Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genres of History Outline
Genres of History Outline
Uploaded by
AlexanderBarreraCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- DLL Week 5 21st Century Quater 1Document4 pagesDLL Week 5 21st Century Quater 1GRACE TUBILNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Lesson Plan - Inductive Grammar Approach - MTeflSystemDocument10 pagesActivity 1 - Lesson Plan - Inductive Grammar Approach - MTeflSystemInés Amaya DíazNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report GPTADocument2 pagesAccomplishment Report GPTAJOAN CAMANGA50% (4)
- Tasks Requiring Specific Genres OutlineDocument1 pageTasks Requiring Specific Genres OutlineAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- History of ArchitectureDocument167 pagesHistory of ArchitectureEliza Mae Aquino100% (2)
- Scheme History Form 1.docx OrientationDocument7 pagesScheme History Form 1.docx OrientationHope JohnNo ratings yet
- Reading 1: Curriculum Genres in The Secondary ContextDocument5 pagesReading 1: Curriculum Genres in The Secondary ContextLachlan BarrattNo ratings yet
- The Novel TodayDocument3 pagesThe Novel Todaylennon tanNo ratings yet
- Resume of Presentation - Modul 4 - Febrian SururiDocument16 pagesResume of Presentation - Modul 4 - Febrian SururiSururi FebrianNo ratings yet
- Grade 7english Instructional Plan Q4Document8 pagesGrade 7english Instructional Plan Q4Imelda Quintos0% (1)
- Webquest Assessment RubricDocument2 pagesWebquest Assessment Rubricapi-360154838No ratings yet
- Historical StoryDocument2 pagesHistorical StoryScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- G 9 Hist Annual PlanAbune Gorgorios School History Annual Plan GRADEDocument5 pagesG 9 Hist Annual PlanAbune Gorgorios School History Annual Plan GRADEDawit BerheNo ratings yet
- PKS History Sept 2020 RBDocument10 pagesPKS History Sept 2020 RBKhoerun NisaNo ratings yet
- Seminario de San Jose: Diary Curriculum MapDocument8 pagesSeminario de San Jose: Diary Curriculum MapKARLO MARKO VALLADORESNo ratings yet
- Costanzo - 2008 - Giedeon As Guide (+ Inleiding The Baroque in Architectural Culture)Document13 pagesCostanzo - 2008 - Giedeon As Guide (+ Inleiding The Baroque in Architectural Culture)charlotteNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument1 pageReportapi-571254062No ratings yet
- Final MYP2 Unit MapDocument1 pageFinal MYP2 Unit MapDurba RayNo ratings yet
- Genres of Science OutlineDocument1 pageGenres of Science OutlineAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- June 3, 2019 Objectives Topics References IM's Activities RemarksDocument13 pagesJune 3, 2019 Objectives Topics References IM's Activities RemarksAilyn C. IyanaNo ratings yet
- Martin MayaSuperstates 1995Document7 pagesMartin MayaSuperstates 1995CHrisNo ratings yet
- ST ND: Scheme of Work of History Form One For 2023 Term I & Ii 1 / 9Document9 pagesST ND: Scheme of Work of History Form One For 2023 Term I & Ii 1 / 9peter jagoNo ratings yet
- LK Modul English For Entertaiment Modul 4Document6 pagesLK Modul English For Entertaiment Modul 4Nopita RinggoNo ratings yet
- LK Modul English For EntertaimentDocument6 pagesLK Modul English For EntertaimentNopita RinggoNo ratings yet
- LK Modul English For Entertaiment Modul 4Document6 pagesLK Modul English For Entertaiment Modul 4Nopita RinggoNo ratings yet
- GUNE Tense Mood PDFDocument230 pagesGUNE Tense Mood PDFMantrinNo ratings yet
- Core Subjs (SHS)Document71 pagesCore Subjs (SHS)EDGAR RIVERANo ratings yet
- G5 Q3W4 DLL ENGLISH (MELCs)Document11 pagesG5 Q3W4 DLL ENGLISH (MELCs)Shy Nd DelNo ratings yet
- Creative NonfictionDocument15 pagesCreative NonfictionABIGAIL D. ESGUERRANo ratings yet
- Zelenak - Two Versions of ConstructivismDocument18 pagesZelenak - Two Versions of ConstructivismElizabeth MataNo ratings yet
- Krauss - Photography's Discursive Spaces - Landscape-View - 1982Document10 pagesKrauss - Photography's Discursive Spaces - Landscape-View - 1982Noam GonnenNo ratings yet
- Nichols VoiceofDocDocument7 pagesNichols VoiceofDocignacio gonzalez100% (1)
- Historical Thinking Skills For APUSH: Chronological ReasoningDocument3 pagesHistorical Thinking Skills For APUSH: Chronological ReasoningDiki Jayan DikaNo ratings yet
- Mind Map of Prose and TheaterDocument1 pageMind Map of Prose and TheaterScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- University of Rizal SystemDocument2 pagesUniversity of Rizal SystemMichaella AcebucheNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing About LiteratureDocument1 pageReading and Writing About LiteraturesameerfiservNo ratings yet
- Some Strategies For Coding Sentential Subjects in English: From Exaptation To GrammaticalizationDocument41 pagesSome Strategies For Coding Sentential Subjects in English: From Exaptation To GrammaticalizationAlina RNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature CODocument7 pages21st Century Literature COMICHELLE NAVAREZNo ratings yet
- N N N N N N: Grade 7 Grade 8Document3 pagesN N N N N N: Grade 7 Grade 8api-202727113No ratings yet
- Table of Specification: Learning Competencies Cognitive Process DimensionDocument6 pagesTable of Specification: Learning Competencies Cognitive Process DimensionAngelica RocamoraNo ratings yet
- Modul Profesional 4Document6 pagesModul Profesional 4ainul yaqinNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Complexity Matrix OnlyDocument5 pagesCognitive Complexity Matrix Onlyapi-486317294No ratings yet
- CM Q1eng.10Document3 pagesCM Q1eng.10andrea mea sumauangNo ratings yet
- July 2-5, 2019Document3 pagesJuly 2-5, 2019JUAN DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Azimio La KaziDocument8 pagesAzimio La KaziJuma MpangaNo ratings yet
- LukePitcher 2009 5WritingAncientHistor WritingAncientHistoryDocument20 pagesLukePitcher 2009 5WritingAncientHistor WritingAncientHistoryAndrei GandilaNo ratings yet
- Neil L. Whitehead Ethnic Transformation and Historical Discontinuity in Native Amazonia and Guayana, 1500-1900Document22 pagesNeil L. Whitehead Ethnic Transformation and Historical Discontinuity in Native Amazonia and Guayana, 1500-1900joao carlosNo ratings yet
- DLL WEEK 4 21st CENTU 1st QuarterDocument4 pagesDLL WEEK 4 21st CENTU 1st QuarterGRACE TUBILNo ratings yet
- Léon Wieger - Chinese Characters - Their Origin, Etymology, History, Classification and Signification. A Thorough Study From Chinese Documents by L. Wieger, S.J. Translated Into English by L. DavroutDocument1,162 pagesLéon Wieger - Chinese Characters - Their Origin, Etymology, History, Classification and Signification. A Thorough Study From Chinese Documents by L. Wieger, S.J. Translated Into English by L. DavroutJamesNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work: We Are An Emerging Division Where Excellence Is A Habit and Allegiance For Quality Is A PledgeDocument8 pagesBudget of Work: We Are An Emerging Division Where Excellence Is A Habit and Allegiance For Quality Is A PledgeHezl Valerie ArzadonNo ratings yet
- F1 - GeogDocument7 pagesF1 - Geogjumajumbe150No ratings yet
- Drama and Theater: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocument2 pagesDrama and Theater: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldAngelo QuintoNo ratings yet
- The Seated Figure Iconographic ComplexDocument12 pagesThe Seated Figure Iconographic ComplexbreshxNo ratings yet
- LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri: No Butir Refleksi Respon/JawabanDocument3 pagesLK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri: No Butir Refleksi Respon/JawabanMuhammad RuswanNo ratings yet
- Geog Form 3Document5 pagesGeog Form 3De Silver BettoNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work (B.O.W.) : 21St Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocument3 pagesBudget of Work (B.O.W.) : 21St Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldCarmela BlanquerNo ratings yet
- Ie and DozokuDocument6 pagesIe and DozokuFilsa ArifaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map-English 7Document20 pagesCurriculum Map-English 7Robert Kane100% (1)
- New Historicism MindmapDocument1 pageNew Historicism MindmapHazelWeasleyNo ratings yet
- Ackerman, J - A Theory of StyleDocument12 pagesAckerman, J - A Theory of StyleLeonardo NonesNo ratings yet
- Cabre TerminologyDocument37 pagesCabre TerminologyBouchaib EssoussiNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Smart Choice 1 Work Book PRDocument80 pagesToaz - Info Smart Choice 1 Work Book PRAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Emerging Uses of Technology in Language Teaching and Learning (EUTLTL)Document8 pagesEmerging Uses of Technology in Language Teaching and Learning (EUTLTL)AlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- University of The Autonomous Regions of The Nicaraguan Caribbean Coast, Uraccan, Nueva Guinea CampusDocument1 pageUniversity of The Autonomous Regions of The Nicaraguan Caribbean Coast, Uraccan, Nueva Guinea CampusAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Text Analysis On Genres-PE-Alexander&ErnestoDocument1 pageText Analysis On Genres-PE-Alexander&ErnestoAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Content-Based Instruction (CBI)Document10 pagesContent-Based Instruction (CBI)AlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Communicative Language Teaching (CLT)Document11 pagesCommunicative Language Teaching (CLT)AlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Tasks Requiring Specific Genres OutlineDocument1 pageTasks Requiring Specific Genres OutlineAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 Esp PDFDocument61 pagesLesson1 Esp PDFAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- CLIL Lesson Plan-AlexanderDocument4 pagesCLIL Lesson Plan-AlexanderAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- 596 - 4º Strength19-20Document7 pages596 - 4º Strength19-20AlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Eight Parts of SpeechDocument42 pagesEight Parts of SpeechAlexanderBarrera100% (1)
- Spoken and Written Language in CLIL-Some TheoryDocument1 pageSpoken and Written Language in CLIL-Some TheoryAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Tasks Requiring For Specific Genres: ReportsDocument1 pageTasks Requiring For Specific Genres: ReportsAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Lic. Alexander Oporta Lic. Mario MercadoDocument39 pagesLic. Alexander Oporta Lic. Mario MercadoAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Genres of Science OutlineDocument1 pageGenres of Science OutlineAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Customer Service CurriculumDocument451 pagesCustomer Service CurriculumAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- About Parth Yuva MandalDocument3 pagesAbout Parth Yuva MandalAkram Ul HoqueNo ratings yet
- 1st Day Cookery May 2Document4 pages1st Day Cookery May 2Imee Angelie CameroNo ratings yet
- MwaDocument2 pagesMwaRachelle AlcantraNo ratings yet
- CW11Q1W1D1Document6 pagesCW11Q1W1D1Josua GarciaNo ratings yet
- FSK Implementation Guide Release 2.0 - 13.11.2019Document45 pagesFSK Implementation Guide Release 2.0 - 13.11.2019Tiffany LynchNo ratings yet
- CAPE Biology Unit 2 Multiple Choice AnswersDocument1 pageCAPE Biology Unit 2 Multiple Choice AnswersJhace BuckleyNo ratings yet
- Architecture Studio Petra Christian UniversityDocument1 pageArchitecture Studio Petra Christian UniversityAhmjyooNo ratings yet
- MBSImP Assignment RubricDocument3 pagesMBSImP Assignment RubricmahdislpNo ratings yet
- DOST-SEI Hails Qualifiers To The 2022 Undergrad S&T ScholarshipsDocument199 pagesDOST-SEI Hails Qualifiers To The 2022 Undergrad S&T ScholarshipsKhinje Louis CuruganNo ratings yet
- 2024-04-02 GR 12 BSTD Provincial QuizDocument2 pages2024-04-02 GR 12 BSTD Provincial QuizkatalachuchuNo ratings yet
- EvaluationDocument2 pagesEvaluationCharila IsinoNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Engagement of The Tertiary Education Subsidy (TES) Grantees in Central Philippines State UniversityDocument8 pagesEntrepreneurial Engagement of The Tertiary Education Subsidy (TES) Grantees in Central Philippines State UniversityPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Q2 WEEK 1 MODULE - (History and Dev't of Origami)Document8 pagesQ2 WEEK 1 MODULE - (History and Dev't of Origami)Lovely Sunga-AlboroteNo ratings yet
- Eclass For Shs Sample Made by A.C.PDocument59 pagesEclass For Shs Sample Made by A.C.PAnna Ruth de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Travel Unit Lesson Plan 2Document4 pagesTravel Unit Lesson Plan 2api-524805491No ratings yet
- Personal Data SheetDocument18 pagesPersonal Data SheetABM LAWNo ratings yet
- Rephrases: Page - 1Document11 pagesRephrases: Page - 1Diana TudorNo ratings yet
- How Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Work TogetherDocument9 pagesHow Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Work TogetherjohnteecubeNo ratings yet
- Davao Oriental State College of Science and Technology: Educ 140: Practice TeachingDocument2 pagesDavao Oriental State College of Science and Technology: Educ 140: Practice Teachingnika marl TindocNo ratings yet
- Campus Map en 2022Document2 pagesCampus Map en 2022yesihavenNo ratings yet
- COT 4 HealthDocument73 pagesCOT 4 HealthGeralyn Torres CubarNo ratings yet
- RMA G3Scoresheet v3Document17 pagesRMA G3Scoresheet v3Repril RudinasNo ratings yet
- List of Candidates Selected For Winter Internship 2021 at IIT BhubaneswarDocument3 pagesList of Candidates Selected For Winter Internship 2021 at IIT BhubaneswarHunters Of free fireNo ratings yet
- Balvatika 3Document4 pagesBalvatika 3shamim.lalganjNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra NEET UG Counselling Ebook 2024Document89 pagesMaharashtra NEET UG Counselling Ebook 2024t9423757400No ratings yet
- Business English Needs AnalysisDocument1 pageBusiness English Needs AnalysisarifsahidNo ratings yet
- VOCABULARY - FOOD - ESL Worksheet by ALLEBRAMDocument7 pagesVOCABULARY - FOOD - ESL Worksheet by ALLEBRAMDivanildo De Oliveira Ramos JuniorNo ratings yet
- FS2 Episode 9 10Document16 pagesFS2 Episode 9 10Jamesula Dether64% (14)
Genres of History Outline
Genres of History Outline
Uploaded by
AlexanderBarreraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Genres of History Outline
Genres of History Outline
Uploaded by
AlexanderBarreraCopyright:
Available Formats
Faculty of Education University Master in Bilingual Education for Primary and Secondary Schools
SPECIFIC ENGLISH FOR NON-LINGUISTIC SUBJECTS
By Alexander Oporta Barrera
GENRES IN CLIL SUBJECTS
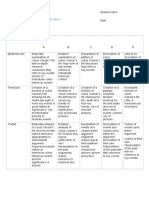
TYPE 2 TYPE 1 DEFINITION MAIN FEATURE
Biographical Recount. In this genre, the This genre allows to develop the
Historical Recount aims at retelling protagonists are presented in relation to the role writer´s experience, personal The generic structure of this genre
historical events in a sequence way. they played in history. Excluding personal recounts, in which events are can be seen as:
The generic structure is: information not relevant to that role. structured sequentially using markers
Period Identification^ Description
Background^Record of The generic structure is: like “and then” and “next”.
Events^(Deduction/Evaluation) Person-Identification^Episodes
(^Evaluation)
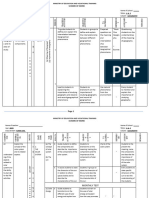
DEFINITION
This genre aims at describing the
characteristics of a historical
period, and so it is set in time rather
RECOUNTS IN HISTORY PERIOD STUDY than moving through time.
DEFINITION
Discussion allows students to provide T
This genre allows to account GENRES OF HISTORY different perspective and position of a
historical event.
Y
P
for why events happened in a The stages are: E
particular sequence, in the (Background)^Issue^Perspective
TYPES 2
past. s^Position
HISTORICAL Exposition aims to make
HISTORICAL HISTORICAL T
MAIN FEATURE arguments for a specific historical
ACCOUNTS EXPLANATIONS ARGUMENT AND event.
Y
P
DISCUSSION The generic structure is: E
The main stages of this genre (Background)^Thesis^Argument
are: ^Reinforcement of Thesis 1
Background^Account
Sequence (^Deduction) DEFINITION
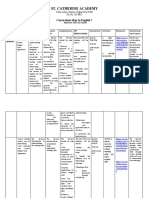
DEFINITION TYPE 1 TYPE 2
Historical Explanations tend to Consequential Explanation aims to Factorial Explanation provides a series These genres develop interpretations of
provide a number of causes of of events and unrelated causes and they the past, and argue about a specific
explain past event by a number of consequences. are not presented in a chronological way.
The generic structure is: position to consider, and evaluate
causes and or consequences, not The generic structure is:
possible interpretations of an event.
Input^ Consequences Outcome^ Factors (^Reinforcement of
chronologically. Two types were (^Reinforcement of Consequences) Factors) There are two types.
found.
Llinares, A., Morton, T., & Whittake, R. (2012), pp. 132-145
You might also like
- DLL Week 5 21st Century Quater 1Document4 pagesDLL Week 5 21st Century Quater 1GRACE TUBILNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Lesson Plan - Inductive Grammar Approach - MTeflSystemDocument10 pagesActivity 1 - Lesson Plan - Inductive Grammar Approach - MTeflSystemInés Amaya DíazNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report GPTADocument2 pagesAccomplishment Report GPTAJOAN CAMANGA50% (4)
- Tasks Requiring Specific Genres OutlineDocument1 pageTasks Requiring Specific Genres OutlineAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- History of ArchitectureDocument167 pagesHistory of ArchitectureEliza Mae Aquino100% (2)
- Scheme History Form 1.docx OrientationDocument7 pagesScheme History Form 1.docx OrientationHope JohnNo ratings yet
- Reading 1: Curriculum Genres in The Secondary ContextDocument5 pagesReading 1: Curriculum Genres in The Secondary ContextLachlan BarrattNo ratings yet
- The Novel TodayDocument3 pagesThe Novel Todaylennon tanNo ratings yet
- Resume of Presentation - Modul 4 - Febrian SururiDocument16 pagesResume of Presentation - Modul 4 - Febrian SururiSururi FebrianNo ratings yet
- Grade 7english Instructional Plan Q4Document8 pagesGrade 7english Instructional Plan Q4Imelda Quintos0% (1)
- Webquest Assessment RubricDocument2 pagesWebquest Assessment Rubricapi-360154838No ratings yet
- Historical StoryDocument2 pagesHistorical StoryScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- G 9 Hist Annual PlanAbune Gorgorios School History Annual Plan GRADEDocument5 pagesG 9 Hist Annual PlanAbune Gorgorios School History Annual Plan GRADEDawit BerheNo ratings yet
- PKS History Sept 2020 RBDocument10 pagesPKS History Sept 2020 RBKhoerun NisaNo ratings yet
- Seminario de San Jose: Diary Curriculum MapDocument8 pagesSeminario de San Jose: Diary Curriculum MapKARLO MARKO VALLADORESNo ratings yet
- Costanzo - 2008 - Giedeon As Guide (+ Inleiding The Baroque in Architectural Culture)Document13 pagesCostanzo - 2008 - Giedeon As Guide (+ Inleiding The Baroque in Architectural Culture)charlotteNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument1 pageReportapi-571254062No ratings yet
- Final MYP2 Unit MapDocument1 pageFinal MYP2 Unit MapDurba RayNo ratings yet
- Genres of Science OutlineDocument1 pageGenres of Science OutlineAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- June 3, 2019 Objectives Topics References IM's Activities RemarksDocument13 pagesJune 3, 2019 Objectives Topics References IM's Activities RemarksAilyn C. IyanaNo ratings yet
- Martin MayaSuperstates 1995Document7 pagesMartin MayaSuperstates 1995CHrisNo ratings yet
- ST ND: Scheme of Work of History Form One For 2023 Term I & Ii 1 / 9Document9 pagesST ND: Scheme of Work of History Form One For 2023 Term I & Ii 1 / 9peter jagoNo ratings yet
- LK Modul English For Entertaiment Modul 4Document6 pagesLK Modul English For Entertaiment Modul 4Nopita RinggoNo ratings yet
- LK Modul English For EntertaimentDocument6 pagesLK Modul English For EntertaimentNopita RinggoNo ratings yet
- LK Modul English For Entertaiment Modul 4Document6 pagesLK Modul English For Entertaiment Modul 4Nopita RinggoNo ratings yet
- GUNE Tense Mood PDFDocument230 pagesGUNE Tense Mood PDFMantrinNo ratings yet
- Core Subjs (SHS)Document71 pagesCore Subjs (SHS)EDGAR RIVERANo ratings yet
- G5 Q3W4 DLL ENGLISH (MELCs)Document11 pagesG5 Q3W4 DLL ENGLISH (MELCs)Shy Nd DelNo ratings yet
- Creative NonfictionDocument15 pagesCreative NonfictionABIGAIL D. ESGUERRANo ratings yet
- Zelenak - Two Versions of ConstructivismDocument18 pagesZelenak - Two Versions of ConstructivismElizabeth MataNo ratings yet
- Krauss - Photography's Discursive Spaces - Landscape-View - 1982Document10 pagesKrauss - Photography's Discursive Spaces - Landscape-View - 1982Noam GonnenNo ratings yet
- Nichols VoiceofDocDocument7 pagesNichols VoiceofDocignacio gonzalez100% (1)
- Historical Thinking Skills For APUSH: Chronological ReasoningDocument3 pagesHistorical Thinking Skills For APUSH: Chronological ReasoningDiki Jayan DikaNo ratings yet
- Mind Map of Prose and TheaterDocument1 pageMind Map of Prose and TheaterScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- University of Rizal SystemDocument2 pagesUniversity of Rizal SystemMichaella AcebucheNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing About LiteratureDocument1 pageReading and Writing About LiteraturesameerfiservNo ratings yet
- Some Strategies For Coding Sentential Subjects in English: From Exaptation To GrammaticalizationDocument41 pagesSome Strategies For Coding Sentential Subjects in English: From Exaptation To GrammaticalizationAlina RNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature CODocument7 pages21st Century Literature COMICHELLE NAVAREZNo ratings yet
- N N N N N N: Grade 7 Grade 8Document3 pagesN N N N N N: Grade 7 Grade 8api-202727113No ratings yet
- Table of Specification: Learning Competencies Cognitive Process DimensionDocument6 pagesTable of Specification: Learning Competencies Cognitive Process DimensionAngelica RocamoraNo ratings yet
- Modul Profesional 4Document6 pagesModul Profesional 4ainul yaqinNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Complexity Matrix OnlyDocument5 pagesCognitive Complexity Matrix Onlyapi-486317294No ratings yet
- CM Q1eng.10Document3 pagesCM Q1eng.10andrea mea sumauangNo ratings yet
- July 2-5, 2019Document3 pagesJuly 2-5, 2019JUAN DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Azimio La KaziDocument8 pagesAzimio La KaziJuma MpangaNo ratings yet
- LukePitcher 2009 5WritingAncientHistor WritingAncientHistoryDocument20 pagesLukePitcher 2009 5WritingAncientHistor WritingAncientHistoryAndrei GandilaNo ratings yet
- Neil L. Whitehead Ethnic Transformation and Historical Discontinuity in Native Amazonia and Guayana, 1500-1900Document22 pagesNeil L. Whitehead Ethnic Transformation and Historical Discontinuity in Native Amazonia and Guayana, 1500-1900joao carlosNo ratings yet
- DLL WEEK 4 21st CENTU 1st QuarterDocument4 pagesDLL WEEK 4 21st CENTU 1st QuarterGRACE TUBILNo ratings yet
- Léon Wieger - Chinese Characters - Their Origin, Etymology, History, Classification and Signification. A Thorough Study From Chinese Documents by L. Wieger, S.J. Translated Into English by L. DavroutDocument1,162 pagesLéon Wieger - Chinese Characters - Their Origin, Etymology, History, Classification and Signification. A Thorough Study From Chinese Documents by L. Wieger, S.J. Translated Into English by L. DavroutJamesNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work: We Are An Emerging Division Where Excellence Is A Habit and Allegiance For Quality Is A PledgeDocument8 pagesBudget of Work: We Are An Emerging Division Where Excellence Is A Habit and Allegiance For Quality Is A PledgeHezl Valerie ArzadonNo ratings yet
- F1 - GeogDocument7 pagesF1 - Geogjumajumbe150No ratings yet
- Drama and Theater: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocument2 pagesDrama and Theater: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldAngelo QuintoNo ratings yet
- The Seated Figure Iconographic ComplexDocument12 pagesThe Seated Figure Iconographic ComplexbreshxNo ratings yet
- LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri: No Butir Refleksi Respon/JawabanDocument3 pagesLK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri: No Butir Refleksi Respon/JawabanMuhammad RuswanNo ratings yet
- Geog Form 3Document5 pagesGeog Form 3De Silver BettoNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work (B.O.W.) : 21St Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocument3 pagesBudget of Work (B.O.W.) : 21St Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldCarmela BlanquerNo ratings yet
- Ie and DozokuDocument6 pagesIe and DozokuFilsa ArifaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map-English 7Document20 pagesCurriculum Map-English 7Robert Kane100% (1)
- New Historicism MindmapDocument1 pageNew Historicism MindmapHazelWeasleyNo ratings yet
- Ackerman, J - A Theory of StyleDocument12 pagesAckerman, J - A Theory of StyleLeonardo NonesNo ratings yet
- Cabre TerminologyDocument37 pagesCabre TerminologyBouchaib EssoussiNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Smart Choice 1 Work Book PRDocument80 pagesToaz - Info Smart Choice 1 Work Book PRAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Emerging Uses of Technology in Language Teaching and Learning (EUTLTL)Document8 pagesEmerging Uses of Technology in Language Teaching and Learning (EUTLTL)AlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- University of The Autonomous Regions of The Nicaraguan Caribbean Coast, Uraccan, Nueva Guinea CampusDocument1 pageUniversity of The Autonomous Regions of The Nicaraguan Caribbean Coast, Uraccan, Nueva Guinea CampusAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Text Analysis On Genres-PE-Alexander&ErnestoDocument1 pageText Analysis On Genres-PE-Alexander&ErnestoAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Content-Based Instruction (CBI)Document10 pagesContent-Based Instruction (CBI)AlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Communicative Language Teaching (CLT)Document11 pagesCommunicative Language Teaching (CLT)AlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Tasks Requiring Specific Genres OutlineDocument1 pageTasks Requiring Specific Genres OutlineAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 Esp PDFDocument61 pagesLesson1 Esp PDFAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- CLIL Lesson Plan-AlexanderDocument4 pagesCLIL Lesson Plan-AlexanderAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- 596 - 4º Strength19-20Document7 pages596 - 4º Strength19-20AlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Eight Parts of SpeechDocument42 pagesEight Parts of SpeechAlexanderBarrera100% (1)
- Spoken and Written Language in CLIL-Some TheoryDocument1 pageSpoken and Written Language in CLIL-Some TheoryAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Tasks Requiring For Specific Genres: ReportsDocument1 pageTasks Requiring For Specific Genres: ReportsAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Lic. Alexander Oporta Lic. Mario MercadoDocument39 pagesLic. Alexander Oporta Lic. Mario MercadoAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Genres of Science OutlineDocument1 pageGenres of Science OutlineAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Customer Service CurriculumDocument451 pagesCustomer Service CurriculumAlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- About Parth Yuva MandalDocument3 pagesAbout Parth Yuva MandalAkram Ul HoqueNo ratings yet
- 1st Day Cookery May 2Document4 pages1st Day Cookery May 2Imee Angelie CameroNo ratings yet
- MwaDocument2 pagesMwaRachelle AlcantraNo ratings yet
- CW11Q1W1D1Document6 pagesCW11Q1W1D1Josua GarciaNo ratings yet
- FSK Implementation Guide Release 2.0 - 13.11.2019Document45 pagesFSK Implementation Guide Release 2.0 - 13.11.2019Tiffany LynchNo ratings yet
- CAPE Biology Unit 2 Multiple Choice AnswersDocument1 pageCAPE Biology Unit 2 Multiple Choice AnswersJhace BuckleyNo ratings yet
- Architecture Studio Petra Christian UniversityDocument1 pageArchitecture Studio Petra Christian UniversityAhmjyooNo ratings yet
- MBSImP Assignment RubricDocument3 pagesMBSImP Assignment RubricmahdislpNo ratings yet
- DOST-SEI Hails Qualifiers To The 2022 Undergrad S&T ScholarshipsDocument199 pagesDOST-SEI Hails Qualifiers To The 2022 Undergrad S&T ScholarshipsKhinje Louis CuruganNo ratings yet
- 2024-04-02 GR 12 BSTD Provincial QuizDocument2 pages2024-04-02 GR 12 BSTD Provincial QuizkatalachuchuNo ratings yet
- EvaluationDocument2 pagesEvaluationCharila IsinoNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Engagement of The Tertiary Education Subsidy (TES) Grantees in Central Philippines State UniversityDocument8 pagesEntrepreneurial Engagement of The Tertiary Education Subsidy (TES) Grantees in Central Philippines State UniversityPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Q2 WEEK 1 MODULE - (History and Dev't of Origami)Document8 pagesQ2 WEEK 1 MODULE - (History and Dev't of Origami)Lovely Sunga-AlboroteNo ratings yet
- Eclass For Shs Sample Made by A.C.PDocument59 pagesEclass For Shs Sample Made by A.C.PAnna Ruth de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Travel Unit Lesson Plan 2Document4 pagesTravel Unit Lesson Plan 2api-524805491No ratings yet
- Personal Data SheetDocument18 pagesPersonal Data SheetABM LAWNo ratings yet
- Rephrases: Page - 1Document11 pagesRephrases: Page - 1Diana TudorNo ratings yet
- How Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Work TogetherDocument9 pagesHow Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Work TogetherjohnteecubeNo ratings yet
- Davao Oriental State College of Science and Technology: Educ 140: Practice TeachingDocument2 pagesDavao Oriental State College of Science and Technology: Educ 140: Practice Teachingnika marl TindocNo ratings yet
- Campus Map en 2022Document2 pagesCampus Map en 2022yesihavenNo ratings yet
- COT 4 HealthDocument73 pagesCOT 4 HealthGeralyn Torres CubarNo ratings yet
- RMA G3Scoresheet v3Document17 pagesRMA G3Scoresheet v3Repril RudinasNo ratings yet
- List of Candidates Selected For Winter Internship 2021 at IIT BhubaneswarDocument3 pagesList of Candidates Selected For Winter Internship 2021 at IIT BhubaneswarHunters Of free fireNo ratings yet
- Balvatika 3Document4 pagesBalvatika 3shamim.lalganjNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra NEET UG Counselling Ebook 2024Document89 pagesMaharashtra NEET UG Counselling Ebook 2024t9423757400No ratings yet
- Business English Needs AnalysisDocument1 pageBusiness English Needs AnalysisarifsahidNo ratings yet
- VOCABULARY - FOOD - ESL Worksheet by ALLEBRAMDocument7 pagesVOCABULARY - FOOD - ESL Worksheet by ALLEBRAMDivanildo De Oliveira Ramos JuniorNo ratings yet
- FS2 Episode 9 10Document16 pagesFS2 Episode 9 10Jamesula Dether64% (14)