cash crop: A crop that is grown to sell for money
rather than for use by the growers
Settlement areas
• The economy of the Virginia colony depended on
agriculture as a primary source of wealth. • English and other Europeans settled primarily in
Coastal Plain (Tidewater) and Piedmont regions.
– Tobacco became the most profitable agricultural
product because it was sold in England as a cash • Germans and Scots-Irish settled primarily in the
crop. Shenandoah Valley, which was along the migration
route.
The successful planting of
tobacco depended on a • Africans were brought primarily to the Coastal Plain
steady and inexpensive (Tidewater) and Piedmont regions to work in tobacco
source of labor. fields which required a great deal of labor.
– For this reason, • Prior to the arrival of the settlers, American Indians
African men, lived throughout Virginia.
women, and – After the settlers arrived, most were forced
children were inland.
brought to the Virginia colony and enslaved to Migration and living in new areas caused people to adapt old
work on the plantations. customs to their new environment.
– The Virginia colony became dependent on slave
labor, and the dependence lasted a long time. STANDARD VS.4C
STANDARD VS.4B CAPITAL MOVES TO WILLIAMSBURG
CULTURE REFLECTS ORIGINS A variety of factors explain the reasons for moving
Virginia’s capital.
The culture of colonial Virginia reflected beliefs,
customs, and architecture of Europeans, Africans, and Reasons why the capital was moved from Jamestown to
American Indians living there. Williamsburg
Although a colony of England, Virginia developed a • Drinking water in Jamestown was contaminated by
unique culture different from that of England. seepage of salt water.
Culture of colonial Virginia • Unhealthy living conditions caused diseases.
Whenever people settle an area, they change the • Fire destroyed wooden and brick buildings at
landscape to reflect their culture and customs. Examples Jamestown.
of architecture that reflect different cultures include • Williamsburg was an already established town.
• barns
• homes
• places of worship (e.g., churches)
Place names reflecting culture
• English—Richmond
• American Indian - Roanoke
STANDARD VS.4D
MONEY, BARTER, CREDIT STANDARD VS.4E
Money was not often used in the early Virginia colony. EVERYDAY LIFE
Because farmers could not pay for goods until their Resources were used in colonial Virginia to produce the
crops were harvested, credit was important in Virginia. goods and services that people needed.
Terms to know Everyday life was different for whites, enslaved African
• Money: A medium of exchange (currency, which Americans, and free African Americans in colonial Virginia.
includes coins and paper
People living in colonial Virginia depended on natural, human,
bills)
and capital resources to produce the goods and services they
• Barter: Trading/exchanging needed.
of goods and services
without the use of money Food:
• Food choices were limited
• Credit: Buying a good or
service now and paying for • Meals were made of local produce and meats
it later Housing:
• Debt: A good or service owed to another • Most people lived in one-room homes with dirt floors
• Saving: Money put away to save or to spend at a later • Some wealthy people (farmers) lived in large houses
time
Clothing:
Few people had paper money and coins to use to buy goods
and services. • Women in households made clothes for family
members
– Barter was commonly used instead of money.
• Most clothing was made of cotton, wool, and/or
– Tobacco was used as money. A tobacco farmer leather.
could use his tobacco to pay for goods and
services. Most white Virginians made their living from the land as small
farmers.
Farmers and other consumers could also buy goods and
services on credit and pay their debts when their crops were – A few owned large farms (plantations).,
harvested and sold. Most enslaved African Americans worked tobacco, crops, and
Colonial Virginia had no banks livestock.
– Enslaved African Americans were denied basic
rights.
– Some free African Americans owned land but
were denied basic rights.
You might also like
- Slavery ContractDocument4 pagesSlavery ContractAlfee Azli Yajid100% (1)
- Middle Passage Questions PDFDocument5 pagesMiddle Passage Questions PDFJonathan Mlawski100% (3)
- 8th Grade Social Studies STAAR Review by ErasDocument12 pages8th Grade Social Studies STAAR Review by ErasElsa De Leon100% (2)
- Naima Van Tyn - Homegoing Close Reading AnalysisDocument3 pagesNaima Van Tyn - Homegoing Close Reading Analysisapi-439121896No ratings yet
- Mistress Ezada Sinns Male Chastity ContractDocument4 pagesMistress Ezada Sinns Male Chastity ContractPaul100% (2)
- 5th Grade HistoryDocument8 pages5th Grade HistoryBrett Sparrgrove100% (1)
- Reading Comprehension Worksheet Abraham LincolnDocument2 pagesReading Comprehension Worksheet Abraham Lincolnbayefall kandji88% (8)
- Lesson 3 PPDocument7 pagesLesson 3 PPapi-507996900No ratings yet
- Socials 11 Counterpoints - Notes Chapter 1: A Different CanadaDocument3 pagesSocials 11 Counterpoints - Notes Chapter 1: A Different CanadawallaceyuenNo ratings yet
- Failed Colonies and Early Successful English Settlements in North AmericaDocument49 pagesFailed Colonies and Early Successful English Settlements in North AmericaLucas AccastelloNo ratings yet
- 13 ColoniesDocument25 pages13 Colonieser9rughNo ratings yet
- Life of Indigenous People in AmericaDocument13 pagesLife of Indigenous People in AmericaAnshika GargNo ratings yet
- The Acadian ExpulsionsDocument20 pagesThe Acadian ExpulsionsLuke Marchand100% (1)
- Weebly Unit 1a Part 6 - Life in Colonial AmericaDocument26 pagesWeebly Unit 1a Part 6 - Life in Colonial Americaapi-327777794No ratings yet
- Slave Trade and ColonialismDocument21 pagesSlave Trade and ColonialismTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument2 pagesHistoryCharisma MasongsongNo ratings yet
- Life in The King CottonDocument13 pagesLife in The King Cottonapi-327653481100% (1)
- VS.2 - V G, N P: D G Irginia Eography Ative EoplesDocument2 pagesVS.2 - V G, N P: D G Irginia Eography Ative Eoplesapi-297727492No ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document16 pagesChapter 21Urshia Wren Basiyo HolgadoNo ratings yet
- Comparing and Contrasting The North and SouthDocument1 pageComparing and Contrasting The North and SouthGenesis Lissette Loyola OrtizNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography: The Big IdeaDocument16 pagesPhysical Geography: The Big IdeakanikaNo ratings yet
- 1 Colonization of AmericaDocument52 pages1 Colonization of Americamarinusm100% (1)
- THE WAY WEST (Chapter 13 Notes.)Document5 pagesTHE WAY WEST (Chapter 13 Notes.)swampfsNo ratings yet
- African Americans Help Create A New NationDocument51 pagesAfrican Americans Help Create A New NationAnanya Varahabhatla Student - PantherCreekHSNo ratings yet
- 13 Colonies Study GuideDocument3 pages13 Colonies Study Guideحمـزه HamzahNo ratings yet
- The Making of A Global World Part 2Document18 pagesThe Making of A Global World Part 2amulyajadhav119No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 EARLY FILIPINOS AND THEIR CULTURE AutosavedDocument31 pagesChapter 1 EARLY FILIPINOS AND THEIR CULTURE AutosavedbngynreaNo ratings yet
- CH 18Document3 pagesCH 18Dessi Anjelika CeballosNo ratings yet
- The Southern ColoniesDocument2 pagesThe Southern ColoniesRosalba DallamyNo ratings yet
- Plenary 4 2017Document14 pagesPlenary 4 2017Safiya JamesNo ratings yet
- SpanishDocument43 pagesSpanishJerry De Leon LptNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For ColonizationDocument2 pagesStudy Guide For ColonizationNathan RolfeNo ratings yet
- The Free Village Movement 125-133Document9 pagesThe Free Village Movement 125-133yanique mooreNo ratings yet
- 2021 Chapter 4 and 5Document46 pages2021 Chapter 4 and 5fo25804No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The World Before 1600: Section Notes Video MapsDocument55 pagesChapter 1 - The World Before 1600: Section Notes Video MapsVu YzNo ratings yet
- History Notes-February 10 2011Document3 pagesHistory Notes-February 10 2011infograydonNo ratings yet
- APUSH Period 1 - 1491-1607 Study GuideDocument8 pagesAPUSH Period 1 - 1491-1607 Study GuideElla KalinowskiNo ratings yet
- For Land OwnershipDocument12 pagesFor Land OwnershipFelimar CalaNo ratings yet
- APUSH Notes, Chapters 4-5Document7 pagesAPUSH Notes, Chapters 4-5HelieNo ratings yet
- Sugar Revolution The Mid-To-late 17th CenturyDocument24 pagesSugar Revolution The Mid-To-late 17th CenturypreyaNo ratings yet
- European Rule (1760AD - 1947AD)Document12 pagesEuropean Rule (1760AD - 1947AD)Oyon Nur newazNo ratings yet
- History SBA Auto Saved)Document3 pagesHistory SBA Auto Saved)Rochelle Ramkissoon100% (2)
- Economic and Social Development in E.africa S.3Document16 pagesEconomic and Social Development in E.africa S.3Shafic RuckyNo ratings yet
- Tainos & Caribs: Rediscovering HeritageDocument8 pagesTainos & Caribs: Rediscovering Heritagejoelito mNo ratings yet
- WhenThree Worlds CollideDocument31 pagesWhenThree Worlds Collideer9rughNo ratings yet
- Caribbean Economy and SlaveryDocument22 pagesCaribbean Economy and SlaveryNeiliah Jackson100% (2)
- Group 4 Farmers, Servants, Workers and CraftsmenDocument5 pagesGroup 4 Farmers, Servants, Workers and Craftsmenoneplus du hocNo ratings yet
- Conquistadores, and To Understand The Transformations of Their Communal Lives Through ChangingDocument11 pagesConquistadores, and To Understand The Transformations of Their Communal Lives Through ChangingRicky Faith SantosNo ratings yet
- Life and Works of Rizal 1.0Document16 pagesLife and Works of Rizal 1.0lorenadelejero14No ratings yet
- Firstamericans 2Document31 pagesFirstamericans 2Kizzie SmithNo ratings yet
- 04 Handout 3Document13 pages04 Handout 3Kylee PerezNo ratings yet
- Victorian EnglandDocument17 pagesVictorian Englandbzlara17No ratings yet
- Antebellum SouthDocument67 pagesAntebellum SouthAnna100% (2)
- Chapters 2 and 3Document90 pagesChapters 2 and 3hirahsyed00No ratings yet
- The South 1Document22 pagesThe South 1clarkcarmNo ratings yet
- Riph111 FinalDocument15 pagesRiph111 FinalIVY SUPNETNo ratings yet
- The Establishment of The Peasantry 1838 To 1900Document4 pagesThe Establishment of The Peasantry 1838 To 1900Aswani HarrisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The World Before 1600: Section Notes Video MapsDocument67 pagesChapter 1 - The World Before 1600: Section Notes Video MapsEmily HoardNo ratings yet
- Periods of Caribbean HistoryDocument57 pagesPeriods of Caribbean HistoryCall Mi BlacksNo ratings yet
- Indigenous PeopleDocument26 pagesIndigenous PeopleAbby GoodingsNo ratings yet
- 13 British ColoniesDocument46 pages13 British ColoniesSarah SunNo ratings yet
- Rizal AssignmentDocument1 pageRizal AssignmentmeriiNo ratings yet
- Probability Sol 4Document3 pagesProbability Sol 4api-297727492No ratings yet
- Probability Vocabulary CardsDocument12 pagesProbability Vocabulary Cardsapi-297727492No ratings yet
- VS.2 - V G, N P: D G Irginia Eography Ative EoplesDocument2 pagesVS.2 - V G, N P: D G Irginia Eography Ative Eoplesapi-297727492No ratings yet
- 4Document3 pages4api-504443760No ratings yet
- Sex Trafficking, Rape and ProstitutionDocument24 pagesSex Trafficking, Rape and ProstitutionAna MarkovićNo ratings yet
- Civil War Station Project Question Sheet Set 1: Lincoln DocumentsDocument10 pagesCivil War Station Project Question Sheet Set 1: Lincoln DocumentsNikki Nguyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- Art. 333 - 346 - Crimes Against ChastityDocument6 pagesArt. 333 - 346 - Crimes Against ChastityLeomar Despi LadongaNo ratings yet
- African American Humor EssayDocument4 pagesAfrican American Humor EssayKarla PerezNo ratings yet
- Ask The White GuyDocument192 pagesAsk The White GuywettsjulNo ratings yet
- History SbaDocument12 pagesHistory SbaTrapGNo ratings yet
- Some Thoughts On Haunting and FuturityDocument21 pagesSome Thoughts On Haunting and FuturityNina Hoechtl100% (1)
- Apush DBQ 1Document3 pagesApush DBQ 1Jeremy D AllenNo ratings yet
- 02.09 Just Courage - God's Great Expedition For The Restless Christian (Gary Haughen)Document14 pages02.09 Just Courage - God's Great Expedition For The Restless Christian (Gary Haughen)newbeginningNo ratings yet
- 08 - American Civil WarDocument9 pages08 - American Civil WarHeidy Teresa MoralesNo ratings yet
- According To French Poet Alfred de MussetDocument7 pagesAccording To French Poet Alfred de MussetChelsea JoyeauNo ratings yet
- Conversations Between Michael Albert and Noam ChomskyDocument47 pagesConversations Between Michael Albert and Noam ChomskyJustin SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Research Paper hd341Document7 pagesResearch Paper hd341api-379926458No ratings yet
- History of Black AmericansDocument1 pageHistory of Black AmericansJavier Campos LainezNo ratings yet
- 2016 NHD Theme BookDocument69 pages2016 NHD Theme Bookcorbinmoore1No ratings yet
- Gladiators - of LegendDocument98 pagesGladiators - of LegendBen100% (1)
- Chapte R: Evolution of Industrial Relations in IndiaDocument9 pagesChapte R: Evolution of Industrial Relations in IndianimeshvadhelNo ratings yet
- Santhal RebellionDocument25 pagesSanthal RebellionAnushka DattaNo ratings yet
- Phillis Wheatley - An Eighteenth-Century Genius in Bondage - The Public Domain ReviewDocument18 pagesPhillis Wheatley - An Eighteenth-Century Genius in Bondage - The Public Domain ReviewClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Ñ, Ñ, Ñ, Ñ, Ñ,,,,,,,LLLLLLLDocument3 pagesÑ, Ñ, Ñ, Ñ, Ñ,,,,,,,LLLLLLLVenezuela NocturnaNo ratings yet
- The English Language in British Guiana: Richard AllsoppDocument8 pagesThe English Language in British Guiana: Richard AllsoppPaulo PilarNo ratings yet
- CAPE History 2015 U1 P1Document6 pagesCAPE History 2015 U1 P1Savannah-Rae ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- Lesson 21 Slavery in America, The "Peculiar Institution" StudentDocument25 pagesLesson 21 Slavery in America, The "Peculiar Institution" StudentGabriel Balderrama100% (1)
- Slavery, Religion, and The Philosophy of FreedomDocument3 pagesSlavery, Religion, and The Philosophy of FreedomMark AlznauerNo ratings yet
- Mindslaver DLCDocument6 pagesMindslaver DLCUday SraNo ratings yet